Abstract
There are many successful geothermal projects that exploit the Upper Jurassic aquifer at 2–3 km depth in the German Molasse Basin. However, up to now, only P-wave seismic exploration has been carried out. In an experiment in the Greater Munich area, we recorded S-waves that were generated by the conventional P-wave seismic survey, using 3C receivers. From this, we built a 3D volume of P- to S-converted (PS) waves using the asymptotic conversion point approach. By combining the P-volume and the resulting PS-seismic volume, we were able to derive the spatial distribution of the vp/vs ratio of both the Molasse overburden and the Upper Jurassic reservoir. We found that the vp/vs ratios for the Molasse units range from 2.0 to 2.3 with a median of 2.15, which is much higher than previously assumed. This raises the depth of hypocenters of induced earthquakes in surrounding geothermal wells. The vp/vs ratios found in the Upper Jurassic vary laterally between 1.5 and 2.2. Since no boreholes are available for verification, we test our results against an independently derived facies classification of the conventional 3D seismic volume and found it correlates well. Furthermore, we see that low vp/vs ratios correlate with high vp and vs velocities. We interpret the latter as dolomitized rocks, which are connected with enhanced permeability in the reservoir. We conclude that 3C registration of conventional P-wave surveys is worthwhile.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Deep sedimentary basins can provide geothermal reservoirs, which are mostly explored using active seismic methods, carried out almost exclusively using compressional waves. This allows to image the geological and structural framework and, thus, increase the chance of targeting successful geothermal reservoirs. However, combining compressional and shear waves can provide additional information about the reservoir. S-wave velocities are valuable in characterizing the subsurface, because they reduce the ambiguity associated with only P-wave information, as they react in a different way to, e.g., lithology, porosity, pore fluids, and shape, and anisotropy with respect to P-waves and hence allow better discrimination (Robertson 1987; Tatham and McCormack 1991; Johnston and Christensen 1992; Wang and Szata 1999). For instance, recording both P- and S-waves in parallel enables the derivation of Poisson’s ratio.
The theoretical principles and techniques behind the use of shear waves (S-wave) in seismic exploration were developed about 40 years ago (Puzyrev et al. 1980; Dohr 1985; Tatham 1985). Pure S-wave surveys have not gained widespread popularity, but recording and processing of P-to-S converted waves are applied to a limited extent in exploration nowadays (Hardage et al. 2011, 2014; DeAngelo and Hardage 2014; Donati et al. 2016; Lu et al. 2016), mostly for solving specific tasks, such as illumining beneath gas-rich sediments or inside coal seams, or to derive fracture orientations, among other things (Stewart et al. 2003; Chopra and Stewart 2010; Wei et al. 2014).
Deep geothermal energy extraction often faces the problem of induced seismicity, which may cause failure of the entire project, and many examples are documented worldwide (e.g., Deichmann 2009; Grigoli et al. 2018; Megies and Wassermann 2014). To control the seismicity (Kwiatek et al. 2019), it is helpful to delineate the reservoir beforehand (Cuenot et al. 2008). If induced seismicity occurs, precise determination of the hypocenter location is mandatory, for which knowing both P- and S-wave velocities is advantageous.
The Upper Jurassic in the German Molasse Basin (GMB) is the most important hydrogeothermal reservoir in Germany to date. The city of Munich envisages obtaining a 100% supply of sustainable heat energy in the year 2040; geothermal heat shall contribute the majority of this, using a distributed pattern of geothermal facilities in the southern part of the city (Hecht and Pletl 2015). To this end, a 3D seismic campaign that covered the southern half of Munich was carried out in the winter of 2015/16. The Leibniz Institute for Applied Geophysics (LIAG) accompanied the exploration with a comprehensive research program (Buness et al. 2016), including S-wave measurements. The S-wave acquisition consisted of active and passive experiments (Fig. 1). The active experiment comprised generating S-waves using the ‘Shover’ technique, i.e., vertical vibrators sweeping with opposing phases (Edelmann 1981), as described by Wawerzinek et al. (2017). In this paper, we refer to the passive experiment that recorded the shots of the conventional 3D survey using 3-component MEMS (micro-electro-mechanical systems). The 3D multicomponent data were used to derive the spatial distribution of vp/vs within both overburden and reservoir. We show here the results of this experiment and demonstrate their significance for lithological characterisation of the reservoir, as well as their implications to determine the hypocenters of induced seismicity.
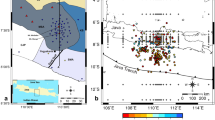
Overview map of seismic measurements in the Greater Munich area. The 3D P-wave conventional survey was carried out in the southern and western part of Munich and accompanied by S-wave experiments. The eastern half of the shots (green dots) was also recorded by 3C receivers (red dots). The black dashed line marks the part of the 3D volume covered by S-wave information. The thick dashed grey line gives the position of the geological section shown in Fig. 2a, the yellow line gives the position of the seismic section shown in Fig. 2b. The large blue rectangle outlines the 3D cube used for PS processing (inlines 1–230, from WSW to ENE; crosslines 1–172, from SSE to NNW). The small blue rectangle marks the area of the vP/vS analysis in the Upper Jurassic unit (Figs. 10–12)
Geological setting
The basement in this area is Palaeozoic in age; locally, it contains small Permo-Carboniferous grabens (Bachmann et al. 1987). Triassic, Early and Middle Jurassic sediments transgressed over the basement, although around Munich, the first Mesozoic sedimentation was Middle Jurassic (Dogger) fine-grained clastics with carbonate beds (Bachmann et al. 1987). The Upper Jurassic (Malm) constitutes a 450–600 m thick series of limestones and marls. The upper 350 − 400 m comprises sponge, algal and coral reef systems with intervening lagoonal deposits. These beds were deposited in a shallow and warm marine environment on the European Tethyian continental shelf (Lemcke 1988; Meyer and Schmidt-Kaler 1990). The Malm carbonates form the major reservoir for geothermal energy, as investigated in this work.
Information about the lithology of the Malm reservoir is available either from outcrops about 100 km to the north, or from a limited number of deep boreholes in the surrounding area (cf. Fig. 1). The main constituents of the carbonate platform are limestones and dolomites of varying facies. Traditionally, the limestone facies is divided into a massive (or reef) facies and a number of bedded facies. The former has a low content of clastics; whereas, the later may contain a considerable portion of clay (Schmid et al. 2005). Two processes have altered locally these primary facies: karstification and dolomitization. Dolines, which are also visible in the seismic volume (Sell et al. 2019), evidence the paleo-karstification during Cretaceous–early Paleogene times. Dolomitization is known from surrounding boreholes, and on the basis of 17 wells that penetrate the reservoir, Böhm et al. (2013) concluded that the main reservoir consists of dolomitized massive facies. Mraz (2018) discovered that different types of dolomites found in the reservoir (planar-anhedral and planar-euhedral) show strongly varying permeability, depending on the porosity of the primary limestone facies and the existence of fault and/or fractures. Since secondary dolomitization needs pathways for Mg-rich fluids, the dolomitization process is more probable in a facies with high primary porosity and in tectonically deformed regions.
