Abstract
Background
American mink forage on land and in water, with aquatic prey often constituting a large proportion of their diet. Their long, thin body shape and relatively poor insulation make them vulnerable to heat loss, particularly in water, yet some individuals dive over 100 times a day. At the level of individual dives, previous research found no difference in dive depth or duration, or the total number of dives per day between seasons, but mink did appear to make more dives per active hour in winter than in summer. There was also no difference in the depth or duration of individual dives between the sexes, but there was some evidence that females made more dives per day than males. However, because individual mink dives tend to be extremely short in duration, persistence (quantified as the number of consecutive dives performed) may be a more appropriate metric with which to compare diving behaviour under different scenarios.
Results
Mink performed up to 28 consecutive dives, and dived continually for up to 36 min. Periods of more loosely aggregated diving (termed ‘aquatic activity sessions’) comprised up to 80 dives, carried out over up to 162.8 min. Contrary to our predictions, persistence was inversely proportional to body weight, with small animals more persistent than large ones, and (for females, but not for males) increased with decreasing temperature. For both sexes, persistence was greater during the day than during the night.
Conclusions
The observed body weight effect may point to inter-sexual niche partitioning, since in mink the smallest animals are females and the largest are males. The results may equally point to individual specialism’s, since persistence was also highly variable among individuals. Given the energetic costs involved, the extreme persistence of some animals observed in winter suggests that the costs of occasional prolonged activity in cold water are outweighed by the energetic gains. Analysing dive persistence can provide information on an animal’s physical capabilities for performing multiple dives and may reveal how such behaviour is affected by different conditions. Further development of monitoring and biologging methodology to allow quantification of hunting success, and thus the rewards obtained under alternative scenarios, would be insightful.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The diving behaviour of semi-aquatic species, defined here as those that live close to water but obtain only part of their food by swimming and diving [1], is still relatively poorly understood. Mammals that forage both on land and in water have to retain the ability to move efficiently in two quite different habitats and therefore, are not as well adapted for diving as are fully aquatic species (e.g. whales), or those that forage exclusively in water and only go on land to breed, moult or rest (e.g. seals) [2, 3]. Semi-aquatic mammals are usually inefficient swimmers and relatively poor divers, as their oxygen stores, oxygen conserving mechanisms, insulation, and appendages are not as well adapted to aquatic living as fully aquatic animals [4–6].
American mink, Neovison vison, are small (~1 kg), semi-aquatic mustelids that consume both terrestrial and aquatic prey [7]. Mink dives tend to be shallow (average 0.45 m) and short duration (average 10.9 s), but some individuals dive over 100 times per day [10, 27], and diving is clearly an important activity for mink since aquatic prey may constitute up to 89% of their diet, in some places, at some times of the year, e.g. [8]. Mink may also dive and swim beneath the surface of the water as an efficient means of travel [9, 10]. In common with other mustelines (e.g. stoats, Mustela ermine, and weasels, Mustela nivalis), mink have high rates of heat loss due to their long, thin body shape [11, 12], and particularly high rates of heat loss when in water, due to the relatively poor insulating properties of their fur [13]. Mink are sexually dimorphic—the smallest females in a population may weigh less than a third of the largest male [14]. Therefore, females may be even more vulnerable to heat loss than males [15]. Additionally, mink eyes are not well adapted to underwater vision [16–18]. Mink are single-prey loading, central place foragers (sensu [19]), that return to land to eat each prey item captured [7].
The native range of the American mink extends as far north as Alaska [7], so mink are clearly able to cope in cold environments. As in other mustelids (e.g. black-footed ferrets Mustela nigripes [20]; weasels M. nivalis [21]; or pine martens Martes martes [22]), mink reduce their general activity levels in winter [23], presumably to avoid excessive heat loss. Other semi-aquatic species such as muskrats Ondatra zibethicus [24] and star-nosed moles Condylura cristata [25] dive less frequently and for shorter periods of time during winter, but no such seasonal effects have been observed in mink diving behaviour [10]. Harrington et al. [10] analysed mink diving behaviour at the level of individual dives and found that mink in winter performed the same number of dives as in summer, but at a higher rate (i.e. more dives per hour of activity [10]). At the level of individual dives, there was no difference between the sexes in dive ability (measured as the depth and duration of dives), but there was some evidence that females spent more time diving and made more dives per day, than males [10]. Further, although mink are generally presumed to be nocturnal [7], they dived predominantly during the day [10]. It is not clear whether this is due to a preference for diving in bright light to compensate for their relatively poor underwater eyesight, or an avoidance of nocturnal competitors (e.g. otters, [26]).
