Abstract
B7-H3 (CD276), a member of the B7 family of proteins, is a key player in cancer progression. This immune checkpoint molecule is selectively expressed in both tumor cells and immune cells within the tumor microenvironment. In addition to its immune checkpoint function, B7-H3 has been linked to tumor cell proliferation, metastasis, and therapeutic resistance. Furthermore, its drastic difference in protein expression levels between normal and tumor tissues suggests that targeting B7-H3 with drugs would lead to cancer-specific toxicity, minimizing harm to healthy cells. These properties make B7-H3 a promising target for cancer therapy.
Recently, important advances in B7-H3 research and drug development have been reported, and these new findings, including its involvement in cellular metabolic reprograming, cancer stem cell enrichment, senescence and obesity, have expanded our knowledge and understanding of this molecule, which is important in guiding future strategies for targeting B7-H3. In this review, we briefly discuss the biology and function of B7-H3 in cancer development. We emphasize more on the latest findings and their underlying mechanisms to reflect the new advances in B7-H3 research. In addition, we discuss the new improvements of B-H3 inhibitors in cancer drug development.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Supporting the immune system to kill cancer cells is a promising treatment strategy in cancer therapy. Immune checkpoints (e.g. PD-1, PD-L1, CTL4) regulate the immune system critical for self-tolerance, preventing autoimmunity, and fighting invading cancer cells [1]. Blocking elements of this checkpoint system has changed the paradigm of cancer therapy and achieved significant success in patient survival [2, 3].
B7-H3 (also known as CD276), a member of the B7 family of immune checkpoint proteins, is highly expressed in cancer cells and activated tumor-infiltrating immune cells, and helps cancer cells to evade the surveillance of cytotoxic T-cells and natural killer cells [4]. Emerging evidence have shown that B7-H3 is involved in tumor proliferation, metastasis, treatment resistance, resulting in poor patient outcome, and hence B7-H3 has emerged as a promising therapeutic target for anti-cancer therapy [5, 6].
Extensive research on B7-H3 has been carried out in the past decade, broadening our understanding of this molecule. In recent several years, new findings on B7-H3 functions and its multifaceted roles in cancer development have been obtained. Here, we provide an overview of the current understanding about B7-H3 and its involvement in the pathogenesis of cancer and potential functions in other health conditions. We put an emphasis on the new developments, including but not limited to the impact of B7-H3 on cancer cell metabolism, senescence, obesity, link to microbiota, cancer cell stemness and posttranslational modification of B7-H3. We also discuss the current trends in drug developments in targeting B7-H3.
The biology of B7-H3
B7 family proteins
The B7 family proteins are a type of integral membrane proteins found on activated antigen-presenting cells and consists of structurally related cell-surface protein ligands that bind to receptors on lymphocytes [7]. B7.1 (CD80) and B7.2 (CD86) are the two major types of B7 proteins, but currently, there are other proteins grouped in the B7 family, including inducible co-stimulator ligand (ICOS-L), and co-inhibitory programmed death-1 ligand (PD-L1), programmed death-2 ligand (PD-L2), B7-H3, and B7-H4 (Table 1).
The B7 family produces a costimulatory or a coinhibitory signal to enhance or decrease the activity of the MHC-TCR signal between the antigen presenting cells (APC) and the T cells. Interaction of B7-family members with costimulatory receptors augments immune responses while interaction with coinhibitory receptors attenuates immune responses [8, 9].
B7-H3 shares 20–27% amino acid identity with other B7 family members [10]. It is a type-I transmembrane protein that primarily functions as a negative immunoregulatory protein, and is overexpressed in various human tumor tissues [4,5,6, 11].
