Abstract
In this paper, general decay synchronization of delayed bidirectional associative memory neural networks with reaction–diffusion terms is studied. First, a useful lemma is introduced to determine the general decay synchronization of considered systems. Furthermore, a type of nonlinear controller is designed. Then, some sufficient conditions are obtained to insure the general decay synchronization of the drive–response systems via using Lyapunov functional method and Poincaré inequality. Finally, the obtained theoretical results are evaluated by giving one numerical example. The exponential synchronization, polynomial synchronization, and some other types of synchronization can be seen as special cases of the general decay synchronization.
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Introduction
In the last two decades, a great number of scholars from science and engineering community have been paying their attention to the investigation of dynamical behavior and control problems of neural networks [1–9]. Among various neural networks, bidirectional associative memory neural network (BAMNN), introduced by Kosko [10, 11], has been studied wildly since this class of neural network has extensive applications in pattern recognition, complex control, and intelligent processing [12]. In addition, the synchronization of chaotic nonlinear systems has received enormous attention in the past two decades for its significant role in many areas, including biology, climatology, sociology, etc. [3–9]. The authors of [13] studied the global asymptotic stability for continuous BAMNNs by using Lyapunov method, while those of [14] considered the synchronization of memristor-based BAMNNs by using linear matrix inequality technique. In [15], a nonlinear feedback controller is designed for a general decay synchronization of delayed BAMNNs.
As it is known to all, the reaction–diffusion effect cannot be neglected when considering the motion of electrons in an asymmetric electromagnetic field [16]. Therefore it is necessary to introduce a diffusion term in neural networks, where this term is expressed by a partial differential equation [16–19]. In [20], the authors studied the global exponential stability and synchronization of the delayed reaction–diffusion neural networks (RDNNs) under the impulsive control. The authors of [21] discussed the global exponential synchronization of delayed BAMNNs with reaction–diffusion terms. In [22], an adaptive synchronization controller is derived for the global asymptotic synchronization of RDNNs with delays. The authors of [23] investigated the state synchronization of BAM neural networks with reaction–diffusion terms via a feedback control law. In [24], the authors have derived sufficient conditions for the \(H_{\infty }\) synchronization of RDNNs with mixed time-varying delays based on an adaptive controller method. In [25], an adaptive pinning controller is designed to guarantee the tracking synchronization for a class of neural networks with coupled reaction–diffusion terms. In [18], a sufficient condition for the ψ-type stability of RDNNs with bounded distributed delays and time-varying discrete delays was presented. In [26], an appropriate nonlinear controller was utilized, and the decay lag antisynchronization criteria were designed for multiweighted coupled RDNNs. However, few researches can be found on the general decay synchronization problem of BAMNNs with reaction–diffusion terms. As mentioned in [15], there exist stable systems which are not exponentially stable, but with a general convergence rate.
Inspired by the above discussions, in this paper, we are concerned with the general decay synchronization for a BAMNN model with reaction–diffusion terms and time-varying delays. By using a novel inequality technique and constructing a suitable Lyapunov–Krasovskii-type functional, we obtained some simple sufficient conditions for the general decay synchronization of considered BAMNNs. Finally, we give a numerical example and its simulations to illustrate the effectiveness of the derived results. The polynomial synchronization, asymptotical synchronization, and exponential synchronization can be seen as special cases of the general decay synchronization.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. In Sect. 2, we will introduce the details of the model and a useful lemma, which plays a critical role in proving the main result of this paper. Then, in Sect. 3, we will design a feedback controller for the general decay synchronization of delayed BAMNNs with reaction–diffusion terms. In Sect. 4, we will give an example to evaluate the effectiveness of theoretical results of this paper. In the final section, we give a brief summary to end up the paper.