Hays et al. [27] (using a subset of the data analysed by [10]) noted that mink dives generally occur in discrete temporal clusters or ‘bouts’, as in many breath-hold divers [28–33]. This observation led to the development of a new analytical method to describe dive patterns by Bagniewska et al. [34], which allowed quantification of dive ‘persistence’ as the number of consecutive dives performed within a cluster (or bout) of dives. Given the extremely short duration of individual dives, persistence may be a more appropriate metric with which to compare diving behaviour under different scenarios, and to test the effect of biological and environmental factors. In this paper, we use persistence (quantified for periods of continual diving, ‘dive clusters’, and for periods of more loosely aggregated diving, ‘aquatic activity sessions’, hereafter AAS, see “Methods” and Figure 1 for details) to further explore the effect of ambient temperature, body weight and daylight, on diving behaviour in American mink. We applied methods developed by [34] that use hidden Markov models performed on two variables (dive depth and inter-dive interval) to identify dive clusters and AAS, which is more appropriate for describing the diving behaviour of a semi-aquatic animal than simpler threshold-based models commonly used to describe dive bouts. Here, we refer to ‘clusters’ and ‘AAS’ rather than ‘bouts’ (although ecologically they are analogous) to distinguish between these methods; for further discussion see [34]. Following on from earlier analyses on the same dataset by Harrington et al. [10], we hypothesised that low ambient temperatures, relatively poor insulation, and the resultant thermoregulatory costs might limit the duration of mink diving in winter, and allometry suggests that smaller animals might be more vulnerable to any such effects. This analysis differs from the earlier analysis in that while the earlier analysis was carried out at the level of individual dives, this analysis was carried out at the level of dive clusters. We predicted that [1] dive persistence would be shorter in winter, and [2] smaller mink would be less persistent than larger mink. We were unable to predict how daylight might affect persistence, but anticipated that persistence might differ under different light levels reflecting differences in visibility, predatory risk, or motivation for diving.
Dive sequence illustrating the differences between dive clusters and aquatic activity sessions (AAS). Dives of mink 187a (female) from 27 January 2006 were assigned to one of three states using a Hidden Markov model algorithm as in [34]: State 1 (white) dives represent a period of continual diving, State 2 (red) dives represent a period of loosely aggregated diving (an AAS), and State 3 (black) dives are terminal dives in a cluster or single dives. Note, however, that an AAS does not necessarily comprise a series of clusters and may simply be a short series of loosely aggregated dives. Hours of darkness are shown by grey shading. This is a modified version of a section of Figure 2 from [34].
Results and discussion
Description of dive clusters and aquatic activity sessions (AAS)
Most (88.3 and 98.6%, respectively) dives occurred in clusters or in AAS (n = 3,714 total dives); only 1.4% dives (n = 53) were single isolated dives. Note that, by definition, all clusters occur within an AAS. For individual datasets, between 60.1 and 100% of dives occurred in clusters (mean = 84.6%), and between 68 and 100% of dives in AAS (mean = 95.4%).
