Abstract
Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1) also known as serpin E1 or endothelial plasminogen activator inhibitor, is produced from endothelial cells and adipose tissue. PAI-1 inhibits tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) and urokinase (uPA) preventing activation of plasminogen and fibrinolysis. Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is defined as glucose intolerance and hyperglycemia during pregnancy. The underlying mechanism of GDM is due to the reduction of insulin secretion or the development of insulin resistance (IR). Normal PAI-1 is a crucial mediator for maintaining pregnancy, though aberrantly high PAI-1 promotes inflammation and thrombosis with increased risk of pregnancy loss. Increasing PAI-1 level had been shown to be an early feature of cardio-metabolic derangement in women with GDM. As well, GDM is regarded as an independent predictor for increasing PAI-1 levels compared to normal pregnancy. Taken together, GDM seems to be the causal factor in the increase of PAI-1 via induction of IR, hyperglycemia and hypertriglyceridemia. In conclusion, GDM triggers expression and release of PAI-1 which linked with GDM severity due to exaggerated pro-inflammatory and inflammatory cytokines with the development of IR. High PAI-1 levels in GDM may induce hypofibrinolysis and thrombotic complications.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1) also known as serpin E1 or endothelial plasminogen activator inhibitor which is produced from endothelial cells and adipose tissue [1]. PAI-1 is also produced from megakaryocytes, platelets, monocytes, macrophages, cardiomyocytes, adipocytes, vascular smooth muscles, endometrium, mesothelium, and hepatocytes [2]. More than 90% of synthesized PAI-1 is stored in the platelets granules, the rest remains circulated or deposited in the subendothelial matrix [3]. These findings suggest that the plasma level of PAI-1 does not reflect its concentration in the formed thrombus, as it is released from platelets when the coagulation cascade is activated.
PAI-1 inhibits tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) and urokinase (uPA), preventing activation of plasminogen and fibrinolysis [4]. Besides, PAI-2 is released from the placenta, and represents the main form of PAI in pregnancy [1]. Of note, protease nexin acts as an inhibitor of urokinase and of PAI. Moreover, PAI-1 inhibits the activity of matrix metalloproteinase (MMPs) [1, 4].
Congenital deficiency of PAI-1 has been shown to cause bleeding tendency due to uncontrolled fibrinolysis. Though, a high PAI-1 level increases the risk of atherosclerosis, thrombosis and cardio-metabolic complications as in obesity, diabetes mellitus (DM), metabolic syndrome and cancer [4,5,6]. A high level of angiotensin II (AngII) induces the expression of PAI-1 causing the development of cardio-metabolic complications [7].
PAI-1 and PAI-2 inhibit both tPA and uPA which provoke the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin. As well, kallikrein and factor XI block this pathway. In addition, α2-antiplasmin and α2-macroglobulin directly block the effect of plasmin [1] (Fig. 1)
On the other hand, gestational DM (GDM) is defining as glucose intolerance and hyperglycemia during pregnancy [8, 9]. The prevalence of GDM is about 14.3% and some studies reported that GDM affects about 3–9% of total pregnancies depending on certain populations [8]. It affects 1% under the age of 20 years whereas it affects more up to 13% of pregnant women over the age of 44 years [10]. GDM is more common among certain ethnic groups including Asians, Australian, American Indians, and Pacific Islanders. It has been reported that GDM was resolved in 90% of cases after delivery [10]. Though, pregnant women with GDM are at high risk for the development of type 2 DM (T2DM), preeclampsia and depression [8, 11, 12]. Neonates from mothers with GDM may develop hypoglycemia, severe jaundice, and large body weight [8]. Besides, long-term complications of children born from mothers with GDM are at risk for the development of overweight and T2DM [8, 10].
The underlying mechanism of GDM is due to the reduction of insulin secretion or the development of insulin resistance (IR) [13]. The risk factors for the development of GDM are overweight, obesity, previous GDM, positive family history of T2DM, and polycystic ovarian syndrome [13]. GDM is prevented by weight reduction and regular exercise. GDM is often managed by regular exercise, controlled diabetic diet, and metformin pharmacotherapy [14, 15]. GDM is classified into type A (gestational diabetes) and type B (pre-gestational diabetes). Type A1 has only abnormal glucose tolerance test with normal fasting and postprandial blood glucose. Type A2 has abnormal glucose tolerance test with high fasting and postprandial blood glucose [14].
Women with GDM are presented with polydipsia, fatigue, vomiting, recurrent urinary tract infections, and blurred vision. High placental hormones and inflammatory cytokines increase the development of IR and pancreatic cell adaptation [13, 14, 16].
