Abstract
Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) functions not only in physiological processes but also participates in the development and progression of cancer. In recent decades, extensive efforts have been made to decipher the role of EpCAM in cancers. Great advances have been achieved in elucidating its structure, molecular functions, pathophysiological mechanisms, and clinical applications. Beyond its well-recognized role as a biomarker of cancer stem cells (CSCs) or circulating tumor cells (CTCs), EpCAM exhibits novel and promising value in targeted therapy. At the same time, the roles of EpCAM in cancer progression are found to be highly context-dependent and even contradictory in some cases. The versatile functional modules of EpCAM and its communication with other signaling pathways complicate the study of this molecule. In this review, we start from the structure of EpCAM and focus on communication with other signaling pathways. The impacts on the biology of cancers and the up-to-date clinical applications of EpCAM are also introduced and summarized, aiming to shed light on the translational prospects of EpCAM.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
EpCAM is a homophilic type I transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the small GA733 protein family [1]. Previous studies demonstrated that EpCAM participated in cell adhesion [2, 3]. However, other reports revealed EpCAM as a negative regulator of classic cadherin-mediated adhesion [4]. These inconsistent results implied the complexity of EpCAM in cancers. Apart from mediating cell adhesion, EpCAM extracellular domain (EpEX) and intracellular domain (EpICD), which can be released from membrane-bound EpCAM following TNF-α-converting enzyme (TACE)- and presenilin-2 (PS-2)-mediated cleavage, act as ligand for signal transduction receptor [5, 6] or as transcriptional cofactor [7,8,9]. These molecular mechanisms further border the functions of EpCAM and complicate its role in cancer progression.
Achievements in EpCAM research suggest its participation in cancer stemness, cell proliferation, metabolism, angiogenesis, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), metastasis, chemo/radio-resistance and immunomodulation [6, 10,11,12,13,14,15]. During tumor progression, EpCAM undergoes crosstalk with many pivotal signaling pathways, such as Wnt/β-catenin, TGF-β/SMAD, EpEX/EGFR, PI3K/AKT/mTOR and p53, to induce biological changes in cancer cells [15,16,17,18], which are detailed in the following sections. Thus, it is not surprising that the role of EpCAM in cancers is highly context dependent. For example, enhanced EpCAM expression promoted invasion by preventing cell–cell adhesion and promoting immune escape, as well as activating downstream oncogenic genes in leukemia and colon cancer [13, 19]. In early esophageal cancer, decreased expression of EpCAM was found to induce EMT, thus promoting metastasis [20]. Given its versatile functions in cancer biology, EpCAM is considered as an attractive target for translational medicine. This molecule is taken as a biomarker for detecting CTCs and CSCs, providing potential new diagnostic and prognostic approaches [21, 22]. In addition, therapeutic methods targeting EpCAM have shown potential for cancer treatment [23, 24].
In this review, we systematically summarize the pathological functions of EpCAM and its crosstalk with other signaling pathways in cancers, as well as its potential role in cancer diagnosis or prognosis. Moreover, therapeutic approaches taking advantage of EpCAM are also introduced to shed light on the translational prospects of EpCAM, from the laboratory bench to the clinical bedside.
Overview of EpCAM
Basic structure
EpCAM is a single-chain membrane-spanning protein consisting of three major domains, termed EpEX, transmembrane domain (TM) and EpICD (Fig. 1). EpEX is consist of a cysteine disulfide-bonding N-terminal domain (ND), a thyroglobulin-type A1 (TY) domain formed by a cysteine-rich motif, and a C-terminal domain (CD) [25]. EpEX contains two epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like repeats, followed by a cysteine-free region (Fig. 1) [26]. Consistent with EGF-like peptide in the EpEX domain, signaling mediated by the EpEX is involved in EGFR-mediated signaling pathways, which is specified in the following section [17].
Schematic illustration of EpCAM structure. The premature EpCAM molecule is comprised of 314 amino acids (AA), including a signal peptide, which is cleaved during maturation. The mature membrane-bound EpCAM protein consists of an extracellular domain (EpEX), a transmembrane domain (TM) and an intracellular domain (EpICD). EpEX contains an N-terminal domain (ND), thyroglobulin-domain (TY) and C-terminal domain (CD), including three N-glycosylation sites. Four cleavage sites (α, β, γ, ε-sites) locate on EpCAM molecule, in which can be cleaved into soluble EpEX, TM and free EpICD. Human EpCAM contains two α-sites for ADAM protases, a β-site for BACE1 cleavage, and γ-secretase mediated cleavage on γ-sites and ε-sites
The transmembrane domain of EpCAM is a highly conserved valine-rich and leucine-poor helix [25]. Pavsic et al. demonstrated that the two neighboring TMs located close to each other and the cis-oriented subunits of TM helices enhance the stability of the EpCAM cis-dimer [25]. In addition, EpCAM-induced ERK and myosin downregulation was blocked in TM mutant Madin-Darby canine kidney cells, indicating its involvement in signaling transduction [27].
EpCAM can generate a membrane-tethered C-terminal fragment (EpCTF) by proteolytic cleavage. The EpCTF molecule is subsequently processed by γ-secretase into EpICD, a short tail of 26 amino acids [28].
Epigenetic and posttranslational modifications of EpCAM
Early investigation unveiled that intact p53 could maintain EpCAM DNA methylation and inhibit the gene amplification [29]. Previous study indicated low expression of EpCAM suggested more invasive phenotypes. In this subgroup, EpCAM gene was shown abundant with hypermethylated histone 3 lysine 9. Treating with demethylating agents or histone deacetylase inhibitor could increase EpCAM expression and inhibit invasiveness [30]. In cells with hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) expression, downregulation of suppressor of SUZ12 and ZNF198 induced histone modifications of the EpCAM promoter. Similar results were found in tumors derived from X/c-Myc transgenic mice. In addition, activation of DNA demethylation increased EpCAM expression and other acquisition of oncogenic processes [31].
The effects of protein glycosylation on cell proliferation, invasion, adhesion and signaling transduction have been reported in numerous studies [32]. In malignant tumors, such as breast cancer (BC), EpCAM was found to be hyperglycosylated [33]. N-Glycosylation mutation of EpCAM significantly impaired the EMT process in BC, thus inhibiting invasion and metastasis [14]. In addition, proliferation and apoptosis were correlated with the state of glycosylation in BC [10]. Proliferating human mammary epithelial cells (HMECs) express predominantly glycosylated EpCAM isoforms, while in confluent and contact-inhibited situations, the glycosylation of EpCAM is abolished [34]. Asn74, Asn111 and Asn198 were identified as three N-linked glycosylation sites of EpCAM (Fig. 1). The glycosylation of Asn198 is crucial for protein stability, with mutants Asn198 for Ala showing decreased overall expression and half-life of the molecule on the cell surface [33].
Cleavage of EpCAM
Membrane-bound EpCAM can be cleaved via regulated intramembrane proteolysis (RIP) (Fig. 2a), which is frequently activated by cell–cell contact or soluble EpEX in cancers [7, 35]. Additionally, hypoxia was also reported to promote RIP, which usually appears in the tumor microenvironment [11]. Four sites (α, β, γ, ε-sites) on the molecule were shown to be essential for proteolytic cleavage (Fig. 1) [36]. Sequential cleavage of EpCAM RIP initiates α-secretase (ADAM)- and β-secretase (BACE)-induced EpEX shedding, leaving the EpCTF fragment. Subsequently, γ-secretase catalyzes the EpCTF fragment and releases EpICD [28]. The shedding of EpEX promotes the release of EpICD and may be a prerequisite for the cleavage of the intracellular domain of EpCAM [7]. Additionally, ADAM and BACE1 cleavage varies among different species and pH conditions [37]. The process of γ-secretase proteolysis is rather slow and the majority of free EpICD is degraded by the proteasome [28].
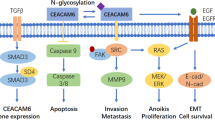
Roles of EpCAM in cancer development and progression. a EpCAM on CSCs membrane surface was cleaved by ADAM17 and γ-secretase, generating EpICD. Most of the EpICD is degraded by proteasome, while the remaining EpICD can bind with FHL2, β-catenin and Lef-1, forming the trans-nuclear complex to activate proliferation and pluripotency related genes. b EpEX/EGFR pathway and EpICD trans-nuclear complex can promote cell proliferation. EGF and TGF-β pathway can regulate EMT markers and EpCAM expression. c In hypoxic condition, EpCAM is upregulated in ATP-high state, whereas in ATP-low situation, HIF-1α is upregulated. CAIX is overexpressed mediated by HIF-1α. CAIX+, together with higher EpCAM and K19 expression HCC subgroup exhibited with high resistance to chemoembolization. Additionally, N-glycosylated EpCAM can regulate HIF-1α and promote EMT and stemness related properties. d MHC-I/TCR interaction serves as T cell activation signals. While activated EpEX/EGFR/ERK pathway results in reduction of PD-L1 ubiquitination degradation. PD-L1 on tumor surface hampers activation of CD8+ T cells and leading to immune escape. CAIX carbonic anhydrase-IX, ECM extracellular matrix, FHL2 four and a half LIM domain protein 2, HIF-1α hypoxia inducible factor 1α, K19 keratin 19, Lef-1 lymphoid enhancer factor 1
In addition to RIP, EpCAM is also a substrate of matriptase, a membrane-anchored protease [38]. During cleavage, the short N-terminus of EpCAM remains attached to EpEX via a disulfide bond [39]. Moreover, the EpCAM monomer is relatively sensitive to matriptase proteolysis. Intact EpCAM-claudin stabilization is crucial for the homeostasis of intestinal epithelial cells, but the interaction is blocked by matriptase cleavage [39].
EpCAM and Trop2
Trop2 is mostly studied in isolation, regardless of its high similarity with EpCAM. Proteolytic cleavage in ectodomain of Trop2 is mediated by ADAM17 and in intracellular domain by γ-secretase [40]. Apart from ADAM17, a recent study found that Trop2 could be cleaved by ADAM10 at Arg87-Thr88. Their reports indicated that cleavage at Arg87-Thr88 is mandatory for Trop2 induced tumor growth [41]. Analog to EpCAM, the ectodomain of Trop2, Trop2EX, forms a Trop2 dimer. Compared with EpCAM, the ND in Trop2 is more exposed. Moreover, the ADAM17 cleavage site in Trop2 dimer is on the exposed edge of a β-strand, which makes it possible for the proteolysis in a dimeric form [42]. Reports demonstrated that Trop2EX could modulate α5β1 integrin to promote prostate cancer metastasis [43]. The cytosolic tail, Trop2IC was also demonstrated to obtain stem-like properties via β-catenin [40]. Similar to EpCAM, Trop2 was reported to induced EMT mediated by β-catenin [44]. Apart from RIP, matriptase-mediated cleavage of EpCAM and Trop2 was shown to destabilize their interaction with claudins [38]. In fact, the redundancy of researches on EpCAM or Trop2 could inspire each other and may should be compiled to take a step forward the truth [2]. Comprehensive reviews of Trop2 can be refereed to Liu et al. [45] and Lenart et al. [46].
