Abstract
Background
Anaplasma phagocytophilum is currently regarded as a single species. However, molecular studies indicate that it can be subdivided into ecotypes, each with distinct but overlapping transmission cycle. Here, we evaluate the interactions between and within clusters of haplotypes of the bacterium isolated from vertebrates and ticks, using phylogenetic and network-based methods.
Methods
The presence of A. phagocytophilum DNA was determined in ticks and vertebrate tissue samples. A fragment of the groEl gene was amplified and sequenced from qPCR-positive lysates. Additional groEl sequences from ticks and vertebrate reservoirs were obtained from GenBank and through literature searches, resulting in a dataset consisting of 1623 A. phagocytophilum field isolates. Phylogenetic analyses were used to infer clusters of haplotypes and to assess phylogenetic clustering of A. phagocytophilum in vertebrates or ticks. Network-based methods were used to resolve host-vector interactions and their relative importance in the segregating communities of haplotypes.
Results
Phylogenetic analyses resulted in 199 haplotypes within eight network-derived clusters, which were allocated to four ecotypes. The interactions of haplotypes between ticks, vertebrates and geographical origin, were visualized and quantified from networks. A high number of haplotypes were recorded in the tick Ixodes ricinus. Communities of A. phagocytophilum recorded from Korea, Japan, Far Eastern Russia, as well as those associated with rodents had no links with the larger set of isolates associated with I. ricinus, suggesting different evolutionary pressures. Rodents appeared to have a range of haplotypes associated with either Ixodes trianguliceps or Ixodes persulcatus and Ixodes pavlovskyi. Haplotypes found in rodents in Russia had low similarities with those recorded in rodents in other regions and shaped separate communities.
Conclusions
The groEl gene fragment of A. phagocytophilum provides information about spatial segregation and associations of haplotypes to particular vector-host interactions. Further research is needed to understand the circulation of this bacterium in the gap between Europe and Asia before the overview of the speciation features of this bacterium is complete. Environmental traits may also play a role in the evolution of A. phagocytophilum in ecotypes through yet unknown relationships.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Communities of organisms co-evolve across time and space [1,2,3,4]. Recent studies have stressed the need to capture the ecological relationships of large sets of interacting species [5, 6]. Many tick-borne pathogens have a considerable impact on human, livestock and wildlife health. The different species of ticks and associated pathogens differ largely in the level of specialization for different wildlife hosts. Due to this complexity, the understanding of transmission cycles of most pathogens and the resulting phylogeny is still rudimentary. The application of graph analysis is a promising approach to understand the coevolution of the foci of ticks and associated pathogens [5, 7]. Properties of network analysis allow for the visualization and quantification of the peculiarities of their ecological relationships [8], revealing more or less distinct and/or nested subgroups of interacting organisms [9]. Modularity is a key element in these constructs, characterizing the degree of interactions of organisms among themselves and with other members of the network. For the interacting triad of ticks, pathogens and their vertebrate hosts, a high clustering and nestedness seem to be the rule rather than the exception [10]: some organisms interact more frequently among them than with other species, generating nested “communities” when the complete set of interactions is analyzed.
Anaplasma phagocytophilum is the etiological agent of human granulocytic anaplasmosis (HGA), and tick-borne fever in domesticated animals [11,12,13]. Although a wide range of wildlife species can be infected with A. phagocytophilum, the impact of these infections on wildlife health is unclear [14]. The main vectors of A. phagocytophilum are ticks of the Ixodes ricinus complex: Ixodes ricinus in Europe, Ixodes persulcatus in eastern Europe and East Asia, and Ixodes scapularis and Ixodes pacificus in North America, although several other Ixodes species have been implicated in maintaining A. phagocytophilum in enzootic cycles as well [12, 13, 15]. The transmission dynamics of A. phagocytophilum predominantly rely on horizontal transmission between ticks and vertebrate hosts and on transstadial transmission in its vectors. While its vertical transmission (transovarial) has only been documented for Dermacentor albipictus in laboratory conditions [16], no conclusive evidence of such a route has been reported in Ixodes ticks. Therefore, A. phagocytophilum is exposed to the evolutionary pressures of complex interactions among the vertebrate reservoirs and its vectors, which are instrumental in shaping the underlying tapestry of the genetic constellation of A. phagocytophilum.
The role of wildlife species in the circulation of A. phagocytophilum is yet to be clearly determined, but several species of wild ruminants are thought to be important reservoirs [17]. Free ranging ruminants, such as the roe deer (Capreolus capreolus) in Europe [18] and the white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) in America [19], also largely contribute to the propagation of the ticks. Small mammals, on the other hand, contribute more to the feeding of immature stages of I. ricinus species [18,19,20]. These animals also harbour nidicolous ticks, such as Ixodes acuminatus and Ixodes trianguliceps, which have been implicated to circulate A. phagocytophilum in cryptic cycles [21]. Domesticated animals sometimes act as super-spreaders of ticks, and maybe also of A. phagocytophilum, since they boost amplification cycles by feeding large numbers of ticks [22]. Genetic analyses could help to further elucidate the pathogenicity and zoonotic potential of particular A. phagocytophilum isolates, as well as the direction of spill-over between livestock and wildlife.
Since its reclassification in 2001 [23], A. phagocytophilum is viewed as a single species based on genetic analyses of 16S rRNA, groEL and surface protein genes. This taxon includes what formerly had been recorded as Ehrlichia equi, the etiological agent of equine ehrlichiosis, the unnamed causative agent of human granulocytic ehrlichiosis, and Ehrlichia phagocytophila. However, the circulating variants of A. phagocytophilum do not equally infect different hosts or result in the same clinical picture. While 16S rRNA is valuable for rough phylogenetic reconstruction, more variable genes such as ankA, msp4 and groEL heat-shock operons are preferred to capture strains and population structure [15, 24, 25]. Two studies proposed the existence of four clusters of A. phagocytophilum strains based on the ankA gene [24, 26]. Both studies concur in the clear separation of variants recorded in humans and roe deer. A distinct lineage associated with rodents in Europe has also been described, which is believed to be vectored by I. trianguliceps [21]. Furthermore, one multi-locus approach [27] showed that strains from roe deer, voles and shrews did not fall into the same clonal complex as the variants infecting humans, dogs and horses, while wild boars (Sus scrofa) and hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) could be reservoirs for a zoonotic A. phagocytophilum variant. Red deer (Cervus elaphus) have also been suspected of harbouring zoonotic types [28], as well as pathogenic variants of domestic ruminants [26, 27, 29, 30]. A previous study [31] supported these findings, and identified four different ecotypes in Europe based on a fragment of the groEl gene. The study revealed that the zoonotic ecotype could be linked to a multitude of hosts, but did not cluster with the bird, rodent or roe deer ecotypes.
