Abstract
Background
Given the trend toward value-based care, there has been increased interest in minimizing hospital length of stay (LOS) after orthopedic procedures. Outpatient total ankle arthroplasty (TAA) has become more popular in recent years; however, research on surgical outcomes of this procedure has been limited. This study sought to employ large sample, propensity score-matched analyses to assess the safety of outpatient and short-stay discharge pathways following TAA.
Methods
The ACS NSQIP database was used to identify 1141 patients who underwent primary and revision TAA between 2007 and 2017. Propensity score matching was used to match patients based on several factors, including age, sex, body mass index (BMI), American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) classification, and several comorbidities. The incidence of various 30-day complications was compared between the short and standard LOS groups to assess for any differences in short-term outcomes.
Results
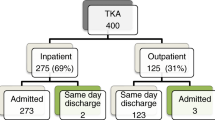
A total of 892 patients were included in the final propensity score-matched analysis, with 446 patients in each group. The short LOS group had a significantly lower rate of medical complications (0.2% vs. 2.5%, p = 0.006) and non-home discharge (1.3% vs. 12.1%, p < 0.001). There was no significant difference in operative complications (0.4% vs. 1.8%, p = 0.107), unplanned readmission (0.4% vs. 1.1%, p = 0.451), reoperation (0.2% vs. 0.4%, p > 0.999), return to the OR (0.2% vs. 0.9%, p = 0.374), or mortality (0.7% vs. 0.0%, p > 0.249) between the short and standard LOS groups.
Conclusions
Outpatient and short-stay hospitalization had comparable safety to standard inpatient hospitalization after TAA. Outpatient or short-stay TAA should be considered for patients with low risk of short-term complications.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
As the outcomes of total ankle arthroplasty (TAA) have continued to improve over the last two decades—with the advent of improved third-generation prostheses and refined operative techniques—the number of TAAs performed in the USA has continued to increase [1,2,3]. TAA has the potential to provide substantial improvement in ankle pain and function in patients with end stage ankle arthritis [4,5,6,7]. The benefits of TAA relative to traditional ankle arthrodesis (AA), however, are uncertain and controversial. Some studies have suggested that TAA may provide better long-term pain relief and patient-perceived postoperative function relative to fusion, although others have argued that the two procedures have similar long-term outcomes [8,9,10,11,12]. Nonetheless, ankle replacement has continued to rise in popularity, and the number of providers offering TAA has increased substantially in the last decade [2].
Value-based care and cost minimization continue to be an important factor in modern healthcare delivery. The average postoperative length of stay (LOS) is often used as an indicator of efficiency and value-based care in orthopedic surgery. A substantial percentage of the costs associated with elective joint replacement surgery comes from inpatient hospitalization and subsequent readmissions and/or reoperations [13]. Readmission, in particular, has become an important quality metric tied to reimbursement [14]. Minimizing hospitalization after surgical procedures, where appropriate, has therefore been of increasing importance.
Within the last decade, there has been substantial interest in performing various elective orthopedic procedures in outpatient or short-stay inpatient settings in order to reduce costs and improve patient satisfaction. Much of the research efforts have been dedicated to total hip and knee arthroplasty, given the high disease burden and volume of these procedures performed annually. Several studies have demonstrated substantial cost savings for outpatient and/or short-stay inpatient hospitalization after total knee and hip arthroplasty [15, 16]. However, the findings regarding the risk of short-term complications in patients with shorter hospital stays have been conflicting. Some studies have suggested that outpatient hip and knee arthroplasty may have higher rates of short-term complications relative to inpatient procedures, while others have suggested that there is not a substantial difference in short-term outcome measures between the two groups [17,18,19]. Many of these studies have utilized national databases that provide large enough sample sizes to investigate even the rarest of complications.
Although shorter hospital stays have been investigated for hip and knee arthroplasty, the same cannot be said for TAA, which presents its own unique challenges. Three separate studies have described outpatient TAA with excellent short-term outcomes and minimal complications [20,21,22]. However, these studies all shared the limitation of a small sample size (N < 100), making it difficult to quantify short-term outcomes, particularly rare complications. A population database study of 591 patients undergoing TAA between 2006 and 2015 demonstrated that outpatient TAA did not yield higher rates of short-term complications relative to standard inpatient TAA [23]. However, this study used unadjusted direct comparisons between the outpatient and inpatient cohorts, and the inpatient cohort had substantially more operative risk factors, including older age and higher comorbidity burden, namely, diabetes [23]. Therefore, directly comparing these populations without adjustment likely introduced confounding and sample bias.
