Abstract
Background
Health-related quality of life (HRQOL) in cancer patients has attracted increasing attention, which may be associated with self-rated health (SRH), anxiety, and depression. However, limited studies have focused on the mediating role of anxiety and depression in the relationship between SRH and HRQOL among cancer patients. Therefore, this study aims to explore the serial multiple mediating effects of anxiety and depression between SRH and HRQOL in cancer patients.
Methods
This cross-sectional study investigated a total of 565 hospitalized cancer patients in Anhui province in China from November 2020 to October 2021. SRH was assessed using a single-item measure, anxiety and depression were assessed using the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) and HRQOL was assessed using the EuroQol-5 Dimension (EQ-5D, three-level version). Socio-demographic and clinical characteristics were analyzed using descriptive statistics. The relationships between SRH, anxiety, depression, and HRQOL were evaluated by Pearson correlation analysis. The serial multiple mediation of anxiety and depression was assessed by SPSS PROCESS macro.
Results
SRH, anxiety, depression and HRQOL were significantly correlated(P < 0.001). In comparison to the fair SRH, the good SRH exhibited a significantly positive direct effect (Effect = 0.2366, Bootstrap 95%CI: 0.0642 ~ 0.4090) and total effect on HRQOL (Effect = 0.4761, Bootstrap 95%CI: 0.2975 ~ 0.6546). Conversely, the poor SRH demonstrated a significantly negative total effect on HRQOL (Effect= -0.4321, Bootstrap 95%CI: -0.7544~ -0.1099). When considering the fair SRH as the reference group, the poor SRH displayed a negative indirect effect on HRQOL through the single mediation of anxiety (Effect= -0.1058, Bootstrap 95%CI: -0.2217~ -0.0107) and the serial mediation of anxiety and depression (Effect= -0.0528, Bootstrap 95%CI: -0.1233~ -0.0035). Conversely, the good SRH had a positive indirect impact on HRQOL through the single mediation of anxiety (Effect = 0.1153, Bootstrap 95%CI: 0.0583 ~ 0.1900) and depression (Effect = 0.0667, Bootstrap 95%CI: 0.0206 ~ 0.1234), as well as the serial mediation of anxiety and depression (Effect = 0.0575, Bootstrap 95%CI: 0.0192 ~ 0.1030).
Conclusion
SRH can improve HRQOL through the decrease of anxiety and depression in cancer patients. Focusing on SRH would be beneficial for their mental health and HRQOL in cancer patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Cancer is highly prevalent and the second leading cause of death around the world [1]. China is also facing unprecedented challenges in cancer control, due to the growth of aging population and socioeconomic development. It is reported that cancer has been the principal cause of death in China (126.9 per 100,000 persons), causing about one-fourth of all deaths [2]. Cancer patients frequently experience long-term and late effects of treatment, which lead to deleterious effects on health-related quality of life (HRQOL) [3]. HRQOL refers to those aspects of self-perceived well-being that are associated with or affected by the disease or treatment [4, 5].
According to previous study, a larger number of cancer patients in China have pain/discomfort problems with worsened HRQOL [2]. Most studies have focused on some sociodemographic and clinical characteristics, such as age and cancer stage, which are risk factors associated with HRQOL in cancer patients [6, 7]. However, given that demographic characteristics are unchangeable, identifying the potentially modifiable factors associated with HRQOL can help patients to improve self-management. Recently, a study has begun to explore the association between some psychological factors like anxiety or depression and HRQOL in laryngeal and hypopharyngeal cancer patients [8].
In general, patients will present negative emotional responses to cancer diagnosis and therapy, and depression and anxiety are the most common [9]. The prevalence of depression and anxiety in cancer patients was higher than that in healthy individuals [10]. It has been reported that the incidence of anxiety is 49.69% in cancer patients, which is higher than in the general population (18.37%) [9, 11]. Cancer-related anxiety is multifactorial and may stem from patients’ psychological response to cancer and changes in body image, sexual function, work, and social interactions [12,13,14]. Similarly, in China, the incidence of depression is 54.9% in cancer patients, which is significantly higher than in the general population (17.5%) [9, 11]. Moreover, depression is associated with poor prognosis, a deterioration of health status, chronic pain, and complications of treatment [1, 15].