2 Preliminaries
In this paper, we consider the following delayed BAMNNs with reaction-0diffusion terms:
with the following Neumann boundary condition:
and the following initial condition:
where \(x=(x_{1},x_{2},\dots ,x_{\ell })^{T}\in \varOmega \), Ω is a bounded open subset of \(\mathbb{R}^{\ell }\) with a \(C^{2}\) boundary ∂Ω, and \(|\varOmega |>0\) (where \(|\varOmega |\) is the volume of Ω); \(\nabla \nu := (\frac{\partial \nu }{\partial x_{1}}, \frac{\partial \nu }{\partial x_{1}}, \dots , \frac{\partial \nu }{\partial x_{\ell }} )^{T}\) stands for the gradient of function ν, \(u_{i}\) and \(v_{j}\) for \(i\in \mathcal{I}=\{1,2,\dots ,m\}\), \(j\in \mathcal{J}=\{1,2,\dots ,n\}\) denote to the state variables of the ith and jth neuron at time t and in space point x, respectively; \(D_{ik}\geq 0\) and \(\tilde{D}_{jk}\geq 0\) represent transmission diffusion coefficients along the ith and jth neuron, respectively; \(p_{i}\) and \(q_{j}\) stand for the passive decay rates to the state of ith and jth neuron, respectively; \(b_{ji}\), \(\tilde{b}_{ji}\), \(d_{ij}\), and \(\tilde{d}_{ij}\) are the connection strengths between the neurons; \(f_{j}(\nu )\) and \(g_{i}(\nu )\) correspond to the respective neuron activation functions; \(\theta _{ji(t)}\) and \(\tau _{ij}\) correspond to the continuous time-varying discrete delays, respectively satisfying \(0\leq \theta _{ji}(t)\leq \theta _{ji}\) and \(0\leq \tau _{ij}(t)\leq \tau _{ij}\); \(I_{i}\) and \(J_{j}\) denote to the external inputs on the ith and jth neuron, respectively.
Through out the paper, we assume that the neuron activation functions \(f_{j}(\nu )\), \(g_{j}(\nu )\) and time-varying delays \(\tau _{ij}(t)\), \(\sigma _{ij}(t)\) satisfy the following assumptions:
Assumption 1
For any \(i\in \mathcal{I}\), \(j\in \mathcal{J}\), there exist constants \(L_{j}^{f}\) and \(L_{i}^{g}\) such that
Assumption 2
Time-varying delays \(\theta _{ji}(t)\) and \(\tau _{ij}(t)\) are differentiable, and there exist constants \(\mu _{ji}, \kappa _{ij}\in (0,1)\) such that
The corresponding system of (1) is given as
where \(\phi _{i}(t,x)\) and \(\varphi (t,x)\) are the external control inputs to be designed.
Let \(e_{i}(t,x)=\tilde{u}_{i}(t,x)-u_{i}(t,x)\) and \(z_{j}(t,x)=\tilde{v}_{j} (t,x) - v_{j}(t,x)\), then the error system between (1) and (4) is rewritten as
where
Definition 1
([26])
If the function \(\psi (t):\mathbb{R}^{+}\rightarrow (0,+\infty )\) satisfies the following four conditions:
-
(1)
\(\psi (t)\) is differentiable and nondecreasing;
-
(2)
\(\psi (0)=1\) and \(\psi (+\infty )=+\infty \);
-
(3)
\(\tilde{\psi }(t):=\frac{\dot{\psi }(t)}{\psi (t)}\) is nonincreasing;
-
(4)
\(\psi (\mu +\nu )\leq \psi (\mu )\psi (\nu )\) for all \(\mu ,\nu \geq 0\),
then the function \(\psi (t)\) is called a ψ-type function.
Definition 2
If there exists a scalar \(\varepsilon >0\) such that
where \(e(t,x)=(e_{1}(t,x),e_{2}(t,x),\dots ,e_{m}(t,x))^{T}\), \(z(t,x)=(z_{1}(t,x),z_{2}(t,x),\dots ,z_{n}(t,x))^{T}\), and \(\psi (t)\) is a ψ-type function defined in Definition 1, then drive–response systems (1) and (4) are said to be general decay synchronized.
Lemma 1
If there exist a function \(\varrho (t)\in C(\mathbb{R},\mathbb{R}^{+})\), a Lyapunov functional \(V(t):\mathbb{R}^{+} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}^{+}\), and constants \(r_{1}\), \(r_{2}\)satisfying the following:
where ε is defined in Definition 2, while \(\psi (t)\)and \(\tilde{\psi }(t)\)are defined in Definition 1, then the drive–response systems (1) and (4) are general decay synchronized.