Dive clusters consisted of 2–28 dives (grand median = 4, n = 633 dive clusters in total across all datasets; range of individual medians: 2–7.5, Figure 2a); AAS of 2–80 dives (grand median = 7, n = 299; range of individual medians: 3–31, Figure 2b). As for total number of dives per day, and depth and duration of individual dives [10], both dive cluster length and AAS length were extremely variable within individuals (coefficient of variation [CV]clusters 0.32–0.76; CVAAS 0.43 − >1) and differed significantly among individuals (ANOVAcluster: F13, 619 = 7.3, P < 0.001; ANOVAAAS: F13, 285 = 10.59, P = < 0.001). The short duration of individual dives [10] meant that despite the high numbers of dives that could occur in either clusters or AAS, both dive clusters and AAS were, on average, also short in duration: cluster duration ranged from 9 s to 36.1 min (grand median = 2.3 min; range of individual medians: 57 s to 12.9 min, Figure 2c) and AAS duration 11.0 s to 162.8 min (grand median = 20.3 min; range of individual medians: 11.3–49.6 min, Figure 2d). The overall median length of pauses between dives within a cluster was 17 s, and individual median pauses ranged between 8 and 81.1 s (data were very strongly right-skewed, with the maximum pause between dives being 249 s; 95% of data points were <127 s, 90% < 89s). Bagniewska et al. [34] described an AAS as a period of aquatic activity (diving and swimming) that may include brief terrestrial periods and events such as jumping out onto the bank (when aquatic prey items may be consumed) or runs to the burrow, whereas a dive cluster represents continuous diving. However, we cannot rule out the possibility that small prey items are taken to the riverbank and consumed during the occasional long inter-dive intervals within a dive cluster (small prey items, e.g. aquatic beetles Dytiscidae may even be consumed during short intervals at the water’s surface). Therefore, a dive cluster does not necessarily represent an attempt to obtain a single prey item.
Effect of ambient temperature, body size and light
For the number of dives in both clusters and AAS, there was a significant interaction between ambient temperature and sex (LMEcluster: F 1,609 = 5.06, P = 0.025; LMEAAS: F1,273 = 6.90, P = 0.009), indicating that the response of males and females to ambient temperature differed. The main effect for ambient temperature was also significant, and highly significant for AAS (LMEcluster: F1,609 = 8.92, P = 0.003; LMEAAS: F1,273 = 15.03, P < 0.001). There was no significant effect of sex (LMEcluster: F1,12 = 0.35, P = 0.568; LMEAAS: F1,12 = 0.01, P = 0.91), but the effect of animal weight was significant (highly significant for AAS; LMEcluster: F1,609 = 8.79, P = 0.003; LMEAAS: F1,273 = 18.33, P < 0.001), with the number of dives decreasing with increasing weight (Figure 3). The effect of light was also significant (LMEcluster: F1,609 = 9.11, P = 0.003; LMEAAS: F1,273 = 8.16, P = 0.005), with the number of dives greater during the day than during the night (Figure 4).
Effect of mink weight on persistence. a shows the relationship between animal weight and the median and maximum number of dives per cluster, and b—per AAS. The dashed vertical line indicates the break in body weight between males (>1 kg) and females (<1 kg). Data points are one deployment on one individual; in some cases, there were two or three deployments on the same individual (see Additional file 1 for deployment details). Solid lines show the model fit with individual included as a random effect.
To compare effects on average and maximal persistence, the analyses were repeated on summary statistics for each individual, using median and maximum values for the number of dives in a cluster, and the number of dives in an AAS (Table 1). The effect of animal weight was significant for both median and maximum values of cluster and AAS length (Figure 3). The main effect for ambient temperature was not statistically significant for either median or maximum persistence; however, the interaction between temperature and sex was (for maximum cluster length, and maximum AAS length, but not for median cluster length or AAS length). Plotting maximum persistence against ambient temperature for both sexes separately revealed that for females the maximum number of dives increased with decreasing temperature, but for males there was no evidence of a similar relationship (Figure 5). No other effects were statistically significant.
Effect of ambient temperature on persistence. The figure depicts the relationship between temperature and the number of dives per a cluster and b aquatic activity session for females (red) and for males (black). The slopes for significant relationships for females are included in the figures (clusters: persistence [no. of dives] = −0.53(ambient temperature)[oC] + 21.93; F1,8 = 8.89, R2[adjusted] = 0.47, P = 0.0175. AAS: persistence [no. of dives] = −1.76 (ambient temperature)[°C] + 58.92; F1,8 = 6.19 R2[adjusted] = 0.37, P = 0.038).
Contrary to our predictions based on allometry and thermoregulation, small mink were more persistent divers than large mink (Figure 3), and (maximum) persistence was greater when it was colder; but the latter was only true for females (Figure 5). Although the effect of body size was apparent for both median and maximum persistence, it was greatest for maximum cluster length and maximum AAS length, with the result that, on average, maximum cluster length for females (<1 kg body weight) was approximately twice that of males (>1 kg body weight). Maximal female cluster lengths ranged between 11 and 28 dives (grand median = 17), whereas maximal male cluster lengths ranged between 4 and 18 dives in a cluster (grand median = 9), although the apparent difference between sexes was due to differences in overall body size, rather than in sex per se.