From the late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous times, the water depth receded, ultimately causing exposure of the carbonates and, thus, strong karstification. At the end of the Cretaceous, and with the renewed onset of sedimentation, the area turned into a foredeep in front of the Alpine Orogen (Ziegler et al. 1995; Shipilin et al. 2020). In the study area, the Jurassic carbonate platform is overlain in places by thin (< 50 m) Cretaceous Purbeck units and Eocene Priabonian limestones, which are considered in the seismic image as the top of the carbonate platform sensu lato, because of their strong and continuous reflection character.
The formation of the Molasse foreland basin (i.e., the GMB) from the Eocene onwards was due to either simple collision of the African and Adriatic microplates (Frisch 1979; Allen et al. 1991; Ziegler et al. 1995; Ziegler 1987), or the African, Iberian and European plates, previous to the Alpine Orogeny (Kley and Voigt 2015). As a consequence of the down-flexure of the European crust, synthetic and antithetic, Alpine orogen-parallel striking normal faults developed (e.g. Meyer and Schmidt-Kaler 1990; Roeder and Bachmann 1996; Dussel et al. 2016; von Hartmann et al. 2016; Shipilin et al. 2020).
The Tertiary Molasse sediments consist of a succession of marine and fluviatile layers (Sissingh 1997). The thickness of the Molasse increases from north to south in general; in the study area, the Molasse reaches a thickness of 2.0–2.8 km (Fig. 2). The Molasse can be subdivided into five groups, in order of stratigraphic age, from oldest to youngest: Lower Marine Molasse (Rupelian), Lower Freshwater Molasse (Chattian–Aquitanian), Upper Marine Molasse (Burdigalian), Freshwater–Brackish Molasse (late Burdigalian), Upper Freshwater Molasse (Langhian–Tortonian).
Geological cross sections. a Geological N–S cross section through the Bavarian Molasse Basin, east of Munich (redrawn after GeoMol 2015), showing the general downdip to the south, and faults due to lithospheric bending setting. Black rectangle is the section shown in b. b Interpreted seismic P-wave section through the 3D volume, showing that the reservoir (blue; Top Berriasian–base Tithonian) dips to the south and is cut by normal faults. The location of the Fig. 11 is shown. Locations of both sections are shown in Fig. 1
Survey
The 3D seismic survey covered 170 km2 in the southern and western parts of Munich and was carried out from November 2015 to March 2016 (Fig. 1). The acquisition was targeted on the Upper Jurassic (Malm) reservoir. The top of the Malm carbonates varies at depths between 2000 m in the north and 2800 m in the south. To account for this, the survey layout used increasing line distances from 400 m in the northwest to 500 m in the southeast (Schuck and Hecht 2017), with shot and geophone distances of 50 m. Three 12 t vibrators excited a 12 s long sweep with a frequency of 12–96 Hz, nine times at each location. The shots were recorded by groups of 12 1C geophones spread over 50 m, with a sampling rate of 2 ms and a record length of 5 s to include S-wave signals.
About half of the ~ 7000 shots were additionally recorded at 467 3C receivers that were deployed along one main profile, running WNW–ESE and on two perpendicular crosslines, in the eastern part of the survey (Fig. 1). This layout was chosen because of the active S-wave experiment (Wawerzinek et al. 2017). The 3C recordings used single micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS, Sercel DSU3 sensors). The horizontal H1 components were aligned along the direction of each line, i.e. the H1-components on the main line point towards 100°N, geophones on the crosslines point towards 190°N. To discriminate both datasets, the normal 3D seismic survey is referred to hereafter as ‘conventional’ survey and the multicomponent survey is referred to as ‘3D3C’ survey.
Methods
The processing of the P-wave data of the whole conventional survey recorded by geophones followed the usual steps including refraction and residual static, spherical divergence correction, deconvolution, time-variant band-pass filtering, velocity analysis and CRS stacking (e.g., Yilmaz 2001). The final sections (Fig. 2) were derived by pre-stack depth migration, the velocity model was produced by a tomographic inversion of residual moveouts. In our study, the conventional data set is used for the facies classification and the P-wave reflectivity analysis.
To ensure comparability of the individual components of the 3D3C data set to each other, we applied a similar processing sequence to the individual components, but a few differences did occur (e.g., rotation, binning). The 3C data recorded by MEMS were first integrated to transfer the acceleration recordings of the MEMS into velocity values comparable to the geophone recordings. The next step was a rotation of the horizontal components of the recordings into a radial and transversal coordinate system, according to the receiver-shot positions. We also tested rotation based on the maximization of energy around the P-wave onset on one of the horizontal components. Only 7% of the receivers showed deviations larger than 30°. Since the first-break signal quality breaks down at offsets > 1500 m, we chose to keep rotation based on geometry.
Furtheron, we applied elevation datum statics, true amplitude recovery, a bandpass filter of 12–60 Hz, automatic gain control of 500 ms, and performed an interactive velocity analysis on the 3C data (for P- and PS-waves) before stacking. Despite rotation, no clear reflection events were evident in the PS-waves, neither in the shot- or CDP domains, nor even in CDP supergathers. Since we did not know at the beginning whether we had registered (1) reflected S-waves, generated at or in the vicinity of the seismic source, or (2) signals converted at the reflecting point, we tested a binning schema developed for P-to-S conversion (Tessmer and Behle 1988). This takes into account the different wavetypes for the downgoing- and upgoing legs by calculating an asymptotic conversion point (ACP, Fig. 3a). The distance between the conversion point and the receiver (xp) is calculated according to:
where vp and vs are velocities for P- and S-waves, respectively. Strictly, this point gives the exact position only for an infinite depth of the reflector and leads to reflector point dispersal and hence smearing effects, if the offset exceeds the reflector depth. Whereas this condition is met for most of the traces regarding the horizons below the top of the carbonate platform (Fig. 3b), lateral blurring of horizons above has to be taken into account. A further problem was that the vp/vs ratio was not known beforehand. In this study, we use a nearby VSP survey to derive initial values (see below). Since the reflection points move towards the receiver, we observe a higher fold in a smaller area (Fig. 3c). To improve the signal-to-noise ratio, we increased the bin size from 25 m used in the conventional P-wave processing data to 50 m for the 3C data processing. After stacking, we applied a mild f-xy deconvolution to attenuate random noise and a FD time migration on the 3C data (for P- and PS-waves).
