Abstract
The core of self-assessment (CSA) and critical thinking (CT) empower learners to observe and evaluate themselves. Although the literature on CSA and CT reflects a long history, little is known about their contributions to the learners’ academic engagement (AE) and self-esteem (SE), particularly in the EFL context. Therefore, the present investigation intended to explore a structural model of English as a Foreign Language (EFL) university students’ CSA, CT, and SE. Accordingly, the Core of Self-assessment Questionnaire (CSAQ), Watson–Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal-form A (WGCTA), The SInAPSi Academic Engagement Scale (SAES), and The Foreign Language Learning Self-esteem Scale (FLLSES), were administered to 427 Iranian EFL university learners. The results of Structural Equation Modelling (SEM) indicated that EFL university students with high levels of CSA were more engaged and could build up high SE. Moreover, the effective role of CT in boosting AE and SE was also confirmed. The implications of this study may unveil new prospects for implementing learning-oriented assessment in the classroom and CT practices in language learning instruction and assessment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Assessment is an indispensable part of Instruction. Teachers’ applied methodology and teaching style preferences, directly and indirectly, affect how they design and administer their assessments in the classroom. To ensure the educational and psychological well-being of the students, learning-oriented assessment in the classroom is highly recommended (Bachman, 2015). In CSA, learners are involved in critically evaluating their progress (Tavousi & Pour Sales, 2018). CSA is basically an integrated personality structure referring to the students’ assessment and interpretation of their own learning (GuoJie, 2021). Put it in other words, CSA is intended to activate the learners to feel more responsible and reflect on every step of their learning experiences (Wongdaeng, 2022). Investment in CSA can improve learners’ autonomy, emotion regulation, L2 grit, and social relationships (Heydarnejad et al., 2022; Jiang et al., 2022; Zhuoyuan, 2021).
CT is a higher-order thinking skill that is concentrated using intuition, insight, and artistry to decide about any affairs (Amirian et al., 2022; Heshmat Ghahderijani et al., 2021). According to Li et al. (2022), CT enables individuals to look back and forth to react efficiently in every situation. Thus, CT is a helpful attribution for the learners that guarantee a safe road for learning. While learning, students may face various chaos and complexities that ask for decisive reactions. They need to be armed with CT skills to help them apply their metacognition and cognition to act efficiently. CT allows learners to stop, step back, think deeply, and assess themselves (Syairofi et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2020).
AE is an affective-motivational attribution highlighting learners’ willingness, and involvement in educational activities (Shu, 2022). Engaged learners have high levels of dedication and they are completely immersed in the class activities (Burić & Macuka, 2017; Deng et al., 2022; Topchyan & Woehler, 2020). Today’s continuously challenging environment calls for engaged learners to be self-initiated and self-reliant. Engagement can be regarded as an incentive to extend the level of motivation and progress in individuals’ education. (Namaziandost, Heydarnejad, Rahmani Doqaruni, & Aziai, 2022). In other words, LE can be considered a measure that illustrates the extent and depth of students' participation in all aspects of their education.
SE as a psychological construct is individuals’ beliefs about themselves and their emotional states. Smith and Mackie (2007) stated that " SE is the positive or negative evaluations of the self, as in how we feel about it.” In the educational context, SE refers to the learners’ confidence in their own worth or abilities. SE among learners is more likely to flourish in learning situations when self-assessment is encouraged (Faramarzzadeh & Amini, 2017). Students with a healthy level of self-esteem work toward finding solutions when challenges arise; they also respect generally accepted social rules (Zhang, 2022a, 2022b). It is worth highlighting that practicing SE prepares learners to cope with the demands of the modern world (Mandokhail et al., 2018). Thus, prerequisite factors for the development and attainment of SE are necessary to be taken to the surface layer of educational research. Despite the potential role of CSA, CT, AE, and ES in the well-being of the learners, there remains a paucity of evidence on the extent and direction of the interplay among them. In seeking to understand their associations better, the present study set forth to fill this educational gap. In the following section, the related literature was critically reviewed.
Literature review
The Core of Self-assessment (CSA)
Assessment is the systematic basis for making inferences about students’ progress and their learning (Bachman, 2015). Through the years, different methods were defined to facilitate assessment and increase its validity and reliability. CSA is a type of assessment in which learners are actively involved in the “assessment or evaluation of oneself or one's actions, attitudes, or performance. That is why each learner should be encouraged and trained to go through a process of self-assessment”, (Bachman et al., 2010, p. 12). According to Andrade (2019), CT, metacognition, monitoring, and self-regulated learning are the major principles of CSA. Furthermore, Judge et al. (1997) CSA is considered a type of higher-order trait involving self-esteem, generalized self-efficacy, neuroticism, and locus of control.
CSA can be generated intrinsically and extrinsically (Bourke & Mentis, 2007). External values, feedback from others, and grades define the extrinsic phase of CSA. Internal values and goal setting define the extrinsic phase of CSA. Sociocultural settings as well as the learner’s self-determination and self-identity are critical in CSA formulation (Bourke & Mentis, 2007, 2013). Learners need to evaluate their learning process and be involved in solving problems. The high levels of CSA armed learners to overcome different challenges and decide thoughtfully (Al-Mamoory & Abathar Witwit, 2021). According to Hu (2022), CSA empowers learners to regulate their emotions. It means that self-assessment influences both cognitive and affective aspects of learners’ educational lives. The high state of CSA, especially in language learning can manage emotional experiences and improve academic achievement (Bijani et al., 2022; Punpromthada et al., 2022).
As the literature on CSA echoes, practicing self-assessment inhibits cognitive and metacognitive skills among EFL learners (Heydarnejad et al., 2022; Nemati et al., 2021; Wei, 2020). Moreover, Jahara et al. (2022) found that levels of coping style among EFL learners change the state of CSA and stress management. It was also approved that self-assessment is affected by self-efficacy beliefs (Amirian et al., 2022; Zheng et al., 2022), academic emotion (Pekrun et al. 2017), metacognitive skills (Wei, 2020), and critical thinking (Zhang, 2022a, 2022b; Li et al., 2022). Additionally, the impact of L2 grit on CSA and foreign language learning anxiety was investigated by Heydarnejad et al. (2022). The results of SEM indicated that L2 grit increased the level of CSA. That is, gritter students are more powerful in self-monitoring. They can also control and manage the anxiety that may be experienced in language classes.