Structure of B7-H3
The basic structure (2Ig form) of B7-H3 contains a single pair of IgV-like and IgC-like immunoglobulin domains, a transmembrane region, and a short highly diverse cytoplasmic tail [12] (Fig. 1). The dominantly expressed form of human 4IgB7-H3 contains tandemly duplicated VC domains with four Ig-like domains [13]. Although human B7-H3 has two isoforms (2IgB7-H3 and 4IgB7-H3), the mouse B7-H3 has only one isoform (2IgB7-H3) [14]. Serine and arginine-rich splicing factor 3 (SRSF3) involves the splicing of B7-H3 by directly binding to its exon 4 and/or 6 [15]. B7-H3 crystallized as an unusual dimer arising from the exchange of the G strands in the IgV domains of partner molecules, which indicates the dynamic nature and plasticity of the immunoglobulin fold [16]
The Cellular Localization of B7-H3
B7-H3 has been observed to be expressed in different cellular compartments and different cancer types may have different B7-H3 localization profiles. Several immunostaining results show B7-H3 was expressed on the cell membrane and in cytoplasm of tumor tissues [17,18,19]. Zanjani S et al. showed a higher cytoplasmic expression of B7-H3 than that of the membranous expression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) [20]. B7-H3 has been reported to be expressed in the nucleus of 30% of colon cancer and the expression of nuclear B7-H3 was associated with poor overall survival. In addition, B7-H3 expression was detected in tumor-associated vasculature and fibroblasts of most colorectal cancer samples [21]. Confocal microscopy of fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) and T cell co-cultures showed localization of B7-H3 in the region of the T cell-FLS contact point [22]. B7-H3 is expressed mainly in the stromal compartment of gastric cancer [23] and it induces exosome secretion. Intracellular upregulation of B7-H3 increases the presence of B7-H3 in exosomes secreted from cancer cells [24].
The distribution and expression of B7-H3 in normal tissues and cancer
B7-H3 is overexpressed in tumor tissues while its expression is low in normal tissues [25]. B7-H3 overexpression and its negative correlation with patient survival has been reported in various malignancies [17, 26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41]. Additionally, B7-H3 is expressed in immune cells; monocytes, dendritic cells, myeloid derived suppresser cells (MDSCs), neutrophils, macrophages, B cells, and activated T cells. Furthermore, B7-H3 is also expressed in normal tissues and body fluids at very low levels, including epithelial cells, pleural effusion, anterior pituitary progenitor cells and human serum [8, 11, 42, 43].
As shown in the Fig. 2, the human B7-H3 mRNA and protein expression levels were analyzed across human tissues using RNA sequencing datasets from the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx), FANTOM5, and The Human Protein Atlas (HPA) project. Combining all three sources showed that B7-H3 mRNA expression level is highest in placental tissue and lowest in cerebellum tissue (Fig. 2A), whereas protein expression of B7-H3, although low compared to tumor tissues, is highest in normal prostate tissue but almost not detectable in muscle tissues (Fig. 2B).

(Source: https://www.proteinatlas.org)
Human B7-H3 expression levels in different tissues. Human B7-H3 mRNA expression(A) and protein expression(B) level across human tissues
Regulation of B7-H3 expression
Differential expression of B7-H3 at protein level suggests that the post-transcriptional regulation is critical for its expression. To this end, different miRNAs bind directly or indirectly to the B7-H3 RNA and regulate its protein expression levels in cancer cells [44]. MicroRNA-199a, miR-128, and microRNA-187 regulate the expression of B7-H3 in different cancers via direct binding to the 3″ UTR of B7-H3 mRNA. In addition, BRD4, ILT-4 and ELK1 regulate B7-H3 expression through PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling and impact B7-H3 at the transcriptional or epigenetic level [45,46,47,48,49,50]. Zhao S et al. also identified that SUPT20H (SP20H) negatively regulates B7-H3 expression while eIF4E positively regulates B7-H3 expression in various cancer cells. Activation of p38 MAPK-eIF4E signaling axis serves as a key regulator of transcription initiation and protein expression of B7-H3 in tumor cells [51]. Recently, B7-H3 gene promotor was found to be hypomethylated in ankylosing spondylitis patients, whereas B7-H3 expression was significantly elevated, suggesting that B7-H3 gene is under epigenetic control [52].
B7-H3 and cancer pathogenesis
B7-H3 and cancer patient outcome
The temporal and spatial overexpression of B7-H3 in a variety of cancers but low in normal tissues indicated the pathological significance of this immune regulatory protein. Its degree of expression and localization in the blood [53,54,55], cerebrospinal fluid(CSF) [56], in exosomes [57, 58], and nucleus [21] has been associated with clinicopathologic features of cancer and patient survival. Crispen et al. reported that enhanced tumor expression of B7-H3 correlates with adverse clinical and pathologic features of clear cell renal cell carcinoma and independently predicts disease progression and cancer-specific death [59].
Moreover, higher expression of B7-H3 is more frequently observed in patients with metastatic cancer than in those with localized cancer. For example, patients with metastatic prostate cancer, high B7-H3 expression was independently associated with high disease-specific mortality and overall mortality rates [34]. This indicates that B7-H3 is involved in cancer metastasis capacity.