Biological and physiological functions of EpCAM
Puzzles of EpCAM in cell adhesion
The role of EpCAM in cell adhesion is puzzling and controversial, several models have been proposed to explain the involvement of EpCAM in cell adhesion [3]. The initial impression of EpCAM served as an adhesion molecule due to the phenomena that EpCAM transfected L cells, which lack classic cadherin mediate adhesion, frequently formed the cell–cell connections and mediated multicellular aggregation in suspension culture [47]. Later research demonstrated EpCAM cis-dimer and its anchor to actin cytoskeleton with α-actinin provided the potential for cell adhesion [26]. With deeper investigations on the structure of EpEX, TY domain of two neighboring EpCAM was found to form a cis-dimer which could be further enhanced by dimerization interface in TM domain. The dimeric form of EpEX provided references for the hypothesis of trans-tetrameric intercellular unit [25]. Recent reports, however, almost refuted the proposed tetramer for homophilic adhesion. Results indicated that EpEX cis-dimer was highly predominant. The following results further dismissed the possible tetramer model considering its functions and avidity nor native-like orientation [48].
Contrarily, in epithelial cells, EpCAM was found to impair E-cadherin-mediated cell adhesion and overall strength of intercellular adhesion [49]. Later research indicated that EpCAM hampered E-cadherin-mediated adhesion by interfering the α-catenin linkage with F-actin [50]. At the same time, Maghzal et al. demonstrated that EpCAM buffered actomyosin contraction by inhibition of PKC and provided proper cortical tension, which may contribute to non-specific cell–cell adhesion [3]. Another possibility is that EpCAM is a heterophilic cell adhesion molecule with partner still unclear [2].
EpCAM in epithelial integrity and non-malignant diseases
As demonstrated in wild type mice, EpCAM was abundant in developing intestinal, whereas for EpCAM knockout mice, the tight junctions (TJs) structure was abnormal, companied with reduction of claudins, especially claudin-7 [51]. Later investigation found that downregulated EpCAM was correlated with decreased overall level of claudin-1 and claudin-7, but their accumulation in TJs was increased, which suggested EpCAM could recruit and distribute claudins for TJs [52]. Previous report has indicated that mutation of EpCAM was found responsible for congenital turfing enteropathy (CTE), a lethal infancy diarrhea characterized by villus atrophy [53]. Cleavage of EpCAM by matriptase at Arg80 was demonstrated to destabilize EpCAM and claudin-7 interaction, leading to lysosomal degradation of claudin-7. This finding explained the role of EpCAM in intestinal epithelium homeostasis [39]. In addition, for CTE patients, absence of EpCAM was suggested to disrupt the polarity of choanocytes and lead to ductopenia [54]. Apart from CTE, a previous study suggested that intestinal epithelial cells derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) could alleviate inflammatory bowel disease by targeting CD4+ T cell and dendritic cells. Whereas the EVs required EpCAM to localize to gastrointestinal tract [55]. Similar to intestinal epithelial cells, EpCAM were found to regulate claudins in keratinocytes, the constituent of the skin barrier. Matriptase and its cognate inhibitor, hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor proteins, regulated EpCAM cleavage and might offer a novel perspective for matriptase dysregulation-induced ichthyosis [38]. Due to the pivotal biological function, the side effects of therapeutic approaches targeting EpCAM must be taken into consideration.
Crosstalk between EpCAM and other signaling pathways during cancer progression
Transforming growth factor β (TGF-β)
In HBV-infected hepatic progenitor cells, the expression of TGF-β1 and HBx was positively correlated with EpCAM and CD90. TGF-β1 was found to cooperate with HBx to enhance the transcription of miR-199a-3p by activating the JNK/c-Jun signaling pathway, which further elevated the expression of stemness markers, including EpCAM [16]. For breast cancer, TGF-β1 was found to promote EMT by upregulating EpCAM via JNK/AP-1 activation [56] (Fig. 2b). However, during the TGF-β1-induced EMT of esophageal cancer cells, EpCAM expression on the cell surface was substantially reduced [20]. In MCF-10A, A549 and HaCaT cell lines, TGF-β1 was found to downregulate the level of EpCAM, and knocking down EpCAM enhanced TGF-β1-induced EMT [57].
Conversely, TGF-β1 treatment of HMECs with ectopic expression of EpCAM resulted in additional small, strongly light-refracting cells and fewer cells positive for senescence-associated β-galactosidase. These observations demonstrated that EpCAM acted against the induction of growth arrest by TGF-β1 [34]. Pal et al. reported that the TGF-β and cyclin D1 (CCND1) signaling pathways were significantly activated in EpCAM+/CD45− metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer [58]. In non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines, the expression of E-cadherin, EpCAM and αvβ6 was found to induce the transcription of TGF-β1 and TGF-βR1 in normal fibroblasts to modulate tumor progression and therapeutic responsiveness [59].
Wnt/β-catenin
EpCAM exerts its functions by mediating Wnt/β-catenin signaling in multiple cancers. Following RIP processing, shed EpICD forms a transcriptional complex with four and a half LIM domain protein 2 (FHL2), lymphoid enhancer factor 1 (Lef-1) and β-catenin to induce oncogenic transcription (Fig. 2a) [7]. Overexpression of EpICD contributed to elevated β-catenin, c-Myc and CCND1 levels, which were closely correlated with Wnt/β-catenin signaling [9]. In colon cancer, EpICD was found to interact with β-catenin and hypoxia inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) to promote the transcriptional activity of HIF-1α-targeted genes (Fig. 2c) [19]. Downregulation of the transmembrane heparan sulfate proteoglycan syndecan-1 increased the expression of cell stemness markers via the activation of β1-integrins, focal adhesion kinase, and Wnt signaling [60]. In EpCAM+ hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), as well as advanced cirrhosis liver tissues, autocrine Wnt signaling was activated, as evidenced by elevated expression of Wnt3, β-catenin, c-Myc and CCND1 [61].
Reciprocally, Wnt/β-catenin signaling is one of the most significant pathways for modulating EpCAM expression. In HCC, the β-catenin/TCF4 complex was found to regulate EpCAM transcription, promoting the self-renewal of liver CSCs [22]. Downregulation of GSK-3β, a Wnt/β-catenin inhibitor, increased the EpCAM+ subpopulation of cancer cells [62]. Decreased expression of βII-spectrin downregulated the expression of kallistatin, thereby activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling and increasing the EpCAM+ subpopulation of cancer cells [63]. Downregulation of cytokeratin 18 increased EpCAM expression by activating Wnt/β-catenin, leading to partial EMT and elevated stemness of breast cancer cells [64].
PI3K-AKT
Previous studies showed that EpCAM+/CD45+ ovarian cancer acquired a more aggressive and drug-resistant phenotype by upregulating downstream effectors of PI3K/AKT signaling [65]. Knockdown of EpCAM in prostate cancer cell lines inactivated the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, thus sensitizing the cancer cells to chemo/radio-therapy [66]. In nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), enhanced EpCAM expression downregulated PTEN while promoting the phosphorylation of AKT, mTOR, p70S6K and 4EBP1. Correspondingly, administration of the AKT inhibitor MK2206 or rapamycin impaired the invasion and stem-like phenotype of NPC cells by blocking the effects of EpCAM [15]. Additionally, a study demonstrated that deglycosylation of EpCAM in BC promoted the process of autophagy by activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway, thus resulting in a decreased proliferation rate [10].
EGF/EGFR/ERK signaling
In human epithelial ovarian cancers, EGF was found to hinder cell migration by upregulating EpCAM and activating ERK1/2 signaling [67]. At the same time, activated ERK2 signaling suppressed EpCAM transcription in normal epithelial and multiple malignant epithelial cell lines by directly binding to the consensus ERK2-binding site in the EpCAM promoter, as well as indirectly by upregulating the EMT-related transcription factors SNAI1/2, TWIST1 and ZEB1, which bind to E-box sites in the promoter region. Conversely, depletion of EpCAM could enhance EGF-induced EMT [57].
In colon cancer, EpEX binds to EGFR and activates EGFR/ERK1/2/AKT signaling, which further promotes the RIP process [19]. In head and neck squamous carcinomas (HNSCCs), EpEX functions as a ligand of EGFR, whose binding leads to the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and AKT, leading to EGFR-dependent proliferation. HNSCC cells treated with EpEX exhibited a dose-dependent repression of EGF-induced EMT-associated gene transcription. Therefore, the reports suggested that EpCAM impairs EGF-induced EMT by competitively binding with EGFR [5] (Fig. 2b), which is further specified in following section.
P53
EpCAM-expressing stem-like mouse ovary cells developed into tumor-initiating cells following retrovirus-mediated transfection with c-Myc and K-Ras oncogenes and p53 depletion. Moreover, depletion of p53 increased the subpopulation of EpCAM+ primary breast cancer cells and led to enhanced tumorigenesis [68]. Sankpal et al. reported a dose-dependent decrease in EpCAM following the induction of p53, which repressed EpCAM expression by binding to its promoter region. Transcriptional repression of EpCAM contributes to the p53-mediated inhibition of breast cancer aggressiveness [69]. In primary human mammary epithelial cells, overexpression of EpCAM upregulated p27KIP1 and p53 in a posttranscriptional manner [34]. In mouse embryonic fibroblasts, ectopic expression of EpCAM or EpICD led to a significant decrease in p53 RNA levels and phosphorylated p53 protein [70]. In addition, EpCAM and p53 exerted their functions exclusively. In HCC, miR-30e-3p was found to play a tumor-suppressive role via a miR30e-3p/P53/MDM2 feedforward loop. Moreover, miR-30e-3p enhanced sorafenib resistance by targeting PTEN, p27 and EpCAM in cells lacking functional p53 [18].
Other signaling pathways
In NSCLC, gemcitabine was found to decrease EpCAM expression by inactivating the HGF/cMET pathway [71]. p-21 activated kinase 4 (PAK4) was found to enhance stem cell-like characteristics through STAT3 signaling and increase the expression of EpCAM in pancreatic cancer cells. At the same time, PAK4 exhibited higher expression levels in triple-positive (CD24+/CD44+/EpCAM+) pancreatic CSCs than in triple-negative CSCs [72]. As previously stated, hypoxia was found to increase the N-glycosylation of EpCAM in BC, which induced the nuclear translocation of NF-κB, promoting EMT and stemness [11]. For EpCAM-dependent breast cancer invasion, the transcription factor AP-1 was reported to participate in the MEKK1/MKK7/JNK pathway, while EpCAM was shown to modulate the effects of NF-κB and IL-8 during BC progression [73].
Noncoding RNAs (miRNAs, lncRNAs, circRNAs)
Recently, noncoding RNAs have emerged as pivotal players that regulate gene expression and signaling pathways to modulate cancer progression. In HCC, miR-30e-3p was found to bind the 3′UTR of EpCAM mRNA to downregulate its expression, thus inhibiting the stemness and chemoresistance of cancer cells [18]. Downregulated miR‐26b‐5p led to increased EpCAM transcription and a population of EpCAM+ HCC cells, as well as the overexpression of NANOG, OCT4, and SOX2, the direct targets of EpCAM [74].