Critical thinking (CT)
The concept of CT was born about two centuries ago by Socrates, who assumed that reasoning, analyzing, and evaluating were the critical aspects of individuals’ thinking (Fisher, 2001). Despite the long introduction and vast application of CT, no agreed-upon definition is suggested (Fasko, 2003; Halonen, 1995). As Paul (1988) and Halpern (2003) stipulated, CT is a higher-order thinking skill that activates mental processes and cognitive skills. Moreover, Dewey (1933) defined CT as dynamic processes of analysis, synthesis, and evaluation to get an acceptable conclusion. In the definition of CT by Ennis (1996), the intellectual and disciplined process of mind, which is developed by critical reflection, is highlighted. In the same line of inquiry, Thomas and Lok (2015) considered knowledge, skills, and disposition as the basis of CT.
The introduction of CT as an essential part of education was first done by Dewey (1933). Based on his proposal, higher-order thinking skills should be implemented in schools and universities. In this regard, Mason (2008) noted that CT strategies should be taught and teachers should learn how to apply them in the classroom. Reviewing the related literature on CT highlighted the crucial role of teachers in implementing and practicing CT. For instance, Heydarnejad, Fatemi, and Ghonsooly (2021) concluded that EFL teachers’ attitudes toward CT and self-regulation influence their style of teaching. The contribution of CT to the identity formation of the teachers (Sheybani & Miri, 2019), reflective thinking (Heydarnejad et al., 2018), self-efficacy (Amirian et al., 2022), L2 grit (Zheng et al., 2022), and emotion regulation (Namaziandost, Heydarnejad, Rahmani Doqaruni, & Aziai, 2022). When teachers are empowered with higher-order thinking skills, they are more able to help their students cultivate CT skills (Li et al., 2022).
Due to the immense influence of CT on learners’ academic achievement, various studies attempted to investigate the practical strategies for implementing CT among learners. In this regard, Rashtchi and Khoshnevisan (2020) suggested practicing CT strategies by writing tasks among EFL learners. In another study by Sheikhy Behdani and Rashtchi (2019), the role of process writing and its contribution to fostering CT was highlighted. Moreover, Davoudi and Heydarnejad et al. (2022) practice reflective thinking among EFL learners and they found that reflective thinking as a higher-order thinking skill could enhance the student’s language achievement. Zare et al. (2021) also documented that students’ reading comprehension skills were improved with the help of developing dynamic assessment, which is based on CT. From another perspective, Wale and Bishaw (2020) confirmed that inquiry-based learning boosted CT skills in the EFL context. Additionally, Wahyudi et al. (2019) conducted a study to explore the effect of a discovery learning-based assessment module to enhance CT. Based on their findings, the discovery learning-based assessment could improve CT and creativity of the learners, especially in their speaking production.
Academic engagement (AE)
Engagement is a multidimensional construct and entails different aspects. It affects the motivation, cognition, behavior, and emotions of the learners (Robinson & Hullinger, 2008; Sharma & Bhaumik, 2013). Engagement in the domain of education was defined and studied from different perspectives: school engagement (Fredricks et al., 2004), study engagement (Schaufeli et al., 2002), student course engagement (Handelsman et al., 2005; Xu et al., 2022), and teacher engagement (Deng et al., 2022; Namaziandost, Heydarnejad, Rahmani Doqaruni, & Aziai, 2022). To describe engagement different models and theories were proposed. Fredricks et al. (2004) Model of Engagement and Schaufeli et al. (2002) Model of Engagement are the two comment models of engagement due to their reliability and usage in different empirical studies.
Fredricks et al. (2004) Model of Engagement defines engagement as a dynamic and malleable construct including behavioral, cognitive, and emotional dimensions. They believe that these three dimensions are integrated. Engagement from the eyes of Schaufeli et al. (2002) consists of absorption, vigor, and dedication. These two models assess different aspects of students’ engagement, but they believe that engagement is one of the vital aspects of learners’ academic engagement. In these two models, learners’ cognitive engagement and enthusiasm are described as their involvement in school-related activities and willingness to learn (Rezai et al., 2022; Tuominen-Soini & Salmela-Aro, 2014). Fredricks et al. (2004) and Schaufeli et al. (2002) also conceptualize that AE increases learners’ resilience, persistence, and positive attitudes toward learning.
Through the years, AE and its correlation were studied and its contributions to learners’ well-being were highlighted in various empirical studies. For instance, Alonso-Tapia et al. (2022) discovered that AE positively relates to motivation, self-efficacy, emotion, self-regulation, and satisfaction. The reciprocal relationships between AE, school engagement, and motivation were found by Hosseinmardi et al. (2021). Likewise, Amerstorfer and Freiin von Münster-Kistner (2021) conducted a study to investigate the factors that affect AE. As they discussed, AE depends on personal characteristics, the teacher, the teaching methodology, peers, and the learning atmosphere. They believed that cognitive, metacognitive, affective, social, task-related, and foreign language-related factors influence AE. In a recent study by Namaziandost, Heydarnejad, and Rezai (2022), the mediator role of emotion regulation in fostering engagement, self-efficacy, and anger in higher education was confirmed. They concluded that a healthy state of emotion regulation will guarantee a sense of engagement and self-efficacy among university teachers. In such a situation, they can better manage and regulate their anger.
Self-esteem (SE)
SE is confidence in one’s own worth or abilities (Mackinnon, 2015). It is the offspring of the individual’s beliefs about their skills, abilities, and social relationships (Wang & Ollendick, 2001). SE is associated with the generation of self-image and self-conscience. According to Manning et al. (2006), SE is linked to self-evaluation and involves cognitive appraisals relevant to self-worth and affective experiences. Additionally, Dörnyei and Ryan (2015) argued that SE is related to self-concept and self-evaluation. Self-concept refers to individuals’ self-image and self-evaluation addresses the procedures involved in the formation of individuals’ SE. More precisely, Lawrence (2006) defined self-concept as an umbrella term and includes SE, self-image, and ideal self.
SE influences students’ learning and academic success. It means that learners with higher SE are more confident and define higher goals for themselves despite challenges and difficulties (Murk, 2006). Their persistence in attempts helps them to become more successful. SE can also foster self-regulatory strategies as well as the emotional states of individuals (Hosseinmardi et al., 2021). According to Brown (2000), “no successful activity can occur without some degree of self-esteem” (p.145). SE is related to students’ autonomy and can increase their reading comprehension (Zhang, 2022a, 2022b). The mediator role of SE in shaping spoken skills among advanced and intermediate language learners was concluded by Faramarzzadeh and Amini (2017). Based on their findings, language learners with high levels of self-esteem were more successful in total spoken words, total spoken turns, and interruptions in mixed groups. It was also documented that teachers’ positive SE helps the development of positive SE in their students (Mandokhail et al., 2018).