Acquisition principles and parameters. a Principle of ACP-binning (modified after Behle & Dohr 1985). If a downgoing P-wave from shotpoint SP is converted at a reflector, the conversion point (CP) moves towards the receiver (G), compared to a reflection point of the same wavetype (CMP). Black and blue arrows mark polarizations, i.e., particle motions, x is the offset between SP and G, xp and xs are the distances from SP to CP and from CP to G, respectively. b Distribution of absolute offset of our 3D3C dataset. The offset varies from 0 to 6852 m, with a median value (black line) of 2756 m. c Map of CMP and ACP fold of our 3D3C dataset. In the case of ACP-binning, the fold is higher but covers a smaller area. The cyan line marks the position of the cross section in Fig. 7. The blue star marks the position of the ACP bin shown in Fig. 3d and the green star marks the center of the supergather shown in Fig. 6. d Offset and azimuthal coverage of an example ACP bin. The azimuthal coverage is limited due to the linear receiver deployment
Once a PS-wave section is constructed, the derivation of the vp/vs ratio is possible, if the reflectors can be associated with those in the P-wave section. In this case, the interval traveltimes allow the derivation of the vp/vs ratio, according to Garotta (1987) and Tessmer and Behle (1988)
where ∆TPS and ∆TP are two-way-traveltime (TWT) differences of PS- and P-waves, respectively. The velocities of P-, S- and PS-waves are related as follows (Garotta 1987):
In our study, we used the 3D3C P- and PS-wave volume to determine the two-way-traveltime differences.
In principle, multicomponent surveys are suited to infer azimuthal anisotropy or horizontal transverse isotropy (HTI) caused by (near) vertical fractures or horizontal stress, amongst other things (Liu and Martinez 2012). Azimuthal anisotropy splits the medium into a fast and slow direction and leads to azimuthal-dependent arrival times and amplitudes (e.g. Bale et al. 2009, Far and Hardage 2014, Donati et al. 2016). In our survey, the azimuthal coverage was not sufficient to observe traveltime or amplitude variations (Fig. 3d), since only a limited number of receivers was deployed along the 2D lines (cf Fig. 1). Existing anisotropy would cause deterioration of the P-SV stack due to azimuthal-dependent traveltime deviations.
Results
Initial vp/vs ratio derived from VSP measurements
The Stadtwerke München conducted a near-vertical VSP at the borehole Freiham TH-1, just outside the 3D-seismic area (Fig. 1). We rotated the horizontal components into radial and transverse directions, based on maximization of energy around the P-wave first arrivals. After rotation, the data show remarkably clear S-waves, despite the use of a vertical vibrator source. The vertical component (Fig. 4a) shows a strong reflection at the top of the carbonate platform, i.e., Top Priabonian (~ 1600 m below sea level). This reflection is also prominent on the radial component (Fig. 4b), where the reflection of the downgoing P-wave splits into an upgoing P-wave and an upgoing S-wave, i.e., a P-to-S converted wave. Several downgoing S-waves are visible as well, some of them were generated by the transition of the downgoing P-wavefield at interfaces at depth, as confirmed by P-wave reflectivity (Fig. 4a). However, one of the downgoing S-phases can be followed to the position of the vibrator at the surface, indicating that S-waves were also excited directly at the (P-wave) vibrator. Downgoing S-waves also appear on the transverse component, indicating heterogeneity of the uppermost subsurface layer. Similar observations were described by Hardage and Wagner (2014). Theoretically, the differently polarised S-waves of the radial and transverse components allow to estimate anisotropy. In practice, however, this was not feasible, due to the relatively large errors in S-wave picking, due to interference with other wavetypes.
VSP record at Freiham TH-1 (for location, see Fig. 1). (Left) vertical component, (middle) radial component, (right) transverse component, after bandpass filtering and trace equalization. All components show a strong reflection at the top of the carbonate platform at ~ 1600 m bsl. The radial component shows splitting of the downgoing P-wavefield into upgoing P- and S-waves. Downgoing S-waves are visible in both the radial and the transverse components, despite the fact that a vertical vibrator was used as seismic source
P- and S-wave interval velocities (Fig. 5a) were derived using smoothed first-break onsets, as well as a smoothing operator of 60 m to account for pick uncertainties. The resulting vp/vs values (Fig. 5b) for the Molasse sediments are very high (about 3) at the surface and decrease below 2 at 900 m depth. Below 900 m, we observe stronger variations in the velocity ratios. vp/vs were averaged for the known stratigraphic sequences: The uppermost 500 m has a median value of 2.66; it varies between 1.9 and 2.1 for the deeper Molasse units (Fig. 5b). Unfortunately, only vp/vs ratios for the Cenozoic sediments were determined, since no clear S-wave onsets are visible within the carbonate platform. Another VSP recorded at Geretsried GEN-1 borehole, about ~ 25 km south of Munich (Dussel et al. 2019), revealed a similar high median value of 1.9 for Chattian and Rupelian sediments at a depth interval of 2000–4000 m. Perhaps the greater depth of the formation and consequent stronger consolidation of the Chattian and Rupelian caused the vp/vs ratio at Geretsried to be lower than that at Freiham. Thus, we used the averaged vp/vs ratio of 2.0 (depth interval 515–2015 m) for the initial converted-wave processing (Fig. 6). This resulted in a clear improvement of the stacked signals and enabled a further areal adjustment of the values using normal moveout velocity analysis.
Impact of binning on velocity analysis. Results of CMP- and ACP-binning using the initial vp/vs values derived from the VSP at Freiham TH-1. A CMP supergather shows almost no reflection signal in the gathered data as well as in the semblance analysis, whereas a ACP supergather delivers a visible signal, enabling further velocity analysis. See Fig. 3c for location (green star)
Horizons
The 3D3C P- and PS-wave volume were recorded only along three 2D lines, which resulted in a far lower coverage than the conventional 3D P-wave volume. Nevertheless, the 3D3C P-wave volume imaged similar reflectors to the conventional 3D seismics (cf. Wawerzinek et al. 2017). The signal-to-noise ratio in the PS-section is lower than in the P-wave volume, since the PS conversion is generally weaker than a pure P-reflection (McCamy et al. 1962; Stewart et al. 2002). Nevertheless, we were also able to pick several horizons in the 3D3C P- and PS-volume, to a varying extent for PS-waves (Fig. 7), whereby Top Chattian and Top Priabonian were the most traceable. Therefore, we focus on three horizons to construct traveltime maps: (1) Top Chattian, (2) Top Priabonian and (3) base reservoir. These horizons were selected to investigate the spatial vp/vs distribution in both the Molasse and the reservoir. Using Eq. (2), we derived the vp/vs ratio down to these horizons and between Top Chattian and Top Priabonian as well as between Top Priabonian and base reservoir.
