Abstracts
Background
The aim of this study was to systematically evaluate the diagnostic performance of nCD64 for neonatal sepsis.
Methods
Computer retrieval was conducted for the databases of PubMed, Embase, and Springer databases up to March 18, 2015 to select the relevant studies on nCD64 and neonatal sepsis. Sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio (PLR), negative likelihood ratio (NLR), diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), and 95 % confidence intervals (CI) for diagnostic efficiency of nCD64 were pooled. In addition, the summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve was also conducted based on the sensitivity and specificity.
Results
Seventeen studies including 3478 participants were included in this meta-analysis. The overall pooled sensitivity, specificity, PLR, NLR and DOR were 0.77 (95 % CI: 0.74–0.79), 0.74 (95 % CI: 0.72–0.75), 3.58 (95 % CI: 2.85–4.49), 0.29 (95 % CI: 0.22–0.37) and 15.18 (95 % CI: 9.75–23.62), respectively. In addition, the area under the SROC curve (AUC) was 0.8666, and no threshold effect was found based on the Spearman correlation analysis (P = 0.616). Besides, subgroup analysis showed higher sensitivity, specificity and AUC in term infants and proven infection group than those in preterm infants and clinical infection group, respectively.
Conclusions
The n CD64 expression alone is not a satisfactory marker for diagnosing neonatal sepsis with relatively low sensitivity, specificity, PLR and NLR, in spite of relatively high SROC area. Therefore, the n CD64 expression used in diagnosis of neonatal sepsis should be treated with caution.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Neonatal sepsis is one of the important causes of neonatal mortality. Despite the improvement in management of newborn infant, the mortality caused by neonatal sepsis remains high (~10 %) [1]. It is difficult to diagnose neonatal sepsis during early stage because of the nonspecific and variable clinical symptoms. Blood culture is the current golden standard for confirming the neonatal sepsis. However, the results of blood culture could be available within 24–48 h of culture. Usually, the antibiotics would be discontinued if the blood culture results were negative by 48 h [2, 3]. Moreover, the results are negative in cases with meningitis and pneumonia [4]. There is a high false-negative rate of blood culture [5]. Therefore, considering the limitations of blood culture in neonatal sepsis diagnosis, new biomarkers for early and rapid diagnosis of neonatal sepsis should be developed.
Recently, neutrophil CD64 (nCD64) has been reported as a diagnostic marker of neonatal sepsis, because nCD64 expression is stable for 24 h and can be detected rapidly by flow cytometer with minimal blood volumes [6]. However, the diagnostic accuracy of nCD64 remains unclear due to the large range of sensitivity (0.26–0.95) and specificity (0.62–0.97) in different individual studies [7–9]. Although a meta-analysis has been conducted by Jia et al. in 2013 [10], they combined the results of median monocyte/nCD64 ratio with nCD64 expression, which might be a source of heterogeneity. In addition, recently new individual studies [11, 12] on this topic have reported conflicting results with Jia et al. [10]. Thus, there is a need to update the exploration.
In this study, we performed an updated meta-analysis to systematically evaluate the diagnostic performance of nCD64 for neonatal sepsis.
Methods
Because the data of this manuscript come from the public databases and previous studies, it is not applicable to receive the ethics committee approval or follow the Declaration of Helsinki, and there is no need to get informed consent of patients.
Search strategy
We systematically searched the PubMed, Embase and Springer databases up to 18 March, 2015 with the following search terms: (septicemia or septicaemia or sepsis or infection) and (neutrophil CD64 or nCD64). We also manually searched the printed articles, and the references of the reviews and the included studies.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The studies were included if they met the following criteria: 1) exploring the diagnostic value of the nCD64 for sepsis; 2) reporting the babies within 28 days of birth; 3) providing the golden standard of blood culture; 4) giving the number of true positive (TP), false positive (FP), true negative (TN) and false negative (FN).
The following studies were excluded: 1) the studies were written in a language other than English; 2) reviews, letters and reports.
Data extraction and quality assessment
Two investigators independently extracted the following data using a standard form: name of the first author, publication year, study region, diagnostic golden standard, detection method and cut-off value of nCD64, TP, FP, TN and FN. They exchanged the form after filling out the data extraction. Discrepancies were solved by discussing with each other.