Objectives of the present study
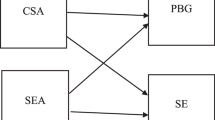
As the review of the existing literature reflected, CSA, CT, AE, as well as SE are student-attributed constructs that foster learning and learners’ well-being. When learners are armed with CSA, CT, AE, and SE, they can act more skillfully and decide better, especially in the face of chaos and complexity. Despite their immense contributions, the possible relationships between CSA, CT, AE, and SE remained uncharted territories, particularly in the realm of language learning. Therefore, the present study intended to take a step forward and uncover the association between CSA, CT, AE, and SE among EFL university students. In this regard, a model was proposed (Figure 1) to picture the relationships between CSA, CT, AE, and SE with the aim of advancing more meaningful learning and initiating future research. This model, based on previous studies and relevant theories, proposed the possible association between CSA, CT, AE, and SE. Thus, the possible contributions of CSA and CT to AE and SE in the EFL context as well as higher education were explored in this study. In so doing, the suggested model was tested via Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) and SEM. The outcomes of this research can both theoretically and empirically assist learners and teachers. Cultivating CSA and higher-order thinking skills can empower learners to be active in their learning processes and the procedures involved in their assessment. To reach these objectives, the following research questions were posed:
-
RQ1: To what extent does EFL university learners’ CSA influence their AE?
-
RQ2: To what extent does EFL university learners’ CSA influence their SE?
-
RQ3: To what extent does EFL university learners’ CT influence their AE?
-
RQ4: To what extent does EFL university learners’ CT influence their SE?
In this regard, the following null hypotheses were formulated:
-
H01. EFL university learners’ CSA does not influence their AE.
-
H02. EFL university learners’ CSA does not affect their SE.
-
H03. EFL university learners’ CT does not influence their AE.
-
H04. EFL university learners’ CT does not affect their SE.
Methodology
In this section, the methodological steps are described in detail:
Participants
This research was conducted among 427 university students (158 males and 269 females) at the MA level from Iran. They were studying different branches of English in state universities of Iran. Among 427 participants, 221 students were studying English Teaching, 54 English Literature, and 152 were English Translation. The criteria for selecting the participants were convenience or opportunity sampling procedures.
Instruments
The Core of Self-assessment Questionnaire (CSAQ)
To investigate the level of EFL university students’ CSA, the Core of Self-assessment Questionnaire (CSAQ) was employed. This instrument was developed by Judge et al. (2003) with 12 items on a five-point Likert scale. The range of obtained scores was from 12 to 60. High scores reflect high levels of self-assessment, while low scores indicate low levels of self-assessment. Based on the report of Cronbach’s alpha (α= 0.879), the reliability of this instrument in our study was acceptable.
Watson–Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal-form A (WGCTA)
University students’ CT was assessed via the Watson–Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal Form A by Watson and Glaser (1980). This scale involves five sections: inference (16 items), recognizing assumptions (16 items), making deductions (16 items), interpretation (16 items), and evaluation (16 items). In this research, the report of Cronbach alpha was satisfactory (α = 0.865).
The SInAPSi Academic Engagement Scale (SAES)
The SInAPSi (Services for active participation and inclusion of university students) Academic Engagement Scale (SAES) was designed and validated by Freda et al. (2021). This instrument aims to gauge university students’ AE. This instrument comprises six dimensions on a five-point Likert scale as follows: (1) university value and sense of belonging (6 items), (2) perception of the capability to persist in the university choice (4 items), (3) value of university course (7 items), (4) engagement with university professors (4 items), (5) engagement with university peers (5 items), and (6) relationships between university and relational net (3 items). In the current investigation, the report of Cronbach was 0.891, which indicated acceptable reliability.
The Foreign Language Learning Self-esteem Scale (FLLSES)
To explore EFL university students’ self-esteem, the Foreign Language Learning Self-esteem Scale (FLLSE) was used. This instrument was developed by Rubio (2007) on a five-point Likert scale (from 1—strongly disagree to 5—strongly agree). FLLSE includes 25 items in four dimensions: (1) language capability, (2) real in-class language utilization, (3) in-class correlations, and 4) attitude toward / behavior in the class of foreign language. The reliability of this instrument was estimated in this study and the result of the Cronbach alpha coefficient was (α = 0.851) acceptable.
Procedures
This study was administered through a web-based platform. The data collection started in May and ended in August 2022. The university students at the MA level were asked to complete an electronic survey form including the CSEQ, WGCTA, FLLSES, and SAES via Google Forms. On the whole, 427 forms were received and the return rate was 85.2%. No data were missed due to the design of the electronic survey that all parts should be linked necessarily. More importantly, in electronic surveys, researchers can gather data from different regions with varying age groups and sociocultural backgrounds.
Data analysis
Firstly, the normality of the data was examined through Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test. Due to the normal distribution of the data, parametric methods were suggested to analyze the data. Thus, CFA and SEM using LISREL (linear structural relationships) 8.80 were applied. As Hair et al. (1998) assert, CFA is used to validate the latent variables. Furthermore, SEM is a robust multivariate procedure to take a confirmatory hypothesis-testing approach for the proposed structural theory (Schreiber et al. 2006).
Results
The results of statistical analysis employed to gauge the relationships between CSA, CT, FLLSE, and SAE are displayed in this part. At first, the descriptive statistics were calculated and displayed in Table 1.
Based on Table 1, the mean score of CSA was 39.129 (SD = 11.076). Among the subscales of CT, interpretation (M = 56.838, SD = 12.005) was at the highest level and evaluation was at the lowest level (M = 20.386, SD = 4.784). Furthermore, in-class correlations got the highest mean score (M = 13.494, SD = 4.183) and real in-class language utilization (M = 13.494, SD = 4.183) received the lowest mean score among the subscales of FLLSES. Considering the subscales of SAES, the highest mean score is related to the perception of the capability to persist in the university choice (M = 13.494, SD = 4.183) and the lowest mean score is related to university value and sense of belonging (M = 11.712, SD = 2.170).
Following this step, the normal descriptions of the data were explored via the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test to decide on applying convenient statistical methods. Table 2 reports the results of the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test.
