Abstract
Background
Although there have been many reports in the genetics of familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) worldwide, studies in regard of Chinese population are lacking. In this multi-center study, we aim to characterize the genetic spectrum of FH in Chinese population, and examine the genotype-phenotype correlations in detail.
Methods
A total of 285 unrelated index cases from China with clinical FH were consecutively recruited. Next-generation sequencing and bioinformatics tools were used for mutation detection of LDLR, APOB and PCSK9 genes and genetic analysis.
Results
Overall, the detection rate is 51.9% (148/285) in the unrelated index cases with a total of 119 risk variants identified including 84 in the LDLR gene, 31 in APOB and 4 in PCSK9 gene. Twenty-eight variants were found in more than one individual and LDLR c.1448G > A (p. W483X) was most frequent one detected in 9 patients. Besides, we found 8 (7 LDLR and 1 APOB) novel variants referred as “pathogenic (or likely pathogenic) variants” according to in silico analysis. In the phenotype analysis, patients with LDLR null mutation had significantly higher LDL cholesterol level than LDLR defective and APOB/PCSK9 mutation carriers and those with no mutations (p < 0.001). Furthermore, 13 double heterozygotes, 16 compound heterozygotes and 5 true LDLR homozygotes were identified and the true LDLR homozygotes had the most severe phenotypes.
Conclusions
The present study confirmed the heterogeneity of FH genetics in the largest Chinese cohort, which could replenish the knowledge of mutation spectrum and contribute to early screening and disease management.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is an inherited disorder mainly caused by the mutation of low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) gene, apolipoprotein B (APOB) gene, or proprotein convertase subtilisin /kexin type 9 (PCSK9) gene in autosomal dominant pattern [1]. The extremely elevated level of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) makes the patients with FH expose to high risk of premature atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) [2]. According to the presence of one or two FH-causing alleles, patients with FH are divided into heterozygotes and homozygotes, whose prevalence was roughly 1 in 200–600 and 1 in 1,000,000 individuals respectively [3].
With the advancement of sequencing technique, the knowledge about molecular basis of FH has been expanded for recent years. Up to now, LDLR gene occupies the majority among the known causative mutations (90–95%), with APOB for 5–10% and PCSK9 for less than 3% [4]. Furthermore, rare proportion of FH is caused by the mutations in the LDLRAP1 gene with two pathological variants in autosomal recessive pattern [5]. To date, more genes including STAP1, APOE, and LIPA have been identified as possible FH-causing genes [6,7,8]. Among them, LDLR gene has acquired comprehensive investigations with an identification of more than 2900 variants in the Leiden Open Variation Database (LVOD) [9]. According to the functional changes, LDLR mutations have been classified into “null” mutations and “defective” mutations [10, 11].
The genotype-phenotype relationship of patients with FH showed high heterogeneity. Previous studies have found that 20–60% of subjects with phenotypic FH did not carry a causative mutation in LDLR, APOB, or PCSK9 genes, which could be explained by multiple small-effect common variants, mutations in unknown FH-associated genes or environmental effect [12,13,14,15,16]. Besides, the phenotypic severity exists on a continuum with a considerable overlap between heterozygous and homozygous FH (including double heterozygotes, compound heterozygotes and true homozygotes), though generally the mean LDL-C level increased as follows: LDLR-negative homozygotes > compound LDLR heterozygotes > LDLR-defective or LDLRAP1 homozygotes > APOB or PCSK9 homozygotes > double heterozygotes > heterozygous FH [17]. In spite of the heterogeneity, genetic diagnosis allows for early diagnosis and intervention for FH patients with the help of cascade screening, especially for the subjects who only meet borderline diagnostic criteria.
The Chinese population is comprised of multiple ethnic groups with distinguish regional distributions. Despite of previous reports in the mainland of China, Hongkong and Taiwan, there are still few systematic studies about molecular basis of Chinese FH population, especially focusing on unrelated index cases [18,19,20]. The aim of the current study is to further characterize the molecular basis of FH in an extended range with unrelated index cases form multiple centers, which could refine the genetic spectrum of FH in China and address the genotype-phenotype correlations.
Materials and methods
Study population
This study consecutively recruited 285 unrelated index cases of clinical FH, among which 279 were adults and 6 were children, from 2011 to 2017 in the division of dyslipidemia of Fuwai Hospital and four other centers. The adult patients were diagnosed with definite or probable FH according to Dutch Lipid Clinic Network (DLCN) criteria with a score ≥ 6. Children who had values of LDL-C above the 95th percentile according to age and gender and family history of high cholesterol and/or premature familial cardiovascular disease were considered to be FH [1].