The quality of the included studies was assessed by using a 14-item Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies (QUADAS) list [13]. Each item was descriptively assessed with yes, unclear or no and scored by 1, 0, -1, respectively [14]. Total scores were produced by plus the scores of each item.
Statistical analysis
The statistical analysis was performed using Meta-disc software (version 1.4) [15]. The sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio (PLR), negative likelihood ratio (NLR), diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) and 95 % confidence interval (CI) for diagnostic efficiency of nCD64 were pooled. The heterogeneity among studies was evaluated by Cochran Q test and I 2 statistic [16]. P < 0.05 or I 2 > 50 % was considered statistically significant and a random effects model was used for pooling the data; otherwise, a fixed effect model was utilized. The summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve was also conducted based on the sensitivity and specificity. The area under the curve (AUC) close to 1 indicated a good diagnostic performance of nCD64 [17]. Threshold effect was assessed using Spearman correlation analysis, and P < 0.05 indicated a significant threshold effect [18]. Subgroup analyses based on the diagnosis standard for infection (clinical or proven infection), type of sepsis (early-onset or late-onset), infants (preterm or term) were conducted. Clinical infection means infection suspected on a clinical basis whereas proven infection means culture proven infections with an identified microorganism. In addition, a meta-regression analysis was conducted based on the above variances to explore the sources of heterogeneity.
Results
Study selection
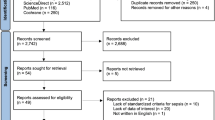
The process of the study selection is shown in Fig. 1. We identified 1,245 studies by the initial search (Embase: 533, PubMed: 225, Springer: 487). Firstly, 211 duplicate studies were removed. Then, by reviewing titles and abstracts, 1,013 studies that did not meet the inclusion criteria were ruled out. In addition, 2 reviews and 2 studies including children population were precluded by reading full-texts. Finally, 17 studies [7–9, 11, 12, 19–30] were included in this meta-analysis.
Characteristics of the included studies
The characteristics of the 17 included studies were listed in Table 1. There were totally 3478 participants involved in this meta-analysis. Nine of the included studies distributed in Asia, 2 in Europe, 5 in America and 1 in Africa. The diagnostic golden standard included clinical test, hematological and biochemical laboratory investigations, and microbiological test-blood culture. The expression of nCD64 was assessed by flow cytometry. As shown in Table 2, the quality of the included studies was relatively high, because most of the total scores ≥ 10.
Pooled analysis
As shown in Fig. 2, the pooled sensitivity and specificity were 0.77 (95 % CI: 0.74–0.79) and 0.74 (95 % CI: 0.72–0.75), respectively. The pooled PLR and NLR were 3.58 (95 % CI: 2.85–4.49) and 0.29 (95 % CI: 0.22–0.37), respectively (Fig. 3). In addition, the pooled DOR was 15.18 (95 % CI: 9.75–23.62, Fig. 4). For all above effect sizes, significant heterogeneities were observed (P < 0.001, I 2 > 50 %). From the SROC in Fig. 4, AUC was 0.8666, and no threshold effect was found based on the Spearman correlation analysis (P = 0.616).
Subgroup analysis
The results of subgroup analyses are summarized in Table 3. Higher sensitivity, specificity, PLR, DOR, AUC and Q*, and lower NLR were observed in the proven infection group (0.82, 0.74, 4.14, 30.58, 0.9136 and 0.8461, and 0.17) compared with those in clinical infection group (0.74, 0.66, 2.19, 6.98, 0.8245 and 0.7576, and 0.39). Slightly higher specificity, PLR and NLR, while lower sensitivity, DOR, AUC, and Q were found in the early-onset sepsis, compared with those in the late-onset sepsis. There were higher sensitivity, specificity, PLR and DOR, and lower NLR in term infants (0.80, 0.85, 5.75 and 24.07, and 0.24) compared with those in preterm infants (0.74, 0.69, 2.76 and 7.83, and 0.37).
Meta-regression analysis
Meta-regression analysis (Table 4) showed that the “infants” was the cause of heterogeneity (P = 0.0147) and other variances were not the sources of heterogeneity (P > 0.05).