Based on Table 2, the sig values for all the instruments and their subscales were higher than 0.05, which showed that the data were normally distributed and that applying parametric methods was logical. Therefore, the LISREL 8.80 statistical package was employed to explore the structural relationships among CSA, WGCTA, FLLSE, and SAE. The chi-square magnitude, the root mean squared error of approximation (RMSEA), the comparative fit index (CFI), and the normed fit index (NFI) were utilized to evaluate the model fit. Based on Jöreskog (1990), the chi-square/df ratio should be lower than three and the chi-square should be non-significant. The root means square error of approximation (RMSEA) is recommended to be lower than 0.1 (Jöreskog, 1990). Moreover, the cut values for the NFI, GFI, and CFI are assumed to be greater than 0.90 (Jöreskog, 1990).
As Table 3 presented, the chi-square/df ratio (2.789) and the RMSEA (0.065) were acceptable. Furthermore, GFI (0.921), NFI (0.917), and CFI (0.952) reached the acceptable fit thresholds.
The standardized estimates and t values were examined to inspect the strengths of the causal relationships among the variables. According to Fig. 2 and Fig. 3, the impact of CSA on FLLSE (β = 0.70, t = 17.65) and SAE (β = 0.65, t = 17.65) was statistically significant and in a positive direction. The influence of CT on FLLSE (β = 0.89, t = 22.69) and SAE (β = 0.76, t = 18.66) was significantly positive. In Table 4, the report of the fit indices in the second model was displayed. The chi-square/df ratio (2.915) and the RMSEA (0.067) presented the acceptable fit thresholds. In addition, GFI (0.916), NFI (0.913), and CFI (0.932) were acceptable.
The contributions of CSA and CT to FLLSE and SAE subscales are shown in Figs. 4 and 5 (model 2). Based on Figs. 4 and 5, CSA significantly and in a positive direction influenced language capability (β = 0.89, t = 33.89), real in-class language utilization (β = 0.81, t = 30.74), in-class correlations (β = 0.73, t = 25.72), attitude toward behavior (β = 0.66, t = 16.64), university value (β = 0.62, t = 13.67), perception of the capability (β = 0.84, t = 29.60), value of university course (β = 0.76, t = 25.59), engagement university professors (β = 0.71, t = 20.70), engagement university peers (β = 0.69, t = 15.85), and relationships (β = 0.56, t = 12.80). Moreover, the effects of CT on FLLSE and SAE subscales were as follows: language capability (β = 0.78, t = 27.56), real in-class language utilization (β = 0.72, t = 21.71), in-class correlations (β = 0.63, t = 14.65), Attitude toward Behavior (β = 0.82, t = 31.85), university value (β = 0.61, t = 14.72), perception of the capability (β = 0.75, t = 25.63), value of university course (β = 0.79, t = 28.78), engagement university professors (β = 0.68, t = 15.66), engagement university peers (β = 0.57, t = 13.55), and Relationships (β = 0.52, t = 11.14)
As the next step, a Pearson product-moment correlation was applied to explore the correlation between CSA, CT, FLLSE subscales, and SAE subscales.
Based on Table 5, CSA and CT correlated significantly and positively with FLLSE subscales and SAE subscales. The correlation between CSA and FLLSE subscales as well as SAE subscales was as follows: language capability (r = 0.912, p < 0.01), real in-class language utilization (r = 0.853, p < 0.01), in-class correlations (r = 0.708, p < 0.01), attitude toward behavior (r = 0.752, p < 0.01), university value (r = 0.684, p < 0.01), perception of the capability (r = 0.891, p < 0.01), value of university course (r = 0.802, p < 0.01), engagement university professors (r = 0.733, p < 0.01), engagement university peers (r = 0.712, p < 0.01), and relationships (r = 0.612, p < 0.01).
Additionally, the correlation between CT and FLLSE subscales as well as SAE subscales were as follows: language capability (r = 0.804, p < 0.01), real in-class language utilization (r = 0.744, p < 0.01), In-class Correlations (r = 0.689, p < 0.01), attitude toward behavior (r = 0.881, p < 0.01), university value (r = 0.683, p < 0.01), perception of the capability (r = 0.789, p < 0.01), value of university course (r = 0.812, p < 0.01), engagement university professors (r = 0.716, p < 0.01), engagement university peers (r = 0.603, p < 0.01), and relationships (r=0.573, p < 0.01).
Discussion
The current research intended to investigate the association between CSA, CT, AE, and SE in the Iranian EFL context. In so doing, the researchers of this study proposed a model to display the association between these constructs and it was tested via SEM. The outcomes of the survey reflected that CSA and CT could predict AE and SE significantly. Model 1 and model 2 portray their relationships and highlight the mediator roles of CSA and CT in fostering learner-oriented assessment in the classroom. Thereby, the first null hypothesis (EFL university learners’ CSA does not influence their AE), the second null hypothesis (EFL university learners’ CSA does not affect their SE), the third null hypothesis (EFL university learners’ CT does not influence their AE), and the fourth one (EFL university learners’ CT does not affect their SE) were rejected.
Based on the findings relevant to the first research question (To what extent does EFL university learners’ CSA influence their AE?), the role of CSA on AE was statistically significant. It means that high levels of CSA enable EFL university learners to be more active in all class activities. In such a situation, university learners feel more responsible for their tasks and assessments. They invest more time in their evaluation, social interaction, and group works. They can cope with difficulties and feel less anxious. The class activities and learning-oriented assessment engage university learners. According to the second model, CSA influenced the subcomponents of AE positively. That is, CSA influenced university value and sense of belonging, perception of the capability to persist in the university choice, the value of university courses, engagement with university professors, engagement with university peers, and relationships between the university and relational net.
This outcome can be discussed theoretically. The idea of CSA is theoretically supported by self-determination and self-identity theories (Bourke & Mentis, 2007, 2013). It can be inferred that learner-oriented assessment explicitly and implicitly helps EFL university learners to achieve positive self-identity, which provides positive attitudes toward learning and educational values. It also affects the students’ social relationships. Furthermore, this finding is in accord with Huang’s findings (2022), who concluded that self-assessment contributes to self-regulation and self-efficacy. Up to now, no empirical studies have ever been conducted to inspect the relationships between CSA and AE and the current research is the first attempt.
Considering the second research question (To what extent does EFL university learners’ CSA influence their SE?), the results indicated that CSA directs university learners’ SE. It means that learners’ attitudes toward self-assessment and self-monitoring affect how they perceive themselves. The more university students practice self-assessment, the higher they find their personal worth and values. It was also concluded and illustrated in the second model that CSA affected the subcomponents of SE (language capability, real in-class language utilization, in-class correlations, and attitude toward behavior in the class of foreign language).