In this study, we follow the working theory of Jahfari et al. [31] that an ecotype is a cluster of genetically similar A. phagocytophilum isolates based on groEL sequences. We expand previous concepts exploring the relationships among haplotypes of A. phagocytophilum, its reservoirs and the ticks involved in its circulation. By unifying methods from the fields of molecular biology, phylogenetics, and network theory, we test whether and quantify how A. phagocytophilum segregates into nested, interconnected networks of ticks and vertebrates, quantifying the levels of hierarchy embedded in the large background. We apply indices of modularity and centrality of the network, together with unambiguous measurements of phylogenetic clustering, to the largest available dataset of haplotypes of the bacterium to show how the ecological relationships of A. phagocytophilum emerge into a robust, nested, and connected epidemiological structure, which the bacterium exploits to diversify, spread into new niches and evolve along different strains.
Methods
Collection of A. phagocytophilum field isolates
The collection of A. phagocytophilum field isolates predominantly relied on convenience sampling from numerous previous or ongoing studies in Europe [32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49]. Ticks and tissue samples from vertebrates were stored below − 20 °C before further processing in the laboratory. All A. phagocytophilum field isolates are described in Additional file 1: Table S1.
DNA extraction and sequencing
DNA from vertebrate samples and engorged ticks was extracted in different laboratories using various techniques [32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48]. DNA from tissues and engorged ticks which were specifically analysed for this study were extracted with the DNeasy® Blood & Tissue kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) as per the manufacturer’s instructions. Ticks from the vegetation were lysed with ammonium hydroxide [50]. These samples were screened for the presence of A. phagocytophilum DNA with a real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) targeting a 77-bp portion of the msp2 gene [51]. Amplification of the qPCR-positive samples was performed, targeting a 530-bp fragment of the groEL gene of A. phagocytophilum following published methods [52]. The PCR-products were analyzed with gel electrophoreses on a 1.5% agarose gel and coloured with SYBR™ Gold Nucleic Acid Gel Stain (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). When the initial PCR did not result in a visible product, a nested PCR was performed using the primers ApNest-F (5′-GTG GAA TTT GAA AAT CCA TAC-3′) and ApNest-R (5′-GTC CTG CTA GCT ATG CTT TC-3′). The PCR program had a pre-incubation step of 95 °C for 15 min, followed by 40 cycles of 30 s at 94 °C, 30 s at 55 °C and 40 s at 72 °C. Final extension was performed using a 10 min step at 72 °C. This nested PCR results in a 366-bp fragment. The PCR products were cleaned with ExoSAP-IT™ PCR Product Cleanup Reagent (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) and sequenced by BaseClear (Leiden, Netherlands). The chromatographs of the sequences were analyzed and the primer sites were trimmed in Bionumerics v.7.6 (Applied Maths, Sint-Martens-Latem, Belgium).
Compilation of the molecular epidemiological dataset
We compiled a dataset with the A. phagocytophilum isolates that had a groEL DNA sequence, the geographical origin (country) and information on vertebrate/tick species from which the isolate originated [31]. A search for additional A. phagocytophilum isolates with an explicit statement of the geographical origin (country) and vertebrate/tick from which the isolate originated was performed in the Entrez Nucleotide Database. Isolates that did not originate from field or case studies, or lacked the minimum required epidemiological information were excluded. Only A. phagocytophilum isolates which contained the DNA fragment from 655 to 1020 (366) bp of the groEL open reading frame, using GenBank entry CP015376 as a reference, were included in the initial dataset. The complete dataset with DNA sequences is included in Additional file 1: Table S1 and consists of 1992 field isolates, including the samples obtained from GenBank. While the size of this fragment had previously been used to identify ecotypes [31], a smaller subset of isolates with groEL sequences that spanned a longer fragment with a higher genetic resolution (LF), from 589 to 1118 (530) bp, was extracted for further analyses. After this selection, the dataset consisted of 1623 field isolates. We acknowledge that the grouping according to large administrative divisions (countries) is too rough to describe the fine geographical structure of segregation of A. phagocytophilum. While data on provinces or localities of collection were available for some samples, their use (instead of the country) reduced the available dataset by about 50%. We thus decided to keep the name of the country as the only geographical indicator, to better exploit a longer list of available data.
Haplotype and cluster delineation
A haplotype was defined here as a group of A. phagocytophilum isolates in the dataset in which all members shared an identical 530-bp fragment of the groEL gene. For this, a multiple alignment based UPGMA tree was generated in BioNumerics with groEl sequences that had been extracted from the dataset. Molecularly similar haplotypes (clusters) were identified according to published methods [31].
Vertebrate and arthropod haplotype distributions between clusters
We tested the possibility of over-representation of a cluster among the isolates using a multinomial model in which an isolate from a single species is evenly associated across all eight clusters, i.e. with the probability of 1/8 per cluster. The Monte Carlo method was used to estimate the probability (P-value) that the number of most numerous clusters in a random realization from the multinomial is equal to or greater than the observed maximum among the isolates. These calculations were performed in Mathematica v.11.3 [53]. A probability of less than 0.05 was considered significant support for selective distribution.
Building associations among ticks-reservoirs-haplotypes: associations of clusters with carriers and geography
Once the list of haplotypes of A. phagocytophilum isolates was completed with data about the species of vertebrate or tick and the country of origin, a network capturing interactions was built. While molecular methods delineate the evolution of the target sequence of the bacterium, a network records how the strains of A. phagocytophilum segregate throughout the ticks and the vertebrates involved in its circulation. In our application, a “record” is a pairwise A. phagocytophilum-tick/vertebrate combination at a single geographical site. Each time a haplotype was found linked to either a vertebrate or a tick, a link was drawn, matching haplotype-vertebrate or haplotype-tick for a given country. The complete network includes the number of times each haplotype was found in each species of vertebrate or tick plus the country. In our application, nodes represent “carriers” (ticks or vertebrates) that are linked to a “cargo” (a haplotype of A. phagocytophilum) in a given country.
We examined several hypotheses regarding the relationships among the partners of the network. Modularity resolves communities of organisms that interact more among themselves than with other members of the network. We used the Louvain algorithm for calculating modularity, as integrated in the software Gephi v.0.92 [54], detecting communities of haplotypes of A. phagocytophilum and the carriers to which they are associated. Modularity resolves the compartmentalization of the network, displaying subnetworks of interacting entities separated from other subnetworks. These nested structures provide information about which elements (carriers, cargo) should be considered a “sub-part” of another larger network element, which is a major indication of clusters of haplotypes being derived from another, probably larger, cluster of samples. We used the algorithm provided by Bastolla et al. [55] for calculation of nestedness. We also calculated the articulation points of these subnetworks, using the package igraph [56] of the R programming environment [57]. Articulation points are the nodes linking two or more different communities, whose removal increases the number of isolated sub-networks.