Seismic profiles through the 3D3C a P-wave volume and b PS-wave volume. The position of the section is shown in Fig. 3c. Note the different scales of the sections. Light orange: Top Chattian, orange: Top Rupelian, dark orange: Top Priabonian, blue: base reservoir (Base Tithonian). The stronger noise on the PS-wave volume is due to the lower reflection coefficients of the PS-waves
VP/VS ratio in the Molasse
The reflection at the top of the carbonate platform is the most prominent throughout the dataset; it could be picked well on both the P- and the PS-sections of the 3D3C volume. The structures of the TWT maps of both sections show good correlation (Fig. 8a, b), indicating reliable picking of the PS section. We could derive the vp/vs ratio (Fig. 8c) for the entire Cenozoic pile (Molasse and Quaternary). The spatial display shows that the velocity ratio increases from the western part to the southeastern part of the study area. The derived vp/vs ratios vary between 2.0 and 2.3, with the median at 2.15, which is in very good accordance to the median value of 2.08 (0–2 km depth) found in the VSP at Freiham (Fig. 5). However, this value is influenced strongly by the very high (> 2.5) ratios in the first few hundred meters.
Traveltime and vp/vs maps. Two-way traveltime (TWT) maps of the top of the carbonate reservoir (Top Priabonian) for a the P-wave section and b the PS-wave section as well as c the derived vp/vs ratio for the entire Cenozoic sediments down to the top of the carbonate platform. The PS-wave section shows the same structural trends as the P-wave section, indicating consistent horizon interpretation. The resulting vp/vs ratio shows a median value of 2.15
To receive a more unbiased spatial distribution, an interval vp/vs ratio between Top Chattian and Top Priabonian was computed. The calculation of interval vp/vs ratio has the advantage that potential time errors (e.g., incompletely corrected static effects) are eliminated. In the lower part of the Molasse about 90% of the values vary smoothly between 1.8 and 2.1, with a median of 1.92 (Fig. 9). The residual 10% of vp/vs ratio spread over a range of 1.5–2.4, probably caused by pick uncertainties due to noisy traces. The median vp/vs ratio is again in good agreement with the ratio of 1.99 found at VSP Freiham in the same stratigraphic interval, but at a slightly shallower position (1350–2015 m). Similar to VSP Freiham, the traveltime-derived vp/vs ratio of the entire strata down to Top Priabonian is generally higher than in the lower part of the Molasse (cf. Figures 8 and 9), reflecting the influence of the higher near-surface vp/vs ratio.
VP/VS ratio in the Upper Jurassic
Reflections inside the reservoir are not as continuous as in the Molasse units, in both 3D3C P- and PS-wave seismic volumes. We could only reliably pick a horizon below the Top Priabonian in the southernmost part of the PS-wave seismic volume, were the fold is higher (cf. Figs. 4 and 7). This horizon is situated ~ 360 ms (PS time) below Top Priabonian; it corresponds presumably to the base of the reservoir. The vp/vs ratio of the reservoir shows a considerably stronger variation than in the lower Molasse units, it varies between 1.5 and 2.2. The variation is organized in a specific pattern, i.e., a circle of low (1.50–1.80) values is surounded by high (1.85–2.20) values (Fig. 10).
vp/vs within the Upper Jurassic unit. vp/vs ratio for the reservoir from Top Priabonian to Base Tithonian (grey areas, see Fig. 1 for stratigraphic position). Each pixel corresponds to a single bin (50 × 50 m2). The relative distribution of the traveltime-derived ratios are collaborated by the sparsely applied velocity analysis points (left- and rightmost figures). The black dashed line in the panels represents the averaged traveltime-derived vp/vs value of the corresponding supergathers (black squares in the map)
The imaging of the picked horizon required velocity analysis of the PS-seismic volume; we did this using a grid of 10 × 10 lines. Due to the relatively low signal-to-noise ratio, supergathers of 25 ACPs were built and yet it was still not possible to determine the velocity function at all grid points. Thus, a refinement of analysis positions did not seem meaningful. Since the shear wave velocity can not directly be determined from velocity analysis, vs was derived using Eq. (3). In terms of absolute values, the vp/vs ratio derived from the velocity analysis at sparse locations in both seismic volumes do not agree exactly with the velocity ratios derived from traveltime differences. But in terms of relative trends, the both ratios correlate with each other (Fig. 10). Since we focus on the spatial distribution of the velocity ratio and its relation with the facies and the lithology, the vp/vs ratio derived from traveltime differences (Eq. 2) will be used in the following.
Discussion
Comparison with classification and reflectivity
To gain insight into the very heterogeneous facies distribution in the Malm units, we used a simple classification scheme and applied it to the conventional 3D seismic volume. Von Hartmann et al. (2019) vertically divided the Malm reservoir into eight approximately 70 m thick layers separated by pseudo-horizons. Each layer was then quantified using three seismic attributes: (1) rms amplitude, (2) dominant frequency and (3) similarity. Each of these quantities were divided into two (similarity) or three (amplitude and frequency) categories. The differentiation of the seismic signals into classes gives a clearer overview of the reflectivity distribution of the subsurface (Fig. 11). Especially circular structures with high coherent amplitudes (reddish colors) enclose a core of lower reflectivity (bluish colors), which are interpreted as carbonate build-ups or bioherms surrounded by sedimentary troughs (Fig. 11; von Hartmann et al. 2019). During the diagenetic processes, the higher primary porosity of these later structures enabled their pronounced dolomitization, in contrast to the adjoining sediments (Mraz et al. 2019).
vp/vs ratio and facies classification of the Upper Jurassic reservoir volume. Seismic facies classification is based on a combination of the following attributes; amplitude, frequency, and similarity in the conventional P-wave volume, after von Hartmann et al. (2019). Classes that show negligible occurrences were combined with the adjacent ones. The black box on the right shows the vp/vs ratio that we derived from the PS data for the location in the left black box. The two independently derived patterns correlate well
Figure 11 shows the resulting seismic facies classification map of the eastern part of the survey, from a layer in the middle level of the carbonate platform (von Hartmann et al. 2019). Its pattern shows good correlation with the vp/vs ratio distribution that was derived in this work for the whole Upper Jurassic reservoir. High amplitudes in the seismic facies classification along an arcuate-shaped structure coincide remarkably well with high vp/vs ratio values. Since the seismic facies classification is dominated by amplitude values, we infer that high vp/vs ratios correlate with high reflectivity. The correlation of the vp/vs ratio and the facies classification extends to the adjacent layers, since the main feature, the arcuate-shaped structure encircling a low amplitude area, is also visible there.