Regarding the third research question (To what extent does EFL university learners’ CT influence their AE?), it was also found that EFL university learners’ CT influenced their AE. It means that higher levels of cognitive and metacognitive skills would guarantee learners’ AE. This outcome can be investigated from the lens of CSA. According to the results of the first research question, CSA and learner-oriented assessment provide the situation for the learners to be involved directly in their assessment and learning procedure. University students, who are armed with higher-order thinking skills are more successful in evaluation, monitoring, and metacognition (Davoudi & Heydarnejad, 2020). Thus, it can be inferred that more investment in CSA increases students’ engagement, especially in higher education. As Deng et al. (2022) concluded, self-monitoring makes individuals aware of the positive and negative aspects of their educational lives and increases self-efficacy and engagement. In the same line of inquiry, Namaziandost, Heydarnejad, and Rezai (2022) evidenced that higher-order thinking skills influence individuals’ well-being to a great extent.
As the second model indicated, the effect of CT on the subcomponents of AE was great and in a positive direction. To put it another way, CT gives direction to learners’ university value and sense of belonging, perception of the capability to persist in the university choice, the value of university courses, engagement with the university professors, engagement with university peers, and relationships between the university and relational net. This outcome seems logical considering the fact that CT skills open the minds of the learners. The findings of the study also displayed that CT could play a mediator role in university learners’ SE (To what extent does EFL university learners’ CT influence their SE?). It means CT skills give a better understanding of self. In other words, CT sets the tone of EFL university learners’ self-image and SE. The more they practice CT strategies, the better they adjust their thoughts and beliefs. That is, CT enables learners to improve their SE. Additionally, the second model presented that CT influenced the subscales of SE (language capability, real in-class language utilization, in-class correlations, and attitude toward behavior in the class of foreign language). This result corroborates with those of Amirian et al. (2022), Heydarnejad, Hosseini Fatemi, and Ghonsooly (2021), and Xiyun et al. (2022). They evinced that higher-order thinking skills, self-regulatory strategies, SE, as well as self-efficacy beliefs are closely related.
Conclusion and implications
In a nutshell, this research documented the contribution of CSA and CT to AE and SE in EFL higher education. The findings pictured that CSA and CT facilitate learning-oriented assessment in the classroom. They promote learners’ AE and SE. In other words, CSA and CT act like a compass for EFL learners and help them to focus on every step taken on the educational road. CSA and CT could have a significant impact on the personal growth and development of their SE. Moreover, CSA opens the eyes of learners in general and EFL learners in partiture. Learning-oriented assessment taps the actual use of language in language learning and deserves more attention from testing specialists. Actually, research on the relationship between CSA, CT, AE, and SE in the educational context, particularly in the EFL context, is quite rare and calls for more attention. The present research was the first attempt to portray the relationship between CSA, CT, AE, and SE. Therefore, the findings can open a new window in educational research and foster the implementation of learning-oriented assessment in the classroom, especially in the EFL domain.
Some pedagogical implications for educators, particularly in higher education are suggested. The provision of learning-oriented assessment in the classroom has received great emphasis. Thus, language learners need to develop and practice CSA and CT while at the same time respecting learners’ attempts in making their own statements and conceptualization. This golden opportunity boost AE and encourage SE. Thus, language teachers need to acquire the related knowledge to implement CSA and CT in classes. In this regard, pre-service and in-service teacher training programs are strongly recommended. Teacher training courses can be developed to teach effective strategies for practicing learning-oriented assessment in the classroom This awareness is also crucial for language teachers, language testers, as well as learners, especially those in higher education should become alert about the advantages of practicing CSA and CT. They also need to learn efficient strategies to practice CSA and CT. The investment in higher-order thinking skills can be achieved through designing and developing appropriate educational materials and tasks as well as functional practice and assessment. Language learners should also learn that they play a crucial role in their process of AE and SE. Thus, they need to practice useful strategies to improve AE and SE.
Similar to other research in the realm of education, this study was limited in some aspects. Firstly, the current investigation is quantitative in nature, thus getting a deeper understanding of the causal links between CSA, CT, AE, and SE. Future studies can apply mixed-method approaches to complete the related outcomes. Secondly, demographic variables and their possible effects on CSA, CT, AE, and SE were not the targets of this study; therefore, they can be a recommendation for future research. Additionally, as a further research avenue, it is suggested to explore the influence of CSA, CT, AE, and SE on other learner-related constructs (i.e., academic buoyancy, self-efficacy, self-regulation, and evaluation apprehension).
Availability of data and materials
The authors state that all the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
Abbreviations
- EFL:
-
English as a Foreign Language
- CSA:
-
Core of Self-assessment
- CSAQ:
-
Core of Self-Assessment Questionnaire
- CT:
-
Critical thinking
- WGCTA:
-
Watson–Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal-form A
- AE:
-
Academic engagement
- SAES:
-
The SInAPSi Academic Engagement Scale
- SE:
-
Self-esteem
- FLLSES:
-
The Foreign Language Learning Self-esteem Scale
- GFI:
-
Good Fit Index
- LISREL:
-
Linear structural relations
- NFI:
-
Normed Fit Index
- RMSEA:
-
Root-mean-squared error of approximation
- CFA:
-
Confirmatory factor analysis
- SEM:
-
Structural equation modeling
References
Al-Mamoory, S., & Abathar Witwit, M. (2021). Critical discourse analysis of oppression in “To Kill a Mockingbird”. Journal of Social Science and Humanities Research, 9(2), 11–24.
Amerstorfer, C. M., & Freiin von Münster-Kistner, C. (2021). Student perceptions of academic engagement and student-teacher relationships in problem-based learning. Frontiers in Psychology, 12, 713057. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.713057.
Andrade, H. L. (2019). A critical review of research on student self-assessment. Frontiers in Education, 4, 87. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2019.00087.
Bachman, L. F. (2015). Justifying the use of language assessments: linking test performance with consequences. JLTA Journal, 18, 3–22.
Bachman, L. F., Palmer, A. S., & Palmer, A. S. (2010). Language assessment in practice: Developing language assessments and justifying their use in the real world. Oxford University Press Oxford.
Bijani, H., Hashempour, B., Ibrahim, K. A. A. A., Orabah, S. S. B., & Heydarnejad, T. (2022). Investigating the effect of classroom-based feedback on speaking assessment: a multifaceted Rasch analysis. Language Testing in Asia, 12(1), 1–28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40468-022-00176-3.
Bourke, R., & Mentis, M. (2007). Self-assessment as a lens for learning. In The SAGE Handbook of Special Education, (pp. 319–330) Retrieved from https://sk.sagepub.com/reference/hdbk_specialedu.