We already demonstrated that the structure of the networks in which tick-transmitted pathogens circulate correlates with critical scales of connectivity between ticks and hosts and that these relationships can be described based on their centrality indices. Centrality measures in ecological networks indicate the presence of “high-ranking nodes in the network that have significantly higher-than-average connectivity” [58]. Identifying the most central nodes was addressed using the betweenness centrality (BNC) defined as the number of shortest paths between pairs of nodes that pass throughout a given node, and the PageRank (PR) defined as the number and quality of links to a node to estimate how important the node is. The underlying assumption is that more important nodes are likely to receive more links from other nodes. We tested whether these high centrality nodes exist in each community, and how they are inter-related. A highly central node is a carrier (tick/vertebrate) found to be infected by many cargo haplotypes that infect many other carriers in the network. The vertebrates or the ticks with the greatest centrality are super-spreaders [59].
We aimed to obtain measures of the phylogenetic diversity of the A. phagocytophilum haplotypes at the level of species of vertebrates and ticks. These calculations are intended to understand if a higher or lower phylogenetic diversity of A. phagocytophilum is linked to some groups of vertebrates/ticks. In other words, we aimed to explicitly demonstrate the association of given haplotypes or their clusters to species of vertebrates or ticks. The phylogenetic tree of haplotypes of A. phagocytophilum implicitly includes a measure of distance among the tips of the tree. Phylogenetic diversity of A. phagocytophilum per vertebrate/tick species was calculated using Faith’s phylogenetic diversity (PD) [60] as the total branch length spanned by the tree, including all of the haplotypes of A. phagocytophilum recorded in a single species of “carrier”. We also calculated the mean pairwise distance (MPD) as described previously [61]. Null models were generated that randomized the tips of the phylogeny to calculate the significance of the phylogenetic association between ticks/vertebrates and haplotypes of A. phagocytophilum evaluating the significance of MPD [61]. The package picante [62] of the R programming environment [57] was used for these calculations. Both PD and MPD aim to demonstrate the significance of associations with portions of the phylogenetic tree of the haplotypes of A. phagocytophilum using different methods. The congruence of results between methods is supportive of such phylogenetic clustering.
Results
Haplotypes of A. phagocytophilum cluster along vertebrate, tick and geographical gradients
We identified 199 unique haplotypes in a total of 1623 isolates of A. phagocytophilum. Tables 1 and 2 summarize the field isolates according to vertebrates and questing or feeding vectors, respectively. In 730 vertebrate isolates, 135 A. phagocytophilum haplotypes were recorded, while 127 haplotypes were detected in 893 ticks: 789 collected from the vegetation and 104 feeding on vertebrates (Tables 1, 2). Haplotypes were grouped into 8 clusters according to the phylogenetic tree using shorter DNA fragments from 1992 isolates (Fig. 1, Additional file 1: Table S1). However, a network analysis of the relationships among haplotypes, ticks and vertebrates (see below) produced a total of 12 communities of interacting organisms. All of these extra-communities, containing only one or a few haplotypes, remained undetected in the phylogenetic tree. We chose to keep the original numbering of clusters based on genetic procedures (i.e. 8 clusters), while retaining the complete structure of the network to show the relationships among interacting partners.
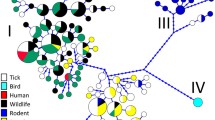
The phylogenetic tree of the clusters of A. phagocytophilum haplotypes detected in this study. Each branch of the tree includes the name of the cluster, with the number of haplotypes that belong to it, and some details of distribution or new carriers. Coloured lines labelled with the “Ecotype” refer to the original groups proposed by Jahfari et al. [31]
Association of A. phagocytophilum haplotypes to countries, hosts and vectors
Anaplasma phagocytophilum haplotypes were linked to the carriers (hosts and vectors) and countries in which they were recorded, resulting in a network (Fig. 2 and Additional file 2: Figure S1). The haplotypes linked to Cluster 1 were present in the widest range of carriers: Artiodactyla, Perissodactyla, Carnivora, Nearctic Rodentia, I. ricinus, I. scapularis, I. pacificus and I. hexagonus. Cluster 1 remained unrecorded in six other species of ticks. Geographically, Cluster 1 was present in the Western Palaearctic and Nearctic regions (Fig. 2, Additional file 3: Figure S2). However, Cluster 1 was found to be absent in rodents in Far Eastern Russia, Japan and Korea. Cluster 4 is a segregated group of haplotypes recorded in South Korea, Ixodes persulcatus ticks in Russia and one vertebrate in Japan. Cluster 5 appeared in rodents and I. trianguliceps in Europe. Cluster 6 was recorded in rodents or rodent-feeding ticks (I. persulcatus) in Japan. Haplotypes similar to those in Cluster 5 were also detected in the group of haplotypes restricted to Far East Russia and Japan. Cluster 7 is a group of haplotypes associated with birds and endophilous ticks associated with them (such as I. frontalis).
a The network of the communities of A. phagocytophilum haplotypes, as linked to carriers (ticks or vertebrates). Circles (nodes) are haplotypes from ticks or vertebrates, but the labels are included only in nodes representing haplotypes of A. phagocytophilum to improve reading (i.e. labels are not included for ticks and vertebrates). Labels are the number of the cluster obtained in the phylogenetic tree in Fig. 1. The colours represent the communities detected by an agglomerative clustering algorithm and the size of each circle is proportional to its centrality in the network. Large circles are organisms that are well represented in the network (i.e. a carrier in which several haplotypes have been detected, or a haplotype that widely circulates among different carriers). The links among nodes represent relationships among interacting organisms (a haplotype and a carrier) displaying the colour of the community. The width of the link is proportional to the number of interactions among the organisms. The complete network with labels for every node is included in Additional file 2: Figure S1. b A reduced version of the network is included to simplify interpretations. Each circle has the same colour as the set of nodes of each cluster in a. Labels identify the communities that do not necessarily match the phylogenetic clusters. Labels enclosed in rectangles are communities that are disconnected from the giant component of the network
The network of interacting organisms (Fig. 2) is a tightly nested set of relationships. The giant component of the network (i.e. the one that stays connected) had 117 articulation points. This means a high resilience of the network against the removal of one of these articulation points, allowing ample circulation of the bacterium. Cluster 1, Cluster 2 (detected in Capra aegagrus, Ovis aries and Rupicapra rupicapra) and Cluster 3 were heavily linked to Ixodes ricinus, highlighting the dominance of this vector in the circulation of most A. phagocytophilum haplotypes in Europe (Fig. 2). The remaining clusters 4 to 8 were either isolated or can be disconnected from the giant component by removing only one articulation point. This finding means that every haplotype recorded in rodents in Europe is independent of the main circulation of other haplotypes in the network. Additionally, this implies that these haplotypes are different from those recorded in rodents and associated ticks in Russia and Japan, but still retain some genetic similarities with haplotypes circulating among rodents in Europe. Haplotypes recorded in South Korea were also independent of the complete network. The disconnection of this group of South Korean haplotypes seems to be derived from the fact that they are associated with different tick species (Haemaphysalis spp.). This finding must be considered with caution since it was impossible to know if A. phagocytophilum is circulated by ticks of the genus Haemaphysalis, because every tick was collected while feeding. Nevertheless, these associations promote a disconnection of these haplotypes with others found in Japan and Far East Russia. Additionally, the haplotypes recorded from birds and engorged I. frontalis (Cluster 7) were disconnected from the main giant network component, even if there was an overlapping geographical distribution with other hosts and I. ricinus (Fig. 2). No clear conclusions can be drawn about the segregation of haplotypes connected to carnivores and their endophilous ticks (such as I. hexagonus) since they shaped a separate cluster but were also tightly connected to the rest of the giant component (Fig. 2 and Additional file 2: Figure S1). The isolates from North America formed a disconnected sub-network (Fig. 2) which resulted from the lack of geographical overlap with the European isolates. In any case, both European and American human isolates belong to Cluster 1. It is noteworthy that a previously unexplored species of tick, I. ventalloi, provided haplotypes belonging to a completely different cluster.