The dependency of reflectivity, the seismic velocities vp and vs, and their ratio can be further clarified by comparing the conventional P-wave seismic sections and the attributes of the 3D3C P- and S-wave volumes (Fig. 12). Two sections are chosen, one dominated in its middle part and to the right by very low vp/vs ratios and another one dominated by high ratios. The left one shows that the variation from 1.5 to 2.0 correlates closely with reflectivity: low ratios corresponds to a diffuse reflectivity and higher values with more coherent reflectivity. Moreover, low values of the ratio correspond to high values of both vp and vs. However, the correlation with reflectivity is much better for the vp/vs ratio than for vp or vs on their own. Similar behavior is shown by the right section in Fig. 12: Strong and continuous reflectivity in the NNW part is characterized by a high vp/vs ratio, although neither the vp nor the vs velocity reach high values. This confirms the superior role of the vp/vs ratio as a discriminator with respect to the values of both seismic velocities.
Correlation of reflectivity, velocity and vp/vs. Two P-wave seismic sections (left and right) from the conventional 3D seismic, overlain with vp/vs ratio, vp and vs velocities. Center; seismic facies classification and vp/vs ratio from Fig. 11, showing position of the sections. The sections were chosen because of their different vp/vs ratios and seismic facies classifications. vp/vs shows a good correlation with P-wave reflectivity. The vp/vs ratio was derived using the interval traveltimes (Eq. 2), whereas the smoothed velocities (vp, vps) were determined using interactive velocity analysis, from which vs was derived using Eq. 3. Top Upper Jurassic (Top Priabonian) horizon is indicated by the green line. The sections are flattened to Top Priabonian
Significance for lithology
Numerous studies have shown that the vp/vs ratio is a good indicator of carbonate lithology, most of them using laboratory experiments (Pickett 1963; Domenico 1984; Marion and Jizba 1997; Johnston and Christensen 1992; Wang and Szata 1999), but also log data (Miller 1992) and reflection seismic data (Miller et al. 1994; Robertson 1987; Pardus et al. 1990). On the basis of laboratory measurements on core samples that cover effective stresses from 0–415 bar and porosities of the carbonates that range from 2–25%, Pickett (1963) concluded that the vp/vs ratio can be used well as a discriminator, since limestones always show a higher ratio than dolomites.
Another major factor that determines the vp/vs ratio, besides lithology, is porosity (e.g., Rafavich et al. 1984). However, the relation between porosity and vp/vs is complex and depends, among other things, on the shape of the pores and/or fractures that form the porosity. According to the commonly used petrophysical model of Toksöz et al. (1976), a high aspect ratio (> 0.1) decreases the vp/vs ratio; whereas, a low aspect ratio increases the vp/vs ratio (Robertson 1987). With regards to experimental data, Robertson (1987) claims positive correlation of porosity and vp/vs ratio, based on a few reflection seismic data, whereas Anselmetti and Eberli (1997) deduced a positive correlation between vp (> 4000 m/s), taken as a proxy for porosity, and the vp/vs ratio, on the basis of laboratory data. Likewise, Ding et al. (2019) found in laboratory experiments vp/vs ratio increases with increasing density of fluid-filled, randomly oriented fractures (and thus decreasing vp). The last two findings (Anselmetti and Eberli 1997; Ding et al. 2019) contradict the hypothesis that higher porosity caused by, e.g., stronger subseismic fracturing might cause the observed decrease of the vp/vs ratio in our data (Fig. 12), since in our case, it is accompanied by an increase in both vp and vs velocity.
So far, we have considered the vp/vs ratio. The velocities of both wave modes in carbonate rocks were investigated by Marion and Jibza (1997). They found that both P- and S-wave velocities of dolomite are higher than those for limestone, independent of porosity.
An example of the application of the technique used here was presented by Pardus et al. (1990) for oil exploration in the Scipio field in the US. They used data of separately measured P- and S-wave profiles to derive vp/vs ratios above and within the reservoir. Although both of their profiles do not show any structural or stratigraphic features, a significant decrease of the velocity ratio coincides with a dolomitized part of the target layer, and even a relative estimate of the amount of dolomitization was possible, verified by a number of boreholes.
In our case, the reason(s) for the strong variation of the vp/vs ratio in the reservoir will definitely be clarified only after the reservoir is drilled and/or cored. However, if our hypothesis is proved, the data will then be valuable for further reservoir analysis.
Implications for seismicity
In the vicinity of our study area, seismicity induced by two geothermal projects has gained public attention (Seithel et al. 2019). They are the Poing project (Ziegler and Heidbach 2020), approximately 15 km to the east, and the Unterhaching project that adjoins the Munich area to the south (see Fig. 1). In the latter area, Unterhaching, seismicity, with Ml up to 2.4, occurred shortly after the production started in 2007, which led to a setup of a local passive seismic network. Megies and Wassermann (2014) found that the majority of the epicenters fall within 500 m of the deepest part of the open-hole section of the injection well Unterhaching GT-2, suggesting it originates from injection. Hypocenter depth was determined to be 1.4–1.9 km below the open-hole section (Fig. 13a). This calculation was based on a vp/vs ratio of 1.65, which Lueschen (2012) derived from a 3D seismic volume in Unterhaching (Lueschen et al. 2011). However, an analysis of earthquake localisation residuals by Megies and Wassermann (2014) resulted in a higher vp/vs ratio: For the case of a half-space model, the minimum of residuals was reached at value of 1.94. This value is very close to the median value of 1.92 that we calculated in this study for the lower part of the Molasse above the carbonate platform. It is lower than the mean vp/vs ratio of 2.1, estimated for the entire Cenozoic and Malm strata combined (depth interval 0–3.1 km). However, this mean value is highly affected by the high near-surface vp/vs. The high vp/vs ratio values are further supported by a S-wave survey carried out in 1985, about 70 km east of Munich: for the majority of the Cenozoic sediments, a value of 1.9–2.0 was derived (Edelmann 1985). The consequences for earthquake hypocenter depth are drastic (Fig. 13b): Hypocenters are translated from deep into the basement (~ 1.5 km) to a position very close to the top of the basement, only some hundreds of meters below the open-hole section.