Further research suggested that there is a significant association between anxiety and depression [16]. Anxiety and depression are closely intertwined and commonly comorbid [17, 18]. Clinical and epidemiological observations consistently indicate that anxiety can be considered as a major contributor to depression [19]. A previous study supported anxiety as a predictor of depression, revealing that anxiety significantly and positively predicted depression more than a decade later, while also showing that people who are anxious often resort to avoidance to cope with this negative emotion, which can lead to more severe depression later in life [20]. Additionally, anxiety and depression could both reduce cancer patients’ HRQOL [21, 22]. Results of a prospective, multi-center longitudinal study of HRQOL in patients with multiple myeloma showed that clinically relevant anxiety and depression as assessed by the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) significantly predicted low levels of HRQOL [23]. The biopsychosocial model also underscores the significance of psychological factors in individual health by proposing that illness and health stem from a complex interplay among biological, psychological, and social factors, where the role of psychological factors is crucial and cannot be overlooked [24]. A study suggested that implementing the biopsychosocial model in clinical practice and integrating interventions that consider psychological factors into treatment is more effective in enhancing both disease management and overall health outcomes compared to approaches solely based on individual variable categories [25]. This model also serves as the theoretical foundation for the research hypothesis of this study.
As a major predictor of HRQOL, self-rated health (SRH) reflects the general state of perceived disease and health [26, 27]. The revised HRQOL model proposed by Wilson and Cleary includes five dimensions, such as personal characteristics; biological functions reflecting the clinical features of the disease; environmental characteristics including social support; functional status and general health perception. The model clearly explains the structural causal relationship between the dimensions of patients’ HRQOL, and proposes that general health perception is a comprehensive concept of an individual’s subjective assessment of their overall health and a key factor influencing patients’ HRQOL, which is the final variable of the revised model proposed by Wilson and Cleary [28]. A previous finding showed that HRQOL increased with general health perception [29]. Besides, it has been revealed that SRH is significantly associated with anxiety and depression in older incarcerated males [30].
Although previous studies have separately explored the relationship between SRH, anxiety, depression, and HRQOL, limited studies have demonstrated these associations in cancer patients. Furthermore, there have been no studies that focus on how SRH affects HRQOL through anxiety and depression. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the nature of the association between SRH and HRQOL in cancer patients, and whether anxiety and depression mediate this potential relationship in a correlated manner. Increased knowledge derived from this study may help implement interventions to improve the management of cancer patients. Based on the foregoing, the present study proposes the following four hypotheses:
Hypothesis 1
SRH can positively predict HRQOL of cancer patients.
Hypothesis 2
SRH can indirectly predict HRQOL of cancer patients through the mediating effect of anxiety.
Hypothesis 3
SRH can indirectly predict HRQOL of cancer patients through the mediating effect of depression.
Hypothesis 4
SRH can indirectly predict HRQOL of cancer patients through the serial mediation of anxiety and depression.
Materials and methods
Participants
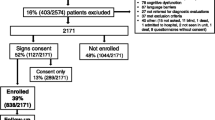
It was a cross-sectional study using a self-reporting survey questionnaire. From November 2020 to October 2021, hospitalized cancer patients were recruited for this study in Anhui province, located in eastern China. This study was approved by the Biomedical Ethics Committee of Anhui Medical University (No.20,180,173). The inclusion criteria were as follows: (a) with a confirmed diagnosis of cancer through medical records; (b) able to speak and read Chinese; and (c) older than 18-year-old. The exclusion criteria included (a) cognitive impairment; (b) not aware of the diagnosis; (c) other major medical diseases; (d) physically deteriorated and (e) unwillingness to cooperate. The purpose of the survey was verbally explained to the participants by the investigators. After informed consent was received, the participants were asked to complete a questionnaire. A total of 599 adult participants were investigated in this study, excluding questionnaires with missing, incomplete, contradictory responses, multiple choice and irregular filled data, and finally 565 qualified questionnaires were obtained, with a qualified rate of 94.32%.
Measures
Demographic and clinical data
Demographic characteristics, including age, gender, education, marital status, and current residence, were collected by questionnaire. Each participant was reviewed using a standardized protocol to confirm the diagnosis and obtain detailed clinical data regarding cancer type and staging from the medical records of the responsible clinician.