Figure 3 includes the values of BNC and PR for the haplotypes, grouped according to clusters. To simplify visualization, we included only haplotypes with a BNC higher than 0 or a PR higher than 0.5. A high BNC value is typical for a major hub in a network, “circulating” many haplotypes. For the complete A. phagocytophilum network, the major hub was I. ricinus, with BNC values in the range of 600–25,000 for the associated haplotypes. Other tick species scored much lower in BNC values: I. ventalloi (BNC = 1098); I. persulcatus (BNC = 264); I. pavlovskyi (BNC = 24); and I. trianguliceps (BNC = 14). Haplotypes with high PR values were connected to well-represented carriers in the network, therefore having larger probabilities for spreading. Both indices were only partially correlated. The correlation between values of BNC and PR was clear for haplotypes in clusters 1 and 3. However, while network indices indicate high values of PR for haplotypes in clusters 5 and 6 (restricted to rodents and geographically separated) and therefore high chances of spread, their low values of BNC confirm that they are poorly connected within the network. This is hypothesized to happen due to a lack of circulation out of the subnetwork(s) containing the vertebrates and ticks in which they have been recorded.
Values of betweenness centrality (BNC) (a) and PageRank (PR) (b) for each of the haplotypes of A. phagocytophilum. Only the haplotypes with values higher than 0 for either BNC or PR are included in each chart. Categories correspond to the phylogenetic clusters shown in Fig. 1. Betweenness centrality represents the relative importance of a haplotype in the complete network. Betweenness centrality is related to the connectivity of a network, in so much as high betweenness vertices have the potential to disconnect graphs if removed. Therefore, a node with high BNC is a node that is very central and connected to many other nodes. PR represents the importance of the nodes to which a given link is connected. It is thus a measure of the potential spread of a node through connected nodes, according to its relative importance
Association of A. phagocytophilum haplotypes with vertebrate and tick species
To further demonstrate how the haplotypes fit into the framework of clusters, the association of vertebrates (Table 3) and (feeding) arthropods (Table 4) to certain clusters was tested with the Monte Carlo method. Confirming the results from the network analysis, a significant support was found for an association of I. ricinus with the large Cluster 1 (Table 4). An association of I. hexagonus, feeding on Erinaceus europaeus, with Cluster 1 was also found (Table 4). We found a significant association of I. ricinus feeding on C. elaphus with Cluster 1 (Table 4), and of I. ricinus feeding on Capreolus capreolus with Cluster 3. Cluster 4 was significantly linked to questing I. persulcatus ticks and Apodemus agrarius, a rodent found in eastern Europe and Asia. This cluster contained different samples, mainly from South Korea and Russia, and was not limited to Soricomorpha-Rodentia and I. trianguliceps like Cluster 5 (Europe) or to only Rodentia and I. pavlovskyi/I. persulcatus ticks like Cluster 6 (eastern Europe and Asia).
Table 5 includes the values of PD for the species of vertebrates for which samples of A. phagocytophilum were obtained. A low PD value means phylogenetic clustering and therefore a lower variability in the samples associated with a given vertebrate. Eighteen species of vertebrates showed values of significant association with a given portion of the phylogenetic tree of A. phagocytophilum. The same index was provided for the arthropods (ticks and one species of insect, Lipoptena cervi) with similar results for I. pacificus, I. ricinus and I. trianguliceps (Table 6). Samples recorded in I. ricinus were separately evaluated for PD according to the geographical origin, resulting in highly significant associations with given haplotypes of A. phagocytophilum. If data from I. ricinus were included in calculations without geographical segregation, the PD value for the tick was 0.94 (highly non-significant). At least in the case of the most prominent tick vector, the associations of A. phagocytophilum with I. ricinus are of a local nature: considering these associations at a continental level could not give evidence to the segregation of haplotypes in the tick, strongly suggesting an adaptation to regional populations of the tick. Tables 7 and 8 include further results about phylogenetic clustering using the mean pairwise genetic distance, comparing the observed phylogenetic relatedness of the haplotypes recorded for vertebrates/arthropods to the pattern expected under a null model of phylogeny or community randomization. Results confirm the findings obtained by PD: there is a phylogenetic clustering of the haplotypes of A. phagocytophilum with the carriers. The highly significant values for I. ricinus and I. trianguliceps are demonstrative of segregation of the bacterium in these ticks, further supported by the significant values found in I. pacificus, a tick with a distribution range disconnected from the main range of the others.
Discussion
Enhancing the understanding of the transmission networks of tick-borne pathogens requires a challenging blend of molecular biology, phylogenetics and network theory. Here, we delineated the existence of a relatively high number of haplotypes of A. phagocytophilum by standard molecular methods, based on the presence of DNA and bacterial groEL sequences originating from a large variety of ticks and vertebrates from a broad geographical range. These haplotypes grouped into eight well-defined genetic clusters. We acknowledge that presence of bacterial DNA in samples of vertebrates or ticks is not sufficient to document the infectivity of the bacterium. In addition, vector competence requires ticks to be infected and passing viable pathogens to the next stage and to a new host. We also recognize that the sampling effort has not been the same for every region, vertebrate or tick. This is, however, currently the most geographically extensive and largest available dataset of groEL sequences of A. phagocytophilum. It provides an unexpected picture of the considerable spread of some haplotypes and the affinity of some others towards well-defined groups of vertebrates, ticks and regions, expanding the previous view on the evolution and segregation of the bacterium [15, 21, 28, 31].
Reservoir-driven rather than vector-driven selection mechanisms?