That the smallest females, with the highest rates of heat loss, showed the greatest persistence, and that this observation occurred during the coldest ambient temperatures experienced during the study, demonstrate that persistence, or ‘time spent diving’ by mink, was not limited by body size or cold temperatures at least within the seasonal temperature range of southern England (mean daily ambient temperature did not drop below 0°C during our study). It is possible that, in colder climates, there is a lower critical temperature beyond which foraging activities are temporarily prohibited. It is also possible that temperature affects diving behaviour differently on different temporal scales (e.g. within a day, or within a period of days).
Several authors have referred to the possibility of inter-sexual niche partitioning in mink with females taking relatively more aquatic prey (fish and amphibians) and males more large terrestrial prey (e.g. lagomorphs in the UK [35]; see also [36, 37]). These data provide some support for that suggestion in that the smallest individuals (the females) exhibited the longest duration aquatic activity, and thus could be inferred to spend the most time pursuing aquatic prey, whereas the largest individuals (the males) performed fewer dives per day [10], the shortest dive clusters, and the shortest aquatic activity sessions, which suggests more time spent in terrestrial habitats, and, accordingly, might reflect greater use of terrestrial prey. However, short monitoring periods and small sample size mean that we cannot dismiss short-term exploitation of a patchy resource (as opposed to consistent, long-term differences), or the possibility of individual specialisation (as opposed to inter-sexual differences; discussed in [10, 14], see also [38]). Further, because we were unable to monitor diving males during the coldest winter temperatures (only 1 male was tagged in winter when ambient temperatures were below 7°C, but this individual dived fewer than five times during the 5- to 6-day monitoring period, and thus was excluded from analysis) we could not determine whether males, the larger individuals, also sometimes performed long dive clusters (or AAS), only that females, the smallest individuals, could.
An alternative explanation of short dive clusters in males might be that males are more efficient at catching aquatic prey (i.e. perhaps they can catch fish quicker, can catch larger fish, and therefore need to spend less time foraging in the water). However, because we cannot identify successful dives, and cannot assume that a single dive cluster relates to an attempt to catch a single fish (or other aquatic prey) it is not possible, given the current data, to draw conclusions regarding either efficiency or success. Further, the number of dive clusters recorded over the 5- to 6-day monitoring period was hugely variable for both males (5–82) and females (8–96), which is inconsistent with clear inter-sexual differences in foraging strategy but perhaps consistent with individual differences.
That the largest effect sizes were seen for maximal persistence rather than median persistence, shows that, on average, there was little difference in persistence between female and male mink (or small and large mink), and no difference in ‘average’ behaviour between winter and summer (i.e. even the small ‘high diving’ females did not perform very long clusters or AAS all the time). Nevertheless, there was clearly no reduction in persistence in winter. Eurasian otters also maintain consistent activity time in the water, regardless of water temperature [39], despite the energetic costs of swimming in 2°C water (approximate minimum British river temperature [40]) being 2.7 times higher than in 20°C water (approximate maximum British river temperature [40]) [41]. The increased thermoregulatory costs of swimming in winter relative to swimming in summer are likely to be even higher for mink due to their smaller body size, relatively greater surface area, and thus greater heat loss rate, compared with otters [15]. Given the energetic costs involved, the extreme persistence observed in winter suggests that the costs of occasional prolonged diving in cold water are outweighed by the energetic gains. Harrington et al. [10] suggest that the relatively high diving rates observed in winter probably reflect the behaviour of some mink capitalising on the increased susceptibility to capture of ectothermic fish in cold water [8, 13]. However, our prediction that these high winter diving rates would be achieved in shorter clusters of dives to minimise prolonged periods of heat loss was not upheld: cluster length (for females) was longer in winter. Unfortunately, the data do not allow us to determine whether long clusters reflect an attempt to catch a single fish (if the chance of catching a large fish in torpor is high, it might be worth pursuing the opportunity for longer) or reflect an extended period of catching several smaller fish (that were consumed in the brief inter-dive intervals). Nor can we distinguish between successful and unsuccessful dives.