In fact, high levels of B7-H3 expression have been found in all the cancer types tested. In a meta-analysis study of 24 observational studies consisting of 4,141 patients, an elevated baseline B7-H3 did significantly correlate with poor overall survival (OS) and recurrence free survival (RFS) across a wide range of tumor types [16]. The study concludes that elevated B7-H3 expression is significantly associated with poor survival in cancer patients. Therefore, although certain earlier studies [60,61,62] reported opposing and inconclusive results about B7-H3 in cancer, numerous studies have demonstrated that the high expression of B7-H3 in various human cancer types correlates with poor patient outcomes, and this molecule has emerged as a promising target for cancer therapy.
Immunologic functions of B7-H3
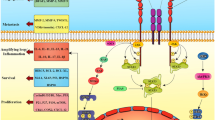
B7-H3 influences immune responses and cancer progression through immunological and non-immunological pathways (64–66). Although the receptor for B7-H3 has not been identified, it is assumed that the activated CD4+ and CD8+ T cells express a receptor that can be recognized by B7-H3 expressed on APC cells or tumor cells [63, 64]. The 2Ig VC and 4Ig VCVC forms of human B7-H3 inhibit T cell proliferation and downregulate cytokine production [16]. Expression of B7-H3 favored an immunosuppressive microenvironment by promoting the production of IL-10, TGF-β1 [65], and inhibiting the activity of CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, γδT cells, CAR-T cells, Vδ2 T cells, Th17 cells, CD3+ T cells, NK cells, macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells, and also inhibiting IFN-γ, IL-2, perforin, granzyme B secretion [66,67,68,69] (Fig. 3).
B7‑H3 regulates the differentiation of tumor‑associated macrophages and promotes the polarization of type 2 macrophages and switching M1 phenotype to the M2 phenotype [70], and B7-H3 also contributes to CCL2–CCR2–M2 macrophage axis-mediated immunosuppression [71]. Moreover, tumor-derived granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) activates neutrophils and induces neutrophil B7-H3 expression via JAK-STAT3 signaling pathway [72], while miR‑34a induces immunosuppression through modulating a SIRT1/NF‑κB/B7‑H3/TNF‑α axis [73]. Furthermore, FOXP3+ regulatory T cells positively associated with B7-H3 expression and resulting an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment [74]. However, some studies reported that patients with high tumoral B7-H3 expression showed increased numbers of immune cells; CD8+ T-cells, CD4+ T cells, natural killer cells, plasmacytoid dendritic cells and interferon-γ production [62, 75].
Non-immune regulatory functions of B7-H3
B7-H3 and tumor proliferation
Cancer is heterogeneous and complex diseases characterized by the development of abnormal cells that divide uncontrollably and can infiltrate and invade normal tissues. The capacity of cancer cells to grow and proliferate is determined by the tumor microenvironment and the cancer cell itself [76]. The role of B7-H3 in the proliferation of cancer cells has been documented in cervical cancer [54], gastric cancer [77] and many other cancer types [78, 79]; whereas in a few studies significant proliferative effect was not observed [80, 81]. In addition to regulating the immunological microenvironment, B7-H3 has been reported to activate signaling pathways such as ERK, PI3K, and Stat3 in cancer cells, which may lead to the accelerated cell proliferation and tumor growth [82, 83] (Fig. 4).
B7-H3 Involvement in angiogenesis and cancer cell metabolism
Angiogenesis is a hallmark of cancer and is intricate in the tumorigenesis of solid tumors. As tumors proliferate and grow, the oxygen availability in the tumor microenvironment decreases and leads to tumor hypoxia. Tumors develop adaptive mechanisms to sustain their growth by activation of hypoxia-inducible factor(HIF) [84], which is the master regulator of the angiogenesis promoting program. Tumor cells can overcome the hypoxic environment by inducing angiogenesis, through the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) [79], a transcriptional target of HIF. B7-H3 is shown to be implicated in angiogenesis in a variety of cancer diseases [79, 85, 86]. B7-H3 promotes angiogenesis by stimulating the secretion of VEGF [87]. In colorectal cancer, using in-vitro and in-vivo experiments, overexpression of B7-H3 promoted tumor angiogenesis by upregulating VEGF expression via activating the NF-κB pathway [79].