Effect of vp/vs on the hypocentral depth (Megies and Wassermann 2014, rearranged). a Original hypocenter depths of seven events at Unterhaching based on a vp/vs ratio of 1.65 (black) and hypocenter depths based on a half-space model (red) with a ratio of 1.94 that was derived from rms residual minimization. b Individual variation of hypocenter depths of the seven events shown for a half-space model. As the vp/vs ratio approaches 2, hypocenter depths move closer to the top of the crystalline basement. Reprinted from Geothermics, 52, Megies T, Wassermann J, Microseismicity observed at a non-pressure-stimulated geothermal power plant, 36–49, (2014), with permission from Elsevier
Conclusions
We recorded about half of the shots of a conventional 3D seismic survey on 467 single 3C receivers spread over three 2D lines. Our results show that most of the recorded energy on the horizontal components is from P-waves that converted to SV-waves. Despite the limited number of 3C receivers, we were able to build a seismic 3D PS-wave volume around the 2D lines that allowed the picking of horizons in the Molasse units as well as in the carbonate platform. We were able to identify the vp/vs ratio for different depth intervals and stratigraphic units. We use it to discriminate between dolomitized and non-dolomitized reservoir rocks. Strong dolomitization in the Malm reservoir is connected with enhanced permeability (Böhm et al. 2013; Mraz et al. 2019). Additionally, the knowledge of the vp/vs ratio of the Molasse units above the reservoir enables more reliable hypocenter determination of induced seismicity.
A starting point for our processing originated from the evaluation of VSP measurements in the surrounding of the study area. In spite of only a P-wave source being used in all cases, some of the VSP show S-waves on the horizontal components. The reason why they only appear on some of the VSPs is unknown and should be further researched. Since almost all VSPs are realized using 3C geophones (except the emerging technique of DAS recording), we recommend they are inspected for S-waves and therefore the recording time during the surveys should be approximately twice as long as necessary for P-waves. This is low cost, and it may give valuable S-wave information.
Wawerzinek et al. (2017) showed that there is no significant loss in data quality using single 3C sensors instead of geophone groups for P-waves. Due to the additional benefit of S-wave information, we argue for the use of 3C single sensors in future surveys in this area, the GMB (and perhaps elsewhere too). By recording 3C on the entire 3D receiver grid, one can achieve a much better-defined S-wave volume than for the sparsely sampled data in this study. Regular distribution of this kind of data would also open the door for more sophisticated interpretation techniques that involve angle and azimuth effects.
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available from Stadtwerke München and Leibniz Institute of Applied Geophysics (LIAG), but restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for the current study, and so are not publicly available. Data are however available from the authors upon reasonable request and with permission of Stadtwerke München and Leibniz Institute of Applied Geophysics (LIAG).
Change history
06 April 2021
Open access funding note was included.
Abbreviations
- ACP:
-
Asymptotic conversion point
- CMP:
-
Common mid-point
- DAS:
-
Distributed acoustic sensing
- GMB:
-
German Molasse Basin
- MEMS:
-
Micro-electro-mechanical system
- P-wave:
-
Compressional wave
- PS-wave:
-
P-to-S converted wave
- S-wave:
-
Shear wave
- vp :
-
P-Wave velocity
- vs :
-
S-Wave velocity
- VSP:
-
Vertical seismic profiling
- 3C:
-
3-Component
References
Allen PA, Crampton SL, Sinclair HD. The inception and early evolution of the North Alpine Foreland Basin. Switzerland Basin Res. 1991;3(3):143–63. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2117.1991.tb00124.x.
Anselmetti FS, Eberli GP. Sonic velocity in carbonate sediments and rocks. In: Palaz I, Marfurt KJ, editors. Carbonate seismology. Geophysical Developments Series 6. Tulsa: Society of Exploration Geophysicists; 1997.
Bachmann GH, Müller M, Weggen K. Evolution of the Molasse Basin (Germany, Switzerland). Tectonophysics. 1987;137:77–92.
Bale R, Gratacos B, Mattocks B, Roche S, Poplavskii K, Li X. Shear wave splitting applications for fracture analysis and improved imaging; some onshore examples. First Break. 2009;27:73–83.
Behle A, Dohr G. Converted waves in exploration seismics. In: Dohr G, editor. Seismic shear waves. Part B: Applications. Handbook of Geophysical Exploration 15B. London/Amsterdam: Geophysical Press; 1985.
Böhm F, Savvatis A, Steiner U, Schneider M, Koch R. Lithofazielle Reservoircharakterisierung zur geothermischen Nutzung des Malm im Großraum München. Grundwasser. 2013;18:3–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00767-012-0202-4.
Buness H, von Hartmann H, Lueschen E, Meneses Rioseco E, Wawerzinek B, Ziesch J, Thomas R. GeoParaMoL: Eine Integration verschiedener Methoden zur Reduzierung des Fündigkeitsrisikos in der bayrischen Molasse. Geothermische Energie. 2016;85:22–3.
Chopra S, Stewart R. Multicomponent seismic. Lead Edge. 2010;29:1210–85.
Cuenot N, Dorbarth C, Dorbath L. Analysis of microseismicity induced by fluid injection at the hot dry rock site of Soultz-sous-Forêt (Alsace, France): implication of the characterization of the geothermal reservoir properties. Pure Appl Geophys. 2008;165:797–828.
DeAngelo MV, Hardage BA. Comparing P-P, P-SV, and SV-P mode waves in the Midland Basin. West Texas Interpretation. 2014;4(2):T183–90.
Deichmann N. Earthquake focal mechanisms of the induced seismicity in 2006 and 2007 below Basel (Switzerland). Swiss J Geosci. 2009;102(3):457–66.
Ding P, Ding W, Guidong D, Xiangyang L. Investigation of the effects of fracture orientation and saturation on the Vp/Vs ratio and their implications. Rock Mech Rock Eng. 2019;52:3293–304.
Dohr G. (ed.) Seismic shear waves. Part B: Applications. Handbook of Geophysical Exploration 15B. London/Amsterdam: Geophysical Press; 1985.
Domenico SN. Rock lithology and porosity determination from shear and compressional wave velocity. Geophysics. 1984;49(8):1188–95.