Normal PAI-1is a crucial mediator for maintaining pregnancy, though aberrantly high PAI-1 promotes inflammation and thrombosis with increased risk of pregnancy loss [17]. Of note, PAI-1 is increased during T2DM and linked with the development of macrovascular complications in T2DM and obesity [18, 19] (Fig. 2). Improvement of bodyweight and IR by insulin-sensitizing agents may reduce PAI-1 and its related complications [20]. As well, polymorphism of PAI-1 is linked with the development of IR and GDM [20].
Role of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1) in diabetes and obesity: Positive energy balance increase tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and PAI-1 leading to reduction in the expression of peroxisome proliferator activator receptor gamma (PPAR-γ) with subsequent development of insulin resistance (IR) and diabetes. Also, the reduction of PPAR-γ increases adipocyte hypertrophy and the development of obesity
Thus, the objective of the present study was to reveal the connection between PAI-1 and the pathogenesis of GDM and related complications.
Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and risk of gestational diabetes
It has been shown that PAI-1 was increased in T2DM and contributes to the hypofibrinolytic state and the development of thrombotic complications by promoting intimal injury and plaque formation [18, 21, 22]. Normally, PAI-1 plasma concentration is 10–50 ng/mL which may increase up to 100 ng/mL in presence of IR, DM and obesity [23]. PAI-1 plasma concentration is peak at the morning which falls in the afternoon due to the stimulation of PAI-1 by cortisol at the morning [23]. PAI-1 is higher in males, though variation in the level of PAI-1 is related to adipose tissue distribution and ethnicity [4, 19].
Of note, increasing of PAI-1 level had been shown to be an early feature of cardio-metabolic derangement in women with GDM [19, 20]. As well, GDM is regarded as an independent predictor for increasing PAI-1 levels compared to normal pregnancy [20]. High PAI-1 is linked with a reduction in insulin sensitivity [24]. In addition, PAI-1 through its dysglycemic effect may induce the risk of coronary heart disease and other cardio-metabolic complications [25, 26]. The potential link between PAI-1 and GDM needs longitudinal studies to confirm this association. Thus, the relationship between GDM and PAI-1 need to be verified in this claim.
In GDM, there are various factors that regulate the expression of PAI-1 including hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, pro-inflammatory cytokines and high AngII [27, 28]. These inflammatory mediators increase the expression of PAI-1 by adipocytes. Besides, PAI-1 induces the expression of AngII leading to endothelial dysfunction and procoagulation state [28]. In addition, IR, hyperinsulinemia, and hyperglycemia induce the expression of PAI-1 through mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) [29]. Levels of active and total PAI-1 are indeed increased in response to heightened inflammatory state and increased insulin levels, nevertheless, GDM is not a causative factor of IR, but rather IR and hyperglycemia elevate the risk of GDM [28].
Interestingly, Cao et al. experimental study confirmed that nod like receptor pyrin 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome was upregulated and involved in the pathogenesis of GDM [30]. In an experimental study, administration of tPA aggravates hyperglycemia-induced stroke through upregulation of NLRP3 inflammasome, high mobility box protein 1 (HMGB-1), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) [31]. These findings proposed that PAI-1 may attenuate hyperglycemia-induced activation of tPA.
Improvement of IR by regular exercise and metformin reduces the level of PAI-1 [1, 32, 33]. It has been reported that metformin can reduce PAI-1 by enhancing insulin sensitivity. Furthermore, polymorphism of PAI-1 is linked with the development of dyslipidemia [34]. Notably, polymorphism of PAI-1 increases the risk for the development of cardiovascular complications in patients with T2DM [35]. Herein, a high PAI-1 level in GDM may counterbalance the development of cardio-metabolic complications. In contrast, a high PAI-1 level in T2DM patients with metabolic syndrome may reduce the protective adiponectin level [36]. A cross-sectional study involved 379 T2DM with metabolic syndrome illustrated that PAI-1 level was higher and adiponectin was lower compared to T2DM without metabolic syndrome [36]. As well, increases in PAI-1 levels are reported when adipocytes are stimulated by TNF-α, transforming growth factor-β, angiotensin II, glucocorticoids, insulin, hypoxia, and ROS suggesting that PAI-1 might play a role in inflammatory mechanisms while also affecting vasculature, adiposity, IR and metabolic syndrome [36, 37].
Taken together, GDM seems to be the causal factor in the increase of PAI-1 through induction of IR and associated hyperglycemia and hypertriglyceridemia (Fig. 3).