The rapidly proliferating cancer cells need metabolic reprogramming to maintain their energy supply. The pathways for nutrient acquisition and preference, synthesis of biomolecules and bioenergetics are reprogrammed such that tumor cells’ proliferation capacity and survival is maintained [88]. Beyond the immune regulation, the B7-H3 protein has been appreciated in non-immune regulatory functions including energy metabolism. B7-H3 is implicated in the regulation of glucose uptake and metabolism in tumor cells. Lim et al. reported that B7-H3 increased the uptake of glucose and lactate production [89] which supports the concept of Warburg effect [90].
It has been shown that B7-H3 increases the reactive oxygen species (ROS) production through an unknown mechanism in the cytosol of tumor cells and promotes the stabilization of HIF-1α to increase glycolysis [89]. In consistence with this finding, in the oral squamous cell carcinoma cells, B7-H3 enhanced glycolysis through the upregulation of HIF-1α and its downstream targets including Glut1 through PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway [91]. A decreased expression of B7-H3 has been noted to reduce glycolytic capacity of breast cancer cells [92]. These studies clearly indicate that B7-H3 is involved in cancer metabolic flux and support its pathogenesis.
Effect of B7-H3 on tumor treatment resistance
Enhanced expression of B7-H3 in tumors has been linked with therapeutic resistance, metastasis potential and poor patient prognosis [93,94,95]. The feature of developing treatment resistance poses a huge burden to the cancer patients and is the major factor for poor prognosis.
B7-H3 has been linked to treatment resistance also in cancer cells [92, 96]. Liu et al. showed the effect of B7-H3 on paclitaxel induced cytotoxicity. In their study, breast cancer cell lines were more sensitive to paclitaxel when B7-H3 was silenced which may be associated with the prevention of the activation of the Jak2/Stat3 pathway [97]. In ovarian cancer cell lines, Zhou et al. reported that overexpression of B7-H3 induced the activation the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and up-regulated BCL-2 in protein level, resulting in the sustained growth and chemo-resistance [98]. These studies demonstrate that B7-H3 plays an important role in inducing therapeutic resistance.
New advances of B7-H3 research
B7-H3 and cancer stem cells
Stem cells are defined as cells that have the ability to self-renewal and produce mature cells of a particular tissue through the process of differentiation [99]. Self-renewal is the hallmark property of stem cells in normal and neoplastic tissues. However, the existence of cancer stem cells (CSCs) has been a subject of controversy for several years. Nevertheless, researchers have identified CSCs in cancers including leukemia, breast, colon, prostate, brain, ovarian and pancreatic cancers [100]. Scientists argue that understanding self-renewal mechanisms or pathways of CSCs is critical for better characterization of the phenotypical features of these stem cells. For instance, it has been reported that Wnt pathway plays a critical role in the initiation and maintenance of CSCs [101].
A failure to maintain cellular homeostasis through repair or early removal of the cells harboring gene mutation by the immune system would lead to uncontrollable proliferation of cells. CSCs play a central role in implementing immune evasion mechanisms. These cells, through their immunomodulatory strategies, can protect themselves against immune monitoring and eradication [102]. Because of this characteristics, CSCs are considered to be responsible for metastasis of the disease, treatment failure, recurrence, and unfavorable patient outcome [103]. It has been documented that traditional chemotherapeutic drugs may only kill cancer cells but spare the CSC population and lead to tumor recurrence [104]. Developing therapeutics targeting pathways so as to minimize the disease recurrence and risk of treatment resistance should be a focus of future studies.
B7-H3 has been found to cause enrichment of CSCs. Liu et al. revealed that B7-H3 in stem cell populations were over- expressed as compared to the bulk of the breast cancer cells. They asserted that over- expression of B7-H3 dramatically increased the cancer stem cell pool size. Furthermore, B7-H3 over- expression enriched the CSCs and contributed to drug resistance [105]. In a prostate cancer cells model, B7-H3 was abundantly expressed in prostate cancer stem cells compared to total tumor cell population [106]. Moreover, in HeLa cervical carcinoma cells, it was found that sphere-forming cells expressed various stem cell markers and that these cells also expressed significant amount of B7-H3 [107], indicating that the expression level of B7-H3 positively correlated with the proliferation, self-renewal, and oncogenesis.
Another significant study performed by Wang, C et al., indicated a higher degree of expression of B7-H3 in CSCs of human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Importantly, high expression of B7-H3 helped CSCs escape immune surveillance in HNSCC initiation, progression, and metastasis. Blockage of B7-H3 with monoclonal antibodies eliminated CSCs and inhibited tumor growth and metastasis by enhancing CD8 + T lymphocyte-mediated anti-tumor immunity [108].