Our study complied with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the hospital’s ethical review board (Fu Wai Hospital & National Center for Cardiovascular Diseases, Beijing, China). Informed written consents were obtained from all the participants.
Clinical and biochemical examination
Clinical data of each participant were collected by physicians and experienced nurses, including the prior lipid levels and use of lipid-lowering medications, family and personal history of dyslipidemia and coronary artery disease (CAD) as well as presence of tendon xanthoma and corneal arcus. In addition, a standardized physical examination consisted of height (m), weight (kg) and blood pressure was performed for each patient.
After at least 12-h fast, blood samples were collected from cubital vein for biochemical measurements. Serum total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and LDL-C were determined using an enzymatic assay with automatic biochemistry analyzer (Hitachi 7150, Tokyo, Japan). The concentrations of apolipoprotein A (apo A) and apolipoprotein (apo B) were measured by a turbidimetric immunoassay.
Genetic sequencing
Peripheral blood samples were well preserved at − 80 °C until the genomic DNA extraction using a commercial DNA extraction kit (Tiangen Biotech, Beijing, China) with standard procedure. After the detection of DNA purity, the qualified samples were prepared for the targeted next generation sequencing (NGS) covering all the coding exons of LDLR (NM_000527), APOB (NM_000384) and PCSK9(NM_174936) genes. The hybridization reactions were carried out on a AB 2720 Thermal Cycler (Life Technologies Corporation, USA) and then DNA fragments were enriched using SureSelect Target Enrichment Kit (Agilent technologies, Inc., USA). Several libraries were pooled, and then bridge amplification on cBot (Illumina, Inc., San Diego, CA). Finally, the sequencing was performed with an Illumina HiSeq Sequencer (illumine, Inc., San Diego, CA) using the 2 × 150 bps paired-end read module to get the FastQ data.
In silico analysis
The FastQ sequence reads were aligned to the human genome reference sequence (hg19) using the Barrows-Wheeler Aligner (BWA) for analysis. The variants with low coverage depth were excluded for further analysis. The called SNVs/InDEL with high quality were annotated using Annovar program. We defined a “novel variant” if: 1) it had no rsID; 2) it has not been recorded in the public database including Human Gene Mutations Database (HGMD) and ClinVar. For the novel variants, PolyPhen-2, Sorting Tolerant From Intolerant (SIFT) and MutationTaster were used to predict the pathogenicity of them. Combined Annotation Dependent Depletion (CADD), Dann and Eigen were used to assess the deleteriousness of insertion/deletions variants. Furthermore, the novel pathological variants were confirmed by Sanger sequencing. Based on HGVS nomenclature, a “null” LDLR mutation referred to the nonsense, frameshift and large rearrangements while a “defective” LDLR mutation was pathogenic point mutations.
Statistical analysis
All the statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 21.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago Illinois, USA). Continuous variables with normal distribution were presented as mean ± SD and median (Q1–Q3 quartiles) represented continuous but with non-normal distribution variables. Categorical variables were presented as number (percentage). To compare the differences among groups, continuous parameters were analyzed with Student’ s t-test, analysis of variance (ANOVA) or Mann-Whitney U test. Categorical variables were analyzed using chi-square test and Fisher’s exact test if applicable. A p-value < 0.05 was considered significantly different.
Results
Patient characteristics
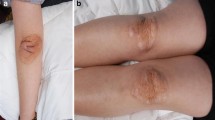
Baseline characteristics of the cohort were shown in Table 1. The mean age of the subjects was 49 ± 12 years old and 61.1% (n = 174) were men. Patients came from all over China while the majority were from northern China. Additionally, a total of 28 patients (9.8%) presented with xanthoma but 81.8% of the subjects had CAD. The average level of TC was 7.03 ± 2.53 mmol/L and LDL-C was 5.22 ± 2.12 mmol/L at enrollment. The majority of the participants (81.1%) were treated with statins and 6.0% were treated with ezetimibe (with statin or alone). The well documented and estimated average level of untreated LDL-C was 7.86 ± 2.25 mmol/L.