Discussion
nCD64 can be detected rapidly by flow cytometer with minimal blood volumes [6] and is reported widely to be used in the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. This meta-analysis showed that the diagnostic performance of nCD64 for neonatal sepsis was not good, because the pooled sensitivity and specificity are not high enough. The PLR and NLR were also not satisfactory. Although the AUC is relatively high, the application of nCD64 for diagnosing neonatal sepsis needs to be cautious.
The pooled sensitivity and specificity of nCD64 were 77 % and 74 %, respectively, which are lower than those of serum procalcitonin (PCT) (81 % and 79 %), although AUC was similar (0.87) [31]. Indicators of nCD64 diagnostic value were lower than CRP (sensitivity 80.8 %, specificity 100 %, AUC 0.90), TNF-α (sensitivity 100 %, specificity 96.6 %, AUC 1) and IL-6 (sensitivity 96.2 %, specificity 89.7 %, AUC 0.97) according data of study of Kocabas E et al. [32]. Compared with the novel marker such as presepsin [33–37], nCD64 also showed a lower diagnostic efficiency. Thus, our results indicate that the nCD64 should not be used as a diagnostic marker alone for neonatal sepsis. It can be combined with other diagnostic methods like serum PCT [38] and hematologic scoring system (sensitivity 93 %; specificity 82 %) [39] to improve the diagnostic accuracy. The hematologic scoring system assigns one score for each of seven indexes (abnormal total leukocyte count, abnormal total neutrophil (PMN) count, elevated immature PMN count, elevated immature to total PMN ratio, Immature to mature PMN ratio ≥ 0.3, platelet count ≤ 150,000/mm3, and pronounced degenerative changes in PMNs) with higher scores indicating greater likelihood [39].
The results of the present study are similar with the previous meta-analysis of 12 studies (sensitivity, 78 %; specificity, 81 %; DOR, 21.27; PLR, 4.53; NLR, 0.23; AUC, 0.89.) [10]. Although nCD64 showed relatively high sensitivity and specificity in some included studies with cutoff of 2.3 % [7], 4000 phycoerythrinmolecules bound per cell [9], and 2.6 % [30], respectively, the small sample size and different cut-off may exaggerate the facticity of the results.
nCD64 expressed normally in non-infected neutrophils, but it could be up-regulated by stimulation of bacterial invasion [40]. It has been shown that the expression of nCD64 was not affected by transient tachypnea of the newborn (TTN), respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) and other non-infective perinatal events [21]. nCD64 expression in adults is different from newborn neonates. In adults, the expression of nCD64 may be higher in gram-negative sepsis than in gram-positive sepsis [41]. However, this difference has not been confirmed in neonates [21]. Neonates may have less expressed neutrophil to gram-negative bacteria infection. Furthermore, the expression of nCD64 may also been increased in leucocytes in patients with streptococcal infection [42]. All these lead to the lower power of nCD64 in diagnosis of neonatal sepsis.
Identification of the cut-off value of a diagnostic marker is difficult. If the cut-off value is high, the false positive rate may be overestimated. On the contrary, the low cut-off value may lead to overestimation of the false negative rate. Therefore, an appropriate cut-off value is necessary for improving the diagnostic accuracy of nCD64. In this study, cut-off values of nCD64 in included studies are different. Various cut-offs used in different studies might result in a threshold effect which is a cause of heterogeneity [43]. In the present study, no threshold effect was found based on the Spearman correlation analysis (P = 0.616), indicating that the threshold effect is not a cause of the high heterogeneity. The heterogeneity may be explained by the characteristics of the included patients. Some included neonates have other infections, which can also regulate the expression of nCD64. In addition, combination of studies with proven and clinical sepsis, data from preterm with term infants, and studies with early- and late-onset sepsis may also introduce heterogeneity. Therefore, we conducted the subgroup analysis based on these factors. The results revealed that higher sensitivity, specificity, PLR, AUC and Q* and lower NLR in the proven infection group than those in clinical infection group. There was higher sensitivity, specificity, PLR, DOR and lower NLR in term infants compared with those in preterm infants. No consistent differences in sensitivity, specificity, PLR, NLR, AUC and Q* were found between early-onset and late-onset sepsis. These results indicated that this method is more suitable for term infants than preterm infants, based on proven infection than other clinically suspected infection.