Self-rated health
SRH have been reported to be a reliable and valid global assessment of health and is an indicator of physical and mental function [31]. In this study, SRH was assessed using a single-item measure: “How would you rate your overall health?” with 5 possible responses: (1) poor, (2) fair, (3) good, (4) very good, (5) excellent [32]. A higher score indicated better self-perceived health status. To enhance the interpretability of the results, this study categorizes SRH as a multi-categorical variable in both the regression model and the mediation effect analysis. Specifically, it combines the categories of “(3) good”, “(4) very good” and “(5) excellent” into a single category labeled as “good”. Consequently, SRH is then categorized as poor, fair, and good [33].
Health-related quality of life
Europol Five-Dimensional Health Questionnaire (EQ-5D-3 L), covering five dimensions: mobility, self-care, usual activity, pain/discomfort, and anxiety/depression was used to evaluate the HRQOL in this study [34]. Each dimension has three levels: 1 = no problems, 2 = some problems, and 3 = extreme problems. The EQ-5D-3 L descriptive system can convert each health state into a utility score using a country-specific value set based on social preferences [35]. The utility score varied from 0 (representing death) to 1 (representing perfect health). In the context of HRQOL, death signifies an individual being in the most adverse state—experiencing extreme problems in all five dimensions: mobility, self-care, usual activities, pain/discomfort, and anxiety/depression. Conversely, attaining perfect health indicates that the individual is at their optimal state—experiencing no problems across all five dimensions. A preference weight set for the Chinese population was applied to estimate the mean EQ-5D utility score [36]. The Cronbach’s α coefficient was 0.659 in this study.
Anxiety and depression
HADS was used to screen for depression and anxiety among cancer patients in this study. It is a valid and reliable self-rating scale that measures anxiety and depression in both hospitals and communities, which consists of two subscales: HADS-A (detect anxious states) and HADS-D (detect depressive states) [37]. Each subscale consists of seven items rated on a 4-point scale [38]. Higher scores reflected higher levels of anxiety or depression. Participants responded to each item by thinking about how they felt and/or behaved in the past month. In this study, the Cronbach’s α coefficients of HADS-A and HADS-D were 0.778 and 0.775 respectively.
Statistical analysis
The statistical software SPSS (SPSS, Chicago, IL), version 22.0, was used for the data analysis. A descriptive analysis was performed for the socio-demographic and clinical features of the participants. The relationships between SRH, anxiety, depression, and HRQOL were evaluated by Pearson correlation analysis (see Table 2). The mediation analyses were carried out using the PROCESS macro (model 6) developed by Hayes [39], employing ordinary least squares regression to calculate path coefficients for total, direct, and indirect effects (see Tables 3 and Table 4). In the model, SRH and HRQOL were determined to be the independent variable and the dependent variable, respectively. Anxiety and depression acted as mediating variables, establishing pathways from SRH to HRQOL. In regression and multiple mediation analyses, this study adjusted for all the demographic and clinical characteristics. The total effect (c or C) refers to the relationship between SRH and HRQOL without controlling for anxiety and depression. The direct effect (c’ or C’) refers to the relationship between SRH and HRQOL after controlling for anxiety and depression, while the indirect effects were the effects of SRH on HRQOL through anxiety or through depression, or through both anxiety and depression in the multiple mediation analysis (see Fig. 1). A 95% confidence interval (CI) was calculated with 5,000 bootstrapping resamples. The indirect effect of the mediation path was considered statistically significant if the 95% CI range did not include 0.
The serial mediation model. ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, SRH: self-rated health, Ref: reference category. a1: effect of the poor SRH on anxiety, a2: effect of the poor SRH on depression, a3: effect of anxiety on depression, b1: effect of anxiety on HRQOL, b2: effect of depression on HRQOL, A1: effect of the good SRH on anxiety, A2: effect of the poor SRH on depression, c: total effect of the poor SRH on HRQOL, c': direct effect of the poor SRH on HRQOL, C: total effect of the good SRH on HRQOL, C': direct effect of the poor SRH on HRQOL
Results
Demographic and clinical characteristics
Of all cases, 51.5% were males and 48.5% were females. Most of the patients (88.0%) were married, and 66.7% were aged between 50 and 70 years. More than half of the participants (68.7%) came from rural areas. The proportions of patients at stage I, stage II, stage III, and stage IV were 3.2%, 6.9%, 14.2% and 75.8% respectively. The top 3 cancer types were lung (25.5%), breast (15.9%) and colorectal (13.8%). The demographic and clinical characteristics of all participants are summarized in Table 1.