To the authors’ knowledge, there have not been any large sample, propensity score-matched analyses to assess outcomes of outpatient or short-stay hospitalization following TAA, while controlling for comorbidities and other confounding variables. Although decreasing LOS has the potential to increase quality of care, minimize costs, and improve patient satisfaction, careful consideration must be taken to avoid complications and readmission. The present study sought to examine risk factors for various short-term complications following TAA and used propensity score matching to compare the risks of these complications in outpatient and short-stay inpatient hospitalization versus standard inpatient hospitalization.
Methods
Sample selection
The American College of Surgeon’s National Surgery Quality Improvement Program (ACS NSQIP) database was queried to identify all patients undergoing TAA between January 1, 2007 and December 31, 2017. Both primary and revision procedures were considered using Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes 27702 and 27703. The ACS NSQIP database reports de-identified patient data and has been deemed HIPPA compliant. The Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Northwestern University approved this study as a retrospective cohort study.
The data provided in the ACS NSQIP database have been extensively investigated in various surgical fields, often to determine the incidence of short-term complications, identify risk factors for adverse short-term outcomes, and risk stratify patients for various procedures [24,25,26,27]. ACS NSQIP reports over 150 variables, including patient demographics, comorbidities, lifestyle factors, preoperative laboratory values, operative variables, 30-day operative and medical complications, and 30-day disposition outcomes (e.g., return to OR, reoperation, and readmission). Given the substantial number of cases, the database is ideal for assessing low incidence complications after various procedures. ACS NSQIP has been shown to have excellent validity, reliability, and a consistently low rate of reporting error [28,29,30]. Data sampling methodologies at participating institutions are routinely monitored, and interrater reliability audits are regularly performed to ensure data accuracy.
Measures
The total number of TAAs performed was identified for each year between 2011 and 2017. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Games-Howell post-hoc test was used to compare the mean postoperative LOS after TAA for each year. For analysis of outcomes, only data between 2011 and 2017 were considered because 2011 was the first year that ACS NSQIP began reporting certain 30-day outcomes, including unplanned readmission, reoperation, and return to the operating room.
Prior to propensity score matching, several patient variables—sex, age group, race/ethnicity, BMI classification, ASA classification, and comorbidities (diabetes, smoking, COPD, congestive heart failure, hypertension, dialysis, chronic steroid use)—were compared for patients with outpatient or short-stay hospitalization (LOS ≤ 1 day) versus standard inpatient hospitalization (LOS > 1 day). Pearson’s chi-squared test or Fisher’s exact test, where appropriate, were used to compare these categorical variables and various 30-day outcome measures between the two samples, including non-home discharge, mortality, return to the OR, readmission, reoperation, operative complications (surgical site infection, dehiscence, bleeding), and medical complications (wound infection, pneumonia, reintubation, failure to wean intubation, pulmonary embolism, renal insufficiency, renal failure, urinary tract infection, cerebral vascular accident, cardiac arrest, myocardial infarction, deep venous thrombosis, systemic sepsis, septic shock).
Propensity score matching and statistical analysis
Propensity score matching was used to control for the differences in both modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors between the two disposition groups (LOS ≤ 1 day and LOS > 1 day). Specifically, patients from the two groups were paired in a 1:1 manner using a balanced, nearest neighbor approach based on the following variables: sex, age, BMI, ASA classification, and comorbidities (diabetes, smoking, COPD, CHF, hypertension, and chronic steroid use). All categorical variables (sex, ASA classification, and comorbidities) were matched exactly between the two groups. Continuous variables (age and BMI) were matched with a pre-defined tolerance of ± 10 years and ± 5 kg/m2, respectively. Additionally, age was divided into five groups: under 50, between 50 and 59, between 60 and 69, between 70 and 79, and 80 and over. BMI was divided into six groups: underweight (BMI < 18.5), normal (BMI 18.5 to 24.9), overweight (BMI 25.0 to 29.9), obesity class I (BMI 30.0 to 34.9), obesity class II (BMI 35.0 to 39.9), and obesity class III (BMI ≥ 40.0). After propensity score matching, Pearson’s chi-squared test and, where appropriate, Fisher’s exact test were used to compare the rate of the patient and operative variables described previously to ensure these factors were statistically equivalent between the two groups. Lastly, the same statistical tests described previously were used to compare the rate of the 30-day complications between the matched groups. All statistical analyses were completed using IBM SPSS Version 24 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY). The criterion for statistical significance was set at p ≤ 0.05.