Mutation analysis
Overall, we sequenced the LDLR, APOB and PCSK9 genes and identified 137 distinct variants altogether. However, 18 variants without report were predicted to be benign. Thus, we identified 119 distinct risk variants in 148 patients with a detection rate 51.9%. in other word, in 137 patients with a clinical diagnosis of FH, we did not find a mutation. Of the 148 patients with a positive mutation, 77 patients were LDLR heterozygotes (25 with null mutation and 52 with defective mutations, respectively), 33 were APOB mutation carriers and 4 were PCSK9 carriers. Furthermore, 13 double heterozygotes, 16 compound heterozygotes and 5 true LDLR homozygotes were also identified.
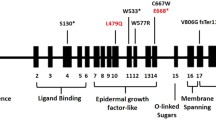
The distribution of types of the 119 risk variants was shown in Fig. 1. In detail, of the 119 distinct variants, 84 were in LDLR gene accounting for 70.59% with 58 nonsynonymous mutations, 8 frameshift mutations, 5 splicing and 13 stopgain mutations. The APOB and PCSK9 variants accounted for 26.05% (31/119) and 3.36% (4/119) respectively. Twenty-eight variants were found in more than one individual and LDLR c.1448G > A (p. W483X) was most frequent one detected in 9 patients. The variants of LDLR distributed on a total of 17 exons with the most frequent ones on exon 4 (n = 19) while APOB variants appeared on the exon 26 most (n = 13) but we also detected variants on other 13 exons.
Besides, we found 8 (7 LDLR and 1 APOB) novel variants referred as “pathogenic variants” according to in silico analysis shown in Table 2. There were two frameshift deletion mutations on the LDLR gene and five nonsynonymous mutations. The only one APOB novel variant was located on exon 26 and was a nonsynonymous one.
Furthermore, we have listed the most common LDLR mutations found in the current study and shown their geographic distributions in Table 3. Three mutations only distributed in the northern regions (c.769C > T; c.1765G > A; c.1864G > T) and the splicing mutation (c.1187-10G > A) was mainly located in the east. The other three mutations (c.1448G > A; c.1879G > A; c.1747C > T) distributed both in the north and south.
Genotype-phenotype correlation
To correlate genotype to phenotype, we compared the clinical characteristics, especially lipid levels, between index cases with different genotypes. Patients carrying LDLR null mutations showed significantly higher lipid levels compared with those carrying LDLR defective mutations, APOB/PCSK9 mutations as well as no mutations (Table 4). Of note, we compared the untreated LDL-C level and found the same results though the group of LDLR null mutations carriers received significantly fewer lipid lowering treatment.
As for the homozygote in regard of genotype, the 5 patients with true LDLR homozygous mutations showed the most severe phenotype at younger age (23 ± 9 vs. 42 ± 14 and 46 ± 12, respectively). They present much more xanthoma and higher level of TC and LDL-C but significantly lower level of HDL-C. Without doubt, double heterozygotes showed a much milder phenotype compared to the compound and true homozygotes (Table 5). Besides, the mutation spectrum was significantly different between patients with DLCN 6–8 score group and DLCN > 8 score group (Fig. 2). The latter had higher positive mutation detection rate with more LDLR and two FH-causing mutations (p < 0.05).
Discussion
In this genetic study, we screened 285 unrelated index cases with clinical definite/probable FH in the three FH-causing genes LDLR, APOB and PCSK9 using NGS. Overall, we got a FH mutation detection rate of 51.9% and found 8 novel variants response for FH in such unrelated index cases. Furthermore, our study also confirmed the genotype –phenotype correlations of FH. To our knowledge, this has been the largest cohort to characterize the genetic spectrum of Chinese population originating from almost the whole mainland China so far.
The detection rate of FH-causing mutations varies depending on the ethnic groups, screening method and diagnostic criteria. In the current study, we identified a positive mutation in 51.9% of the 285 unrelated probands diagnosed with DLCN criteria, which was similar to the previous studies conducted in Singapore, European and Brazilian populations [21,22,23]. With the deepening understanding of genetic basis of FH, studies have demonstrated that the marked elevation of LDL-C was due to far more than the traditional “monogenic FH”. Other reasons that lead to the occurrence of FH includes rare mutations in known FH genes, mutations in a novel gene, polygenic FH secondary to the cumulative effect of LDL-C raising single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), and other acquired phenocopies [24, 25]. Besides, mutations in the gene ABCG5 and ABCG8 could cause sitosterolemia, which may lead to misdiagnosis of FH because of similar phenotypes [26].