Bourke, R., & Mentis, M. (2013). Self-assessment as a process for inclusion. International Journal of Inclusive Education, 17(8), 854–867. https://doi.org/10.1080/13603116.2011.602288.
Brown, H. D. (2000). Principles of Language Learning and Teaching. Pearson Education.
Burić, I., & Macuka, I. (2017). Self-efficacy, emotions and work engagement among teachers: A two wave cross-lagged analysis. Journal of Happiness Studies, 19(7), 1917–1933. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-017-9903-9.
Davoudi, M., & Heydarnejad, T. (2020). The interplay between reflective thinking and language achievement: a case of Iranian EFL learners. Language Teaching Research Quarterly, 18, 70–82.
Deng, J., Heydarnejad, T., Farhangi, F., & Farid Khafaga, A. (2022). Delving into the relationship between teacher emotion regulation, self-efficacy, engagement, and anger: a focus on English as a foreign language teachers. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 1019984. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1019984.
Dewey, J. (1933). How we think: a restatement of the relation of reflective thinking to the educative process. D.C. Heath & Co Publishers.
Dörnyei, Z., & Ryan, S. (2015). The psychology of the language learner revisited. Routledge.
Ennis, R. (1996). Critical thinking dispositions: their nature and assessability. Information Logic., 18, 165–182. https://doi.org/10.22329/il.v18i2.2378.
Faramarzzadeh, R., & Amini, D. (2017). The relationship between self-esteem and conversational dominance of Iranian EFL learners’ speaking. The Journal of Applied Linguistics and Applied Literature: Dynamics and Advances, 5(1), 55–68. https://doi.org/10.22049/jalda.2018.26306.1081.
Fasko, D. (2003). Critical thinking: origins, historical development, future direction. In D. Fasko (Ed.), Critical thinking and reasoning: Current research, theory, and practice, (pp. 3–20). Hampton Press.
Fisher, A. (2001). Critical thinking: an introduction. Cambridge University Press.
Fredricks, J. A., Blumenfeld, P. C., & Paris, A. H. (2004). School engagement: Potential of the concept, state of the evidence. Review of Educational Research, 74(1), 59–109. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543074001059.
GuoJie, M. (2021). The role of athletic psychology, athlete engagement in athletic performance and athletes’ sports success in China: does coaching behavior moderates? Revista De Psicología Del Deporte (Journal of Sport Psychology), 30(3), 191–204 https://www.rpd-online.com/index.php/rpd/article/view/485.
Hair, J. F., Anderson, R. E., Tatham, R. L., & Black, W. C. (1998). Multivariate data analysis, (5th ed.,). Prentice Hall
Halonen, J. S. (1995). Demystifying critical thinking. Teaching of Psychology, 22, 75–81. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15328023top2201_23.
Halpern, D. F. (2003). Thinking critically about creative thinking. In M. A. Runco (Ed.), Critical Creative Processes, (pp. 189–207). Hampton Press.
Handelsman, M. M., Briggs, W. L., Sullivan, N., & Towler, A. (2005). A Measure of College Student Course Engagement. The Journal of Educational Research, 98(3), 184–191. https://doi.org/10.3200/JOER.98.3.184-192.
Heydarnejad, T., Ebrahimi, M. R., & Najjari, H. (2018). On the associations among critical thinking, reflective thinking, and emotions: a case of Iranian EFL Teachers. International Journal of Applied Linguistics and English Literature., 7(6), 97–103. https://doi.org/10.7575/aiac.ijalel.v.7n.6p.97.
Heydarnejad, T., Fatemi, A. H., & Ghonsooly, B. (2021). The relationship between critical thinking, self-regulation, and teaching style preferences among EFL teachers: a path analysis approach. Journal of Language and Education, 7, 98–110. https://doi.org/10.17323/jle.2021.11103.
Heydarnejad, T., Hosseini Fatemi, A., & Ghonsooly, B. (2021). The interplay among self-regulation, emotions and teaching styles in higher education: a path analysis approach. Journal of Applied Research in Higher Education, 14(2), 594–609. https://doi.org/10.1108/jarhe-08-2020-0260.
Heydarnejad, T., Ismail, S. M., Shakibaei, G., & Saeedian, A. (2022). Modeling the impact of L2 grit on EFL learners’ core of self-assessment and foreign language anxiety. Language Testing in Asia, 12, 50. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40468-022-00200-6.
Hosseinmardi, A. A., Ghorban Shiroodi, S., Zarbakhshbahri, M. R., & Tizdast, T. (2021). The relationship of academic engagement, school engagement and school belonging with academic achievement by mediated the academic achievement motivation in male students. Iranian Journal of Educational Society, 14(2), 178–189. https://doi.org/10.22034/ijes.2021.534830.1123.
Hu, N. (2022). Investigating Chinese EFL learners’ writing strategies and emotional aspects. LEARN Journal: Language Education and Acquisition Research Network, 15(1), 440–468.
Huang, Q. (2022). Influence of EFL teachers’ self-assessment on their self-regulation and self-efficacy. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 891839. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.891839.
Jahara, S. F., Hussain, M., Kumar, T., Goodarzi, A., & Assefa, Y. (2022). The core of self-assessment and academic stress among EFL learners: the mediating role of coping styles. Language Testing in Asia, 12, 21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40468-022-00170-9.
Jöreskog, K. G. (1990). New developments in LISREL: analysis of ordinal variables using polychoric correlations and weighted least squares. Quality and Quantity, 24(4), 387–404. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00152012.
Judge, T. A., Ereza, A., Bono, J. E., & Thoreson, C. J. (2003). The core self-evaluation scale (CSAs): Development of a measure. Personnel Psychology, 56, 303–331.
Judge, T. A., Locke, E. A., & Durham, C. C. (1997). The dispositional causes of job satisfaction: a core evaluations approach. Research in Organizational Behavior, 19, 151–188.
Koosha, M., Abdollahi, A., & Karimi, F. (2016). The relationship among EFL learners’ self-esteem, autonomy, and reading comprehension. Theory and Practice in Language Studies, 6(1), 68–78. https://doi.org/10.17507/Tpls.0601.09.
Lawrence, D. (2006). Enhancing self-esteem in the classroom. Pine Forge Press.
Li, M., Heydarnejad, T., Azizi, Z., Rezaei, & Gashti, Z. (2022). Modeling the role of emotion regulation and critical thinking in immunity in higher education. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 1005071. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1005071.
Mackinnon, N. J. (2015). Self-esteem and beyond. Palgrave Macmillan.