This study corroborated the preferential and differential association of lineages of the bacterium to several groups of vertebrates and ticks, also showing a geographical variation in pathogen-host-vector associations. Observed delineation of A. phagocytophilum could be driven by geographical isolation (environmental traits acting on ticks or reservoirs), or by peculiarities of the life-cycle or interacting molecular phenomena of ticks and/or reservoirs, including immune peculiarities differing across hosts. The different geographical distribution of some groups of Artiodactyla in which A. phagocytophilum has been recorded is a support for a geographical isolation. However, it has been demonstrated that haplotypes circulating in Cervus elaphus are different from those associated with Alces alces, even if some mix of haplotypes can be found in both vertebrates because of habitat overlap and a shared tick vector being the same (I. ricinus) [41]. This provides support for reservoir-driven delineation and appears to exclude a vector-driven selection mechanism of haplotypes. Reservoir-driven delineation is also supported by the finding that the cluster of haplotypes associated with birds is separated from the main set of haplotypes circulating through mammals. While birds are prominent hosts for the immature stages of I. ricinus [63] they do not seem competent hosts of the main mammals-associated haplotypes, and birds could filter these haplotypes and prevent their spread through birds carrying I. ricinus. This is an interesting outcome of our study, since only a few (4 out of 857) A. phagocytophilum-positive I. ricinus from the vegetation and mammals were infected with haplotypes associated with birds [64], likely due to a tick strictly specific to birds, I. frontalis, being vector of the bird-associated haplotypes. This would contribute to the restricted circulation of most mammal-associated haplotypes through birds carrying I. ricinus.
Geographical differences in haplotype clustering
Previous studies demonstrated the potential of networks to disentangle the complex relationships among ticks, transmitted pathogens and vertebrates in general [22] and the tight association between strains of Borrelia burgdorferi (s.l.) and allopatric species of ticks [58]. The former study set the basics for unravelling these ecological associations, the later outlined the segregation of B. burgdorferi (s.l.) according to the species of vector ticks. These general insights into networks of ticks, pathogens and hosts were also found in A. phagocytophilum: considered as a single species, it seems to evolve along different lines that shape clusters of haplotypes that are, in some cases, tightly circumscribed to particular combinations of vertebrates and ticks. The combined use of both molecular and network-derived methods pointed out that rodents have at least two different clusters of haplotypes. The first one, already outlined [31], is linked with rodents in the Western Palaearctic, while the other cluster is linked with rodents (and ticks feeding on rodents) in the Far Eastern Russia and Japan. Of most importance, the present results from the networks point to a restricted circulation of these clusters, even when the ecological communities suggest they could have the potential for a wider circulation. Moreover, phylogenies clearly point to a close relationship between Cluster 5 (former ecotype III, rodents in Europe) and Cluster 6 (rodents plus feeding ticks in Far Eastern Russia and Japan), suggesting that the disconnection of these clusters could be derived from the gap in obtaining isolates in the large territory between Western and Eastern Russia. We hypothesize that these clusters associated with rodents and ticks of the I. ricinus complex could actually be a gradient of variability of strains of A. phagocytophilum throughout most of the Palaearctic, of which we captured “the picture” at both extremes.
It is striking that a high phylogenetic clustering of A. phagocytophilum in I. ricinus has been found only when the geographical component has been considered in calculations. This result strongly points to a separation of haplotypes not only regarding specific combinations of ticks and vertebrates, but also to a selection by an environmental gradient shaping the life-cycle of tick vectors, at least in the widespread I. ricinus. Since ticks are ectothermic organisms, climate strongly regulates their development and mortality rates, therefore resulting in populations of the tick exhibiting adaptations to a specific set of weather conditions [65]. A further selection of haplotypes of A. phagocytophilum by this mechanism, emerging as definite associations among haplotypes and populations of the tick, should not be discarded, since it has been already demonstrated for Anaplasma marginale [66]. An explicit examination of the effects of the environment, such as temperature and humidity, on the phylogenetic diversity of circulating haplotypes in ticks could not be addressed in this study because of the lack of coordinates of the isolates. The handling of the effects of environmental diversity assuming large areas like countries is not possible because of the considerable variety of environmental traits that can exist within a single geographical category.
The role of other tick species
Other outcomes of this study provided unexpected relationships between A. phagocytophilum, vertebrates and other species of ticks. The largely neglected I. ventalloi has already been pointed out as carrier of A. phagocytophilum [67] but our results suggest a dual role for this tick regarding the circulation of the bacterium. Available data outlined that this tick species is involved in both a subnetwork of haplotypes with restricted circulation, serving as an articulation point with the giant component of haplotypes of the Cluster 1, and thus directly connected with haplotypes circulated by I. ricinus. This seems to derive from the large spectrum of hosts of I. ventalloi (formerly considered to be specific to the European rabbit, Oryctolagus cuniculus) and its sympatry with I. ricinus in its southern European range [68]. Interestingly, the cluster of haplotypes associated with I. ventalloi is more divergent than the Cluster 1, circulated by I. ricinus, which suggest a secondary evolution of the bacterium in the niche of I. ventalloi and its hosts. The results obtained for I. ventalloi support the finding that this tick constitutes an articulation point in the evolutionary pressures of haplotypes in the Clusters 1 and 8, the latter so far found exclusively in this tick. Both I. ricinus and I. ventalloi overlap in portions of their environmental niche in the southern portion of the distribution range of the former and share some hosts, the latter observing a semi-endophilic behaviour. It is thus not unexpected that a different cluster of haplotypes segregated in I. ventalloi because of its different life habits and environmental niche.
Future studies and remaining challenges
Our data on the phylogenetic segregation of haplotypes of A. phagocytophilum in ticks revealed interesting results and potential for future studies. Of these, the most obvious is the high variability of haplotypes (low phylogenetic clustering) found in I. persulcatus, I. pavlosvkyi and I. ventalloi. Ixodes pavlovskyi exploits a portion of the environmental niche of I. persulcatus [58] and both are involved in the circulation of rodent haplotypes in Far Eastern Russia and Japan. This suggests the need of wide surveys collected in the gap between eastern Europe and Japan, incorporating new information to the network-derived construct, opening additional perspectives to the view presented here, and contributing to a better understanding of the evolution of such a singular bacterium.