Overall, B7-H3, though well documented to be highly expressed in bulk cancer cells, is even higher expressed in CSCs and contributes to the initiation of tumor development, progression, metastasis, and therapeutic resistance.
B7-H3 and cellular senescence
Senescence is the steady process of stopping cell cycle and cellular growth. This process not only contributes to aging and age-related illnesses but also protects cells from not be cancerous [109]. Senescent cells have been observed in diseases such as diabetes, atherosclerosis, diabetes, and cancer [110, 111].
Cellular senescence can be induced by a variety of endogenous and exogenous stress and damage signals which can be accumulated during their lifetime. Telomere shortening, oncogenic stress, nutrient depletion, cancer chemotherapies, and lysosomal or endoplasmic reticulum stress are fairly known as stimuli triggering cellular senescence [112].
Cells of colon cancer, prostate cancer, lymphomas and breast cancer have been observed to show senescence markers during their development [113, 114]. Tumor cell senescence has been appreciated as the homeostatic and protective barrier against tumor initiation and development. Therefore, inducing tumor cell senescence by anticancer interventions may be used as a strategy for cancer treatment [115]. As an immune check point molecule, B7-H3 inhibits cytotoxic immune cells in the tumor microenvironment and contributes to tumor growth. A few studies reported the involvement of B7-H3 in cancer cell senescence. For instance, Lehmann et al. showed that radiation therapy induced senescence was associated with a significantly increased release of exosome-like microvesicles which were enriched with B7-H3 [58].
Wang, R. et al., also reported that higher expression of B7-H3 worsens the resistance to a low-dose doxorubicin-induced senescence in colorectal cancer [116]. They showed that higher expression of B7-H3 prevented cellular senescence and growth arrest through the AKT/TM4SF1/SIRT1 pathway. Importantly, blocking the AKT/TM4SF1/SIRT1 pathway significantly reversed the B7-H3-induced resistance to cellular senescence. These reports indicated a possible involvement of B7-H3 in therapy- induced cancer cell senescence. Therefore, detailed understanding of the role of B7-H3 in cellular senescence is warranted as targeting B7-H3 might be a promising treatment strategy to promote cancer cell senescence.
B7-H3 and adipose tissue, obesity, and diabetes mellitus
Several studies have shown that B7-H3 contributes to the supply of energy for proliferative tumor cells by controlling aerobic glycolysis [117, 118] suggesting its involvement in regulating cellular energy metabolism. The expression of B7-H3 in normal tissues is very low as compared to activated immune cells and cancer cells. However, Picarda et al., (2022) showed that B7-H3 is abundantly expressed in mouse and human adipose tissues, with preferential expression in adipocyte progenitors (APs) [119] (Fig. 5).
Further, they showed that APs lacking B7-H3 experienced a reduction in the glucose and oxidative metabolism. Moreover, white adipocytes derived from B7-H3 silenced adipocyte progenitors showed features of impaired mitochondrial function and increased lipid storage. B7-H3 knock out mice which were on regular chow diet gained significant weight as compared to wild-type controls. These mice developed spontaneous obesity, which was also observed to exhibit diminished regulatory control on metabolic and immune homeostasis. This study shows in addition to its immune regulatory functions, B7-H3 plays an important role in adipocyte progenitor cell differentiation, lipid oxidation, and obesity. The study warrants further research on the role of B7-H3 in this important area.
Moreover, this study reveals a plausible link between diabetes mellitus (DM) and B7-H3. Mice knocked out for B7-H3 showed an increase in tendency toward obesity and associated metabolic syndrome [119]. Therefore, the B7-H3 pathway might be involved in the pathogenesis of type I DM (via immunoregulatory role) and type II DM (obesity and insulin resistance). In this regard, to our knowledge, only one descriptive study reported the association between type I DM and the serum level of B7-H3 [120]. In this study the serum level of B7-H3 in type 1 DM was significantly higher as compared to healthy controls. Given this evidence, the role of B7-H3 in the pathological process in DM should be further explored.
Effects of post-translational modifications on B7-H3
Post-translational modification of proteins (PTMs) is a covalent modification in protein side chains after translation. PTMs increase the functional diversity of the proteins by the covalent addition of functional groups, proteolytic cleavage of regulatory subunits, or degradation of partial or entire proteins. These modifications include phosphorylation, glycosylation, ubiquitination, nitrosylation, methylation, acetylation, and lipidation and PTMs affect normal cellular functions and may contribute to disease pathogenesis including cancer [121].