Across nations, the molecular spectrum of FH differs significantly. In some European countries, a founder effect exists with the predomination of a few mutations because of the relatively univocal population [27, 28]. While a previous study from central south region of China found only 43 mutations in 219 FH patients [19], the present study identified a total of 119 FH-associated variants in 285 patients and found that the variant LDLR c.1448G > A (p. W483X) presented the highest frequency but with only 9 carriers. The data suggested a high genetic heterogeneity for FH in Chinese population which may attribute to the boarder geographical regions and nationalities. Similar to the previous studies, we also found that mutations in the LDLR gene made up the vast majority and most variants of LDLR located in the exon 4. A systematic review concluded that c.1879G > A, c.1448G > A and c.1864G > T were the primary LDLR mutations in 295 probands from mainland china, which were consistent with the present study [29]. Also, the mutation LDLR c.1747C > T reported most in southern China, Taiwan and Singapore was also common in the patients from northern China in our study [30]. Interestingly, after analyzing the genotype of the compound heterozygotes, we found that 4 probands carried the same alleles: LDLR c.769 C > T(p.R257W) + LDLR c.1765 G > A(p.D589N). Nevertheless, we have also identified the well-known APOB mutation c.10579C > T(p.R3527W) and c.10580G > A(p.R3527Q) but in only one patient respectively. The most common FH-associated APOB variant in the current population was c.4163G > A(p.R1388H), which was previously reported in Malaysia [31]. In fact, we found variants in other 13 exons besides exon 26, the most well know mutation cluster in APOB gene, thus the sequencing should cover the entire gene. Furthermore, we also detected 4 distinct variants in the PCSK9 gene which needed more functional studies with less descriptions before in Chinese population.
Nine novel “pathogenic” or “likely pathogenic” mutations have been identified in this study with seven in LDLR gene and one in APOB gene. In detail, five novel mutations are encoded in the ligand binding domain of LDLR, which is important for the binding of LDL to the receptor [32]. Another two novel mutations are located in the EGF-like domain of LDLR and may affect the receptor dissociation in endocytosis and recycling to the cell surface [32]. The APOB mutation was located in the exon 26, the proposed LDL-receptor-binding domain, and may affect the process of endocytosis [33].
Not surprisingly, the severity of phenotype varies across the genotype. Mounting evidence have demonstrated that carriers of LDLR mutation, especially those with LDLR null mutation, had the highest lipid levels in patients with heterozygous FH, which is in agreement with the present study [34, 35]. Furthermore, the phenotype of homozygous and compound heterozygous LDLR mutation carriers overlaps to a large extent with worse manifestations. But the double heterozygotes, usually combination of LDLR and APOB/PCSK9 mutation, are suspected to have an intermediate phenotype because of the milder phenotype of APOB/PCSK9 carriers [36, 37]. In the current study, we found that patients with double heterozygous FH had relatively lower lipid levels. Of note, the representation of the date may be weakened by the small sample size.
There are limitations in our study. First, despite the greatest cohort from multiple centers in mainland China at present, it still cannot represent the precise genetic spectrum of Chinese population because of the unawareness and underdiagnoses of FH in China. Second, partial untreated LDL-C levels were not available and we estimated them by correction factors according to treatment potency [38]. Third, we were not able to perform co-segregation and functional analysis in patients with novel variants.
Conclusion
In summary, the current study replenished the knowledge of mutation spectrum of FH in China and further confirmed the heterogeneity of FH genetics and genotype-phenotype correlations in Chinese population. Data could help design a nationwide future screening plan to fill the gap of genetic basis of FH in China and further promote early screening and disease management.
Abbreviations
- APOB:
-
Apolipoprotein B
- ASCVD:
-
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
- CAD:
-
Coronary artery disease
- DLCN:
-
Dutch Lipid Clinic Network
- FH:
-
Familial hypercholesterolemia
- HDL-C:
-
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- LDL-C:
-
Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- LDLR:
-
Low-density lipoprotein receptor
- NGS:
-
Next generation sequencing
- PCSK9:
-
Proprotein convertase subtilisin /kexin type 9
- TC:
-
Total cholesterol
- TG:
-
Triglyceride
References
Nordestgaard BG, Chapman MJ, Humphries SE, et al. Familial hypercholesterolaemia is underdiagnosed and undertreated in the general population: guidance for clinicians to prevent coronary heart disease: consensus statement of the European Atherosclerosis Society. Eur Heart J. 2013;34:3478–90a.