A high clustering indicates a higher affinity of some haplotypes for a carrier than expected by chance, and therefore a segregation of haplotypes according to carriers, which would circulate different haplotypes. Our analysis revealed a higher than expected clustering of haplotypes of A. phagocytophilum for most species of vertebrates or ticks, with a few exceptions, such as the common blackbird Turdus merula, or the wild goat C. aegagrus. One could argue that the high values of phylogenetic clustering of A. phagocytophilum in vertebrates/ticks could be derived from the low sample sizes for some taxa, which is likely for some of our isolates. However, high values of phylogenetic clustering were also obtained with well-represented vertebrates, such as C. elaphus, C. capreolus or Myodes spp. The same is applicable to the ticks I. ricinus and I. trianguliceps, the former exceptionally well surveyed, the latter under-represented. Therefore, we contemplate these results reflect true phylogenetic relationships between the bacterium and either vertebrate or vector (or both). Anaplasma phagocytophilum has to survive in and colonize both a vertebrate and an arthropod, a dual mode of life, and therefore the still not completely studied metabolic adaptations of the bacterium need to cope with a large gradient of conditions regarding the defensive mechanisms of both partners. It is thus expected that the adaptive plasticity of the bacterium can be detected as a result of its fitness to particular conditions. Empirical studies exist about the tight interactions between the tick and the pathogen, demonstrating that A. phagocytophilum is able to rewire literally dozens of the tick metabolic pathways [69] and that infected ticks have an increased expression of some proteins, such as heat-shock proteins [70], allowing a prolonged survival under otherwise adverse environmental conditions. This kind of molecular adaptation has led to the ubiquitous occurrence of this bacterium both geographically and in terms of vertebrate and arthropod hosts which is an example of ecological fitting [71] that will enable its further spread. Studies from samples collected in the still unsurveyed gap would incorporate new information to the network-derived construct. Other than rodents, the role of birds in segregation of A. phagocytophilum should be further investigated, opening additional perspectives to the view presented here, and contributing to a well-focused overview of the evolution of such a singular bacterium.
Conclusions
Our study incorporated methods from different fields, aiming to uncover the variability of haplotypes of A. phagocytophilum using the largest available set of isolates from ticks and vertebrates in the widest geographical area so far. The use of molecular methods, phylogenetic clustering and network-based associations of interacting organisms provided results about an unexpected molecular variability in the groEL gene of A. phagocytophilum. Results widely exceeded the previous view of the evolution of the bacterium, recording 199 haplotypes. These haplotypes conform so far to eight clearly separated clusters, either widely circulating in the Western Palaearctic, confined to specific taxa of vertebrates, or restricted to smaller regions and patently segregated from the main network. While I. ricinus is still unquestionably the driving force behind the circulation of most haplotypes, evidence is accumulating about the role of other ticks (I. ventalloi, I. persulcatus, I. pavlovskyi, I. frontalis and I. trianguliceps) circulating different clusters that remain unconnected with the main giant component of the network. Our data also suggest that the two clusters of haplotypes associated with rodents could actually be the extremes of a large gradient of evolving strains of the bacterium.
Availability of data and materials
Data supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article and its additional files. The complete dataset of haplotypes is provided in Additional file 1. Representative sequences generated in this study were submitted to the GenBank database under the Accession Numbers MN093151–MN093291.
Abbreviations
- rRNA:
-
Ribosomal RNA
- qPCR:
-
Quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- BNC:
-
Betweenness Centrality
- PR:
-
PageRank
- PD:
-
Faith’s phylogenetic diversity
- MPD:
-
mean pairwise distance
References
Ehrlich PR, Raven PH. Butterflies and plants: a study in coevolution. Evolution. 1964;18:586–608.
Thompson JN. The geographic mosaic of coevolution. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press; 2005.
Bascompte J, Jordano P, Olesen JM. Asymmetric coevolutionary networks facilitate biodiversity maintenance. Science. 2006;312:431–3.
Thompson JN. The coevolutionary process. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 1994.
Bascompte J, Jordano P, Melián CJ, Olesen JM. The nested assembly of plant-animal mutualistic networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:9383–7.
Jordano P, Bascompte J, Olesen JM. Invariant properties in coevolutionary networks of plant-animal links. Ecol Lett. 2003;6:69–81.
Vázquez DP, Aizen MA. Asymmetric specialization: a pervasive feature of plant-pollinator interactions. Ecology. 2004;85:1251–7.
Streicker DG, Fenton A, Pedersen AB. Differential sources of host species heterogeneity influence the transmission and control of multihost parasites. Ecol Lett. 2013;16:975–84.
Newman MEJ. Networks: an introduction. Oxford-New York: Oxford University Press; 2010.
Rigaud T, Perrot-Minnot M-J, Brown MJF. Parasite and host assemblages: embracing the reality will improve our knowledge of parasite transmission and virulence. Proc R Soc London B Biol Sci. 2010;277:3693–702.
Chen SM, Dumler JS, Bakken JS, Walker DH. Identification of a granulocytotropic Ehrlichia species as the etiologic agent of human disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1994;32:589–95.
Stuen S, Granquist E, Silaghi C. Anaplasma phagocytophilum—a widespread multi-host pathogen with highly adaptive strategies. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2013;3:31.
Bakken JS, Dumler JS. Human granulocytic ehrlichiosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2000;31:554–60.
André MR. Diversity of Anaplasma and Ehrlichia/Neoehrlichia agents in terrestrial wild carnivores worldwide: implications for human and domestic animal health and wildlife conservation. Front Vet Sci. 2018;5:293.
Bown KJ, Lambin X, Ogden NH, Begon M, Telford G, Woldehiwet Z, et al. Delineating Anaplasma phagocytophilum ecotypes in coexisting, discrete enzootic cycles. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009;15:1948–54.
Baldridge GD, Scoles GA, Burkhardt NY, Schloeder B, Kurtti TJ, Munderloh UG. Transovarial transmission of Francisella-like endosymbionts and Anaplasma phagocytophilum variants in Dermacentor albipictus (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 2009;46:625–32.
Woldehiwet Z. Anaplasma phagocytophilum in ruminants in Europe. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1078:446–60.
Hofmeester TR, Coipan EC, van Wieren SE, Prins HHT, Takken W, Sprong H. Few vertebrate species dominate the Borrelia burgdorferi s.l. life cycle. Env Res Lett. 2016;11:043001.
Barbour A, Fish D. The biological and social phenomenon of Lyme disease. Science. 1993;260:1610–6.
Walls JJ, Greig B, Neitzel DF, Dumler JS. Natural infection of small mammal species in Minnesota with the agent of human granulocytic ehrlichiosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1997;35:853–5.
Blaňarová L, Stanko M, Carpi G, Miklisová D, Víchová B, Mošanský L, et al. Distinct Anaplasma phagocytophilum genotypes associated with Ixodes trianguliceps ticks and rodents in central Europe. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014;5:928–38.
Estrada-Peña A, de la Fuente J, Ostfeld RS, Cabezas-Cruz A. Interactions between tick and transmitted pathogens evolved to minimise competition through nested and coherent networks. Sci Rep. 2015;5:10361.
Dumler JS, Barbet AF, Bekker CP, Dasch GA, Palmer GH, Ray SC, et al. Reorganization of genera in the families Rickettsiaceae and Anaplasmataceae in the order Rickettsiales: unification of some species of Ehrlichia with Anaplasma, Cowdria with Ehrlichia and Ehrlichia with Neorickettsia, descriptions of six new species combinations and designation of Ehrlichia equi and ‛HGE agentʼ as subjective synonyms of Ehrlichia phagocytophila. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2001;51:2145–65.