Correlation between SRH, anxiety, depression and HRQOL
The mean scores for anxiety, depression, HRQOL and SRH were 12.36 ± 3.88, 11.34 ± 4.01, 0.87 ± 0.16, and 3.76 ± 0.93, respectively. Pearson correlation analysis was employed to assess the relationships among SRH, anxiety, depression, and HRQOL (see Table 2). The results of the correlation analysis showed that anxiety was significantly positively correlated with depression (r = 0.676, P < 0.001), while HRQOL was significantly negatively correlated with anxiety and depression (r= -0.403, P < 0.001; r= -0.405, P < 0.001). It can be observed that the SRH was significantly correlated with anxiety (r= -0.318, P < 0.001), depression (r= -0.392, P < 0.001) and HRQOL (r = 0.319, P < 0.001). More details are presented in Table 2.
Regression analysis for SRH, anxiety, depression and HRQOL
In exploring the connections among SRH, anxiety, depression, and HRQOL, our study implemented regression analysis to investigate potential influencing mechanisms. Anxiety, depression, and HRQOL were considered as dependent variables, and the regression model was adjusted for demographic and clinical characteristics (see Table 3). The results revealed that the poor SRH had a significant negative impact on HRQOL (β= -0.432, t= -2.634, P < 0.01) in comparison to fair SRH, while the good SRH exhibited a significant positive effect (β = 0.476, t = 5.237, P < 0.001). Regarding anxiety as the dependent variable, the poor SRH demonstrated a positive correlation with anxiety (β = 0.434, t = 2.665, P < 0.01) versus the fair SRH, whereas good SRH exhibited a significantly negative association with anxiety (β= -0.473, t= -5.241, P < 0.001). Considering depression as the dependent variable, the good SRH displayed a significant negative correlation with depression compared to the fair SRH (β= -0.348, t= -4.962, P < 0.001), while the link between the poor SRH and depression was insignificant. Furthermore, anxiety emerged as a substantial positive predictor of depression (β = 0.633, t = 19.704, P < 0.001). Inclusion of both anxiety and depression revealed that, compared to the fair SRH, the positive influence of the good SRH on HRQOL remained significant (β = 0.237, t = 2.695, P < 0.01), while the impact of the poor SRH was not statistically significant. Meanwhile, anxiety (β= -0.244, t= -4.740, P < 0.001) and depression (β= -0.192, t= -3.681, P < 0.001) displayed negative associations with HRQOL.
The mediating effect of anxiety and depression between SRH and HRQOL
Figure 1 displays the coefficients and significance of each path, and Table 4 presents the bootstrap results for the indirect effect. The results of the mediation analysis indicated that in comparison to the fair SRH, the good SRH exhibited a significant positive direct effect on HRQOL (Effect = 0.2366, Bootstrap 95%CI: 0.0642 ~ 0.4090), while the direct effect of the poor SRH was found to be not significant. In the examination of total effects, the good SRH showed a significant positive total effect on HRQOL compared to the fair SRH (Effect = 0.4761, Bootstrap 95%CI: 0.2975 ~ 0.6546), whereas the poor SRH demonstrated a significant negative total effect on HRQOL (Effect= -0.4321, Bootstrap 95%CI: -0.7544~ -0.1099).
The findings of the relative indirect effect analysis revealed that in Path 1, using the fair SRH as the reference category, the poor SRH exhibited a detrimental indirect effect on HRQOL through the mediating pathway of anxiety (Effect= -0.1058, Bootstrap 95%CI: -0.2217~ -0.0107), whereas the good SRH demonstrated a beneficial indirect impact on HRQOL via the mediating pathway of anxiety (Effect = 0.1153, Bootstrap 95%CI: 0.0583 ~ 0.1900). Moving to Path 2, in comparison to the fair SRH, the good SRH had a positive indirect influence on HRQOL through the mediating role of depression (Effect = 0.0667, Bootstrap 95%CI: 0.0206 ~ 0.1234), however, the relative indirect effect of depression in the association between the poor SRH and HRQOL was not statistically significant. In Path 3, relative to the fair SRH, the good SRH displayed a positive indirect effect on HRQOL through the serial mediation of anxiety and depression (Effect = 0.0575, Bootstrap 95%CI: 0.0192 ~ 0.1030), in contrast to the poor SRH which presented a negative indirect effect on HRQOL through the serial mediation of anxiety and depression (Effect= -0.0528, Bootstrap 95%CI: -0.1233~ -0.0035).