Additionally, lncRNAs participate in the regulation of EpCAM expression. Lnc-TCF7 was demonstrated to upregulate EpCAM expression by binding and decreasing the abundance of miR-200c in a competitive endogenous RNA manner in glioma cells [75]. Lnc-DILC expression was found to be suppressed in EpCAM+ liver CSCs, and correspondingly, the EpCAM+ liver CSC subpopulation was increased following lnc-DILC depletion. Mechanistically, lnc-DILC suppresses autocrine IL-6/STAT3 signaling by binding to the promoter region of IL-6 and inhibiting the crosstalk between TNF-α/NF-κB signaling and the autocrine IL-6/STAT3 cascade in the EpCAM+ subpopulation [76]. High levels of lnc-THOR were observed in EpCAM+ liver CSCs. This increased the population of liver CSCs by stabilizing the mRNA of β-catenin, thus leading to increased chemoresistance [77]. In addition, 11 up- and 12 down-regulated circRNAs were identified in the livers of EpCAM−/− mice compared with wild-type mice, implying the potential involvement of circRNAs in the regulation and activity of EpCAM signaling [78].
Roles of EpCAM in tumor biology
Cancer stemness
A previous study demonstrated that EpCAM is widely expressed on human embryonic stem cells and plays a pivotal role in differentiation [79]. Kuan et al. reported that EpEX and EpCAM could enhance the reprogramming efficiency of OCT4, SOX2, KLF4, as well as c-MYC, and induce fibroblasts into pluripotent stem cells through STAT and HIF-2α [80].
For cancers, EpCAM is a well-regarded marker of CSCs. Tumor cells expressing EpCAM exhibited an enhanced capacity to initiate cancer formation, as well as other stemness properties (chemo/radioresistance, elevated tumorigenicity, angiogenesis, hypoxia tolerance and metastatic colony formation ability) [81]. In HCC, the EpCAM+/AFP+ subgroup displayed self-renewal and differentiation abilities [62]. EpCAM+ leukemia and prostate cancer cells exhibited increased resistance to chemotherapies, and knocking down EpCAM sensitized the chemotherapeutic agent-induced cell apoptosis [13, 82]. In line with these findings, elevated EpCAM expression in breast CSCs exhibited increased resistance to radiotherapy and a more aggressive metastatic phenotype [83]. In addition, after doxorubicin (DOX) treatment, the proportion of EpCAM+/CD133+ was significantly increased in the EpCAM−/CD133− nonstem HCC population, accompanied by more stemness properties and elevated tumor-forming ability [84]. Recently, one possible mechanism suggested that EpCAM could regulate the Nrf2/ARE (antioxidant response elements) pathway to acquire chemoresistance and reduce reactive oxygen species activity. Based on their investigation, the EpCAM/Nrf2 pathway might contribute to CSC features and chemoresistance [85].
Cell proliferation promotion and cell death resistance
The presence of EpCAM+ cells indicated stronger growth and colony formation abilities in BC and HNSCC [85, 86]. In HCC, EpCAM+ and CD90+ cells were found to have distinct localization. CD90+ CSCs are an indicator of higher metastatic capacity, while EpCAM+ CSCs are associated with rapid growth [87]. In addition, nuclear EpICD accumulation was implied to be correlated with HCC cell proliferation [88]. The transcription of cell proliferation-associated genes (CCND1, Rb, Ki67, etc.) is induced by a nuclear complex consisting of EpICD together with FHL2 and the Wnt pathway components β-catenin and Lef-1 [7, 9]. The expression of EpCAM was found to be correlated with Ki67, CCND1 and phosphorylated Rb in many types of cancer [9, 35]. In addition, in lung cancer cells, reports suggested that SOX2 induced EpCAM/p21/cyclin A2 by binding to the EpCAM promoter, leading to enhanced cell proliferation. SOX9 attenuated the expression level of SOX2, resulting in reduced proliferation ability and a more invasive phenotype [89].
EpCAM is also involved in cell death modulation. Genome-wide RNA interference screening suggested that mitochondrial processing peptidase subunit beta (PMPCB) ensured sustainable development for EpCAM+ HCC. Blockade of PMPCB suppressed EpCAM expression and Wnt/β-catenin signaling, thus resulting in apoptosis of EpCAM+ HCC cells and tumor suppression [90]. A recent study revealed that deglycosylated EpCAM inhibited proliferation but activated the process of autophagy and apoptosis in BC [10].
Cell metabolism and angiogenesis
In HCC, a subgroup of cells positive for carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX), a hypoxia-related marker, was positively related to the expression of EpCAM and keratin 19 (K19). Additionally, EpCAM+/K19+ HCC cells under hypoxia showed resistance to arterial embolization therapy, resulting in poorer outcomes [91]. A distinct ATP state is associated with different levels of EpCAM and phenotypes. ATP-low MDA-MB-231 BC cells showed a higher level of HIF-1α, whereas EpCAM was found to be upregulated, together with a more invasive and metastatic potential in the ATP-high subgroup [92]. Furthermore, EpCAM was demonstrated to act as a regulator via the NF-κB pathway to modulate HIF-1α-dependent stemness and EMT properties [11] (Fig. 2c).
Notably, CSCs display flexible energy metabolism, ranging from mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) to glycolysis under oxidative or hypoxic conditions [81]. EpCAM+ HCC exhibited more active expression of lipid metabolism-related genes [93]. Similarly, fatty acids, as well as their synthesis genes, were found to be significantly increased in EpCAM+ cells isolated from colon cancer patients [94]. Dichloroacetate was recently found to be able to divert metabolism toward OXPHOS, which downregulated the CSC markers CD24/CD44/EpCAM. More importantly, dichloroacetate inhibited the formation and viability of EpCAM+ pancreatic cancer cells [95]. Additionally, a recent study implied that EpCAM affected glycogen synthesis, which was associated with diseases of glycogen storage and might participate in liver-related diseases [78].
A comparison of four subgroups of HCC with distinct expression of EpCAM and AFP indicated that the EpCAM+/AFP+ population exhibited higher microvessel density and higher expression levels of vascular epithelial growth factor [12]. Furthermore, Sankpal et al. reported that EpCAM could modulate IL-8 and NF-κB transcription factor activity in BC invasion and angiogenesis [73]. Enhanced effectiveness by bispecific antibody targeting VEGFR2/EpCAM and its modulation of angiogenesis by decreasing IL-8 and IL-6 implied that EpCAM may be a promising target in preventing angiogenesis in cancer progression [96].
Immune evasion and modulation
EpCAM was found to be involved in tumor immune modulation. Park et al. concluded that EpCAM-high HCC resisted natural killer (NK) cell-mediated cytotoxicity by upregulating carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 [97]. Similarly, EpCAM+CD45+ ovarian cancer cells escaped NK-cell-mediated immune surveillance by overexpressing major histocompatibility complex class I antigen (MHC-I) [65]. Additionally, NK cells were implied to promote HCC in HBV transgenic mice. Later, experiments on HBV transgenic mice revealed that NK-cell-derived IFN-γ promoted HCC via the EpCAM/EMT axis [98]. In leukemia, EpCAM was found to hinder immune surveillance by activating Wnt5B signaling. Accordingly, inhibition of EpCAM could enhance the sensitivity of tumor cells to immune surveillance [13]. Moreover, in xenograft mouse models, the protective environment for leukemia in the bone marrow could be counteracted by EpCAM antibodies. In vivo experiments showed that EpCAM blockade could enhance macrophage infiltration to efficiently eliminate tumor cells [13].
PD-L1 is considered a major aspect of the failure of immune surveillance by CD8+ T-cell-mediated cytotoxicity [99]. EGF/EGFR signaling triggered the release of EpEX from cell-surface EpCAM, after which the shed EpICD bound with EGFR to stabilize PD-L1 through the EGFR/ERK pathway in cancer cells (Fig. 2d) [6]. EpCAM and PD-L1 were also found to be upregulated in CD4+ T cells derived from colon cancer patients, which was regarded as an ineffective immune response. Further analysis indicated that p38/MAPK might be a potential target for EpCAM+/CD4+ T-cell-rich colon cancer patients [100]. Moreover, EpCAM antibodies succeeded in downregulating the PD-L1 level and enhanced the therapeutic efficacy of atezolizumab [6].
Dynamic expression and context-dependent roles during EMT
EpCAM plays a dynamic and context-dependent role in EMT (Fig. 2d). As an adhesive molecule, the expression of EpCAM was speculated to be downregulated to increase the mobility of cancer cells [20]. However, EpCAM can reduce E-cadherin-mediated cell–cell adhesion by interfering with the link between α-catenin and F-actin [50]. Furthermore, EpCAM is suggested to be positively correlated with the expression of EMT-related genes, including N-cadherin, snail and vimentin [11, 87]. Indeed, inconsistent results were observed in different studies. During TGF-β1-induced EMT in esophageal cancer cells, EpCAM expression on the surface of the cell membrane was substantially reduced, together with enhanced migration, invasion and dissemination ability [20]. Similarly, low EpCAM expression enhanced EMT of cancer cells and was correlated with advanced tumor stage and lymph node metastasis in endometrial carcinoma [101]. However, EpCAM expression was elevated in TGF-β1-treated MCF-7 BC cells, which was demonstrated to promote EMT and cell migration [56].
A hypothesis was proposed to integrate the inconsistent observations in the cancer EMT process. Driemel et al. considered the expression of EpCAM to be dynamic rather than consistent. EpCAM was speculated to have low expression in normal epithelial cells for tissue integrity. Elevated expression in primary tumor formation might participate in proliferation and adhesion. During EMT or dissemination, downregulation of EpCAM was considered to be associated with migration and invasion. Finally, re-expression in distant micrometastatic lesions contributed to proliferation signals [20] (Fig. 3a).
Changes and developments of EpCAM in metastasis, detection and immunotherapy. a Dynamic expression of EpCAM in EMT process of cancer cells. b EpCAM related CTC detection methods, advantages and their limitations. c Development of EpCAM mediated immunotherapies. ADC antibody–drug conjugate, ADCC antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, CDC complement-dependent cytotoxicity, CRS cytokine release syndrome
Another interesting point is that the role of EpCAM is context dependent. EGF/EGFR signaling promoted HNSCCs proliferation and migration. EMT induced by EGF treatment was completely blocked by ERK inhibitor (Cetuximab, Erlotinib, and AZD6244) but not by AKT-inhibitor MK2206 in HNSCCs. And following EGF treatment, FaDu (EMT-responsive) cells induced a rapid and strong activation of ERK1/2, whereas Cal27 cells (EMT-nonresponsive) were only moderately and more transiently activated. These results implied the dominant role of ERK1/2 in EGF-mediated EMT. However, as the competitor of EGF to EGFR, EpEX was demonstrated to activate ERK to a moderate level. Only high dose of EpEX could promote cell proliferation and counteracted EGF-induced migration. Consistently, EpCAMhigh/EGFlow HNSCCs patients presented with proliferative phenotypes, while EpCAMlow/EGFhigh of carcinomas exhibited enhanced EMT abilities and poor survival [5]. Additionally, EGF treatment was indicated to trigger cleavage of membrane EpCAM. Later, the EpICD translocated complex could regulate cell mobility-related genes and exhibit EMT properties [102]. Sankpal et al. concluded that when ERK activation dominates invasiveness during EMT, upregulated EpCAM expression may counteracts pro-metastatic ERK signaling. Correspondingly, when activated ERK signaling does not contribute to a more aggressive phenotype, nuclear localization of EpICD, which also potentiates cell growth and EMT, as well as other mechanisms, may be the predominant drivers of cancer progression [57].
Applications of EpCAM in clinical oncology
The expression pattern and prognostic value of EpCAM in cancers
Given its versatile functions in cancers, EpCAM participates in multiple steps of cancer progression. In addition to its diagnostic and prognostic value for the prediction of metastasis and the detection of CTCs, its unique expression patterns in cancers potentiate it as a valuable biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis, which are detailed in Table 1.