Mandokhail, S., Khan, F. R., & Malghani, M. (2018). Impact of ESL learners’ self-esteem on their oral proficiency. International Journal of English Language and Linguistics, 8, 210–222. https://doi.org/10.5539/ijel.v8n3p210.
Manning, M. A., Bear, G. G., & Minke, K. M. (2006). Self-concept and self-esteem. In G. G. Bear, & K. M. Minke (Eds.), Children’s needs III: Development, prevention, and intervention, (pp. 341–356). National Association of School Psychologists.
Mason, M. (2008). Critical thinking and learning. Blackwell Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781444306774.
Murk, J. C. (2006). Self-esteem research, theory, and practice. In Toward a positive psychology of self-esteem, (3rd ed., ). Springer Publishing Company.
Nemati, M., Ghafoori, M., Birjandi, P., & Izadpanah, S. (2021). Self-assessment, peer assessment,teacher assessment and their comparative efect on EFL learners’ second language writing strategy development. Journal of English Language Teaching and Learning, 13(28), 201–216. https://doi.org/10.22034/ELT.2021.48543.2456.
Paul, R. (1988). Critical thinking in the classroom. Teaching K-8., 18, 49–51.
Pekrun, R., & Linnenbrink-Garcia, L. (2014). International handbook of emotions in education. In R. Pekrun, & L. Linnenbrink-Garcia (Eds.), International Handbook of Emotions in Education, (pp. 1–10). Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203148211.
Pekrun, R., Lichtenfeld, S., Marsh, H. W., Murayama, K., & Goetz, T. (2017). Achievement Emotions and Academic Performance: Longitudinal Models of Reciprocal Effects. Child Development, 88(5), 1653–1670. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.12704
Punpromthada, A., Bhanthumnavin, D. E., Bhanthumnavin, D. L., Meekun, K., Sitsira-at, S., Pimthong, S., & Yaemyuen, A. (2022). Why has COVID-19 easily spread at home and which psycho-behavioral model can better explain it in university students. Educational Sciences: Theory and Practice, 22(1), 101–115. https://doi.org/10.12738/jestp.2022.1.0009.
Rashtchi, M., & Khoshnevisan, B. (2020). Lessons from critical thinking: how to promote thinking skills in EFL writing classes. European Journal of Foreign Language Teaching, 5(1), 34–47. https://doi.org/10.46827/ejfl.v5i1.3153.
Robinson, C. C., & Hullinger, H. (2008). New benchmarks in higher education: Student engagement in online learning. Journal of Education for Business, 84(2), 101–108.
Rubio, F. (2007). Self-Esteem and Foreign Language Learning: An introduction. In F. Rubio (Ed.), Self-esteem and foreign language learning, (pp. 2–12). Cambridge Scholars Publishing.
Schreiber, J. B., Nora, A., Stage, F. K., Barlow, E. A., & King, J. (2006). Reporting structural equation modeling and confrmatory factor analysis results: A review. The Journal of Educational Research, 99(6), 323–338. https://doi.org/10.3200/joer.99.6.323-338
Schaufeli, W. B., & Salanova, M. (2011). Work engagement: on how to better catch a slippery concept. European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology, 20(1), 39–46. https://doi.org/10.1080/1359432X.2010.515981.
Schaufeli, W. B., Salanova, M., Gonzalez-Roma, V., & Bakker, A. (2002). The Measurement of Engagement and Burnout: A Two Sample Confirmatory Factor Analytic Approach. Journal of Happiness Studies, 3, 71–92.
Schaufeli, W. B., Taris, T. W., & van Rhenen, W. (2008). Workaholism, burnout, and work engagement: three of a kind or three different kinds of employee well-being? Applied Psychology, 57(2), 173–203. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-0597.2007.00285.x.
Sharma, B. R., & Bhaumik, P. K. (2013). Student Engagement and Its Predictors: An Exploratory Study in an Indian Business School. Global Business Review, 14(1), 25–42. https://doi.org/10.1177/0972150912466364.
Sheikhy Behdani, R., & Rashtchi, M. (2019). Process writing and enhancement of critical thinking ability: Is writing a vehicle or an ingredient of critical thinking? Iranian Journal of Applied Language Studies, 11(1), 181–200. https://doi.org/10.22111/ijals.2019.4937.
Sheybani, M., & Miri, F. (2019). The relationship between EFL teachers’ professional identity and their critical thinking: a structural equation modeling approach. Cogent Psychology, 9(1), 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311908.2019.1592796.
Shu, K. (2022). Teachers’ Commitment and Self-Efficacy as Predictors of Work Engagement and Well-Being. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 850204. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.850204.
Smith, E. R., & Mackie, D. M. (2007). Social psychology, (3rd ed., ). Psychology Press/Taylor & Francis (UK).
Tavousi, N., & Pour Sales, H. (2018). The role of optimism in the relationship between core self-evaluation and hardiness with life satisfaction. Contemporary Psychology, 11(2), 52–66.
Thomas, K., & Lok, B. (2015). Teaching critical thinking: an operational framework. In M. Davies, & R. Barnett (Eds.), The Palgrave Handbook of Critical Thinking in Higher Education, (pp. 93–104). Palgrave Macmillan. https://doi.org/10.1057/9781137378057_6.
Tuominen-Soini, H., & Salmela-Aro, K. (2014). Schoolwork engagement and burnout among Finnish high school students and young adults: Profiles, progressions, and educational outcomes. Developmental Psychology, 50(3), 649–662. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0033898.
Wahyudi, R., Rukmini, D., & Bharati, D. A. L. (2019). Developing discovery learning-based assessment module to stimulate critical thinking and creativity of students’ speaking performance. English Education Journal., 9(2), 172–180 http://journal.unnes.ac.id/sju/index.php/eej.
Wale, B. D., & Bishaw, K. S. (2020). Effects of using inquiry-based learning on EFL students’ critical thinking skills. Asian-Pacific Journal of Second and Foreign Language Education., 5(9), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40862-020-00090-2.
Wang, Y., & Ollendick, T. H. (2001). A cross-cultural and developmental analysis of self-esteem in Chinese and Western children. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 4, 253–271.
Watson, G., & Glaser, E. M. (1980). Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal Manual. Psychological Corporation.
Wei, X. (2020). Assessing the metacognitive awareness relevant to L1-to-L2 rhetorical transfer in L2 writing: The cases of Chinese EFL writers across proficiency levels. Assessing Writing, 44, 100452.
Wongdaeng, M. (2022). The role of metacognition in the learning of English as a foreign language. In N. Siddiqui, & S. Gorard (Eds.), Making your doctoral research project ambitious: Developing Large-Scale Studies with Real-World Impact. Routledge.