Results
A total of 1231 TAA procedures (106 revision TAA and 1125 primary TAA) were identified in the ACS NSQIP database between 2007 and 2017. The total number of procedures reported in the ACS NSQIP database increased significantly over the decade (4 in 2007 to 286 in 2017). Additionally, the average postoperative LOS following TAA surgery decreased between 2011 and 2017 (Fig. 1). In the final analysis, 1141 TAA procedures (106 revision TAA and 1035 primary TAA) were included from years 2011 through 2017. Data prior to this period were excluded because 30-day outcomes were not reported until 2011. The majority of patients were between 60 and 79 years old (63.9%), white (74.7%), overweight or obese (85.8%), and had an ASA score of 2 or 3 (93.9%). A substantial minority had one or more reported comorbidity (12.4% with diabetes, 8.1% with active smoking, and 5.1% with chronic steroid use).
Patients with shorter LOS after TAA (LOS ≤ 1) tended to be younger and healthier overall at baseline (Table 1). This group had more patients between ages 50 and 59 (26.0% vs. 20.9%, p = 0.043), a lower prevalence of diabetes (10.5% vs. 14.3%, p = 0.050), and fewer individuals with an ASA class of 3 (32.2% vs. 43.4%, p < 0.001). However, the short LOS group tended to have higher rates of active smoking (10.0% vs. 6.2%, p = 0.020).
The unmatched data demonstrated that patients with shorter LOS after TAA had better outcomes with fewer complications relative to the standard LOS group (Table 2). Specifically, the short LOS group demonstrated lower rates of non-home discharge (1.4% vs. 14.5%, p < 0.001), operative complications (0.4% vs. 2.1%, p = 0.013), and medical complications (0.4% vs. 2.1%, p = 0.013), particularly urinary tract infections (0.0% vs. 1.4%, p = 0.015).
Table 3 compares the same patient and operative variables summarized in Table 1 after propensity score matching. A total of 892 patients were included in this analysis, with 446 patients per group. After matching, there were no statistically significant differences in sex, age group, BMI group, comorbidities (diabetes, active smoking, COPD, CHF, hypertension, dialysis, and chronic steroid use), ASA classification, or primary vs. revision TAA (ps > 0.05) between the two groups. Table 4 compares the rate of various 30-day complications and outcome measures between the matched groups. The short LOS group had a significantly lower rate of medical complications (0.2% vs. 2.5%, p = 0.006) and non-home discharge (1.3% vs. 12.1%, p < 0.001) relative to the standard LOS group. There was no significant difference in operative complications (0.4% vs. 1.8%, p = 0.107), unplanned readmission (0.4% vs. 1.1%, p = 0.451), reoperation (0.2% vs. 0.4%, p > 0.999), return to the OR (0.2% vs. 0.9%, p = 0.374), or mortality (0.7% vs. 0.0%, p > 0.249) between the short and standard LOS groups.
Discussion
The number of TAA procedures performed in the USA has been increasing given improvements in prostheses, an aging population with a high burden of end-stage arthritis, and increasing provider experience with TAA [1,2,3]. Providing value-based care and optimizing the associated costs of total ankle replacement are, therefore, of significant importance. Additionally, as the average postoperative LOS after TAA continues to decrease, as demonstrated in our results, the potential risk of short-term complications needs to be investigated thoroughly to ensure patient safety.
Although outpatient and short-stay discharge pathways can be used as a tool to decrease costs, these measures must not underscore patient safety. Additionally, these cost savings can be readily countermanded in the event of costly readmissions and reoperations resulting from premature hospital discharge. Notably, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has been utilizing readmission as a surrogate for the quality and efficiency of healthcare delivery, with financial penalties given for above-average risk-adjusted readmission rates for certain conditions [31,32,33]. Therefore, discharge pathways should be optimized to account for the risk of poor short-term outcomes.