EpCAM-based CTC detection and diagnostic methods
CTCs are considered as a promising diagnostic target for the detection of cancer metastasis [103]. EpCAM is proposed as a marker for detecting CTCs, given that it is rarely expressed on the surface of leukocytes but highly expressed in the majority of epithelium-derived cancers, such as BC, HCC and colorectal cancer (Fig. 3b) [104]. Since CTCs are defined as nucleated EpCAM+/CK+/CD45− cells, EpCAM-based CTC detection, the CellSearch system has been applied for CTC detection [105]. Expanded coverage of cytokeratin or other indicators (e.g., vimentin) and EpCAM showed promising future in arterial and venous blood CTC monitoring and prognostic values [21, 104]. Nevertheless, the traditional detection of CTCs via EpCAM has its drawbacks. Conventional EpCAM-based CTC detection strategies were restricted to EpCAM-positive CTCs and carried the risk of overlooking the most aggressive HCC CTC subgroups because of EMT, resulting in an underestimate of the overall number of CTCs in circulation [106]. In fact, a recent study suggested that prostate CTCs cocultured with platelets showed decreased EpCAM expression levels but elevated platelet marker CD61, accompanied by a higher proliferation rate during EMT. The results indicated that CD61, rather than EpCAM, might be an alternative diagnostic marker in this situation [107].
Advances have been made with the aim of overcoming the nonnegligible false negative rate of CTC detection via EpCAM. Alternative markers have been applied for combined marker-based CTC detection. Investigation suggested that for CTCs not expressing EpCAM, CD44v6 detection is an alternative approach for the subgroup. That is, CD44v6 defined a new CTC population without EpCAM [108]. Similarly, the same report demonstrated that for urothelial cell carcinoma, EpCAM and urokinase plasminogen activator receptor are complementary targets in cancer diagnosis [109]. Recently, Court et al. demonstrated that with a multimarker panel of EpCAM, ASGPR, and GPC3, 97% of patients with HCC were CTC positive [110].
Furthermore, a comprehensive label-free approach was optimized for the detection of HCC-CTCs by phenotypic and karyotypic characterization. In addition, the quantity of polyploid (≥ pentasomy 8) EpCAM+ CTCs (cutoff: ≥ 1 cell), small EpCAM− CTCs with trisomy 8 (≥ 5 cells), positive detection of circulating tumor microemboli (≥ 1), and increased triploid CTCs were linked with a poor prognosis in postoperative patients [111]. EpCAM-related and non-EpCAM methods have been universally applied in CTC detection [112].
EpCAM in extracellular vesicles
As an intercellular communication medium, exosomes and microsomes have been shown to play pivotal roles during cancer pathogenesis by transferring bioactive substances [113]. A study revealed that serum-derived microsomes/exosomes in prostate cancer showed a four- to fivefold increase in the expression levels of EpCAM compared to healthy controls [114]. Quantitative analysis of EpCAM and other biomarkers on exosomes has shown prospects in blood sample identification of pancreatic and breast cancer [115]. Apart from carcinomas, for osteosarcoma-derived exosomes, analysis of EpCAM, CD63 and vimentin expression levels has exceeded traditional histological biopsy with high specificity and accuracy, as well as a low risk of tumor spread [116]. Furthermore, considering that EVs may fuse with the membranes of cancer cells, these biomarkers on EVs can be localized to cell membranes and serve as therapeutic targets. EpCAM and CD73 bispecific antibodies could selectively targeting EpCAM+ carcinoma-derived EVs. Moreover, enhanced efficacy to inhibit CD73 EVs-mediated immune suppression was found compared with targeting CD73 alone [117].
Chemical modification and targeted treatment
Compared to conventional antibody-mediated tumor therapy, aptamers can be utilized to enhance the specificity and affinity of pharmacological reagent delivery. Since EpCAM is broadly expressed on cancer cells, especially CSCs, EpCAM-targeting aptamers are widely used in cancer treatment.
Conjugation of EpCAM-specific aptamers to DOX resulted in a high concentration and prolonged maintenance of DOX in the nuclei of EpCAM-expressing colorectal CSCs [118]. Furthermore, an EpCAM-aptamer-based platform for specific gene knockdown may be a novel therapeutic approach to overcome cancer resistance and immune evasion [23]. In human HER2+ and basal-A triple-negative BC, EpCAM aptamer-linked small-interfering RNA chimeras (AsiCs) enhanced the immune response against tumors that are insensitive to checkpoint blockade. AsiC mixtures were more effective than individual AsiCs and exhibited a synergistic effect with anti-PD-1 checkpoint inhibitors. Additionally, AsiC combinations could effectively induce the expression of neoantigens and cytokine production for cytotoxicity and increase tumor phagocytosis [23]. Similar to the bispecific antibody, simultaneously targeting CD44 and EpCAM with a bispecific aptamer showed higher efficacy than either aptamer alone. Moreover, the aptamer exhibited no toxicity to the host and no activation of innate immunity [119].
EpCAM aptamers also find their place in nanoplatforms for delivering therapeutics. Given the expression of CD47 and PD-L1 during tumorigenesis, designed EpCAM-targeted cationic liposomes containing si-CD47 and si-PD-L1 could target EpCAM-rich cancer cells to downregulate both CD47 and PD-L1 proteins. Moreover, these multiple nanoparticles exhibited high affinity for EpCAM+ tumor cells and low toxicity to healthy cells, resulting in enhanced immunotherapeutic efficacy [120]. In addition, liposomes based on HER-2 with anti-EpCAM toxin showed promise for BC treatment [121].
Immunotherapeutic applications of EpCAM
EpCAM monoclonal antibodies (mAbs)
Numerous promising EpCAM antibodies for cancer treatment have been reported in preclinical trials (Table 2). The first monoclonal EpCAM antibody, edrecolomab (17-1A), is an IgG2a derived from the ascites of murine. The antibody was applied in various adenocarcinomas and showed limited effects, which may should be blamed to its low affinity with tumors [122, 123]. The human-engineered and humanized antibodies, ING-1 and 3622W94, were then developed and tested in adenocarcinomas [123]. The two antibodies exhibited high affinity with EpCAM, but led to low tolerance and pancreatitis [124]. The full human IgG1 antibody, adecatumumab (MT201) exhibited dose-dependent anti-tumor activities and well-tolerance for metastatic breast cancer (MBC) [125]. For post-prostatectomy cancer patients with baseline PSA levels ≤ 1 ng/ml and high EpCAM-expressing, high dose adecatumumab treatment delayed disease progression [126]. A phase I study for hormone refractory prostate cancer patients and a phase IB study for EpCAM-positive relapsed or refractory advanced-stage breast cancer confirmed the feasibility of adecatumumab [127, 128]. EpAb2-6, a new EpCAM neutralizing antibody, exhibited antitumor effects via inhibiting the nuclear translocation of EpICD/β-catenin complexes and inducing apoptosis in colon cancer cells [19]. Moreover, EpAb2-6 impeded tumor progression by increasing high temperature requirement A2 expression and decreasing PD-L1 protein levels to enhance the cytotoxic activity of CD8+ T cells [6].
EpCAM bispecific antibodies (BsAb) and variations
Bispecific or chimeric antibodies are developed to enhance anti-tumor efficacy (Table 2). Catumaxomab (Removab), with two antigen-binding sites (EpCAM and CD3) and a functional Fc domain, initiates T-cell-mediated lysis, cytokine-related cytotoxicity, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) in vitro [129]. In patients with malignant ascites from a phase II/III study, the catumaxomab-treated group exhibited significantly longer overall survival (OS) [130]. MM-131, a bispecific anti-EpCAM/Met antibody, exhibited both HGF-dependent and -independent inhibition of Met signaling, inhibiting the proliferation of Met-driven HCC, BC, gastric cancer and lung cancer [131].
Bispecific T-cell engaging antibodies (BiTE) enhance the patient’s immune response to tumors by linking T cells to cancer cells, stimulating T-cell activation, tumor killing and cytokine production [132, 133]. EpCAM, as a common highly expressed molecule in cancer cells, is taken as a tumor-associated antigen. Solitomab (MT110), the bispecific T-cell engaging antibodies (BiTE) with two single chain binding to EpCAM and CD3, was effective against primary uterine and ovarian carcinosarcoma [134]. The mechanism of MT110 mainly relies on release of perforin and granzymes after T-cell activation [134, 135]. However, solitomab was finally abandoned due to its gastrointestinal toxicity [136]. Anti-EpCAM BiTE 1H8/CD3 succeed to inhibit the growth of HCC xenografts and reduced the expression of most CSC biomarkers [137]. To avoid harmful cytokine toxicity induced by activation of T cells, bispecific NK-cell engager (BiKE), targeting CD16 on NK cells and EpCAM on tumor cells is developed. It mediates ADCC against EpCAM+ HT-29 colon cancer cells [138]. Modified with interleukin-15 cross-liner, the trispecific NK-cell engager (TriKE) displays improved activation, proliferation and survival on NK cells compared with BiKE [139].
EpCAM antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs)
EpCAM antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs) are also generated for EpCAM+ cancer therapies (Table 2). Oportuzumab monatox is comprised of an anti-EpCAM single-chain variable fragment and a fragment of pseudomonas exotoxin A (ETA), which displays anti-tumor effects after the ADC is internalized and ETA is released [140]. Similarly, citatuzumab bogatox is consist of anti-EpCAM Fab with non-immunogenic toxin of bougainvillea spectabilis [141]. Phase I and II clinical trials in various cancers showed their well tolerance and effectiveness for cancer treatment [142]. Tucotuzumab celmoleukin (EMD 273,066, huKS-IL2) is an immunocytokine by genetically fusing interleukin-2 (IL-2) to a humanized monoclonal antibody against EpCAM [143]. The novel antibody-based therapy may activate lymphocytes by IL-2. In addition, the combination of tucotuzumab celmoleukin with radiofrequency ablation enhanced anti-tumor effects and immunologic memory in murine colon cancer [144]. The safety and effectiveness of tucotuzumab celmoleukin for cancer patients were demonstrated in phase I and IB studies [143, 145]. Some more ADCs are emerging as promising EpCAM-targeting complexes for cancer treatment, evidenced by in vitro cell lines assays and in vivo animal experiments. ChiHEA125-Ama, conjugate of α-amanitin with a chimerized anti-EpCAM monoclonal antibody, exhibits tumor-suppressing potential in pancreatic, breast and various other cancers [146]. Correspondingly, attachment of indolinobenzodiazepine pseudodimers (IGN) to EpCAM (EpCAM-IGN) antibodies exhibited dose-dependent anti-tumor activity [147].
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells
Apart from antibody-mediated treatments, cellular immunity, especially T-cell therapy, shows prospects in cancer treatment. A recent study revealed that CD8+ T cells with ectopic expression of miR-200c and EpCAM exhibited reduced apoptosis and enhanced responses to both solid and liquid tumors. They suggested that the miR-200/EpCAM axis promoted the state for T cells to be poised for memory-like features [148].