Scharf W, Schauer S, Freyburger F, Petrovec M, Schaarschmidt-Kiener D, Liebisch G, et al. Distinct host species correlate with Anaplasma phagocytophilum ankA gene clusters. J Clin Microbiol. 2011;49:790–6.
de la Fuente J, Kocan KM, Blouin EF, Zivkovic Z, Naranjo V, Almazán C, et al. Functional genomics and evolution of tick-Anaplasma interactions and vaccine development. Vet Parasitol. 2010;167:175–86.
Chastagner A, Dugat T, Vourc’h G, Verheyden H, Legrand L, Bachy V, et al. Multilocus sequence analysis of Anaplasma phagocytophilum reveals three distinct lineages with different host ranges in clinically ill French cattle. Vet Res. 2014;45:114.
Huhn C, Winter C, Wolfsperger T, Wüppenhorst N, Strašek Smrdel K, Skuballa J, et al. Analysis of the population structure of Anaplasma phagocytophilum using multilocus sequence typing. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e93725.
Rymaszewska A. Divergence within the marker region of the groESL operon in Anaplasma phagocytophilum. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2008;27:1025–36.
Petrovec M, Bidovec A, Sumner J, Nicholson W, Childs J, Avsic-Zupanc T. Infection with Anaplasma phagocytophila in cervids from Slovenia: Evidence of two genotypic lineages. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2002;114:641–7.
Dugat T, Chastagner A, Lagrée A-C, Petit E, Durand B, Thierry S, et al. A new multiple-locus variable-number tandem repeat analysis reveals different clusters for Anaplasma phagocytophilum circulating in domestic and wild ruminants. Parasit Vectors. 2014;7:439.
Jahfari S, Coipan EC, Fonville M, van Leeuwen AD, Hengeveld P, Heylen D, et al. Circulation of four Anaplasma phagocytophilum ecotypes in Europe. Parasit Vectors. 2014;7:365.
Heylen D, Fonville M, van Leeuwen A, Stroo A, Duisterwinkel M, van Wieren S, et al. Pathogen communities of songbird-derived ticks in Europeʼs low countries. Parasit Vectors. 2017;10:497.
Jahfari S, Ruyts S, Frazer-Mendelewska E, Jaarsma R, Verheyen K, Sprong H. Melting pot of tick-borne zoonoses: the European hedgehog contributes to the maintenance of various tick-borne diseases in natural cycles urban and suburban areas. Parasit Vectors. 2017;10:134.
Hofmeester TR, Krawczyk AI, van Leeuwen AD, Fonville M, Montizaan MGE, van den Berge K, et al. Role of mustelids in the life-cycle of ixodid ticks and transmission cycles of four tick-borne pathogens. Parasit Vectors. 2018;11:600.
Hing M, Woestyn S, Van Bosterhaut B, Desbonnet Y, Heyman P, Cochez C, et al. Diagnosis of human granulocytic anaplasmosis in Belgium by combining molecular and serological methods. New Microbes New Infect. 2014;2:177–8.
Hovius E, de Bruin A, Schouls L, Hovius J, Dekker N, Sprong H. A lifelong study of a pack Rhodesian ridgeback dogs reveals subclinical and clinical tick-borne Anaplasma phagocytophilum infections with possible reinfection or persistence. Parasit Vectors. 2018;11:238.
Jahfari S, Hofhuis A, Fonville M, van der Giessen J, van Pelt W, Sprong H. Molecular detection of tick-borne pathogens in humans with tick bites and erythema migrans, in the Netherlands. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016;10:e0005042.
Krawczyk AI, van Leeuwen A, Jacobs-Reitsma W, Wijnands LM, Bouw E, Jahfari S, et al. Presence of zoonotic agents in engorged ticks and hedgehog faeces from Erinaceus europaeus in (sub) urban areas. Parasit Vectors. 2015;8:210.
Hofmeester TR, Jansen PA, Wijnen HJ, Coipan EC, Fonville M, Prins HHT, et al. Cascading effects of predator activity on tick-borne disease risk. Proc Biol Sci. 2017;284:20170453.
Sprong H, Tijsse-Klasen E, Langelaar M, De Bruin A, Fonville M, Gassner F, et al. Prevalence of Coxiella burnetii in ticks after a large outbreak of Q fever. Zoonoses Public Health. 2012;59:69–75.
Stigum VM, Jaarsma RI, Sprong H, Rolandsen CM, Mysterud A. Infection prevalence and ecotypes of Anaplasma phagocytophilum in moose Alces alces, red deer Cervus elaphus, roe deer Capreolus capreolus and Ixodes ricinus ticks from Norway. Parasit Vectors. 2019;12:1.
Kazimírová M, Hamšíková Z, Špitalská E, Minichová L, Mahríková L, Caban R, et al. Diverse tick-borne microorganisms identified in free-living ungulates in Slovakia. Parasit Vectors. 2018;11:495.
Santos AS, de Bruin A, Veloso AR, Marques C, da Fonseca I, de Sousa R, et al. Detection of Anaplasma phagocytophilum, Candidatus Neoehrlichia sp, Coxiella burnetii and Rickettsia spp in questing ticks from a recreational park, Portugal. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2018;9:1555–64.
Szekeres S, van Leeuwen A, Tóth E, Majoros G, Sprong H, Földvári G. Road-killed mammals provide insight into tick-borne bacterial pathogen communities within urban habitats. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2019;66:277–86.
Szekeres S, Coipan EC, Rigó K, Majoros G, Jahfari S, Sprong H, et al. Candidatus Neoehrlichia mikurensis and Anaplasma phagocytophilum in natural rodent and tick communities in Southern Hungary. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2015;6:111–6.
Földvári G, Jahfari S, Rigó K, Jablonszky M, Szekeres S, Majoros G, et al. Candidatus Neoehrlichia mikurensis and Anaplasma phagocytophilum in urban hedgehogs. Emerg Infect Dis. 2014;20:496–8.
de Bruin A, van Leeuwen AD, Jahfari S, Takken W, Földvári M, Dremmel L, et al. Vertical transmission of Bartonella schoenbuchensis in Lipoptena cervi. Parasit Vectors. 2015;8:176.
Overzier E, Pfister K, Thiel C, Herb I, Mahling M, Silaghi C. Anaplasma phagocytophilum in questing Ixodes ricinus ticks: comparison of prevalences and partial 16S rRNA gene variants in urban, pasture, and natural habitats. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013;79:1730–4.