A previous study utilizing the ACS NSQIP database demonstrated that outpatient TAA was not associated with a higher incidence of short-term complications relative to inpatient TAA, although this study did not utilize propensity score matching to account for differences in patient-specific risk factors [23]. Given that the patients with shorter hospitalization after elective TAA were younger and healthier in our population-based sample, it is important to control for these potential confounding risk factors. Our study consists of the largest known sample to date that utilized propensity score matching to specifically address the association of hospital LOS and short-term complications following TAA. The data discussed in this study indicate that outpatient and short-stay discharge pathways do not necessarily pose a greater risk of short-term complications than standard inpatient discharge pathways after TAA. These results suggest that shorter hospital stays can reasonably be considered for appropriate patients.
Shortened hospital stays after elective orthopedic procedures have also been associated with excellent patient satisfaction scores [34,35,36]. Although patient-reported outcome data are not collected by the ACS NSQIP database, these measures are another variable to consider when selecting a discharge plan. Additionally, shared decision-making would ideally play an important role in this process, with an emphasis on educating patients regarding common complications and signs that warrant readmission. As more data pertaining to short-term outcomes of TAA become available, these discussions can become more meaningful and evidence-based.
Although the findings in this study are promising, there are certain limitations that should be addressed. Of note, the sample size herein is substantially lower than similar studies assessing more common joint replacement procedures (e.g., hip and knee arthroplasty) [19, 37]. The fact that the incidence of short-term complications after elective TAA was so low further warrants the need for studies with larger sample sizes. Substantially, more cases would be required to risk-stratify individual patients and create a precise decision-making algorithm for different discharge pathways. Additionally, the retrospective nature of this study further limits the level of evidence and conclusions that can be drawn.
Furthermore, there are several patient-specific variables that are not captured within the ACS NSQIP database, but would likely influence decisions regarding postoperative length of stay and discharge. For example, regardless of underlying health conditions, the patient’s baseline activity level and overall independence may influence a decision to pursue outpatient surgery. Other factors include the patient’s comfort level and attitude towards outpatient surgery, their eagerness to return to normal activity, their ability to cooperate and successfully participate in the rehabilitation process, and their home support system (e.g., caretakers, family members, spouse). Each individual’s situation is inherently different, and other factors besides the patient’s overall health are certainly important factors that may influence decision-making.
Future investigations, specifically with larger prospective cohorts, are logical next steps to accurately risk stratify patients and determine the ideal candidate for outpatient or short-stay hospitalization after elective TAA.
Conclusions
The results of this analysis suggest that, after controlling for various risk factors, outpatient and short-stay discharge do not inherently increase the incidence of short-term complications and poor outcomes relative to standard inpatient hospitalization after TAA. The optimal discharge plan following TAA should address both individual and operative risk factors associated with poor short-term outcomes. Short-stay or outpatient TAA can reasonably be considered for low-risk patients. Further investigation, specifically with prospective cohorts, is warranted to improve the current level of evidence regarding this topic.
Availability of data and materials
The American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program and the hospitals participating in the ACS NSQIP are the source of the data used; herein, they have not verified and are not responsible for the statistical validity of the data analysis or the conclusions derived by the authors. The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available in the ACS NSQIP Participant Use Data File repository, https://www.facs.org/quality-programs/acs-nsqip/participant-use.
References
Terrell RD, Montgomery SR, Pannell WC, Sandlin MI, Inoue H, Wang JC, et al. Comparison of practice patterns in total ankle replacement and ankle fusion in the United States. Foot Ankle Int. 2013;34(11):1486–92.
Pugely AJ, Lu X, Amendola A, Callaghan JJ, Martin CT, Cram P. Trends in the use of total ankle replacement and ankle arthrodesis in the United States Medicare population. Foot Ankle Int. 2014;35(3):207–15.
Zhou H, Yakavonis M, Shaw JJ, Patel A, Li X. In-patient trends and complications after total ankle arthroplasty in the United States. J Orthop. 2016;39(1):e74–e9.
Nunley JA, Caputo AM, Easley ME, Cook C. Intermediate to long-term outcomes of the STAR Total Ankle Replacement: the patient perspective. J Bone Joint Surg. 2012;94(1):43–8.