Donati M, Piazza JL, Rollet A, Baillon S, Marin D, Belz V, Toubiana H, Castro J, Bouheouira A, Raha M. 3D–3C Multicomponent Seismic – A successful fracture characterization case study in Algeria. First Break. 2016;34(1):35–47.
Dussel M, Lueschen E, Thomas R, Agemar T, Fritzer T, Sieblitz S, Huberc B, Birner J, Schulz R. Forecast for thermal water use from Upper Jurassic carbonates in the Munich region (South German Molasse Basin). Geothermics. 2016;60:13–30.
Dussel M, Wolfgramm M, Stockinger G, Mraz E, Budach I, Moeck I. Characterization of Fault Zones as Geothermal Targets in the Deep North Alpine Foreland Basin (Southern Bavarian Molasse Basin). Conference Proceedings; European Geothermal Congress; 2019. http://europeangeothermalcongress.eu/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/303.pdf.
Edelmann HAK. SHOVER shear-wave generation by vibration orthogonal to the polarization. Geophys Prospect. 1981;29:541–9.
Edelmann HAK. Shear-wave energy sources. In: Dohr G, editor. Seismic Shear Waves, Part B: Applications. Handbook of Geophysical Exploration 15B. London/Amsterdam: Geophysical Press; 1985. p. 134–177.
Frisch W. Tectonic progradation and plate tectonic evolution of the Alps. Tectonophysics. 1979;69:121–39.
Far M, Hardage, B. Interpretation of fractures and stress anisotropy in Marcellus Shale using multicomponent seismic data. Interpretation. 2014; 2,2:SE105-SE115. DOI: 10.1190 / INT-2013–0108.1
Garotta R. Two component acquisition as a routine procedure. In: Danbom SH, Domenico SN, editors. Shear Wave Exploration, Geophysical Developments Series 1. Tulsa: Society of Exploration Geophysicists, 1987.
GeoMol. GeoMol – Assessing subsurface potentials of the Alpine Foreland Basins for sustainable planning and use of natural resources. Project Report (Bayerisches Landesamt für Umwelt LfU, Augsburg). 2015. 188 pp.
Grigoli F, Luca S, Boese M, Weber B, Wiemer S, Clinton JF. Pick- and waveform-based techniques for real-time detection of induced seismicity. Geophys J Int. 2018;213(2):868–84.
Hardage B, DeAngelo M, Murray P, Sava D. Multicomponent Seismic Technology. Geophysical Reference Series 18. Tulsa: Society of Exploration Geophysics; 2011.
Hardage B, Wagner D. Generating direct-S modes with simple, low-cost, widely available seismic sources. Multicomponent seismic interpretation. Special section, Interpretation. 2014;2:SE1-SE15. https://doi.org/10.1190/INT-2013-0095.1
Hardage B, DeAngelo M, Sava D, Wagner D, Murray P, Sullivan C, Simmons J, Ebrom D, Roche D, Zhou R. Multicomponent seismic interpretation. Special section, Interpretation. 2014;2:SE1-SE135.
Hecht C, Pletl C. Das Verbundprojekt GRAME – Wegweiser für eine geothermische Wärmeversorgung urbaner Ballungsräume. Geothermische Energie. 2015;82:8–9.
Johnston J, Christensen N. Shear wave reflectivity, anisotropies, Poisson’s ratios, and densities of a southern Appalachian Paleozoic sedimentary sequence. Tectonophysics. 1992;210:1–20.
Kley J, Voigt T. Late Cretaceous intraplate thrusting in central Europe: Effect of Africa-Iberia-Europe convergence, not Alpine collision. Geology. 2015;36(11):839–42. https://doi.org/10.1130/G24930A.1.
Kwiatek G, Saarno T, Ader T, Bluemle F, Bohnhoff M, Chendorain M, Dresen G, Heikkinen P, Kukkonen I, Leary P, Leonhardt M, Malin P, Martínez-Garzón P, Passmore K, Passmore P, Valenzuela S, Wollin C. Controlling fluid-induced seismicity during a 6.1-km-deep geothermal stimulation in Finland. Science Advances. 2019;5:1–11.
Lemcke K. Geologie von Bayern I. Das bayerische Alpenvorland vor der Eiszeit. Stuttgart: E. Schweizerbart’sche Verlagsbuchhandlung; 1988.
Liu E, Martinez A. Seismic fracture Characterization – Concepts and Practical Applications. Education Tour Series: EAGE Publications bv; 2012.
Lu J, Meng X, Wang Y, Yang Z. Prediction of coal seam details and mining safety using multicomponent seismic data: A case history from China. Geophysics. 2016;81(5):B149–65. https://doi.org/10.1190/GEO2016-0009.1.
Lueschen E, Dussel M, Thomas R, Schulz R. 3D seismic survey for geothermal exploration at Unterhaching, Munich. Germany First Break. 2011;29:45–54. https://doi.org/10.3997/1365-2397.2011002.
Lueschen E. 3D-Seismik in der Umgebung der Bohrung Unterhaching Gt 2. In: Schulz, R., Thomas, R. (Eds.), Geothermische Charakterisierung von karstig-klüftigen Aquiferen im Großraum München – Endbericht (Geothermal Characterization of Karstic-Fractured aquifers in the Area of Greater Munich). Final Report. Leibniz-Institut für Angewandte Geophysik, Hannover; 2012. p. 11–15.
Marion D, Jizba D. Acoustic properties of carbonate rocks: Use in quantitative interpretation of sonic and seismic measurements. In: Palaz I, Marfurt KJ, editors. Carbonate seismology. Geophysical Developments Series 6. Tulsa: Society of Exploration Geophysicists; 1997. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.9781560802099.ch5.
McCamy K, Meyer RP, Smith TJ. Generally applicable solutions of Zoeppritz amplitude equations. Bull Seismol Soc Am. 1962;52(4):923–55.
Megies T, Wassermann J. Microseismicity observed at a non-pressure-stimulated geothermal power plant. Geothermics. 2014;52:36–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2014.01.002.
Meyer R, Schmidt-Kaler H. Paläogeographie und Schwammriffentwicklung des süddeutschen Malm – ein Überblick. Facies. 1990;23:175–84.
Miller S. Well log analysis of vp and vs in carbonates. CREWES research report 4, Chapter 12; 1992.
Miller S, Harrison M, Szata K, Stewart R, Lawton D. Interpretation of a carbonate reservoir using P-P and P-SV seismic data. SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts. 1994;64:471–3. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1932130.
Mraz E. Reservoir characterization to improve exploration concepts of the Upper Jurassic in the southern Bavarian Molasse Basin. Munich, Germany: Phd TUM; 2018.