Proof
It can be easily obtained that
from which we can get following by utilizing (6) and (9):
Using the condition \(\psi (0)=1\) in Definition 1 and (7), we get
then, using (8), one has
Thus there must exist a constant \(M>0\) such that
which yields
Finally,
This completes the proof. □
Lemma 2
(Poincaré inequality)
Assume Ω is a bounded open subset of \(\mathbb{R}^{n}\)and suppose \(u\in H_{0}^{1}(\varOmega )\). Then we have
3 Main results
In this paper, the external control inputs \(\phi _{i}(t,x)\) and \(\varphi _{j}(t,x)\) are designed as
where \(\eta _{i}\) for \(i\in \mathcal{I}\) and \(\lambda _{j}\) for \(j\in \mathcal{J}\) are positive control gains.
Theorem 1
Suppose that Assumptions 1and 2hold, and there exists a function \(\varrho (t)\in C(\mathbb{R},\mathbb{R}^{+})\)satisfying (7) with a ψ-type function satisfying (6), then (4) can be general decay synchronized with system (1) under the feedback controller (11) if the control gains \(\eta _{i}\)and \(\lambda _{j}\)satisfy the following inequalities:
Proof
Consider the following Lyapunov functional:
where
It is not difficult to prove that there exist positive scalars \(\xi >1\) and \(\gamma >1\) such that
where \(\alpha = \min_{i\in \mathcal{I}}\{\alpha _{i}\}\), \(\beta =\min_{j \in \mathcal{J}}\{\beta _{j}\} \) with
where \(D_{i}=\min_{k}\{D_{ik}\}\) and \(\tilde{D}_{j} =\min_{k}\{\tilde{D}_{jk}\}\) for all \(k\in \{1,2, \dots ,\ell \}\).
Now, calculate the time derivative of \(V_{1}(t)\) and \(V_{2}(t)\):
where
Since \(D_{i} = \min_{k}\{D_{ik}\}\) for all \(k\in \{1,2,\dots ,\ell \}\), one gets the following inequality via Lemma 2:
Therefore,
In the light of Assumption 1, we have
Here we used the following inequality:
Due to \(0\leq ab/(a+b)\leq a\) for any \(a>0\) and \(b>0\), where \(\eta =\max_{i\in \mathcal{I}}\{\eta _{i}\}>0\),
Similarly,
where \(\lambda =\max_{j\in \mathcal{J}}\{\lambda _{j}\}>0\). Then we have
Then, there exists a small enough δ satisfying \(\delta \xi \leq \alpha \) and \(\delta \gamma \leq \beta \) such that
and we have
Therefore, by Lemma 1, the drive–response systems (1) and (4) achieve general decay synchronization under the nonlinear feedback controller (11). The convergence rate of \(e(t)\) and \(z(t)\) approaching zero is δ. The proof is completed. □
Remark 1
In this paper, we firstly studied the general decay synchronization of BAMNN with reaction–diffusions terms and time-varying delay by introducing a novel nonlinear feedback controller and using some inequality techniques. It it not difficult to see that the results obtained in [13, 16, 21, 23] can be seen as special cases of our results when the general decay function is chosen as \(\psi (t) = e^{\alpha t} \) or \(\psi (t) = (1 + t)^{\alpha }\) for any \(\alpha > 0\). From this viewpoint, our results are more general and have better applicability.
4 Numerical examples
In this section, a numerical example is provided to validate the effectiveness of the established theoretical results in this paper.
Example
For \(\ell =1\), \(n=m=2\), consider the following BAMNN with reaction–diffusion terms,
for \(x\times t \in [-5,5]\times [0,1]\), with the following Neumann boundary condition:
where the parameters of system (17) are taken as \(D_{i1} =\tilde{D}_{j1}=0.1\), \(p_{i}=1\), \(q_{j}= 1.05\), \(b_{11}=1.8\), \(b_{12}=-0.15\), \(b_{21}=-5.2\), \(b_{22}=3.5\), \(\tilde{b}_{11} = -1.7\), \(\tilde{b}_{12} = -0.12\), \(\tilde{b}_{21} = -0.26\), \(\tilde{b}_{22} = -2.5\), \(d_{11}=1.71\), \(d_{12}=-0.1425\), \(d_{21}=-4.94\), \(d_{22}=3.325\), \(\tilde{d}_{11} = -1.87\), \(\tilde{d}_{12} = -0.132\), \(\tilde{d}_{21} = -0.286\), \(\tilde{d}_{22} = -2.75\), \(I_{i}=J_{j}=0\), neuron activation functions are chosen as \(f_{i}(\nu ) =g_{j}(\nu )=\tanh (\nu )\), and time-varying delays are chosen as \(\theta _{ji}(t)=\tau _{ij}(t)=\frac{e^{t}}{1+e^{t}}\) for \(i,j\in \{1,2\}\). The initial conditions of system (17) are chosen as
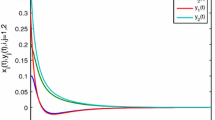
Matlab simulations of the drive system (17) under the above initial conditions are presented in Figs. 1–8, where we can see that the drive system (17) has a chaotic attractor.