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) and thrombotic complications: GDM induces insulin resistance (IR) and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines (PICs), by which leads to hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia. These changes induce the expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1) with subsequent hypofibrinolysis and thrombotic complications
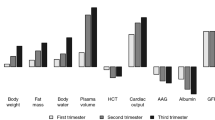
The present review had several limitations including paucity of clinical studies and sequential levels of PAI-1 in the different trimesters were not revealed. However, this review highlighted that PAI-1 could be a surrogate biomarker for the severity of GDM.
Conclusions
PAI-1 level is linked with GDM severity due to exaggerated pro-inflammatory cytokines and inflammatory cytokines with the development of IR. High PAI-1 level in GDM may induce hypofibrinolysis and thrombotic complications. PAI-1 is not a potential cause of GDM, but it seems to be a consequence of metabolic derangements. Experimental, preclinical and clinical studies are warranted in this regards.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- PAI-1:
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1
- tPA:
-
Tissue plasminogen activator
- uPA:
-
Urokinase
- GDM:
-
Gestational diabetes mellitus
- IR:
-
Insulin resistance
- MMPs:
-
Matrix metalloproteinases
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- AngII:
-
Angiotensin II
- T2DM:
-
Type 2 DM
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen activated protein kinase
- NLRP3:
-
Nod like receptor pyrin 3
- HMGB-1:
-
High mobility box protein 1
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor alpha
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa B
- PPAR-γ:
-
Peroxisome proliferator activator receptor gamma
References
Lijnen HR. Pleiotropic functions of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. J Thromb Haemost. 2005;3(1):35–45.
Cesari M, Pahor M, Incalzi RA. Review: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1): a key factor linking fibrinolysis and age-related subclinical and clinical conditions. Cardiovasc Ther. 2018;28:e72–91.
Charlton P. The status of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 as a therapeutic target. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 1997;6:539–54.
Somodi S, Seres I, Lőrincz H, Harangi M, Fülöp P, Paragh G. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 level correlates with lipoprotein subfractions in obese nondiabetic subjects. Int J Endocrinol. 2018;30:2018.
Ye Y, Vattai A, Zhang X, Zhu J, Thaler CJ, Mahner S, et al. Role of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 in pathologies of female reproductive diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(8):1651.
Al-Naimi MS, Rasheed HA, Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI. Berberine attenuates olanzapine induced-metabolic syndrome. J Pak Med Assoc. 2019;69(Suppl 3):S88-92.
Al-Kuraishy HM, Hussien NR, Al-Naimi MS, Al-Buhadily AK, Al-Gareeb AI, Lungnier C. Renin–Angiotensin system and fibrinolytic pathway in COVID-19: one-way skepticism. Biomed Biotechnol Res J. 2020;4(5):33.
Kim SY, England JL, Sharma JA, Njoroge T. Gestational diabetes mellitus and risk of childhood overweight and obesity in offspring: a systematic review. Exp Diabetes Res. 2011;2011:1–9.
Rasheed HA, Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Hussien NR, Al-Nami MS. Effects of diabetic pharmacotherapy on prolactin hormone in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Bane or Boon. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2019;10(4):163.
Das Gupta R, Gupta S, Das A, Biswas T, Haider MR, Sarker M. Ethnic predisposition of diabetes mellitus in the patients with previous history of gestational diabetes mellitus: a review. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. 2018;13(3):149–58.
Zhai J, Li Z, Zhou Y, Yang X. The role of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in gynecological and obstetrical diseases: an update review. J Reprod Immunol. 2022;150: 103490.
Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Al-Maiahy TJ. Concept and connotation of oxidative stress in preeclampsia. J Lab Physicians. 2018;10(03):276–82.
Johns EC, Denison FC, Norman JE, Reynolds RM. Gestational diabetes mellitus: mechanisms, treatment, and complications. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2018;29(11):743–54.
Rasmussen L, Poulsen CW, Kampmann U, Smedegaard SB, Ovesen PG, Fuglsang J. Diet and healthy lifestyle in the management of gestational diabetes mellitus. Nutrients. 2020;12(10):3050.
Al-Kuraishy HM, Sami OM, Hussain NR, Al-Gareeb AI. Metformin and/or vildagliptin mitigate type II diabetes mellitus induced-oxidative stress: the intriguing effect. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2020;11(3):142.
Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Waheed HJ, Al-Maiahy TJ. Differential effect of metformin and/or glyburide on apelin serum levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: concepts and clinical practice. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2018;9(3):80.
Cho HY, Park HS, Ahn EH, et al. Association of Polymorphisms in plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), and renin (REN) with recurrent pregnancy loss in Korean women. J Pers Med. 2021;11(12):1378.
Morrow GB, Whyte CS, Mutch NJ. A serpin with a finger in many PAIs: PAI-1’s central function in thromboinflammation and cardiovascular disease. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8: 653655.