Discussion
The results of our study showed that SRH was positively correlated with HRQOL among cancer patients. And anxiety and depression played separately mediating effect between SRH and HRQOL, respectively. In addition, anxiety and depression also had a serial mediation effect between SRH and HRQOL.
According to our finding, better SRH is associated with higher HRQOL, which implies that SRH was a significant predictor of HRQOL. The regression analysis results also revealed that among cancer patients, those with poor SRH were negatively associated with HRQOL, whereas cancer patients with good SRH were positively associated HRQOL compared to those with fair SRH. It is consistent with a previous study in Korean [6]. The level of SRH depends not only on the cancer patients’ actual status of health, but also on their perceived status of health. On the other hand, HRQOL is highly correlated with perceived health and symptoms of disease. It was more influenced by the perception of health than by the physically adverse effects of disease [40, 41]. Consequently, cancer patients with better SRH are likely to have higher HRQOL, which may be due to better health status or accurate perception of health status. This accurate perception can enable cancer patients to remain optimistic, and then promote the improvement of HRQOL. Current evidence combined with our results suggests that raising awareness of disease and health can help to respond to the adverse effects of cancer patients.
Based on a multiple mediation model, this study confirmed the mediating effect of anxiety between SRH and HRQOL among cancer patients. Compared to the fair SRH, anxiety significantly mediated the relationship between the poor SRH and HRQOL, as well as the relationship between the good SRH and HRQOL. It is suggested that better SRH is less likely to cause anxiety and further improve HRQOL, which is consistent with the results of previous studies [30, 42]. This might be due to the fact that cancer patients with better SRH tend to have more social support, as well as better family intergenerational relationship. These can help cancer patients relieve stress and promote their mental health [43]. On the contrary, the decrease in SRH leads to increased anxiety, which can affect the physical and mental health of patients, and further leads to the lower HRQOL [22]. Thus, improving social and family support and relationship can reduce the anxiety among cancer patients, which can positively impact their HRQOL.
This study also demonstrated that in comparison to individuals reporting fair SRH, those with good SRH exhibited a favorable indirect impact on HRQOL mediated by depression. The results indicated that patients with better SRH had low levels of depression, which in turn improved their HRQOL. Cancer patients often report a variety of symptoms such as pain, nausea, vomiting, and fatigue [44], which are the main risk factors for increased depression in cancer patients [45]. Therefore, the symptoms of discomfort will lead to not only the deterioration of SRH, but also the occurrence of depression. Moreover, like previous studies, our study also found a significant negative association between depression and HRQOL. This might be due to the dysregulation of both the innate and adaptive immune systems in patients with depression, which hinders favorable prognosis [46]. Therefore, paying attention to mental health is an important strategy to improve the quality of life for cancer patients.
At last, our findings reveal a significant positive correlation between anxiety and depression. Moreover, compared to the fair SRH, anxiety and depression play significant serial multiple mediating roles in the relationship between the poor SRH and HRQOL, as well as in the relationship between the good SRH and HRQOL. The discoveries of serial-multiple mediation model further extend the theory of the beneficial effect of SRH on HRQOL improvement. The significant indirect effects support the causal relationship between anxiety and depression in the serial mediation model. Therefore, this study proposes that the causal relationship between anxiety and depression is an essential part of the effect of SRH on HRQOL. The model unveils that cancer patients who lack accurate perception of their own health status have poor SRH, accompanied by increased level of anxiety. Although there may be enhancements in their objective health condition post-treatment, certain individuals persist in perceiving a decline subjectively. Cancer patients with anxiety might employ avoidance as a coping strategy to lessen their negative feelings [20]. It conferred higher levels of later depression, and further caused a decline in HRQOL.
This study has developed a comprehensive framework that clarifies the relationship among SRH, anxiety, depression, and HRQOL, offering empirical implications to enhance the prognosis of cancer patients. Hence, in practice, the government should actively promote the dissemination of knowledge about prevalent diseases like cancer through a range of promotional initiatives and diverse health education programs, aiming to improve public awareness of primary behavioral risk factors and fundamental disease information. Communities and families should offer sufficient emotional and psychological support to individuals affected by cancer, attentively addressing their needs and providing compassionate care. In addition, healthcare providers are advised to promptly assess and recognize cancer patients experiencing psychological challenges, deliver psychological counseling, aid patients in mental adjustment, and support them in managing feelings of depression and anxiety. Healthcare professionals should also popularize disease-related information to ensure patients gain accurate insights into their health conditions and enhance their confidence in combatting illnesses.