From a thermoregulation perspective, Williams [13] estimates that mink, swimming in water at 20°C, are only able to maintain their body temperature for ca. 5 min. Although we did not measure body temperature, and we cannot quantify total time spent swimming, our results show that mink were able to remain active (diving) in the water for much longer than 5 min although they did not often do so. Mink were recorded continuously diving for 36 min with brief inter-dive intervals of only a few minutes at most, at ambient temperatures of between 2.5 and 5.5°C (water temperature recorded at our study site in winter, [27]).
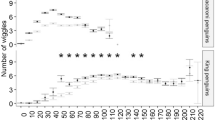
Both males and females performed longer dive clusters and AAS during the day than during the night (Figure 4a), although, in general, male mink were more nocturnal in their diving than females (Figure 4b). Three possible explanations for increased persistence during the daylight are: (1) hunting underwater is more profitable in daylight for an animal with relatively poor underwater vision in daylight, and thus worth greater time investment; (2) hunting is more risky at night due to the presence of larger, nocturnal competitors (e.g. otters [26], and thus restricted to shorter periods; (3) day and night dives have different functions (e.g. hunting and travelling), that might be characterised by different temporal structures. As surface swimming may be interrupted by periods of underwater swimming to reduce drag, or as an evasive manoeuvre [42], clusters of dives might also represent periods of travelling in the water. Presumably, underwater visual acuity is not as crucial for travelling as for hunting, and so travelling dives might be more likely to take place at night; however, it is not obvious why clusters of travelling dives would be shorter than clusters of hunting dives. Further study of the diving behaviour of mink, in the absence of otters, is required to distinguish between the first two possibilities. Harrington et al. [26] suggest that male mink may be less affected by competition with otters, which may explain the apparent diurnal difference between the sexes in diving behaviour, if mink dive during the day to avoid otters. Alternatively, males may spend more time travelling than females, partly because they have larger home ranges [14, 43], and so may dive more during the night, if mink dive during the night predominantly for travel.
Conclusions
Analysing dive persistence can provide information on an animal’s physical capabilities for performing multiple dives and may reveal how such behaviour is affected by different conditions. Our results show that mink were continually active in water in winter for much longer than might have been predicted on the basis of earlier laboratory experiments and estimated rates of heat loss. However, it is still not clear how dive patterns relate to hunting success, are influenced by inter-sexual and/or individual variation, or by competitor interactions, and these questions are further complicated by the fact that diving in a semi-aquatic species may have multiple functions. Mink are known to dive in much colder aquatic environments than southern England (e.g. Alaska and Iceland) and presumably the rewards associated with aquatic activity in these potentially challenging environments are high. Further development of monitoring and biologging methodology to allow quantification of hunting success, and thus of rewards obtained under alternative scenarios, would be insightful.
Methods
Data collection
The dataset used in this study has previously been described in [10] in a study of the diving ability and behaviour of American mink at the individual dive level. CEFAS G5 TDRs (31 × 8 mm; CEFAS Technology Ltd, Lowestoft, UK, http://www.cefastechnology.co.uk; [27], Figure 6) were deployed on 24 free-living American mink on the rivers Thames and Cherwell in the Upper Thames valley in Oxfordshire, UK (approximate latitude, longitude: 51.62°N, 1.08°W) between January 2006 and January 2008. Site details are described in [10]. Mink were caught in wire traps placed on floating rafts (Figure 7) secured to the riverbank [44], anaesthetised (methods in [27]), weighed (kg), and fitted with collars to which a TDR had been attached (details in [10]), see Figures 8 and 9. Animal handling was completed within 10–30 min and mink recovered from anaesthesia within 10–25 min. TDRs were recovered a week after deployment (or as soon as possible thereafter), and collars were removed using the same procedures; there were no cases of injuries due to the collars.
A floating raft. Instead of a wire trap, this raft contains a clay plate used to detect the presence of a mink before placing a trap inside [44]. Photo: Lauren A. Harrington.