Daniels TR, Mayich DJ, Penner MJ. Intermediate to long-term outcomes of total ankle replacement with the Scandinavian Total Ankle Replacement (STAR). J Bone Joint Surg. 2015;97(11):895–903.
Gougoulias NE, Khanna A, Maffulli N. History and evolution in total ankle arthroplasty. Br Med Bull. 2009;89(1):111–51.
Gougoulias NE, Khanna A, Maffulli N. How successful are current ankle replacements?: A systematic review of the literature. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468:199–208.
Pedowitz D, Kane J, Smith G, Saffel H, Comer C, Raikin S. Total ankle arthroplasty versus ankle arthrodesis: a comparative analysis of arc of movement and functional outcomes. Bone Jnt J. 2016;98(5):634–40.
Wąsik J, Stołtny T, Pasek J, Szyluk K, Pyda M, Ostałowska A, et al. Effect of total ankle arthroplasty and ankle arthrodesis for ankle osteoarthritis: a comparative study. Med Sci Monitor. 2019;25:6797.
Flavin R, Coleman SC, Tenenbaum S, Brodsky JW. Comparison of gait after total ankle arthroplasty and ankle arthrodesis. Foot Ankle Int. 2013;34(10):1340–8.
Dalat F, Trouillet F, Fessy M-H, Bourdin M, Besse J-L. Comparison of quality of life following total ankle arthroplasty and ankle arthrodesis: retrospective study of 54 cases. Orthopaed Traumatol. 2014;100(7):761–6.
Daniels TR, Younger AS, Penner M, Wing K, Dryden PJ, Wong H, et al. Intermediate-term results of total ankle replacement and ankle arthrodesis: a COFAS multicenter study. J Bone Joint Surg. 2014;96(2):135–42.
Bosco JA III, Karkenny AJ, Hutzler LH, Slover JD, Iorio R. Cost burden of 30-day readmissions following Medicare total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(5):903–5.
Siddiqi A, White PB, Mistry JB, Gwam CU, Nace J, Mont MA, et al. Effect of bundled payments and health care reform as alternative payment models in total joint arthroplasty: a clinical review. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(8):2590–7.
Huang A, Ryu J-J, Dervin G. Cost savings of outpatient versus standard inpatient total knee arthroplasty. Can J Surg. 2017;60(1):57.
Aynardi M, Post Z, Ong A, Orozco F, Sukin DC. Outpatient surgery as a means of cost reduction in total hip arthroplasty: a case-control study. HSS J. 2014;10(3):252–5.
Nelson SJ, Webb ML, Lukasiewicz AM, Varthi AG, Samuel AM, Grauer JN. Is outpatient total hip arthroplasty safe? J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(5):1439–42.
Courtney PM, Boniello AJ, Berger RA. Complications following outpatient total joint arthroplasty: an analysis of a national database. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(5):1426–30.
Lovecchio F, Alvi H, Sahota S, Beal M, Manning D. Is outpatient arthroplasty as safe as fast-track inpatient arthroplasty? A propensity score matched analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(9):197–201.
Mulligan RP, Parekh SG. Safety of outpatient total ankle arthroplasty vs traditional inpatient admission or overnight observation. Foot Ankle Int. 2017;38(8):825–31.
Gonzalez T, Fisk E, Chiodo C, Smith J, Bluman EM. Economic analysis and patient satisfaction associated with outpatient total ankle arthroplasty. Foot Ankle Int. 2017;38(5):507–13.
Borenstein TR, Anand K, Li Q, Charlton TP, Thordarson DB. A review of perioperative complications of outpatient total ankle arthroplasty. Foot Ankle Int. 2018;39(2):143–8.
Tedder C, DeBell H, Dix D, Smith WR, McGwin G Jr, Shah A, et al. Comparative analysis of short-term postoperative complications in outpatient versus inpatient total ankle arthroplasty: a database study. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2019;58(1):23–6.
Cima RR, Lackore KA, Nehring SA, Cassivi SD, Donohue JH, Deschamps C, et al. How best to measure surgical quality? Comparison of the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Patient Safety Indicators (AHRQ-PSI) and the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (ACS-NSQIP) postoperative adverse events at a single institution. Surgery. 2011;150(5):943–9.