There are some limitations in this study. For example, the cross-sectional design of this study does not determine a strong causal relationship among the four variables and the time sequence of their occurrences. Longitudinal research is needed to further examine the interactions of SRH, anxiety, depression in predicting HRQOL. Second, the convenience sampling used in this study may lead to potential selection bias. Third, HADS was used to assess depressive and anxious symptoms, while it just functions as screening but cannot diagnose depression and anxiety.
Despite these limitations mentioned above, compared with previous studies, the present study can provide some new information: (1) the latest situation of SRH, anxiety, depression, and HRQOL in Chinese cancer patients; (2) the relationship between SRH and HRQOL in cancer patients; (3) the single and serial mediating roles of anxiety and depression in the relationship between SRH and HRQOL in cancer patients. The results support the 4 hypotheses of this study that SRH can positively predict HRQOL in cancer patients. Meanwhile, SRH can indirectly predict HRQOL of cancer patients through the mediating effect of anxiety, depression and the serial mediating effect between anxiety and depression. These findings provide important implications for elucidating the potential mechanism of the relationship between SRH and HRQOL. To our knowledge, this is the first study to explore the single mediating and serial mediating roles of anxiety and depression in the relationship between SRH and HRQOL in Chinese cancer patients by well-established measurement.
Conclusion
Our study showed that SRH significantly affected HRQOL in cancer patients. And anxiety and depression played a separately mediating effect between SRH and HRQOL in cancer patients. Meanwhile, anxiety and depression had a serial mediation effect between SRH and HRQOL. This implies that improving SRH through improving mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression can help improve the quality of life of cancer patients.
All models were adjusted for the demographic and clinical characteristics, such as age, gender, education, marital status, current residence, cancer stage and cancer diagnosis.
Data availability
The dataset in this study is available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Liu ST, Wu X, Wang N, Zhao QQ, Xiao L, Fang CK, et al. Serial multiple mediation of demoralization and depression in the relationship between hopelessness and suicidal ideation. Psychooncology. 2020;29(8):1321–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/pon.5439.
Su M, Hua X, Wang J, Yao N, Zhao D, Liu W, et al. Health-related quality of life among cancer survivors in rural China. Qual Life Res. 2019;28(3):695–702. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-018-2038-6.
Han X, Robinson LA, Jensen RE, Smith TG, Yabroff KR. Factors Associated with Health-Related Quality of Life among Cancer survivors in the United States. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2021;5(1). https://doi.org/10.1093/jncics/pkaa123.
Ebrahim S. Clinical and public health perspectives and applications of health-related quality of life measurement. Soc Sci Med. 1995;41(10):1383–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/0277-9536(95)00116-o.
Yan R, Che B, Lv B, Wu P, Lu X, Zhang Y, et al. The association between physical activity, sedentary time and health-related quality of life in cancer survivors. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2021;19(1):213. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12955-020-01575-x.
Kim K, Kim JS. Factors influencing health-related quality of life among Korean cancer survivors. Psychooncology. 2017;26(1):81–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/pon.4105.
Cui C, Wang L, Wang X. Health-related quality of life and social constraints among Chinese breast cancer patients: a cross-sectional study. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2021;19(1):238. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12955-021-01871-0.
Wulff NB, Dalton SO, Wessel I, Arenaz Bua B, Lofhede H, Hammerlid E, et al. Health-Related Quality of Life, Dysphagia, Voice Problems, Depression, and anxiety after total laryngectomy. Laryngoscope. 2022;132(5):980–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.29857.
Wang Y, Mei C, Fu Y, Yue Z, Jiang Y, Zhu J. Anxiety and depression among tibetan inpatients with cancer: a multicenter investigation. Ann Palliat Med. 2020;9(6):3776–84. https://doi.org/10.21037/apm-20-1721.
Mitchell AJ, Ferguson DW, Gill J, Paul J, Symonds P. Depression and anxiety in long-term cancer survivors compared with spouses and healthy controls: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14(8):721–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(13)70244-4.