In fact, EpCAM has already found its place in CAR T cells for cancer treatment (Table 2). EpCAM+ acute myeloid leukemia (AML) displays enhanced tumorigenicity and chemoresistance compared to EpCAM− AML cells. Neither normal bone marrow cells nor peripheral blood mononuclear cells express EpCAM. Thus, CAR T targeting EpCAM stand out as an ideal method for treating AML. Moreover, rapamycin pretreatments can attenuate mTORC1 activity and upregulate CXCR4, which promotes the migration and penetration abilities of EpCAM CAR T cell for eliminating acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in bone marrow [149]. The expression level of EpCAM corelated with prognosis and metastasis of colorectal cancer, CAR T cells targeting EpCAM selectively destroy cancer cells with high EpCAM expression. Moreover, Wnt pathway inhibitor hsBCL9CT-24 has shown the potential to improve T cell infiltration, to promote effector T cells and to impede exhaustion of CAR T cells [150]. A current study demonstrated that bispecific CAR T cells targeting EpCAM and intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) displayed superior efficacy in eradicating solid tumors. Moreover, activated CAR T cells against EpCAM result in upregulation of ICAM-1, leading the tumors to be more susceptible to bispecific CAR T cells [24].
Patients with CAR T cell therapies may suffer with cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and immune effector cell associated neurotoxicity syndrome, while CAR NK cell treatments have demonstrated the advantages in the unique biological attributes and safety [151]. CAR NK-92 cells therapy has demonstrated significant efficacy against human colorectal cancer. Cotreated with regorafenib improves EpCAM CAR NK-92 cells by enhancing immune cell infiltration, downregulating immune suppressive cell subsets and improving tumor vasculature [152]. Additionally, induced EpCAM CAR NK cells derived from modified induced pluripotent stem cells displays anti-tumor activities as well, which provides a novel approach to generate CAR NK cells more efficiently [153].
Conclusions and perspectives
With advances in basic research, EpCAM was revealed to be a multifaceted player in cancer progression (Fig. 4). Beyond its classic role in cell adhesion, which is also context dependent, EpCAM fulfills versatile functions by meditating cell signaling from both extracellular and intracellular compartments. EpCAM orchestrates cancer progression by modulating cellular characteristics such as proliferation, stemness, mobility, chemo/radio-therapy resistance and so on. Furthermore, the immune microenvironment can also be modulated by pathological expression of EpCAM. In particular, the functions of EpCAM are highly context-dependent and dynamic. It is arbitrary to assert it as oncogenic or tumor-suppressive. Nevertheless, from the clinical perspective, EpCAM has great potential value for the diagnosis and prognosis of cancer patients. In addition to improving its sensitivity and specificity as a biomarker of CTCs, human antibodies targeting EpCAM in cancer have been applied in clinical trials. Furthermore, EpCAM expression in cancer cells provides a valuable target for precision therapy. With the increase in our knowledge of cancer characteristics, the mystery of the role of EpCAM in cancers may be further elucidated, leading to more valuable applications in cancer management.
Functions and applications of EpCAM. EpCAM participates in aspects of cancer pathological processes and leads to various cancerous properties, including EMT, hypoxic metabolism, stemness, angiogenesis and immune evasion. Due to its versatile functions in cancer development, diverse clinical applications are displayed and come into use. EpCAM-targeting immunotherapy and modified microparticles have shown clinical prospects for cancer therapy. In addition, EpCAM is used for CTC detection, as well as a CSC marker for diagnosis and prognosis values
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- ADAM17:
-
A disintegrin and metalloproteinase 17
- ADCs:
-
Antibody–drug conjugates
- ADCC:
-
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity
- AML:
-
Acute myeloid leukemia
- AsiCs:
-
Aptamer-linked small-interfering RNA chimeras
- BC:
-
Breast cancer
- BiKE:
-
Bispecific NK-cell engager
- BiTE:
-
Bispecific T-cell engager
- BMP:
-
Bone morphogenetic protein
- CAR:
-
Chimeric antigen receptor
- CCND1:
-
Cyclin D1
- CD:
-
C-terminal domain
- CDC:
-
Complement-dependent cytotoxicity
- circRNAs:
-
Circular RNAs
- CRS:
-
Cytokine release syndrome
- CSCs:
-
Cancer stem cells
- CTCs:
-
Circulating tumor cells
- CTE:
-
Congenital tufting enteropathy
- DFS:
-
Disease-free survival
- DOX:
-
Doxorubicin
- DSS:
-
Disease-specific survival
- EAC:
-
Esophageal adenocarcinoma
- EGF(R):
-
Epidermal growth factor (receptor)
- EMT:
-
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition
- EpCAM:
-
Epithelial cell adhesion molecule
- EpCTF:
-
EpCAM C-terminal fragment
- EpEX:
-
EpCAM extracellular domain
- EpICD:
-
EpCAM intracellular domain
- Erα:
-
Estrogen receptor alpha
- EVs:
-
Extracellular vesicles
- FHL2:
-
Four and a half LIM domain protein 2
- HBx:
-
Hepatitis B virus X protein
- HIF-1α(2α):
-
Hypoxia inducible factor 1α(2α)
- HMECs:
-
Human mammary epithelial cells
- HNSCC:
-
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- ICAM-1:
-
Intercellular adhesion molecule 1
- IGN:
-
Indolinobenzodiazepine pseudodimer
- IL-2:
-
Interleukin-2
- Lef-1:
-
Lymphoid enhancer Factor 1
- K19:
-
Keratin 19
- lncRNA:
-
Long non-coding RNAs
- MBC:
-
Metastatic breast cancer
- miRNAs:
-
MicroRNAs
- MHC-1:
-
Major histocompatibility complex class I antigen
- ND:
-
N-terminal domain
- NPC:
-
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- OXPHOS:
-
Oxidative phosphorylation
- PAK4:
-
P-21 activated kinase 4
- PMPCB:
-
Mitochondrial processing peptidase subunit beta
- PS-2:
-
Presenilin-2
- RIP:
-
Regulated intramembrane proteolysis
- TACE:
-
TNF-α converting enzyme
- TGF-β(1):
-
Transforming growth factor-β(1)
- TM:
-
Transmembrane domain
- TriKE:
-
Trispecific NK-cell engager
- Trop2:
-
Trophoblast cell surface antigen 2
- TY:
-
Thyroglobulin-type A1 domain
References
Herlyn D, Herlyn M, Ross AH, Ernst C, Atkinson B, Koprowski H. Efficient selection of human tumor growth-inhibiting monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1984;73(1):157–67.
Fagotto F, Aslemarz A. EpCAM cellular functions in adhesion and migration, and potential impact on invasion: a critical review. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2020;1874(2): 188436.
Maghzal N, KayaliHulya A, Rohani N, Kajava Andrey V, Fagotto F. EpCAM controls actomyosin contractility and cell adhesion by direct inhibition of PKC. Dev Cell. 2013;27(3):263–77.
Balzar M, Winter MJ, de Boer CJ, Litvinov SV. The biology of the 17-1A antigen (Ep-CAM). J Mol Med (Berl). 1999;77(10):699–712.
Pan M, Schinke H, Luxenburger E, Kranz G, Shakhtour J, Libl D, et al. EpCAM ectodomain EpEX is a ligand of EGFR that counteracts EGF-mediated epithelial–mesenchymal transition through modulation of phospho-ERK1/2 in head and neck cancers. PLoS Biol. 2018;16(9): e2006624.
Chen HN, Liang KH, Lai JK, Lan CH, Liao MY, Hung SH, et al. EpCAM signaling promotes tumor progression and protein stability of PD-L1 through the EGFR pathway. Cancer Res. 2020;80(22):5035–50.
Maetzel D, Denzel S, Mack B, Canis M, Went P, Benk M, et al. Nuclear signalling by tumour-associated antigen EpCAM. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11(2):162–71.
Munz M, Baeuerle PA, Gires O. The emerging role of EpCAM in cancer and stem cell signaling. Cancer Res. 2009;69(14):5627–9.
Chaves-Perez A, Mack B, Maetzel D, Kremling H, Eggert C, Harreus U, et al. EpCAM regulates cell cycle progression via control of cyclin D1 expression. Oncogene. 2013;32(5):641–50.
Yang L, Wang Q, Zhao Q, Yang F, Liu T, Huang X, et al. Deglycosylated EpCAM regulates proliferation by enhancing autophagy of breast cancer cells via PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Aging. 2022;14(1):316–29.
Zhang D, Yang L, Liu X, Gao J, Liu T, Yan Q, et al. Hypoxia modulates stem cell properties and induces EMT through N-glycosylation of EpCAM in breast cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(4):3626–33.
Shan YF, Huang YL, Xie YK, Tan YH, Chen BC, Zhou MT, et al. Angiogenesis and clinicopathologic characteristics in different hepatocellular carcinoma subtypes defined by EpCAM and alpha-fetoprotein expression status. Med Oncol. 2011;28(4):1012–6.
Zheng X, Fan X, Fu B, Zheng M, Zhang A, Zhong K, et al. EpCAM inhibition sensitizes chemoresistant leukemia to immune surveillance. Cancer Res. 2017;77(2):482–93.
Liu X, Yang L, Zhang D, Liu T, Yan Q, Yang X. Deglycosylation of epithelial cell adhesion molecule affects epithelial to mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(4):4504–14.
Wang MH, Sun R, Zhou XM, Zhang MY, Lu JB, Yang Y, et al. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule overexpression regulates epithelial–mesenchymal transition, stemness and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via the PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(1):2.
Dong KS, Chen Y, Yang G, Liao ZB, Zhang HW, Liang HF, et al. TGF-beta1 accelerates the hepatitis B virus X-induced malignant transformation of hepatic progenitor cells by upregulating miR-199a-3p. Oncogene. 2020;39(8):1807–20.
Kuan II, Lee CC, Chen CH, Lu J, Kuo YS, Wu HC. The extracellular domain of epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) enhances multipotency of mesenchymal stem cells through EGFR-LIN28-LET7 signaling. J Biol Chem. 2019;294(19):7769–86.
Gramantieri L, Pollutri D, Gagliardi M, Giovannini C, Quarta S, Ferracin M, et al. MiR-30e-3p influences tumor phenotype through MDM2/TP53 axis and predicts sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2020;80(8):1720–34.
Liang KH, Tso HC, Hung SH, Kuan II, Lai JK, Ke FY, et al. Extracellular domain of EpCAM enhances tumor progression through EGFR signaling in colon cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2018;433:165–75.
Driemel C, Kremling H, Schumacher S, Will D, Wolters J, Lindenlauf N, et al. Context-dependent adaption of EpCAM expression in early systemic esophageal cancer. Oncogene. 2014;33(41):4904–15.
Liu Y, Li Q, Chen T, Shen T, Zhang X, Song P, et al. Clinical verification of vimentin/EpCAM immunolipid magnetic sorting system in monitoring CTCs in arterial and venous blood of advanced tumor. J Nanobiotechnol. 2021;19(1):185.
Deng Y, Li M, Zhuo M, Guo P, Chen Q, Mo P, et al. Histone demethylase JMJD2D promotes the self-renewal of liver cancer stem-like cells by enhancing EpCAM and Sox9 expression. J Biol Chem. 2021;296: 100121.
Zhang Y, Xie X, Yeganeh PN, Lee DJ, Valle-Garcia D, Meza-Sosa KF, et al. Immunotherapy for breast cancer using EpCAM aptamer tumor-targeted gene knockdown. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2021;118(9): e2022830118.