Heterogeneity is a common limitation of meta-analysis, especially in diagnostic meta-analysis. In the present study, meta-regression revealed that types of infants was one cause of the heterogeneity. Although subgroup analysis was performed based on the diagnostic method, types of sepsis (early-onset or late-onset), and preterm or term, the influences of other factors like the cutoff values were not assessed due to the lack of included studies and unavailable data. This reminds the clinical researchers providing more details of the patients in further studies, including the stage and types of neonatal sepsis. In addition, the appropriate and uniform cut-off value of nCD64 should be confirmed in further clinical studies.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the n CD64 expression alone is not a satisfactory marker for diagnosing neonatal sepsis with relatively low sensitivity, specificity, PLR and NLR, in spite of relatively high SROC area. Therefore, the n CD64 expression used in diagnosis of neonatal sepsis should be treated with caution.
References
Bryce J, et al., WHO estimates of the causes of death in children. Lancet. 2005; 365(9465): p. 1147-1152.
Janjindamai W, Phetpisal S. Time to positivity of blood culture in newborn infants. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2006;37(1):171.
Jardine L, Davies MW, Faoagali J. Incubation time required for neonatal blood cultures to become positive. J Paediatr Child Health. 2006;42(12):797–802.
Panero A et al. Interleukin 6 in neonates with early and late onset infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1997;16(4):370–5.
Benitz WE. Adjunct laboratory tests in the diagnosis of early-onset neonatal sepsis. Clin Perinatol. 2010;37(2):421–38.
Buhimschi CS et al. Proteomic biomarkers of intra-amniotic inflammation: relationship with funisitis and early-onset sepsis in the premature neonate. Pediatr Res. 2007;61(3):318–24.
Bhandari V et al. Hematologic profile of sepsis in neonates: neutrophil CD64 as a diagnostic marker. Pediatrics. 2008;121(1):129–34.
Layseca-Espinosa E et al. Expression of CD64 as a potential marker of neonatal sepsis. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2002;13(5):319–27.
Ng PC et al. Neutrophil CD64 expression: a sensitive diagnostic marker for late-onset nosocomial infection in very low birthweight infants. Pediatr Res. 2002;51(3):296–303.
Jia L.-Q, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of neutrophil CD64 expression in neonatal infection: A meta-analysis. J Int Med Res. 2013: 41(3):934-943.
Du J et al. Diagnostic utility of neutrophil CD64 as a marker for early-onset sepsis in preterm neonates. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e102647.
Elawady S et al. Neutrophil CD64 as a diagnostic marker of sepsis in neonates. J Investig Med. 2014;62(3):644–9.
Whiting P et al. The development of QUADAS: a tool for the quality assessment of studies of diagnostic accuracy included in systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2003;3(1):25.
Whiting PF et al. Evaluation of QUADAS, a tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2006;6(1):9.
Zamora J et al. Meta-DiSc: a software for meta-analysis of test accuracy data. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2006;6(1):31.
Higgins JP et al. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. Br Med J. 2003;327(7414):557.
Moses LE, Shapiro D, Littenberg B. Combining independent studies of a diagnostic test into a summary ROC curve: Data‐analytic approaches and some additional considerations. Stat Med. 1993;12(14):1293–316.
Devillé WL et al. Conducting systematic reviews of diagnostic studies: didactic guidelines. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2002;2(1):9.
Streimish I et al. Neutrophil CD64 as a diagnostic marker in neonatal sepsis. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2012;31(7):777–81.
Choo YK et al. Comparison of the accuracy of neutrophil CD64 and C-reactive protein as a single test for the early detection of neonatal sepsis. Korean J Pediatr. 2012;55(1):11–7.
Dilli D et al. Predictive values of neutrophil CD64 expression compared with interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein in early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. J Clin Lab Anal. 2010;24(6):363–70.
Genel F et al. Evaluation of adhesion molecules CD64, CD11b and CD62L in neutrophils and monocytes of peripheral blood for early diagnosis of neonatal infection. World J Pediatr. 2012;8(1):72–5.