Yang YL, Liu L, Wang Y, Wu H, Yang XS, Wang JN et al. The prevalence of depression and anxiety among Chinese adults with cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Bmc Cancer. 2013;13. http://doi.org/Artn393 https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-13-393.
Stark DP, House A. Anxiety in cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 2000;83(10):1261–7. https://doi.org/10.1054/bjoc.2000.1405.
Pitman A, Suleman S, Hyde N, Hodgkiss A. Depression and anxiety in patients with cancer. BMJ. 2018;361:k1415. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.k1415.
Oberoi S, Yang J, Woodgate RL, Niraula S, Banerji S, Israels SJ, et al. Association of Mindfulness-based interventions with anxiety severity in adults with Cancer: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(8):e2012598. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.12598.
Ostuzzi G, Matcham F, Dauchy S, Barbui C, Hotopf M. Antidepressants for the treatment of depression in people with cancer. Cochrane Db Syst Rev. 2018(4). http://doi.org/ARTNCD011006https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD011006.pub3.
Erim DO, Bennett AV, Gaynes BN, Basak RS, Usinger D, Chen RC. Associations between prostate cancer-related anxiety and health-related quality of life. Cancer Med-Us. 2020;9(12):4467–73. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.3069.
Middeldorp CM, Cath DC, Van Dyck R, Boomsma DI. The co-morbidity of anxiety and depression in the perspective of genetic epidemiology. A review of twin and family studies. Psychol Med. 2005;35(5):611–24. https://doi.org/10.1017/S003329170400412x.
Su Y, Wang SB, Zheng H, Tan WY, Li X, Huang ZH, et al. The role of anxiety and depression in the relationship between physical activity and sleep quality: a serial multiple mediation model. J Affect Disord. 2021;290:219–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2021.04.047.
Jacobson NC, Newman MG. Anxiety and depression as bidirectional risk factors for one another: a Meta-analysis of Longitudinal studies. Psychol Bull. 2017;143(11):1155–200. https://doi.org/10.1037/bul0000111.
Jacobson NC, Newman MG. Avoidance mediates the relationship between anxiety and depression over a decade later. J Anxiety Disord. 2014;28(5):437–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.janxdis.2014.03.007.
Mosleh SM. Health-related quality of life and associated factors in Jordanian cancer patients: a cross-sectional study. Eur J Cancer Care. 2018;27(5). http://doi.org/ARTNe12866 https://doi.org/10.1111/ecc.12866.
Zhang LJ, Zhang HZ, Zhong QL, Luo QH, Gong N, Zhang YH, et al. Predictors of quality of life in patients with breast Cancer-related Lymphedema: Effect of Age, Lymphedema Severity, and anxiety. Lymphat Res Biol. 2021;19(6):573–9. https://doi.org/10.1089/lrb.2020.0073.
Ramsenthaler C, Gao W, Siegert RJ, Edmonds PM, Schey SA, Higginson IJ. Symptoms and anxiety predict declining health-related quality of life in multiple myeloma: a prospective, multi-centre longitudinal study. Palliat Med. 2019;33(5):541–51. https://doi.org/10.1177/0269216319833588.
Engel GL. The need for a new medical model: a challenge for biomedicine. Science. 1977;196(4286):129–36. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.847460.
Alvarez AS, Pagani M, Meucci P. The clinical application of the biopsychosocial model in mental health: a research critique. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2012;91(13 Suppl 1):S173–80. https://doi.org/10.1097/PHM.0b013e31823d54be.
Idler EL, Benyamini Y. Self-rated health and mortality: a review of twenty-seven community studies. J Health Soc Behav. 1997;38(1):21–37.
Woo D, Lee Y, Park S. Associations among working hours, sleep duration, self-rated health, and health-related quality of life in Korean men. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020;18(1):287. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12955-020-01538-2.
Jung HM, Kim HY. A health-related quality of life model for patients undergoing haemodialysis. J Clin Nurs. 2020;29(3–4):613–25. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.15113.
Kang GW, Lee IH, Ahn KS, Lee J, Ji Y, Woo J. Clinical and psychosocial factors predicting health-related quality of life in hemodialysis patients. Hemodial Int. 2015;19(3):439–46. https://doi.org/10.1111/hdi.12271.
Vogel CE, Molinari V, Andel R, Barry LC. Self-rated health and mental health among older incarcerated males. Aging Ment Health. 2021;25(11):2100–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/13607863.2020.1795621.