Yang Y, McCloskey JE, Yang H, Puc J, Alcaina Y, Vedvyas Y, et al. Bispecific CAR T cells against EpCAM and inducible ICAM-1 overcome antigen heterogeneity and generate superior antitumor responses. Cancer Immunol Res. 2021;9(10):1158–74.
Pavsic M, Guncar G, Djinovic-Carugo K, Lenarcic B. Crystal structure and its bearing towards an understanding of key biological functions of EpCAM. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4764.
Balzar M, Briaire-de Bruijn IH, Rees-Bakker HA, Prins FA, Helfrich W, de Leij L, et al. Epidermal growth factor-like repeats mediate lateral and reciprocal interactions of Ep-CAM molecules in homophilic adhesions. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21(7):2570–80.
Barth AIM, Kim H, Riedel-Kruse IH. Regulation of epithelial migration by epithelial cell adhesion molecule requires its Claudin-7 interaction domain. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(10): e0204957.
Huang Y, Chanou A, Kranz G, Pan M, Kohlbauer V, Ettinger A, et al. Membrane-associated epithelial cell adhesion molecule is slowly cleaved by gamma-secretase prior to efficient proteasomal degradation of its intracellular domain. J Biol Chem. 2019;294(9):3051–64.
Nasr AF, Nutini M, Palombo B, Guerra E, Alberti S. Mutations of TP53 induce loss of DNA methylation and amplification of the TROP1 gene. Oncogene. 2003;22(11):1668–77.
Tai KY, Shiah SG, Shieh YS, Kao YR, Chi CY, Huang E, et al. DNA methylation and histone modification regulate silencing of epithelial cell adhesion molecule for tumor invasion and progression. Oncogene. 2007;26(27):3989–97.
Zhang H, Diab A, Fan H, Mani SK, Hullinger R, Merle P, et al. PLK1 and HOTAIR accelerate proteasomal degradation of SUZ12 and ZNF198 during hepatitis B virus-induced liver carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2015;75(11):2363–74.
Pinho SS, Reis CA. Glycosylation in cancer: mechanisms and clinical implications. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015;15(9):540–55.
Munz M, Fellinger K, Hofmann T, Schmitt B, Gires O. Glycosylation is crucial for stability of tumour and cancer stem cell antigen EpCAM. Front Biosci. 2008;13:5195–201.
Martowicz A, Rainer J, Lelong J, Spizzo G, Gastl G, Untergasser G. EpCAM overexpression prolongs proliferative capacity of primary human breast epithelial cells and supports hyperplastic growth. Mol Cancer. 2013;12:56.
Denzel S, Maetzel D, Mack B, Eggert C, Barr G, Gires O. Initial activation of EpCAM cleavage via cell-to-cell contact. BMC Cancer. 2009;9:402.
Tsaktanis T, Kremling H, Pavsic M, von Stackelberg R, Mack B, Fukumori A, et al. Cleavage and cell adhesion properties of human epithelial cell adhesion molecule (HEPCAM). J Biol Chem. 2015;290(40):24574–91.
Hachmeister M, Bobowski KD, Hogl S, Dislich B, Fukumori A, Eggert C, et al. Regulated intramembrane proteolysis and degradation of murine epithelial cell adhesion molecule mEpCAM. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(8): e71836.
Wu CJ, Lu M, Feng X, Nakato G, Udey MC. Matriptase cleaves EpCAM and TROP2 in keratinocytes, destabilizing both proteins and associated claudins. Cells. 2020;9(4):1027.
Wu CJ, Feng X, Lu M, Morimura S, Udey MC. Matriptase-mediated cleavage of EpCAM destabilizes claudins and dysregulates intestinal epithelial homeostasis. J Clin Invest. 2017;127(2):623–34.
Stoyanova T, Goldstein AS, Cai H, Drake JM, Huang J, Witte ON. Regulated proteolysis of Trop2 drives epithelial hyperplasia and stem cell self-renewal via beta-catenin signaling. Genes Dev. 2012;26(20):2271–85.
Trerotola M, Guerra E, Ali Z, Aloisi AL, Ceci M, Simeone P, et al. Trop-2 cleavage by ADAM10 is an activator switch for cancer growth and metastasis. Neoplasia. 2021;23(4):415–28.
Pavsic M. Trop2 forms a stable dimer with significant structural differences within the membrane-distal region as compared to EpCAM. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(19):10640.
Trerotola M, Jernigan DL, Liu Q, Siddiqui J, Fatatis A, Languino LR. Trop-2 promotes prostate cancer metastasis by modulating beta(1) integrin functions. Cancer Res. 2013;73(10):3155–67.
Zhao W, Jia L, Kuai X, Tang Q, Huang X, Yang T, et al. The role and molecular mechanism of Trop2 induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition through mediated beta-catenin in gastric cancer. Cancer Med. 2019;8(3):1135–47.
Liu X, Deng J, Yuan Y, Chen W, Sun W, Wang Y, et al. Advances in Trop2-targeted therapy: novel agents and opportunities beyond breast cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 2022;239: 108296.
Lenart S, Lenart P, Smarda J, Remsik J, Soucek K, Benes P. Trop2: jack of all trades, master of none. Cancers. 2020;12(11):3328.
Litvinov SV, Velders MP, Bakker HA, Fleuren GJ, Warnaar SO. Ep-CAM: a human epithelial antigen is a homophilic cell–cell adhesion molecule. J Cell Biol. 1994;125(2):437–46.
Gaber A, Kim SJ, Kaake RM, Bencina M, Krogan N, Sali A, et al. EpCAM homo-oligomerization is not the basis for its role in cell–cell adhesion. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):13269.
Litvinov SV, Balzar M, Winter MJ, Bakker HA, Briaire-de Bruijn IH, Prins F, et al. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (Ep-CAM) modulates cell–cell interactions mediated by classic cadherins. J Cell Biol. 1997;139(5):1337–48.
Winter MJ, Nagelkerken B, Mertens AE, Rees-Bakker HA, Briaire-de Bruijn IH, Litvinov SV. Expression of Ep-CAM shifts the state of cadherin-mediated adhesions from strong to weak. Exp Cell Res. 2003;285(1):50–8.
Lei Z, Maeda T, Tamura A, Nakamura T, Yamazaki Y, Shiratori H, et al. EpCAM contributes to formation of functional tight junction in the intestinal epithelium by recruiting claudin proteins. Dev Biol. 2012;371(2):136–45.
Wu CJ, Mannan P, Lu M, Udey MC. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) regulates claudin dynamics and tight junctions. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(17):12253–68.
Sivagnanam M, Mueller JL, Lee H, Chen Z, Nelson SF, Turner D, et al. Identification of EpCAM as the gene for congenital tufting enteropathy. Gastroenterology. 2008;135(2):429–37.
Zhan Y, Ward SC, Fiel MI, Teruya-Feldstein J, McKay EM, Dekio F. EpCam is required for maintaining the integrity of the biliary epithelium. Liver Int. 2021;41(9):2132–8.
Jiang L, Shen Y, Guo D, Yang D, Liu J, Fei X, et al. EpCAM-dependent extracellular vesicles from intestinal epithelial cells maintain intestinal tract immune balance. Nat Commun. 2016;7:13045.
Gao J, Yan Q, Wang J, Liu S, Yang X. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition induced by TGF-beta1 is mediated by AP1-dependent EpCAM expression in MCF-7 cells. J Cell Physiol. 2015;230(4):775–82.
Sankpal NV, Fleming TP, Sharma PK, Wiedner HJ, Gillanders WE. A double-negative feedback loop between EpCAM and ERK contributes to the regulation of epithelial–mesenchymal transition in cancer. Oncogene. 2017;36(26):3706–17.
Pal SK, Patel J, He M, Foulk B, Kraft K, Smirnov DA, et al. Identification of mechanisms of resistance to treatment with abiraterone acetate or enzalutamide in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). Cancer. 2018;124(6):1216–24.
Eberlein C, Rooney C, Ross SJ, Farren M, Weir HM, Barry ST. E-Cadherin and EpCAM expression by NSCLC tumour cells associate with normal fibroblast activation through a pathway initiated by integrin alphavbeta6 and maintained through TGFbeta signalling. Oncogene. 2015;34(6):704–16.
Kumar Katakam S, Tria V, Sim WC, Yip GW, Molgora S, Karnavas T, et al. The heparan sulfate proteoglycan syndecan-1 regulates colon cancer stem cell function via a focal adhesion kinase-Wnt signaling axis. FEBS J. 2021;288(2):486–506.
Khosla R, Rastogi A, Ramakrishna G, Pamecha V, Mukhopadhyay A, Vasudevan M, et al. EpCAM+ liver cancer stem-like cells exhibiting autocrine Wnt signaling potentially originate in cirrhotic patients. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(3):807–18.
Yamashita T, Ji J, Budhu A, Forgues M, Yang W, Wang HY, et al. EpCAM-positive hepatocellular carcinoma cells are tumor-initiating cells with stem/progenitor cell features. Gastroenterology. 2009;136(3):1012–24.
Zhi X, Lin L, Yang S, Bhuvaneshwar K, Wang H, Gusev Y, et al. betaII-Spectrin (SPTBN1) suppresses progression of hepatocellular carcinoma and Wnt signaling by regulation of Wnt inhibitor kallistatin. Hepatology. 2015;61(2):598–612.
Shi R, Liu L, Wang F, He Y, Niu Y, Wang C, et al. Downregulation of cytokeratin 18 induces cellular partial EMT and stemness through increasing EpCAM expression in breast cancer. Cell Signal. 2020;76: 109810.
Akhter MZ, Sharawat SK, Kumar V, Kochat V, Equbal Z, Ramakrishnan M, et al. Aggressive serous epithelial ovarian cancer is potentially propagated by EpCAM(+)CD45(+) phenotype. Oncogene. 2018;37(16):2089–103.
Ni J, Cozzi P, Hao J, Beretov J, Chang L, Duan W, et al. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) is associated with prostate cancer metastasis and chemo/radioresistance via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013;45(12):2736–48.
Fan Q, Cheng JC, Qiu X, Chang HM, Leung PC. EpCAM is up-regulated by EGF via ERK1/2 signaling and suppresses human epithelial ovarian cancer cell migration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;457(3):256–61.
Motohara T, Masuko S, Ishimoto T, Yae T, Onishi N, Muraguchi T, et al. Transient depletion of p53 followed by transduction of c-Myc and K-Ras converts ovarian stem-like cells into tumor-initiating cells. Carcinogenesis. 2011;32(11):1597–606.
Sankpal NV, Willman MW, Fleming TP, Mayfield JD, Gillanders WE. Transcriptional repression of epithelial cell adhesion molecule contributes to p53 control of breast cancer invasion. Cancer Res. 2009;69(3):753–7.
Huang HP, Chen PH, Yu CY, Chuang CY, Stone L, Hsiao WC, et al. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) complex proteins promote transcription factor-mediated pluripotency reprogramming. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(38):33520–32.
Liao ZJ, Guo YH, Zhao Z, Yao JT, Xu R, Nan KJ. Gemcitabine inhibits the micrometastasis of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting the EpCAM-positive circulating tumor cells via the HGF/cMET pathway. Int J Oncol. 2014;45(2):651–8.
Tyagi N, Marimuthu S, Bhardwaj A, Deshmukh SK, Srivastava SK, Singh AP, et al. p-21 activated kinase 4 (PAK4) maintains stem cell-like phenotypes in pancreatic cancer cells through activation of STAT3 signaling. Cancer Lett. 2016;370(2):260–7.