Pugely AJ, Callaghan JJ, Martin CT, Cram P, Gao Y. Incidence of and risk factors for 30-day readmission following elective primary total joint arthroplasty: analysis from the ACS-NSQIP. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(9):1499–504.
Dhungel B, Diggs BS, Hunter JG, Sheppard BC, Vetto JT, Dolan JP. Patient and peri-operative predictors of morbidity and mortality after esophagectomy: American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (ACS-NSQIP), 2005–2008. J Gastrointest Surg. 2010;14(10):1492–501.
Nelson JA, Fischer JP, Chung CU, West A, Tuggle CT, Serletti JM, et al. Obesity and early complications following reduction mammaplasty: an analysis of 4545 patients from the 2005–2011 NSQIP datasets. J Plastic Surg Hand Surg. 2014;48(5):334–9.
Shiloach M, Frencher SK Jr, Steeger JE, Rowell KS, Bartzokis K, Tomeh MG, et al. Toward robust information: data quality and inter-rater reliability in the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program. J Am Coll Surg. 2010;210(1):6–16.
Huffman KM, Cohen ME, Ko CY, Hall BL. A comprehensive evaluation of statistical reliability in ACS NSQIP profiling models. Ann Surg. 2015;261(6):1108–13.
Sellers MM, Merkow RP, Halverson A, Hinami K, Kelz RR, Bentrem DJ, et al. Validation of new readmission data in the American college of surgeons national surgical quality improvement program. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;216(3):420–7.
Bozic KJ, Grosso LM, Lin Z, Parzynski CS, Suter LG, Krumholz HM, et al. Variation in hospital-level risk-standardized complication rates following elective primary total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 2014;96(8):640–7.
Dailey EA, Cizik A, Kasten J, Chapman JR, Lee MJ. Risk factors for readmission of orthopaedic surgical patients. J Bone Joint Surg. 2013;95(11):1012–9.
Dorr LD, Thomas DJ, Zhu J, Dastane M, Chao L, Long WT. Outpatient total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2010;25(4):501–6.
Husted H, Holm G, Jacobsen S. Predictors of length of stay and patient satisfaction after hip and knee replacement surgery: fast-track experience in 712 patients. Acta Orthop. 2008;79(2):168–73.
Gondusky JS, Choi L, Khalaf N, Patel J, Barnett S, Gorab R. Day of surgery discharge after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: an effective perioperative pathway. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(3):516–9.
Krywulak SA, Mohtadi NG, Russell ML, Sasyniuk TM. Patient satisfaction with inpatient versus outpatient reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament: a randomized clinical trial. Can J Surg. 2005;48(3):201.
Ravi B, Jenkinson R, Austin PC, Croxford R, Wasserstein D, Escott B, et al. Relation between surgeon volume and risk of complications after total hip arthroplasty: propensity score matched cohort study. BMJ. 2014;348:g3284.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank ACS NSQIP for furnishing the data used in this study.
Funding
The present study received no funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The research question, study design, and IRB protocol were developed and executed by MAP, AES, and ARK. MAP and AES queried the data from ACS-NSQIP, performed the propensity score matching, and ran subsequent statistical analyses. MAP was the primary contributor in writing the manuscript. AES and ARK assisted in this role as well. The final manuscript was reviewed and approved by all authors.
Authors’ information
MAP and AES are medical students at the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. AES is also an MBA student at the Kellogg School of Management. ARK is an Associate Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery at the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. ARK is also an attending physician at Northwestern Medicine specializing in foot and ankle surgery.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The present study was approved by the IRB of Northwestern University as a retrospective review using a pre-existing national dataset (IRB ID: STU00210936). Because patients were not directly contacted in this study, consent was not obtained.
Consent for publication
No individual patients were contacted as part of this study. Therefore, patient consent was not directly obtained. ACS NSQIP has provided consent for publication of this manuscript using their data.
Competing interests
ARK receives royalties from Acumed and Depuy/Synthes and serves as a consultant for Arthrex. MAP and AES have no competing interests to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Plantz, M.A., Sherman, A.E. & Kadakia, A.R. A propensity score-matched analysis comparing outpatient and short-stay hospitalization to standard inpatient hospitalization following total ankle arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg Res 15, 292 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-020-01793-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-020-01793-5