Silaghi C, Nieder M, Sauter-Louis C, Knubben-Schweizer G, Pfister K, Pfeffer M. Epidemiology, genetic variants and clinical course of natural infections with Anaplasma phagocytophilum in a dairy cattle herd. Parasit Vectors. 2018;11:20.
Schouls LM, Van De Pol I, Rijpkema SG, Schot CS. Detection and identification of Ehrlichia, Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato, and Bartonella species in Dutch Ixodes ricinus ticks. J Clin Microbiol. 1999;37:2215–22.
Courtney JW, Kostelnik LM, Zeidner NS, Massung RF. Multiplex real-time PCR for detection of Anaplasma phagocytophilum and Borrelia burgdorferi. J Clin Microbiol. 2004;42:3164–8.
Alberti A, Zobba R, Chessa B, Addis MF, Sparagano O, Pinna Parpaglia ML, et al. Equine and canine Anaplasma phagocytophilum strains isolated on the Island of Sardinia (Italy) are phylogenetically related to pathogenic strains from the United States. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005;71:6418–22.
Wolfram Research, Inc. Mathematica, version 11.3. Champaign, IL, USA: Wolfram Research, Inc; 2018.
Bastian M, Heymann S, Jacomy M. Gephi: an open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. In: International AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media; 2009. gephi.org. Accessed 1 Feb 2019.
Bastolla U, Fortuna MA, Pascual-García A, Ferrera A, Luque B, Bascompte J. The architecture of mutualistic networks minimizes competition and increases biodiversity. Nature. 2009;458:1018.
Csardi G, Nepusz T. The igraph software package for complex network research. InterJournal Complex Systems 1695; 2006.
R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2018.
Estrada-Peña A, Sprong H, Cabezas-Cruz A, de la Fuente J, Ramo A, Coipan EC. Nested coevolutionary networks shape the ecological relationships of ticks, hosts, and the Lyme disease bacteria of the Borrelia burgdorferi (s.l.) complex. Parasit Vectors. 2016;9:517.
Craft ME, Caillaud D. Network models: an underutilized tool in wildlife epidemiology? Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis. 2011;2011:676949.
Faith DP. Conservation evaluation and phylogenetic diversity. Biol Conserv. 1992;61:1–10.
Webb CO, Ackerly D, Mcpeek MA, Donoghue MJ. Phylogenies and community ecology. Annu Rev Ecol Syst. 2002;33:475–505.
Kembel SW, Cowan PD, Helmus MR, Cornwell WK, Morlon H, Ackerly DD, et al. Picante: R tools for integrating phylogenies and ecology. Bioinformatics. 2010;26:1463–4.
Marsot M, Henry PY, Vourc’h G, Gasqui P, Ferquel E, Laignel J, et al. Which forest bird species are the main hosts of the tick, Ixodes ricinus, the vector of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato, during the breeding season? Int J Parasitol. 2012;42:781–8.
de la Fuente J, Estrada-Peña A, Cabezas-Cruz A, Brey R. Flying ticks: anciently evolved associations that constitute a risk of infectious disease spread. Parasit Vectors. 2015;8:538.
Dinnis R, Seelig F, Bormane A, Donaghy M, Vollmer S, Feil E, et al. Multilocus sequence typing using mitochondrial genes (mtMLST) reveals geographic population structure of Ixodes ricinus ticks. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014;5:152–60.
Estrada-Peña A, Naranjo V, Acevedo-Whitehouse K, Mangold AJ, Kocan KM, de la Fuente J. Phylogeographic analysis reveals association of tick-borne pathogen, Anaplasma marginale, MSP1a sequences with ecological traits affecting tick vector performance. BMC Biol. 2009;7:57.
Santos AS, Santos-Silva MM. Ixodes ventalloi Gil Collado, 1936: a vector role to be explored. London: Intechopen; 2018. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.81615.
Estrada-Peña A, Venzal JM, Nava S. Redescription, molecular features, and neotype deposition of Rhipicephalus pusillus Gil Collado and Ixodes ventalloi Gil Collado (Acari, Ixodidae). Zootaxa. 2018;4442:262–76.
Estrada-Peña A, Villar M, Artigas-Jeronimo S, López V, Alberdi P, Cabezas-Cruz A, et al. Use of graph theory to characterize human and arthropod vector cell protein response to infection with Anaplasma phagocytophilum. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018;8:265.
de la Fuente J, Estrada-Peña A, Cabezas-Cruz A, Kocan KM. Anaplasma phagocytophilum uses common strategies for infection of ticks and vertebrate hosts. Trends Microbiol. 2016;24:173–80.
Nylin S, Agosta S, Bensch S, Boeger WA, Braga MP, Brooks DR, et al. Embracing colonizations: a new paradigm for species association dynamics. Trends Ecol Evol. 2018;33:4–14.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Zuzana Hamsikova who processed a large set of DNA samples for the groEl gene fragment from questing ticks from Slovakia, Germany and the Czech Republic and vertebrate hosts from Slovakia. We thank Sándor Szekeres for contributing to sample collection and laboratory work with the Hungarian samples. Furthermore, we are grateful to Lianne Smink, Sacha Trim, Ilse Schutte and Nikita Burggraaf for their help with collecting questing ticks and field samples from sheep in The Netherlands, and Natashja Buijs for collecting tissue samples from Dutch wildlife.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Dutch Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport (VWS), the ERD Funds (CePaViP 16_019/0000759) and by the Czech Grant Agency (17-16009S), and by the Grant 17896-4/2018/FEKUTSTRAT of the Hungarian Ministry of Human Capacities and the grant “In the light of evolution: theories and solutions” (GINOP-2.3.2-15-2016-00057). The Swedish ‘Alvins fond’ funded small mammal sampling close to Umeå, Sweden.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HS and AE-P initiated the study. All authors contributed to data and sample collection. RIJ performed the DNA extraction, qPCR and preparation of data for sequencing under supervision of HS. RIJ analysed the sequences and compiled the dataset. AE-P, RIJ and KT analysed the data. RIJ, AE-P and HS wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was carried out according to the national animal welfare regulations of each country from which samples were derived.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Additional files
Additional file 1: Table S1.
The dataset including all haplotypes recorded in this study, with details on the source of isolate (tick or vertebrate), the phylogenetic cluster in which it is classified and the complete sequence of the fragment.
Additional file 2: Figure S1.
The complete network of haplotypes of A. phagocytophilum with labels for every node, including the number of haplotype, carriers (ticks or vertebrates) and geographical origin. Symbols and colours in the network are identical to those in Fig. 2.
Additional file 3: Figure S2.
The geographical distribution (countries) recorded so far for the phylogenetic clusters of haplotypes of A. phagocytophilum.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Jaarsma, R.I., Sprong, H., Takumi, K. et al. Anaplasma phagocytophilum evolves in geographical and biotic niches of vertebrates and ticks. Parasites Vectors 12, 328 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-019-3583-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-019-3583-8