The positioning of the TDR on the collar. The image shows how the TDR is fitted to the collar using fishing line. Prior to deployment it is also covered with protective plastic tubing; it is important that the pressure sensor is recessed within the tubing to protect it from damage. Photo: Andrew L. Harrington.
Research on live animals followed ASM guidelines; all procedures were carried out under United Kingdom Home Office licences PPL30/1826, PIL30/6530, and PIL30/6917 and were approved by Oxford University Zoology Department Ethical Review Committee. Mink were re-released for monitoring under Section 16 of the Wildlife and Countryside Act 1981, Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs licence WCA/06/4 and Natural England licences NNR/2007/0024, NNR/2007/0022.
Twenty TDRs were retrieved from 16 individual animals (6 males and 10 females), containing temperature and pressure data recorded every 5 and 1 s, respectively, for a period of up to 7 days. One data-logger failed prematurely and only recorded for 2 days. Two individuals for which we recorded fewer than 20 dives were excluded from further analysis [10].
Ambient air temperature measurements (daily means) were obtained from the Radcliffe Meteorological Station (http://www.geog.ox.ac.uk/research/climate/rms/intro.html), within 40 km of the study sites. Dawn and dusk times for Oxford were taken from timeanddate.com (http://www.timeanddate.com/worldclock/sunrise.html).
Data analysis
Individual dive data were extracted from the raw time series using MULTITRACE (Jensen Software Systems, Laboe, Germany, http://www.jensen-software.com), using a dive threshold of 0.2 m (precision of TDRs 0.05 m [27]), as in [10]. A Hidden Markov model algorithm was applied to individual dive data in MATLAB 7.8 (The MathWorks™, http://www.themathworks.com), as described in [34]. This method identified dives in three behavioural states, where dives in State 1 occur in a temporal cluster of dives, characterised by continual diving; dives in State 2 occur in a period of more loosely aggregated diving, and dives in State 3 are the terminal dive of a cluster or AAS or a single, isolated dive (i.e. they represent a state change). For analysis, dives were grouped into ‘dive clusters’—a series of State 1 dives ending with a State 2 or 3 dive—and ‘aquatic activity sessions (AAS)’—a series of State 2, or State 1 and 2, dives ending with a State 3 dive (Figure 1). Persistence was defined as the length in number of dives of a cluster or AAS. Since the data were right-skewed, we used the median as the measure of central tendency. All individual dives were categorised as occurring during daylight or in darkness on the basis of dawn and dusk times, we did not attempt to include dawn and dusk light levels in the analysis due to the relatively limited number of dives occurring during these periods.
Statistical analysis was carried out in R (version 3.0.1, R Core Team 2013). We used linear mixed effects models (lme function in nlme package [45]) to investigate the relationship between persistence and ambient temperature, animal weight, and light (daylight/darkness). Sex was also included in the model, and individual was included as a random effect to avoid bias due to pseudoreplication due to multiple datasets from a few individuals. We used LME with a weighted variance, with cluster length or AAS length as a response, and ambient temperature, animal weight and light as predictors. We used ANOVA to test for differences in cluster length and AAS length among individuals. In all tests, p = 0.05 was accepted as significant. Example LME code is:
lme(length ~ ambtemp+weight+light+sex+sex*ambtemp, data = clusters, random = ~1|individual, na.action = na.exclude, weights = varIdent(form = ~1|weight)).
Cluster lengths were treated as independent. This was verified by autocorrelation on clusters, which showed no significance.