Sankpal NV, Fleming TP, Gillanders WE. EpCAM modulates NF-kappaB signaling and interleukin-8 expression in breast cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2013;11(4):418–26.
Khosla R, Hemati H, Rastogi A, Ramakrishna G, Sarin SK, Trehanpati N. miR-26b-5p helps in EpCAM+cancer stem cells maintenance via HSC71/HSPA8 and augments malignant features in HCC. Liver Int. 2019;39(9):1692–703.
Zhao J, Zhang L, Zheng L, Hong Y, Zhao L. LncRNATCF7 promotes the growth and self-renewal of glioma cells via suppressing the miR-200c-EpCAM axis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;97:203–8.
Wang X, Sun W, Shen W, Xia M, Chen C, Xiang D, et al. Long non-coding RNA DILC regulates liver cancer stem cells via IL-6/STAT3 axis. J Hepatol. 2016;64(6):1283–94.
Cheng Z, Lei Z, Yang P, Si A, Xiang D, Zhou J, et al. Long non-coding RNA THOR promotes liver cancer stem cells expansion via beta-catenin pathway. Gene. 2019;684:95–103.
Yang Y, Liu S, Lei Z, Chen G, Huang L, Yang F, et al. Circular RNA profile in liver tissue of EpCAM knockout mice. Int J Mol Med. 2019;44(3):1063–77.
Ng VY, Ang SN, Chan JX, Choo AB. Characterization of epithelial cell adhesion molecule as a surface marker on undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells. 2010;28(1):29–35.
Kuan II, Liang KH, Wang YP, Kuo TW, Meir YJ, Wu SC, et al. EpEX/EpCAM and Oct4 or Klf4 alone are sufficient to generate induced pluripotent stem cells through STAT3 and HIF2alpha. Sci Rep. 2017;7:41852.
Han J, Won M, Kim JH, Jung E, Min K, Jangili P, et al. Cancer stem cell-targeted bio-imaging and chemotherapeutic perspective. Chem Soc Rev. 2020;49(22):7856–78.
Ni J, Cozzi P, Beretov J, Duan W, Bucci J, Graham P, et al. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) is involved in prostate cancer chemotherapy/radiotherapy response in vivo. BMC Cancer. 2018;18(1):1092.
Mal A, Bukhari AB, Singh RK, Kapoor A, Barai A, Deshpande I, et al. EpCAM-mediated cellular plasticity promotes radiation resistance and metastasis in breast cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8: 597673.
Karabicici M, Alptekin S, FirtinaKaragonlar Z, Erdal E. Doxorubicin-induced senescence promotes stemness and tumorigenicity in EpCAM-/CD133- nonstem cell population in hepatocellular carcinoma cell line, HuH-7. Mol Oncol. 2021;15(8):2185–202.
Noman ASM, Parag RR, Rashid MI, Islam S, Rahman MZ, Chowdhury AA, et al. Chemotherapeutic resistance of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma is mediated by EpCAM induction driven by IL-6/p62 associated Nrf2-antioxidant pathway activation. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(8):663.
Sankpal NV, Mayfield JD, Willman MW, Fleming TP, Gillanders WE. Activator protein 1 (AP-1) contributes to EpCAM-dependent breast cancer invasion. Breast Cancer Res. 2011;13(6):R124.
Lin CW, Liao MY, Lin WW, Wang YP, Lu TY, Wu HC. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule regulates tumor initiation and tumorigenesis via activating reprogramming factors and epithelial–mesenchymal transition gene expression in colon cancer. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(47):39449–59.
Park SY, Bae JS, Cha EJ, Chu HH, Sohn JS, Moon WS. Nuclear EpICD expression and its role in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2016;36(1):197–204.
Lin SC, Chou YT, Jiang SS, Chang JL, Chung CH, Kao YR, et al. Epigenetic switch between SOX2 and SOX9 regulates cancer cell plasticity. Cancer Res. 2016;76(23):7036–48.
Takai A, Dang H, Oishi N, Khatib S, Martin SP, Dominguez DA, et al. Genome-Wide RNAi screen identifies PMPCB as a therapeutic vulnerability in EpCAM(+) hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2019;79(9):2379–91.
Rhee H, Nahm JH, Kim H, Choi GH, Yoo JE, Lee HS, et al. Poor outcome of hepatocellular carcinoma with stemness marker under hypoxia: resistance to transarterial chemoembolization. Mod Pathol. 2016;29(9):1038–49.
Fiorillo M, Scatena C, Naccarato AG, Sotgia F, Lisanti MP. Bedaquiline, an FDA-approved drug, inhibits mitochondrial ATP production and metastasis in vivo, by targeting the gamma subunit (ATP5F1C) of the ATP synthase. Cell Death Differ. 2021;28(9):2797–817.
Ho DW, Tsui YM, Sze KM, Chan LK, Cheung TT, Lee E, et al. Single-cell transcriptomics reveals the landscape of intra-tumoral heterogeneity and stemness-related subpopulations in liver cancer. Cancer Lett. 2019;459:176–85.
Hofmanova J, Slavik J, Ciganek M, Ovesna P, Tylichova Z, Karasova M, et al. Complex alterations of fatty acid metabolism and phospholipidome uncovered in isolated colon cancer epithelial cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(13):6650.
Tataranni T, Agriesti F, Pacelli C, Ruggieri V, Laurenzana I, Mazzoccoli C, et al. Dichloroacetate affects mitochondrial function and stemness-associated properties in pancreatic cancer cell lines. Cells. 2019;8(5):478.
Barzaman K, Samadi M, Moradi-Kalbolandi S, Majidzadeh AK, Salehi M, Jalili N, et al. Development of a recombinant anti-VEGFR2-EPCAM bispecific antibody to improve antiangiogenic efficiency. Exp Cell Res. 2021;405(2): 112685.
Park DJ, Sung PS, Kim JH, Lee GW, Jang JW, Jung ES, et al. EpCAM-high liver cancer stem cells resist natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity by upregulating CEACAM1. J Immunother Cancer. 2020;8(1): e000301.
Chen Y, Hao X, Sun R, Wei H, Tian Z. Natural killer cell-derived interferon-gamma promotes hepatocellular carcinoma through the epithelial cell adhesion molecule-epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition axis in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. Hepatology. 2019;69(4):1735–50.
Akbay EA, Koyama S, Carretero J, Altabef A, Tchaicha JH, Christensen CL, et al. Activation of the PD-1 pathway contributes to immune escape in EGFR-driven lung tumors. Cancer Discov. 2013;3(12):1355–63.
Zhang T, Lv J, Tan Z, Wang B, Warden AR, Li Y, et al. Immunocyte profiling using single-cell mass cytometry reveals EpCAM(+) CD4(+) T cells abnormal in colon cancer. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1571.
Wen KC, Sung PL, Chou YT, Pan CM, Wang PH, Lee OK, et al. The role of EpCAM in tumor progression and the clinical prognosis of endometrial carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 2018;148(2):383–92.
Hsu YT, Osmulski P, Wang Y, Huang YW, Liu L, Ruan J, et al. EpCAM-regulated transcription exerts influences on nanomechanical properties of endometrial cancer cells that promote epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res. 2016;76(21):6171–82.
Schneck H, Gierke B, Uppenkamp F, Behrens B, Niederacher D, Stoecklein NH, et al. EpCAM-independent enrichment of circulating tumor cells in metastatic breast cancer. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(12): e0144535.
de Wit S, van Dalum G, Lenferink AT, Tibbe AG, Hiltermann TJ, Groen HJ, et al. The detection of EpCAM(+) and EpCAM(−) circulating tumor cells. Sci Rep. 2015;5:12270.
Allard WJ, Matera J, Miller MC, Repollet M, Connelly MC, Rao C, et al. Tumor cells circulate in the peripheral blood of all major carcinomas but not in healthy subjects or patients with nonmalignant diseases. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(20):6897–904.
Onidani K, Shoji H, Kakizaki T, Yoshimoto S, Okaya S, Miura N, et al. Monitoring of cancer patients via next-generation sequencing of patient-derived circulating tumor cells and tumor DNA. Cancer Sci. 2019;110(8):2590–9.
Rodriguez-Martinez A, Simon-Saez I, Perales S, Garrido-Navas C, Russo A, de Miguel-Perez D, et al. Exchange of cellular components between platelets and tumor cells: impact on tumor cells behavior. Theranostics. 2022;12(5):2150–61.
Belthier G, Homayed Z, Grillet F, Duperray C, Vendrell J, Krol I, et al. CD44v6 defines a new population of circulating tumor cells not expressing EpCAM. Cancers. 2021;13(19):4966.
Baart VM, van der Horst G, Deken MM, Bhairosingh SS, Schomann T, Sier VQ, et al. A multimodal molecular imaging approach targeting urokinase plasminogen activator receptor for the diagnosis, resection and surveillance of urothelial cell carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 2021;146:11–20.
Court CM, Hou S, Winograd P, Segel NH, Li QW, Zhu Y, et al. A novel multimarker assay for the phenotypic profiling of circulating tumor cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Transpl. 2018;24(7):946–60.
Wang L, Li Y, Xu J, Zhang A, Wang X, Tang R, et al. Quantified postsurgical small cell size CTCs and EpCAM(+) circulating tumor stem cells with cytogenetic abnormalities in hepatocellular carcinoma patients determine cancer relapse. Cancer Lett. 2018;412:99–107.
Ahn JC, Teng PC, Chen PJ, Posadas E, Tseng HR, Lu SC, et al. Detection of circulating tumor cells and their implications as a biomarker for diagnosis, prognostication, and therapeutic monitoring in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2021;73(1):422–36.
Xu R, Rai A, Chen M, Suwakulsiri W, Greening DW, Simpson RJ. Extracellular vesicles in cancer—implications for future improvements in cancer care. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018;15(10):617–38.
Zhou YG, Mohamadi RM, Poudineh M, Kermanshah L, Ahmed S, Safaei TS, et al. Interrogating circulating microsomes and exosomes using metal nanoparticles. Small. 2016;12(6):727–32.
Chen C, Zong S, Liu Y, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Chen B, et al. Profiling of exosomal biomarkers for accurate cancer identification: combining DNA-PAINT with machine-learning-based classification. Small. 2019;15(43): e1901014.
Han Z, Peng X, Yang Y, Yi J, Zhao D, Bao Q, et al. Integrated microfluidic-SERS for exosome biomarker profiling and osteosarcoma diagnosis. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022;217: 114709.
Ploeg EM, Ke X, Britsch I, Hendriks M, Van der Zant FA, Kruijff S, et al. Bispecific antibody CD73xEpCAM selectively inhibits the adenosine-mediated immunosuppressive activity of carcinoma-derived extracellular vesicles. Cancer Lett. 2021;521:109–18.
Xiang D, Shigdar S, Bean AG, Bruce M, Yang W, Mathesh M, et al. Transforming doxorubicin into a cancer stem cell killer via EpCAM aptamer-mediated delivery. Theranostics. 2017;7(17):4071–86.
Zheng J, Zhao S, Yu X, Huang S, Liu HY. Simultaneous targeting of CD44 and EpCAM with a bispecific aptamer effectively inhibits intraperitoneal ovarian cancer growth. Theranostics. 2017;7(5):1373–88.