Xiyun, S., Fathi, J., Shirbagi, N., & Mohammaddokht, F. (2022). A structural model of teacher self-efficacy, emotion regulation, and psychological wellbeing among English teachers. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 904151. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.904151.
Zare, M., Barjesteh, H., & Biria, R. (2021). Enhancing EFL learners' reading comprehension skill through critical thinking-oriented dynamic assessment. Teaching English Language, 15(1), 189–214. https://doi.org/10.22132/TEL.2021.133238.
Zhang, F. (2022a). A theoretical review on the impact of EFL/ESL. Students’ Self-Sabotaging Behaviors on Their Self-Esteem and Academic Engagement. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 873734. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.873734.
Zhang, H., Yuan, R., & He, X. (2020). Investigating university EFL teachers’ perceptions of critical thinking and its teaching: voices from China. The Asia-Pacific Education Researcher, 29(5), 483–493. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-020-00500-6.
Zhang, Y. M. (2022b). The research on critical thinking teaching strategies in college English Class-room. Creative Education, 13, 1469–1485. https://doi.org/10.4236/ce.2022.134090.
Zheng, S., Heydarnejad, T., & Aberash, A. (2022). Modeling the interplay between emotion regulation, self-efficacy, and L2 grit in higher education. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 1013370. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1013370.
Zhuoyuan, Y. (2021). Analysis of public management, psychological work attention, and athletes’ performance in sport industries. Revista De Psicología Del Deporte (Journal of Sport Psychology), 30(3), 168–178 Retrieved from https://www.rpd-online.com/index.php/rpd/article/view/483.
Alonso-Tapia, J., Merino-Tejedor, E., & Huertas, J. A. (2022). Academic engagement: assessment, conditions, and effects—a study in higher education from the perspective of the person-situation interaction. European Journal of Psychology of Education. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-022-00621-0.
Amirian, S. M. R., Ghaniabadi, S., Heydarnejad, T., & Abbasi, S. (2022). The contribution of critical thinking and self-efficacy beliefs to teaching style preferences in higher education. Journal of Applied Research in Higher Education. https://doi.org/10.1108/jarhe-11-2021-0441.
Freda, M. F., Raffaele, D. L. P., Esposito, G., et al. (2021). A new measure for the assessment of the university engagement: the SInAPSi academic engagement scale (SAES). Current Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-021-02189-2.
Heshmat Ghahderijani, B. H., Namaziandost, E., Tavakoli, M., Kumar, T., & Magizov, R. (2021). The comparative effect of group dynamic assessment (GDA) and computerized dynamic assessment (C-DA) on Iranian upper-intermediate EFL learners’ speaking complexity, accuracy, and fluency (CAF). Language Testing in Asia, 11(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40468-021-00144-3.
Jiang, P., Namaziandost, E., Azizi, Z., & Razmi, M. H. (2022). Exploring the effects of online learning on EFL learners’ motivation, anxiety, and attitudes during the COVID-19 pandemic: a focus on Iran. Current Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-04013-x.
Namaziandost, E., Heydarnejad, T., Rahmani Doqaruni, V., & Aziai, Z. (2022). Modeling the contributions of EFL university professors’ emotion regulation to self-efficacy, work engagement, and anger. Current Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-04041-7.
Namaziandost, E., Heydarnejad, T., & Rezai, A. (2022). Iranian EFL teachers’ reflective teaching, emotion regulation, and immunity: examining possible relationships. Current Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-03786-5.
Rezai, A., Namaziandost, E., Miri, M., & Kumar, T. (2022). Demographic biases and assessment fairness in classroom: insights from Iranian university teachers. Language Testing Asia, 12(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40468-022-00157-6.
Syairofi, A., Mujahid, Z., Mustofa, M., Ubaidillah, M. F., & Namaziandost, E. (2022). Emancipating SLA findings to inform EFL textbooks: a look at indonesian school english textbooks. The Asia-Pacific Education Researcher. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-022-00642-9.
Topchyan, R., & Woehler, C. (2020). Do teacher status, gender, and years of teaching experience impact job satisfaction and work engagement? Education and Urban Society, 001312452092616. https://doi.org/10.1177/0013124520926161.
Xu, L., Naserpour, A., Rezai, A., Namaziandost, E., & Azizi, Z. (2022). Exploring EFL learners’ metaphorical conceptions of language learning: a multimodal analysis. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10936-022-09842-2.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
No funding received in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors had equal substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation of data, and writing the manuscript. The authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ information
Tahereh Heydarnejad is a university lecturer at the department of English language, University of Gonabad, Gonabad, Iran. She published many papers in different local and international journals.
Riswanto was born on April 10th 1972 at a small cold town named Curup in Bengkulu province. He is a senior English lecturer at Universitas Islam Negeri Fatmawati Sukarno Bengkulu. He has been teaching at this university since 1999. He finished his Sarjana degree at Bengkulu University 1997 on English education majoring. He completed his master degree from State University of Padang 2007 and in 2014 He was awarded Ph.D. degree from University of Science Malaysia on TESOL Methodology department. The writer is very active in academic activities such as seminars, conferences and workshops both in Indonesia and overseas programs. Besides, the writer is also active in writing scientific papers and references book, book chapters and proceedings as well as journal articles both national and international journals.
Elham Saberi Dehkordi is a lecturer at department of English, Islamic Azad University of Najafabad, Isfahan, Iran.
Bambang Parmadi was born on May 6, 1974 in Sumenep Regency, East Java Province. He is a lecturer in Music Arts Education, Regional Cultural Studies, and Educational Philosophy at Bengkulu University. He has taught at this university since 2010, previously teaching as a teacher at a high school and junior high school in Bengkulu. Completed his undergraduate degree at the Padang Teaching and Education Institute in 1998 majoring in Music Arts Education. He completed his master’s degree from the Surakarta Indonesian Art Institute majoring in Art Creation (Karawitan) in 2008 and in 2018 he was awarded the title of Dr. Cultural Studies of Ethnomusicology Concentration from Udayana University, Denpasar. The author is very active in academic activities such as seminars, conferences and workshops both at home and abroad. In addition, the author is also active in writing scientific papers and reference books, book chapters and proceedings as well as journal articles in both national and international journals.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Riswanto, Heydarnejad, T., Saberi Dehkordi, E. et al. Learning-oriented assessment in the classroom: the contribution of self-assessment and critical thinking to EFL learners’ academic engagement and self-esteem. Lang Test Asia 12, 60 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40468-022-00210-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40468-022-00210-4