References
Sidorovich V, Kruuk H, Macdonald DW, Maran T (1998) Diets of semi-aquatic carnivores in northern Belarus, with implications for popluation changes. Behaviour and ecology of riparian mammals. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Boness DJ, Bowen WD (1996) The evolution of maternal care in pinnipeds. Bioscience 46(9):645–654
Lyamin OI (1993) Sleep in the harp seal (Pagophilus groenlandica). Comparison of sleep on land and in water. J Sleep Res 2(3):170–174
Estes JA (1989) Adaptations for aquatic living by carnivores. In: Gittleman JL (ed) Carnivore behaviour, ecology and evolution. Chapman & Hall, London, pp 242–282
Fish FE (1993) Influence of hydrodynamic-design and propulsive mode on mammalian swimming energetics. Aust J Zool 42(1):79–101
Fish FE (2000) Biomechanics and energetics in aquatic and semi-aquatic mammals: platypus to whale. Physiol Biochem Zool 73:683–698
Dunstone N (1993) The mink. T and AD Poyser Natural History, London
Gerell R (1967) Food Selection in relation to habitat in mink (Mustela vison Schreber) in Sweden. Oikos 18(2):233–246
Williams TM (1983) Locomotion in the North American mink, a semi-aquatic mammal. I. Swimming energetics and body drag. J Exp Biol 103(1):155–168
Harrington LA, Hays GC, Fasola L, Harrington AL, Righton D, Macdonald DW (2012) Dive performance in a small-bodied, semi-aquatic mammal in the wild. J Mammal 93(1):198–210
Brown JH, Lasiewski RC (1972) Metabolism of weasels: the cost of being long and thin. Ecology 53(5):939–943
Boyd IL (1997) The behavioural and physiological ecology of diving. Trends Ecol Evol 12(6):213–217
Williams TM (1986) Thermoregulation of the North American mink during rest and activity in the aquatic environment. Physiol Zool 59(3):293–305
Macdonald DW, Harrington LA, Yamaguchi N, Thom MD, Bagniewska JM (2015, in press) Biology, ecology and reproduction of American mink, Neovison vison, on lowland farmland. In: Macdonald DW, Feber RE (eds) Wildlife conservation on farmland. Conflict in the countryside. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Schmidt-Nielsen K (1984) Scaling: why is animal size so important?. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Sinclair W, Dunstone N, Poole TB (1974) Aerial and underwater visual acuity in the mink Mustela vison Schreber. Anim Behav 22:965–974
Dunstone N, Sinclair W (1978) Comparative aerial and underwater visual acuity of the mink, Mustela vison Schreber, as a function of discrimination distance and stimulus luminance. Anim Behav 26(Part 1):6–13
Dunstone N, Sinclair W (1978) Orienting behaviour during aerial and underwater visual discrimination by the mink (Mustela vison Schreber). Anim Behav 26(Part 1):14–21
Houston AI, McNamara JM (1985) A general theory of central place foraging for single-prey loaders. Theor Popul Biol 28(3):233–262
Richardson L, Clark TW, Forrest SC, III TMC (1987) Winter ecology of black-footed ferrets (Mustela nigripes) at Meeteetse, Wyoming. Am Midl Nat 117(2):225–239
Jędrzejewski W, Jędrzejewska B, Zub K, Nowakowski WK (2000) Activity patterns of radio-tracked weasels Mustela nivalis in Bialowieza National Park (E Poland). Ann Zool Fenn 37(3):161–168
Zalewski A (2000) Factors affecting the duration of activity by pine martens (Martes martes) in the Bialowieza National Park, Poland. J Zool 251(4):439–447
Zalewski A, Bartoszewicz M (2012) Phenotypic variation of an alien species in a new environment: the body size and diet of American mink over time and at local and continental scales. Biol J Linn Soc 105(3):681–693
MacArthur RA (1984) Aquatic thermoregulation in the muskrat (Ondatra zibethicus): energy demands of swimming and diving. Can J Zool 62(2):241–248
McIntyre IW, Campbell KL, MacArthur RA (2002) Body oxygen stores, aerobic dive limits and diving behaviour of the star-nosed mole (Condylura cristata) and comparisons with non-aquatic talpids. J Exp Biol 205(1):45–54
Harrington LA, Harrington AL, Yamaguchi N, Thom MD, Ferreras P, Windham TR et al (2009) The impact of native competitors on an alien invasive: temporal niche shifts to avoid interspecific aggression. Ecology 90(5):1207–1216
Hays GC, Forman DW, Harrington LA, Harrington AL, Macdonald DW, Righton D (2007) Recording the free-living behaviour of small-bodied, shallow-diving animals with data loggers. J Anim Ecol 76(1):183–190