Goldberg A, Hopkins P, Toth P, et al. Familial hypercholesterolemia: screening, diagnosis and management of pediatric and adult patients: clinical guidance from the National Lipid Association Expert Panel on Familial Hypercholesterolemia. J Clin Lipidol. 2011;5:S1–8.
Santos RD, Gidding SS, Hegele RA, et al. Defining severe familial hypercholesterolaemia and the implications for clinical management: a consensus statement from the international atherosclerosis society severe familial hypercholesterolemia panel. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016;4:850–61.
Benn M, Watts GF, Tybjaerg-Hansen A, Nordestgaard BG. Mutations causative of familial hypercholesterolaemia: screening of 98 098 individuals from the Copenhagen general population study estimated a prevalence of 1 in 217. Eur Heart J. 2016;37:1384–94.
Spina R, Noto D, Barbagallo CM, et al. Genetic epidemiology of autosomal recessive hypercholesterolemia in Sicily: identification by next-generation sequencing of a new kindred. J Clin Lipidol. 2018;12:145–51.
Amor-Salamanca A, Castillo S, Gonzalez-Vioque E, et al. Genetically confirmed familial hypercholesterolemia in patients with acute coronary syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70:1732–40.
Fouchier S, Dallinga-Thie G, Meijers J, et al. Mutations in STAP1 are associated with autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia. Circ Res. 2014;115:552–5.
Marduel M, Ouguerram K, Serre V, et al. Description of a large family with autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia associated with the APOE p.Leu167del mutation. Hum Mutat. 2013;34:83–7.
Leigh S, Futema M, Whittall R, et al. The UCL low-density lipoprotein receptor gene variant database: pathogenicity update. J Med Genet. 2017;54:217–23.
Alonso R, Mata N, Castillo S, et al. Cardiovascular disease in familial hypercholesterolaemia: influence of low-density lipoprotein receptor mutation type and classic risk factors. Atherosclerosis. 2008;200:315–21.
Santos PC, Morgan AC, Jannes CE, et al. Presence and type of low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) mutation influences the lipid profile and response to lipid-lowering therapy in Brazilian patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis. 2014;233:206–10.
Bañares V, Corral P, Medeiros A, et al. Preliminary spectrum of genetic variants in familial hypercholesterolemia in Argentina. J Clin Lipidol. 2017;11:524–31.
Sharifi M, Walus-Miarka M, Idzior-Waluś B, et al. The genetic spectrum of familial hypercholesterolemia in South-Eastern Poland. Metab Clin Exp. 2016;65:48–53.
Grenkowitz T, Kassner U, Wühle-Demuth M, et al. Clinical characterization and mutation spectrum of German patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis. 2016;253:88–93.
Durst R, Ibe U, Shpitzen S, et al. Molecular genetics of familial hypercholesterolemia in Israel-revisited. Atherosclerosis. 2017;257:55–63.
Tichy L, Freiberger T, Zapletalova P, et al. The molecular basis of familial hypercholesterolemia in the Czech Republic: spectrum of LDLR mutations and genotype-phenotype correlations. Atherosclerosis. 2012;223:401–8.
Cuchel M, Bruckert E, Ginsberg H, et al. Homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia: new insights and guidance for clinicians to improve detection and clinical management. A position paper from the Consensus Panel on Familial Hypercholesterolaemia of the European Atherosclerosis Society. Eur Heart J. 2014;35:2146–57.
Hu M, Lan W, Lam CW, et al. Heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia in Hong Kong Chinese. Study of 252 cases. Int J Cardiol. 2013;167:762–7.
Xiang R, Fan LL, Lin MJ, et al. The genetic spectrum of familial hypercholesterolemia in the central south region of China. Atherosclerosis. 2017;258:84–8.
Chiou KR, Charng MJ. Common mutations of familial hypercholesterolemia patients in Taiwan: characteristics and implications of migrations from Southeast China. Gene. 2012;498:100–6.
Pek SLT, Dissanayake S, Fong JCW, et al. Spectrum of mutations in index patients with familial hypercholesterolemia in Singapore: single center study. Atherosclerosis. 2017;269:106–16.