Chaotic attractor of \({u}_{1}\) in (17)
Chaotic attractor of \({u}_{2}\) in (17)
Chaotic attractor of \(\tilde{u}_{1}\) in (17)
Chaotic attractor of \(\tilde{u}_{2}\) in (17)
Chaotic attractor of \({u}_{1}\) and \({u}_{2}\) in (17) with \({x}=-4\)
Chaotic attractor of \(\tilde{u}_{1}\) and \(\tilde{u}_{2}\) in (17) with \({x}=-1\)
Chaotic attractor of \({u}_{1}\) and \({u}_{2}\) in (17) with \({x}=1\)
Chaotic attractor of \(\tilde{u}_{1}\) and \(\tilde{u}_{2}\) in (17) with \({x}=3\)
The corresponding response system for the drive system (17) is given as
for \(x\times t \in [-5,5]\times [0,1]\), with the following Neumann boundary condition:
where \(\phi _{i}(t,x)\) and \(\varphi _{j}(t,x)\) are given as follows:
where \(\eta _{1} = 5.6\), \(\eta _{2} = 6.8\), \(\lambda _{1} = 6.2\), \(\lambda _{2} = 7.1\), \(\varrho (t) = e^{-0.1t}\). The other parameters in (19) are the same as of system (17). The initial conditions of (19) are taken as
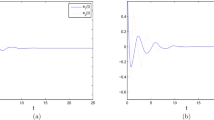
It is not difficult to estimate that \({L^{f}}_{i}=L^{g}_{j}=1\) and \(\mu _{ji}=\kappa _{ij}=1\). Thus, Assumptions 1 and 2 are satisfied. Letting \(\psi (t) = e^{ t}\), inequalities (6), (7), and (12) are satisfied. Therefore, according to Theorem 1, the drive–response systems (17) and (19) can achieve general decay synchronization under the controller (19). The time evolution of synchronization errors between master–slave systems (17) and (19) are show in Figs. 9–12, from where we can see that \(e_{i}(t,x)\) and \(z_{j}(t,x)\) are very close to 0 and maintain this situation as time t increases.
Remark 2
Unlike the synchronization studies for neural networks such as [13, 16, 20, 21, 23], the convergence rate of the synchronization error can be controlled by appropriately choosing the function \(\varrho (t)\) in the paper, this is because general decay synchronization enables us to estimate to convergence rate of synchronization error via defining a more general convergence rate. From this viewpoint, our results are more general and have better applicability.
5 Conclusions
In this paper, first, we introduce a useful lemma to determine the general decay synchronization of the considered drive–response system, and then the nonlinear feedback controllers are designed for synchronization of delayed reaction–diffusion bidirectional associative memory neural networks with Neumann boundary condition via applying Lyapunov functional method and Poincaré inequality, and useful new conditions are obtained. This result generalizes the previous results to some extent [15, 21, 26]. In addition, one numerical example is given to show the effectiveness of the proposed model.