Williams TD, Briggs DR, Croxall JP, Naito Y, Kato A (1992) Diving pattern and performance in relation to foraging ecology in the gentoo penguin, Pygoscelis papua. J Zool 227(2):211–230
Hays GC, Houghton JDR, Isaacs C, King RS, Lloyd C, Lovell P (2004) First records of oceanic dive profiles for leatherback turtles, Dermochelys coriacea, indicate behavioural plasticity associated with long-distance migration. Anim Behav 67(4):733–743
Croxall JP, Naito Y, Kato A, Rothery P, Briggs DR (1991) Diving patterns and performance in the Antarctic blue-eyed shag Phalacrocorax atriceps. J Zool 225(2):177–199
DeLong RL, Stewart BS (1991) Diving patterns of nothern elephant seal bulls. Mar Mamm Sci 7(4):369–384
Krafft B, Lydersen C, Gjertz I, Kovacs K (2002) Diving behaviour of sub-adult harbour seals (Phoca vitulina) at Prins Karls Forland, Svalbard. Polar Biol 25(3):230–234
Monaghan P, Walton P, Wanless S, Uttley JD, Bljrns MD (1994) Effects of prey abundance on the foraging behaviour, diving efficiency and time allocation of breeding Guillemots Uria aalge. Ibis. 136(2):214–222
Bagniewska J, Hart T, Harrington LA, Macdonald DW (2013) Hidden Markov analysis describes dive patterns in semi-aquatic animals. Behav Ecol 24(3):659–667
Birks JDS, Dunstone N (1985) Sex-related differences in the diet of the mink Mustela vison. Holarct Ecol 8(4):245–252
Sealander JA (1943) Winter Food habits of mink in southern Michigan. J Wildl Manag 7(4):411–417
Magnusdottir R, Stefansson RA, Schmalensee MV, Macdonald DW, Hersteinsson P (2012) Habitat- and sex-related differences in a small carnivore’s diet in a competitor-free environment. Eur J Wildl Res 58(4):669–676
Tinker MT, Costa DP, Estes JA, Wieringa N (2007) Individual dietary specialization and dive behaviour in the California sea otter: using archival time-depth data to detect alternative foraging strategies. Deep Sea Res Part II 54(3–4):330–342
Kruuk H, Taylor PD, Mom GAT (1997) Body temperature and foraging behavior of the Eurasian otter (Lutra lutra), in relation to water temperature. J Zool 241:689–697
Otters Kruuk H (2006) Ecology, Behaviour and Conservation. Oxford University Press, UK
Kruuk H, Balharry E, Taylor PT (1994) Oxygen consumption of the Eurasian otter Lutra lutra in relation to water temperature. Physiol Zool. 67:1174–1185
Williams TM (1983) Locomotion in the North American mink, a semi-aquatic mammal. I. Swimming energetics and body drag. J Exp Biol 103(1):155–168
Melero Y, Palazón S, Revilla E, Gosàlbez J (2011) Winter activity patterns in an invading Mediterranean population of American mink (Neovison vison). Folia Zool 60(1):47–53
Reynolds JC, Short MJ, Leigh RJ (2004) Development of population control strategies for mink Mustela vison, using floating rafts as monitors and trap sites. Biol Conserv 120(4):533–543
Pinheiro J, Bates D, DebRoy S, Sarkar D (2014) nlme: linear and nonlinear mixed effects models. R package version 3.1-118
Authors’ contributions
JMB participated in data collection, statistical analysis and interpretation of data, and has been involved in drafting and revising the manuscript; LAH conceived of, and designed, the study, and participated in extracting dive data, interpreting data, drafting and revising the manuscript; TH participated in statistical analysis and has been involved in drafting and revising the manuscript; ALH participated in conception and design of the study, and carried out data collection; LF participated in data collection and extracting dive data; DWM participated in conception and design of the study, and revision of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Fundacja Crescendum Est-Polonia through a scholarship for JMB. Our thanks go to David Righton for sharing his data-logger expertise, Mike Challis for technical support and Paul Johnson for help with statistical analysis.
Compliance with ethical guidelines
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional file
Additional file 1:
Details of deployment, dives, clusters and aquatic activity sessions for each mink. F = female, M = male; cluster and AAS length is expressed as the number of dives.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Bagniewska, J.M., Harrington, L.A., Hart, T. et al. Persistence in diving American mink. Anim Biotelemetry 3, 18 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40317-015-0057-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40317-015-0057-4