Mollaki V, Progias P, Drogari E. Familial hypercholesterolemia in Greek children and their families: genotype-to-phenotype correlations and a reconsideration of LDLR mutation spectrum. Atherosclerosis. 2014;237:798–804.
Jannes C, Santos R, de Souza Silva P, et al. Familial hypercholesterolemia in Brazil: cascade screening program, clinical and genetic aspects. Atherosclerosis. 2015;238:101–7.
Sjouke B, Defesche JC, de Randamie JSE, et al. Sequencing for LIPA mutations in patients with a clinical diagnosis of familial hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis. 2016;251:263–5.
Kwon M, Han SM, Kim DI, et al. Evaluation of polygenic cause in Korean patients with familial hypercholesterolemia - a study supported by Korean Society of Lipidology and Atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 2015;242:8–12.
Brinton EA, Hopkins PN, Hegele RA, et al. The association between hypercholesterolemia and sitosterolemia, and report of a sitosterolemia kindred. J Clin Lipidol. 2018;12:152–61.
Kusters DM, Huijgen R, Defesche JC, et al. Founder mutations in the Netherlands: geographical distribution of the most prevalent mutations in the low-density lipoprotein receptor and apolipoprotein B genes. Neth Hear J. 2011;19:175–82.
Gudnason V, Sigurdsson G, Nissen H, Humphries SE. Common founder mutation in the LDL receptor gene causing familial hypercholesterolaemia in the Icelandic population. Hum Mutat. 1997;10:36–44.
Jiang L, Sun LY, Dai YF, et al. The distribution and characteristics of LDL receptor mutations in China: a systematic review. Sci Rep. 2015;5:17272.
Chiou KR, Charng MJ. Genetic diagnosis of familial hypercholesterolemia in Han Chinese. J Clin Lipidol. 2016;10:490–6.
Lye SH, Chahil JK, Bagali P, et al. Genetic polymorphisms in LDLR, APOB, PCSK9 and other lipid related genes associated with familial hypercholesterolemia in Malaysia. PLoS One. 2013;8:e60729.
Gent J, Braakman I. Low-density lipoprotein receptor structure and folding. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004;61:2461–70.
Boren J, Ekstrom U, Agren B, et al. The molecular mechanism for the genetic disorder familial defective apolipoprotein B100. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:9214–8.
Raal FJ, Sjouke B, Hovingh GK, Isaac BF. Phenotype diversity among patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia: a cohort study. Atherosclerosis. 2016;248:238–44.
Junyent M, Gilabert R, Jarauta E, et al. Impact of low-density lipoprotein receptor mutational class on carotid atherosclerosis in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis. 2010;208:437–41.
Sjouke B, Defesche JC, Hartgers ML, et al. Double-heterozygous autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia: clinical characterization of an underreported disease. J Clin Lipidol. 2016;10:1462–9.
Sanchez-Hernandez RM, Civeira F, Stef M, et al. Homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia in Spain: prevalence and phenotype-genotype relationship. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2016;9:504–10.
Ruel I, Aljenedil S, Sadri I, et al. Imputation of baseline LDL cholesterol concentration in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia on statins or ezetimibe. Clin Chem. 2018;64:355–62.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the staff of the Clinical Laboratory at Fu Wai Hospital for their assistance. The authors also thank all the study investigators, staff, and patients.
Funding
This work was supported by the Capital Health Development Fund (201614035), and CAMS Major Collaborative Innovation Project (2016-I2M-1-011) awarded to Dr. Jian-Jun Li, MD, PhD.
Availability of data and materials
Please contact author for data requests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. SD completed the project, analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. Dr. LJJ designed the study and contributed to critically revising the manuscript. Dr. ZBY and LS contributed to mutation sequencing and data collection, Drs. SNL, HQ, WSL, CYS, GYL, ZCG and WNQ contributed to recruitment of patients. Drs. GY, CCJ and LG contributed to the collections of clinical data, DNA extraction and procedure of laboratory examination. All authors have approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Our study complied with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the hospital’s ethical review board (Fu Wai Hospital & National Center for Cardiovascular Diseases, Beijing, China). Informed written consents were obtained from all the participants.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, D., Zhou, BY., Li, S. et al. Genetic basis of index patients with familial hypercholesterolemia in Chinese population: mutation spectrum and genotype-phenotype correlation. Lipids Health Dis 17, 252 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-018-0900-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-018-0900-8