Mraz E, Wolfgramm M, Moeck I, Thuro K. Detailed fluid inclusion and stable isotope analysis on deep carbonates from the North Alpine Foreland Basin to constrain paleofluid evolution. Geofluids. 2019;2019:8980794. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8980794.
Pardus Y, Conner J, Schuler N, Tatham R. vp/vs and Lithology in Carbonate Rocks: A Case Study in the Scipio Trend in Southern Michigan. SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts. 1990;60:169–72. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1890101.
Pickett GR. Acoustic character logs and their application in formation evaluation. J Petrol Technol. 1963;15:659–67. https://doi.org/10.2118/452-PA.
Puzyrev NN, Brodov LY, Vedernikov GV. Development of the transverse wave method and the problem of multiwave seismic exploration. Soviet Geol Geophys. 1980;21(10):9–19.
Rafavich F, Kendall CHStC, Todd TP. The relationship between acoustic properties and the petrographic character of carbonate rocks. Geophysics. 1984;49:1622–1636.
Robertson J. Carbonate porosity from S/P traveltime ratios. Geophysics. 1987;52(10):1346–54.
Roeder D, Bachmann G. Evolution, structure and petroleum geology of the German Molasse Basin. Memoires du Museum National d’Histoire Naturelle. 1996;170:263–84.
Schmid DU, Leinfelder RR, Schweigert G. Stratigraphy and Palaeoenvironments of the Upper Jurassic of Southern Germany–A Review. Zitteliana. 2005;B26:31–41.
Schuck A, Hecht C. Seismic in the city and the heat vision of Munich. Conference Proceedings; 79th EAGE Conference and Exhibition; 2017. https://doi.org/10.3997/2214-4609.201701767.
Seithel R, Gaucher E, Mueller B, Steiner U, Kohl T. Probability of fault reactivation in the Bavarian Molasse Basin. Geothermics. 2019;82:81–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2019.06.004.
Sell A, Buness H, Tanner DC, Ziesch J, Weller A. FD modelling of deeply-buried paleo-dolines underneath the city of Munich. Conference Proceedings; 1st Conference on Geophysics for Geothermal and Renewable Energy Storage; EAGE; 2019. https://doi.org/10.3997/2214-4609.201902506.
Shipilin V, Tanner DC, von Hartmann H, Moeck I. Multiphase, decoupled faulting in the southern German Molasse Basin — evidence from 3D seismic data. EGU Solid Earth. 2020. https://doi.org/10.5194/se-2020-96.
Sissingh W. Tectonostratigraphy of the North Alpine Foreland Basin: correlation of Tertiary depositional cycles and orogenic phases. Tectonophysics. 1997;282:223–56.
Stewart RR, Gaiser JE, Brown RJ, Lawton DC. Converted-wave seismic exploration: Methods. Geophysics. 2002;67(5):1348–63.
Stewart RR, Gaiser JE, Brown RJ, Lawton DC. Converted-wave seismic exploration: Applications. Geophysics. 2003;68(1):40–57.
Tatham R. Shear waves and lithology. In: Dohr G, editor. Seismic shear waves, Part B: Applications. Handbook of Geophysical Exploration 15B. London/Amsterdam: Geophysical Press; 1985. p. 87–133.
Tatham RH, McCormack MD. Multicomponent seismology in petroleum exploration. Investigations in Geophysics No. 6. Tulsa: Society of Exploration Geophysics; 1991.
Tessmer G, Behle A. Common reflection point data stacking technique for converted waves. Geophys Prospect. 1988;36:671–88.
Toksöz MN, Cheng CH, Timur A. Velocities of seismic waves in porous rocks. Geophysics. 1976;41:621–45.
von Hartmann H, Tanner DC, Schumacher S. Initiation and development of normal faults within the German Alpine Foreland Basin: the inconspicuous role of basement structures. Tectonics. 2016;35(6):1560–74.
von Hartmann H, Shipilin V, Meneses Rioseco E, Buness H. Facies Analysis of an Upper Jurassic Carbonate Geothermal Reservoir. Conference Proceedings; European Geothermal Congress; 2019. http://europeangeothermalcongress.eu/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/73.pdf.
Wang Z, Szata K. Rock physics lithology and porosity prediction in carbonate reservoirs. SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts; 1999. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1820915.
Wawerzinek B, Buness H, Thomas R. S-wave seismic experiments for geothermal exploration of the Upper Jurassic Carbonate platform in the Bavarian Molasse. Conference Proceedings; 4th Sustainable Earth Sciences (SES) Conference; EAGE; 2017. https://doi.org/10.3997/2214-4609.201702128.
Wei S, DeAngelo MV, Hardage BA. Advantages of joint interpretation of P-P and P-SV seismic data in geothermal exploration. Interpretation. 2014;2,2: SE117-SE123. https://doi.org/10.1190/INT-2013-0084.1.
Yilmaz Ö. Seismic Data Analysis: Processing, Inversion, and Interpretation of Seismic Data. Tulsa: Society of Exploration Geophysics; 2001.
Ziegler PA, Cloetingh S, van Wees JD. Dynamics of intra-plate compressional deformation: The Alpine foreland and other examples. Tectonophysics. 1995;252:7–59.
Ziegler PA. Late Cretaceous and Cenozoic intra-plate compressional deformations in the Alpine foreland - a geodynamic model. Tectonophysics. 1987;137:389–420.
Ziegler M, Heidbach O. The 3D stress state from geomechanical–numerical modelling and its uncertainties: a case study in the Bavarian Molasse Basin. Geotherm Energy. 2020;8:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40517-020-00162-z.
Acknowledgements
We thank ‘Stadtwerke München’ for the good collaboration in the project and Ewald Lüschen for promoting the S-wave experiments, especially in the initial project phase. We thank Sonja Wadas for helping to create Fig. 2. Two anomymous reviewer helped to improve the manuscript.
Funding
The authors acknowledge financial support by the German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy. This study was done in the framework of the project GeoParaMoL (project number 0325787B), which is part of the joint project GRAME (project number 0325787A). Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BW carried out data processing, calculations, interpretation and discussion. HB supervised the project and contributed to the discussion. DCT worked on geology and interpretation. HvH calculated and interpreted the seismic facies classification. All authors contributed in writing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Wawerzinek, B., Buness, H., von Hartmann, H. et al. S-wave experiments for the exploration of a deep geothermal carbonate reservoir in the German Molasse Basin. Geotherm Energy 9, 6 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40517-021-00189-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40517-021-00189-w