Lowe WL, Scholtens DM, Sandler V, Hayes MG. Genetics of gestational diabetes mellitus and maternal metabolism. Curr Diabetes Rep. 2016;16(2):1.
Mehmood S, Ye C, Connelly PW, Hanley AJ, Zinman B, Retnakaran R. Rising plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and hypoadiponectinemia characterize the cardiometabolic biomarker profile of women with recent gestational diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018;17(1):1–9.
Aso Y. Plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI)-1 in vascular inflammation and thrombosis. Front Biosci. 2007;12:2957–66.
Abdul-Hadi MH, Naji MT, Shams HA, Sami OM, Al-Harchan NA, Al-Kuraishy HM, et al. Oxidative stress injury and glucolipotoxicity in type 2 diabetes mellitus: the potential role of metformin and sitagliptin. Biomed Biotechnol Res J. 2020;4(2):166.
Tjärnlund-Wolf A, Brogren H, Lo EH, Wang X. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and thrombotic cerebrovascular diseases. Stroke. 2012;43:2833–9.
Retnakaran R, Ye C, Connelly PW, Hanley AJ, Sermer M, Zinman B. Impact of changes over time in adipokines and inflammatory proteins on changes in insulin sensitivity, beta-cell function, and glycemia in women with previous gestational dysglycemia. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(8):e101–2.
Song C, Burgess S, Eicher JD, O’Donnell CJ, Johnson AD. Causal effect of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 on coronary heart disease. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017;6(6): e004918.
Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI. Effects of rosuvastatin alone or in combination with omega-3 fatty acid on adiponectin levels and cardiometabolic profile. J Basic Clin Pharm. 2016;8(1):8.
Abdel Gader AG, Khashoggi TY, Habib F, Awadallah SB. Haemostatic and cytokine changes in gestational diabetes mellitus. Gynaecol Endocrinol. 2011;27(5):356–60.
Tufiño C, Vanegas M, Nevárez RV, López CV, Lugo RA. Divergent impact of gestational diabetes mellitus between the thoracic and abdominal rat aorta: influence of endothelium and angiotensin II receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021;899: 173981.
Michael OS, Olatunji LA. Ameliorative effect of nicotine exposure on insulin resistance is accompanied by decreased cardiac glycogen synthase kinase-3 and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 during oral oestrogen–progestin therapy. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2018;124(2):139–48.
Cao J, Peng Q. NLRP3 inhibitor tranilast attenuates gestational diabetes mellitus in a genetic mouse model. Drugs R D. 2022;22(1):105–12.
Ismael S, Nasoohi S, Yoo A, Ahmed HA, Ishrat T. Tissue plasminogen activator promotes TXNIP–NLRP3 inflammasome activation after hyperglycemic stroke in mice. Mol Neurobiol. 2020;57(6):2495–508.
Ghavimi H, Sheidaei S, Vaez H, Zolali E, Asgharian P, Hamishehkar H. Metformin—attenuated sepsis—induced oxidative damages: a novel role for metformin. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2018;21(5):469.
Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Alblihed M, Guerreiro SG, Cruz-Martins N, Batiha GE. COVID-19 in relation to hyperglycemia and diabetes mellitus. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8: 644095.
Kurtul BE, Elbeyli A, Ozcan SC. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 4G/5G polymorphism and dyslipidemia with branch retinal artery occlusion in a young lady. Oman J Ophthalmol. 2020;13(3):152.
Khalaf FA, Ibrahim HR, Bedair HM, Allam MM, Elshormilisy AA, Ali ST, et al. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene polymorphism as a risk factor for vascular complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Egypt J Med Hum Genet. 2019;20(1):1–3.
Nawaz SS, Siddiqui K. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 mediate downregulation of adiponectin in type 2 diabetes patients with metabolic syndrome. Cytokine X. 2022;4(1):100064.
Alorabi M, Cavalu S, Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Mostafa-Hedeab G, Negm WA, et al. Pentoxifylline and berberine mitigate diclofenac-induced acute nephrotoxicity in male rats via modulation of inflammation and oxidative stress. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;152: 113225.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mustansiriyah University, Baghdad, Iraq, for the great support of the scientific research.
Funding
Open access funding provided by The Science, Technology & Innovation Funding Authority (STDF) in cooperation with The Egyptian Knowledge Bank (EKB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HMA, TJA, AKA and AIA conceptualization, data collection, and writing of the manuscript. GEB, HMS and JSG writing, supervision and editing of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent for publication
All authors gave consent for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Batiha, G.ES., Al-kuraishy, H.M., Al-Maiahy, T.J. et al. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and gestational diabetes: the causal relationship. Diabetol Metab Syndr 14, 127 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13098-022-00900-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13098-022-00900-2