Picard M, Juster R-P, Sabiston CM. Is the whole greater than the sum of the parts? Self-rated health and transdisciplinarity. Health. 2013;05(12):24–30. https://doi.org/10.4236/health.2013.512A004.
Petrella AR, Sabiston CM, Vani MF, Matthew A, Santa Mina D. Psychological needs satisfaction, self-rated Health and the Mediating Role of Exercise among Testicular Cancer survivors. Am J Mens Health. 2021;15(2):15579883211012601. https://doi.org/10.1177/15579883211012601.
Ormiston CK, Mamudu L, McNeel TS, Wang Z, Buckman DW, Williams F. Association of depression and self-reported health status by birthplace and citizenship status: results from the 2010–2018 National Health interview survey. J Affect Disord. 2024;361:157–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2024.06.002.
Wang YQ, Shi JF, Du LB, Huang HY, Wang L, Zhu J, et al. Health-related quality of life in patients with esophageal cancer or precancerous lesions assessed by EQ-5D: a multicenter cross-sectional study. Thorac Cancer. 2020;11(4):1076–89. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.13368.
Zeng X, Sui M, Liu R, Qian X, Li W, Zheng E, et al. Assessment of the health utility of patients with leukemia in China. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2021;19(1):65. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12955-021-01711-1.
Zhuo L, Xu L, Ye J, Sun S, Zhang Y, Burstrom K, et al. Time Trade-Off Value set for EQ-5D-3L based on a nationally Representative Chinese Population Survey. Value Health. 2018;21(11):1330–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2018.04.1370.
Wong LP, Lai LL, See MH, Alias H, Danaee M, Ting CY, et al. Psychological distress among cancer survivors during implementation of a nationwide Movement Control Order over the COVID-19 pandemic. Support Care Cancer. 2021;29(10):6087–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-021-06182-0.
Annunziata MA, Muzzatti B, Bidoli E, Flaiban C, Bomben F, Piccinin M, et al. Hospital anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) accuracy in cancer patients. Support Care Cancer. 2020;28(8):3921–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-019-05244-8.
Herhaus B, Kersting A, Brahler E, Petrowski K. Depression, anxiety and health status across different BMI classes: a representative study in Germany. J Affect Disord. 2020;276:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2020.07.020.
Park S. Pathways linking obesity to health-related quality of life. Qual Life Res. 2017;26(8):2209–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-017-1565-x.
Smith KW, Avis NE, Assmann SF. Distinguishing between quality of life and health status in quality of life research: a meta-analysis. Qual Life Res. 1999;8(5):447–59. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1008928518577.
Zullig KJ, Valois RF, Drane JW. Adolescent distinctions between quality of life and self-rated health in quality of life research. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2005;3:64. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7525-3-64.
Wang M, Pan Q. The rural-urban differences and influencing factors in the anxiety symptoms of Chinese Elderly people. Chin Gen Prac. 2021;24(31):3963–70. https://doi.org/10.18170/DVN/WBO7LK.
Dodd MJ, Miaskowski C, Lee KA. Occurrence of symptom clusters. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 2004;3276–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/jncimonographs/lgh008.
Vorn R, Touch S, Ryu E. Depression and health-related quality of life among Cambodian patients with cancer. Int J Health Plann Manage. 2019;34(4):e1747–59. https://doi.org/10.1002/hpm.2888.
Beurel E, Toups M, Nemeroff CB. The bidirectional relationship of depression and inflammation: double trouble. Neuron. 2020;107(2):234–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2020.06.002.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all the participants in this study.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant NO. 71804002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shuowen Fang: Conceptualization. Lingfeng Xu, Jingsong Liu, Xinzhou Zhang, and Mimi Li: Data collection. Tao Zhang and Lingfeng Xu: Formal analysis. Shuowen Fang: Data analysis. Manman Lu: Supervision. Shuowen Fang: Writing original draft. Shuowen Fang and Manman Lu: Writing review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Biomedical Ethics Committee of Anhui Medical University (No.20180173). This study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki. All patients provided their written informed consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it.The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, S., Xu, L., Liu, J. et al. Self-rated health and health-related quality of life among cancer patients: the serial multiple mediation of anxiety and depression. BMC Psychol 12, 415 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01919-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01919-y