References
Hu, X., Xia, J., Wang, Z., Song, X., Shen, H.: Robust distributed state estimation for Markov coupled neural networks under imperfect measurements. J. Franklin Inst. 357, 2420–2436 (2020)
Shen, L., Xia, J., Wang, Y., Huang, X., Shen, H.: HMM-based \(H_{\infty }\) state estimation for memristive jumping neural networks subject to fading channel. Neurocomputing 393, 66–75 (2020)
Konnur, R.: Synchronization-based approach for estimating all model parameters of chaotic systems. Phys. Rev. E 67, 027204 (2003)
Chen, H.K.: Global chaos synchronization of new chaotic systems via nonlinear control. Chaos Solitons Fractals 23, 1245–1251 (2005)
Rakkiyappan, R., Latha, V.P., Zhu, Q., Yao, Z.: Exponential synchronization of Markovian jumping chaotic neural networks with sampled-data and saturating actuators. Nonlinear Anal. Hybrid Syst. 24, 28–44 (2017)
Dai, M., Xia, J., Xia, H., Shen, H.: Event-triggered passive synchronization for Markov jump neural networks subject to randomly occurring gain variations. Neurocomputing 331, 403–411 (2019)
Wang, H., Liu, P.X., Zhao, X., Liu, X.: Adaptive fuzzy finite-time control of nonlinear systems with actuator faults. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 50(5), 1786–1797 (2020)
Kaviarasan, B., Kwon, O., Park, M.J., Sakthivel, R.: Integrated synchronization and anti-disturbance control design for fuzzy model-based multiweighted complex network. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2019.2960803
Kaviarasan, B., Kwon, O., Park, M.J., Sakthivel, R.: Composite synchronization control for delayed coupling complex dynamical networks via a disturbance observer-based method. Nonlinear Dyn. 99, 1601–1619 (2020)
Kosko, B.: Adaptive bi-directional associative memories. Appl. Opt. 26(23), 4947–4960 (1987)
Kosko, B.: Bi-directional associative memories. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 18(1), 49–60 (1988)
Wang, F., Liu, M.C.: Glopal exponential stability of high-order bidirectional associative memory BAMNNs with time-delays in leakage terms. Neurocomputing 177, 515–528 (2016)
Cao, J.: Global asymptotic stability of delayed-bi-directional associative memory neural networks. Appl. Math. Comput. 142, 333–339 (2003)
Mathiyalagan, K., Park, J.H., Sakthivel, R.: Synchronization for delayed memristive BAM neural networks using impulsive control with random nonlinearities. Appl. Math. Comput. 259, 967–979 (2015)
Sader, M., Abdurahman, A., Jiang, H.J.: General decay synchronization of delayed BAM neural networks via nonlinear feedback control. Appl. Math. Comput. 337, 302–314 (2018)
Bao, T.C., Xu, Y.L.: Global asymptotic stability of BAM neural networks with distributed delays and reaction–diffusion terms. Chaos Solitons Fractals 27, 1347–1354 (2006)
Wang, C., Kao, Y., Yang, G.: Exponential stability of impulsive stochastic fuzzy reaction–diffusion Cohen–Grossberg neural networks with mixed delays. Neurocomputing 89, 55–63 (2012)
Hou, J., Huang, Y., Yang, E.: ψ-Type stability of reaction–diffusion neural networks with time-varying discrete delays and bounded distributed delays. Neurocomputing 340, 281–293 (2019)
Wang, T., Zhu, Q.: Stability analysis of stochastic BAM neral networks with reaction–diffusion, multi-proportional and distributed delays. Physica A 533, 121935 (2019)
Hu, C., Jiang, H., Teng, Z.: Impulsive control and synchronization for delayed neural networks with reaction–diffusion terms. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 21(1), 67–81 (2010)
Zhang, W., Li, J.: Global exponential synchronization of delayed BAM neural networks with reaction–diffusion terms and the Neumann boundary conditions. Bound. Value Probl. 2012, 2 (2012)
Lakshmanan, S., Prakash, M., Rakkiyappan, R., Young, H.J.: Adaptive synchronization of reaction-diffusion neural networks and its application to secure communication. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 99, 1–12 (2018)
Sheng, L., Gao, M.: Synchronization of delayed BAM neural networks with reaction–diffusion terms. In: Proceedings of the 30th Chinese Control Conference, CCC 2011, pp. 2753–2758 (2011)
Wu, H., Zhang, X., Li, R., Yao, R.: Synchronization of reaction–diffusion neural networks with mixed time-varying delays. J. Control Autom. Electr. Syst. 26, 16–27 (2015)
Zhang, H., Pal, N.R.: Distributed adaptive tracking synchronization coupled reaction–diffusion neural network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 30(5), 1462–1475 (2019)
Abdurahman, A.: New results on the general decay synchronization of delayed neural networks with general activation functions. Neurocomputing 275, 2505–2511 (2018)
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant nos. 61703358, 11662020) and the Scientific Research Program of the Higher Education Institution of Xinjiang (Grant no. XJEDU2019Y001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Mahemuti, R., Halik, A. & Abdurahman, A. General decay synchronization of delayed BAM neural networks with reaction–diffusion terms. Adv Differ Equ 2020, 457 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13662-020-02906-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13662-020-02906-4