Groselj-Grenc M et al. Neutrophil and monocyte CD64 indexes, lipopolysaccharide-binding protein, procalcitonin and C-reactive protein in sepsis of critically ill neonates and children. Intensive Care Med. 2009;35(11):1950–8.
Lam HS et al. Early diagnosis of intra-abdominal inflammation and sepsis by neutrophil CD64 expression in newborns. Neonatology. 2011;99(2):118–24.
Motta M et al. Diagnostic accuracy and prognostic value of the CD64 index in very low birth weight neonates as a marker of early-onset sepsis. Scand J Infect Dis. 2014;46(6):433–9.
Ng PC et al. Neutrophil CD64 is a sensitive diagnostic marker for early-onset neonatal infection. Pediatr Res. 2004;56(5):796–803.
Ng PC et al. Quantitative measurement of monocyte HLA-DR expression in the identification of early-onset neonatal infection. Biol Neonate. 2006;89(2):75–81.
Soni S et al. Evaluation of CD64 expression on neutrophils as an early indicator of neonatal sepsis. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2013;32(1):e33–7.
Streimish I et al. Neutrophil CD64 with hematologic criteria for diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Am J Perinatol. 2014;31(1):21–30.
Zeitoun AA et al. Evaluation of neutrophilic CD64, interleukin 10 and procalcitonin as diagnostic markers of early- and late-onset neonatal sepsis. Scand J Infect Dis. 2010;42(4):299–305.
Vouloumanou E et al. Serum procalcitonin as a diagnostic marker for neonatal sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2011;37(5):747–62.
Kocabas E et al. Role of procalcitonin, C-reactive protein, interleukin-6, interleukin-8 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Turk J Pediatr. 2007;49(1):7–20.
Zou Q, Wen W, Zhang X. Presepsin as a novel sepsis biomarker. World J Emerg Med. 2014;5(1):16–9.
Mussap M et al. Soluble CD14 subtype presepsin (sCD14-ST) and lipopolysaccharide binding protein (LBP) in neonatal sepsis: new clinical and analytical perspectives for two old biomarkers. J Mater Fetal Neonatal Med. 2011;24(sup2):12–4.
Yaegashi Y et al. Evaluation of a newly identified soluble CD14 subtype as a marker for sepsis. J Infect Chemother. 2005;11(5):234–8.
Shozushima T et al. Usefulness of presepsin (sCD14-ST) measurements as a marker for the diagnosis and severity of sepsis that satisfied diagnostic criteria of systemic inflammatory response syndrome. J Infect Chemother. 2011;17(6):764–9.
Endo S et al. Usefulness of presepsin in the diagnosis of sepsis in a multicenter prospective study. J Infect Chemother. 2012;18(6):891–7.
Park IH, Lee SH, Yu ST, et al. Serum procalcitonin as a diagnostic marker of neonatal sepsis.[J]. Korean Journal of Pediatrics, 2014;57(10):451-456.
Rodwell RL, Leslie AL, Tudehope DI. Early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis using a hematologic scoring system. J Pediatr. 1988;112(5):761–7.
Wagle S et al. C‐reactive protein as a diagnostic tool of sepsis in very immature babies. J Paediatr Child Health. 1994;30(1):40–4.
Herra C, Keane C, Whelan A. Increased expression of Fcγ receptors on neutrophils and monocytes may reflect ongoing bacterial infection. J Med Microbiol. 1996;44(2):135–40.
Guyre P et al. Monocytes and polymorphonuclear neutrophils of patients with streptococcal pharyngitis express increased numbers of type I IgG Fc receptors. J Clin Investig. 1990;86(6):1892.
Ling DI, Zwerling AA, Pai M. GenoType MTBDR assays for the diagnosis of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: a meta-analysis. Eur Respir J. 2008;32(5):1165–74.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81000263), National Key Development Program of Clinical Specialties (neonatology) (Grant No. 1311200003303).
Authors’ contributions
JS participated in the design of this study and performed the statistical analysis. DPC carried out the study and collected important background information. JS and DPC drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, J., Tang, J. & Chen, D. Meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy of neutrophil CD64 for neonatal sepsis. Ital J Pediatr 42, 57 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13052-016-0268-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13052-016-0268-1