Lian S, Xie R, Ye Y, Xie X, Li S, Lu Y, et al. Simultaneous blocking of CD47 and PD-L1 increases innate and adaptive cancer immune responses and cytokine release. EBioMedicine. 2019;42:281–95.
Shramova E, Proshkina G, Shipunova V, Ryabova A, Kamyshinsky R, Konevega A, et al. Dual targeting of cancer cells with DARPin-based toxins for overcoming tumor escape. Cancers. 2020;12(10):3014.
Macdonald J, Henri J, Roy K, Hays E, Bauer M, Veedu RN, et al. EpCAM immunotherapy versus specific targeted delivery of drugs. Cancers. 2018;10(1):19.
Baeuerle PA, Gires O. EpCAM (CD326) finding its role in cancer. Br J Cancer. 2007;96(3):417–23.
Munz M, Murr A, Kvesic M, Rau D, Mangold S, Pflanz S, et al. Side-by-side analysis of five clinically tested anti-EpCAM monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Cell Int. 2010;10:44.
Schmidt M, Scheulen ME, Dittrich C, Obrist P, Marschner N, Dirix L, et al. An open-label, randomized phase II study of adecatumumab, a fully human anti-EpCAM antibody, as monotherapy in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2010;21(2):275–82.
Marschner N, Ruttinger D, Zugmaier G, Nemere G, Lehmann J, Obrist P, et al. Phase II study of the human anti-epithelial cell adhesion molecule antibody adecatumumab in prostate cancer patients with increasing serum levels of prostate-specific antigen after radical prostatectomy. Urol Int. 2010;85(4):386–95.
Oberneder R, Weckermann D, Ebner B, Quadt C, Kirchinger P, Raum T, et al. A phase I study with adecatumumab, a human antibody directed against epithelial cell adhesion molecule, in hormone refractory prostate cancer patients. Eur J Cancer. 2006;42(15):2530–8.
Schmidt M, Ruttinger D, Sebastian M, Hanusch CA, Marschner N, Baeuerle PA, et al. Phase IB study of the EpCAM antibody adecatumumab combined with docetaxel in patients with EpCAM-positive relapsed or refractory advanced-stage breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(9):2306–13.
Frampton JE. Catumaxomab: in malignant ascites. Drugs. 2012;72(10):1399–410.
Heiss MM, Strohlein MA, Bokemeyer C, Arnold D, Parsons SL, Seimetz D, et al. The role of relative lymphocyte count as a biomarker for the effect of catumaxomab on survival in malignant ascites patients: results from a phase II/III study. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20(12):3348–57.
Casaletto JB, Geddie ML, Abu-Yousif AO, Masson K, Fulgham A, Boudot A, et al. MM-131, a bispecific anti-Met/EpCAM mAb, inhibits HGF-dependent and HGF-independent Met signaling through concurrent binding to EpCAM. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2019;116(15):7533–42.
Huehls AM, Coupet TA, Sentman CL. Bispecific T-cell engagers for cancer immunotherapy. Immunol Cell Biol. 2015;93(3):290–6.
Goebeler ME, Bargou RC. T cell-engaging therapies—BiTEs and beyond. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020;17(7):418–34.
Ferrari F, Bellone S, Black J, Schwab CL, Lopez S, Cocco E, et al. Solitomab, an EpCAM/CD3 bispecific antibody construct (BiTE(R)), is highly active against primary uterine and ovarian carcinosarcoma cell lines in vitro. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2015;34:123.
Cioffi M, Dorado J, Baeuerle PA, Heeschen C. EpCAM/CD3-Bispecific T-cell engaging antibody MT110 eliminates primary human pancreatic cancer stem cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(2):465–74.
Fiedler WM, Wolf M, Kebenko M, Goebeler ME, Ritter B, Quaas A, et al. A phase I study of EpCAM/CD3-bispecific antibody (MT110) in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(15).
Zhang P, Shi B, Gao H, Jiang H, Kong J, Yan J, et al. An EpCAM/CD3 bispecific antibody efficiently eliminates hepatocellular carcinoma cells with limited galectin-1 expression. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2014;63(2):121–32.
Vallera DA, Zhang B, Gleason MK, Oh S, Weiner LM, Kaufman DS, et al. Heterodimeric bispecific single-chain variable-fragment antibodies against EpCAM and CD16 induce effective antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity against human carcinoma cells. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2013;28(4):274–82.
Schmohl JU, Felices M, Taras E, Miller JS, Vallera DA. Enhanced ADCC and NK cell activation of an anticarcinoma bispecific antibody by genetic insertion of a modified IL-15 cross-linker. Mol Ther. 2016;24(7):1312–22.
Brown J, Rasamoelisolo M, Spearman M, Bosc D, Cizeau J, Entwistle J, et al. Preclinical assessment of an anti-EpCAM immunotoxin: locoregional delivery provides a safer alternative to systemic administration. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2009;24(4):477–87.
Cizeau J, Grenkow DM, Brown JG, Entwistle J, MacDonald GC. Engineering and biological characterization of VB6-845, an anti-EpCAM immunotoxin containing a T-cell epitope-depleted variant of the plant toxin bouganin. J Immunother. 2009;32(6):574–84.
Eyvazi S, Farajnia S, Dastmalchi S, Kanipour F, Zarredar H, Bandehpour M. Antibody based EpCAM targeted therapy of cancer, review and update. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2018;18(9):857–68.
Ko YJ, Bubley GJ, Weber R, Redfern C, Gold DP, Finke L, et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics, and biological pharmacodynamics of the immunocytokine EMD 273066 (huKS-IL2): results of a phase I trial in patients with prostate cancer. J Immunother. 2004;27(3):232–9.
Johnson EE, Yamane BH, Buhtoiarov IN, Lum HD, Rakhmilevich AL, Mahvi DM, et al. Radiofrequency ablation combined with KS-IL2 immunocytokine (EMD 273066) results in an enhanced antitumor effect against murine colon adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(15):4875–84.
Connor JP, Cristea MC, Lewis NL, Lewis LD, Komarnitsky PB, Mattiacci MR, et al. A phase 1b study of humanized KS-interleukin-2 (huKS-IL2) immunocytokine with cyclophosphamide in patients with EpCAM-positive advanced solid tumors. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:20.
Moldenhauer G, Salnikov AV, Luttgau S, Herr I, Anderl J, Faulstich H. Therapeutic potential of amanitin-conjugated anti-epithelial cell adhesion molecule monoclonal antibody against pancreatic carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012;104(8):622–34.
Miller ML, Fishkin NE, Li W, Whiteman KR, Kovtun Y, Reid EE, et al. A new class of antibody–drug conjugates with potent DNA alkylating activity. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016;15(8):1870–8.
Zhang M, Zhao Z, Pritykin Y, Hannum M, Scott AC, Kuo F, et al. Ectopic activation of the miR-200c-EpCAM axis enhances antitumor T cell responses in models of adoptive cell therapy. Sci Transl Med. 2021;13(611): eabg4328.
Nian Z, Zheng X, Dou Y, Du X, Zhou L, Fu B, et al. Rapamycin pretreatment rescues the bone marrow AML cell elimination capacity of CAR-T cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27(21):6026–38.
Li W, Zhou Y, Wu Z, Shi Y, Tian E, Zhu Y, et al. Targeting Wnt signaling in the tumor immune microenvironment to enhancing EpCAM CAR T-cell therapy. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12: 724306.
Daher M, Rezvani K. Outlook for new CAR-based therapies with a focus on CAR NK cells: what lies beyond CAR-engineered T cells in the race against cancer. Cancer Discov. 2021;11(1):45–58.
Zhang Q, Zhang H, Ding J, Liu H, Li H, Li H, et al. Combination therapy with EpCAM-CAR-NK-92 cells and regorafenib against human colorectal cancer models. J Immunol Res. 2018;2018:4263520.
Tang SY, Zha S, Du Z, Zeng J, Zhu D, Luo Y, et al. Targeted integration of EpCAM-specific CAR in human induced pluripotent stem cells and their differentiation into NK cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):580.
Ding J, Zhou XT, Zou HY, Wu J. Hedgehog signaling pathway affects the sensitivity of hepatoma cells to drug therapy through the ABCC1 transporter. Lab Invest. 2017;97(7):819–32.
Ralhan R, Cao J, Lim T, Macmillan C, Freeman JL, Walfish PG. EpCAM nuclear localization identifies aggressive thyroid cancer and is a marker for poor prognosis. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:331.
Jariyal H, Gupta C, Srivastava A. Hyaluronic acid induction on breast cancer stem cells unfolds subtype specific variations in stemness and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;160:1078–89.
Ma X, Kang X, He L, Zhou J, Zhou J, Sturm MB, et al. Identification of tumor specific peptide as EpCAM ligand and its potential diagnostic and therapeutic clinical application. Mol Pharm. 2019;16(5):2199–213.
Woopen H, Pietzner K, Richter R, Fotopoulou C, Joens T, Braicu EI, et al. Overexpression of the epithelial cell adhesion molecule is associated with a more favorable prognosis and response to platinum-based chemotherapy in ovarian cancer. J Gynecol Oncol. 2014;25(3):221–8.
Hsu YT, Gu F, Huang YW, Liu J, Ruan J, Huang RL, et al. Promoter hypomethylation of EpCAM-regulated bone morphogenetic protein gene family in recurrent endometrial cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(22):6272–85.
Warneke VS, Behrens HM, Haag J, Kruger S, Simon E, Mathiak M, et al. Members of the EpCAM signalling pathway are expressed in gastric cancer tissue and are correlated with patient prognosis. Br J Cancer. 2013;109(8):2217–27.
Eom BW, Won Ryu K, Man Yoon H, Kook MC. Predictive value of E-cadherin and EpCAM for detection of metastatic lymph node in early gastric cancer. Chin J Cancer Res. 2020;32(5):614–20.
SaeednejadZanjani L, Madjd Z, Axcrona U, Abolhasani M, Rasti A, Asgari M, et al. Cytoplasmic expression of B7–H3 and membranous EpCAM expression are associated with higher grade and survival outcomes in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2020;46: 151483.
Riethmuller G, Schneider-Gadicke E, Schlimok G, Schmiegel W, Raab R, Hoffken K, et al. Randomised trial of monoclonal antibody for adjuvant therapy of resected Dukes’ C colorectal carcinoma. German cancer aid 17-1A study group. Lancet. 1994;343(8907):1177–83.
Punt CJ, Nagy A, Douillard JY, Figer A, Skovsgaard T, Monson J, et al. Edrecolomab alone or in combination with fluorouracil and folinic acid in the adjuvant treatment of stage III colon cancer: a randomised study. Lancet. 2002;360(9334):671–7.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81372327, 81572427, 81874189 and 81874065), State Key Project on Infectious Diseases of China (2018ZX10723204-003-003), National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFA0208904), Major Technological Innovation Projects of Hubei Province (2018ACA137), National Basic Research Program of China (2020YFA0710700), and Tongji Hospital (HUST) Foundation for Excellent Young Scientists (No. 2020YQ05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZH and YL conceptualized this study. YL, YW, SS and ZC drafted the manuscript. BX, ZH, ZD and XS revised the manuscript. BX and ZD obtained funding. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Wang, Y., Sun, S. et al. Understanding the versatile roles and applications of EpCAM in cancers: from bench to bedside. Exp Hematol Oncol 11, 97 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40164-022-00352-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40164-022-00352-4