PTMs of B7-H3 is an under-researched area. Thus far the most studied PTM for B7-H3 is glycosylation. The functionality of several immune checkpoint molecules has been noted to be modulated by PTMs, including B7-H3 [122]. For example, PD-L1 is heavily glycosylated and this modification is required to interact with its receptor, PD-1, and suppress anti-tumor immunity [123, 124].
B7-H3 is a highly glycosylated protein. In a comprehensive study done by Huang et al., a higher expression of glycosylated B7-H3 is associated with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) progression and is a marker of poor patient survival [125]. In addition, they showed that N-glycosylation is required for B7-H3 protein stability and its expression on the surface of cell membrane. Furthermore, N-glycosylation of B7-H3 is required for its immunosuppressive function in TNBC cells. In support of this study, it has been also noted that B7-H3 is aberrantly glycosylated on oral cancer cells [126], although the functional importance of the modification has not been fully elucidated. Other than glycosylation, there are other forms of B7-H3 post-translational modifications (Table 2).
These studies suggest that PTMs of B7-H3 is implicated in the pathogenesis of cancer, and that understanding the molecular mechanisms of modifications and identifications of regulatory factors is warranted. It is also worthwhile to explore the potential impacts of the PTMs on therapeutics targeting B7-H3. To better understand B7-H3’s function and mechanism of actions, more studies should be carried out in this area. Several B7-H3 PTM modification sites have been predicted and Table 2 shows the list of possible PTMs.
Interaction between B7-H3 and microbiota
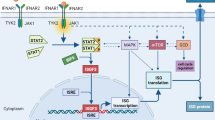
Mounting evidence supports that microbiota is an important factor that exerts profound impact on many aspects of cell functions and is involved in the process of many diseases, including cancer [127,128,129]. Recent reports show that microbiota can affect the expression of B7-H3. H. pylori infection elicits B7-H3 expression on gastric epithelial cells through type 4 secretion system (T4SS) components CagA and cell wall peptidoglycan fragment, and the T4SS cell signaling pathway involves modulation of p38MAPK pathway. Th17 cells, Treg cells and a mixed Th1/Th2 response increased during H. pylori infection. Human biopsy samples collected from gastritis biopsies and gastric tumors showed an increased B7-H3 and Th2 responses in H. pylori strains associated with gastritis [130].
Intriguingly a recent report describes that there is a microbiota-dependent pathway of crosstalk between myeloid cells, T cells, and tumor cells that inhibits CD8+ T cell-dependent anti-tumor immunity through the co-inhibitory protein B7-H3. Bacteria sensing by myeloid cells promote calcineurin and NFAT-dependent IL-6 release and NFAT-dependent IL-6 promotes expression of B7-H3 by tumors and it inhibits CD8+ T cell-dependent anti-tumor immunity, while B7-H3 blockade elicits protective T cell responses [131]. So far, the interaction between B7-H3 and microbiota is an under-researched but important area, which needs more in-depth studies.
Identification of B7-H3 Ligand/Receptor and binding partners
Notwithstanding its promise as a drug target, the receptor(s) for B7-H3 have remained unknown. This has become a major obstacle for B7-H3 research and therapeutic application, since it limits our understanding of its biological functions, challenging the development of therapeutics for B7-H3 targeting [5].
Broadly expressed in many tissues and reports of co-inhibition and co-stimulatory role to T cells, B7-H3 has been previously suspected to bind to the triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells like transcript 2(TREM-like transcript 2, TLT-2) co-stimulating T cell activation [132]. This study showed that overexpression of this molecule renders T cells more responsive to B7-H3 mediated co-stimulation. However, later intensive studies revealed that the human TLT-2 does not bind human B7-H3 and does not serve as a costimulatory receptor for human B7-H3 [133, 134]. Therefore, in these studies, they could not confirm a role of TLT-2 as a B7-H3 receptor.
In attempts to solve the puzzle, Husain et al., (2019) reported the binding of B7-H3 with a coreceptor for several members of the interleukin cytokine family known as Interleukin-20 receptor alpha (IL-20RA) [135]. This group further confirmed the B7-H3/IL20RA interaction by using a recently developed platform for ligand-receptor interactome in HEK293 cell lines [136]. However, the physical association and biological significance of this interaction has not been validated in other experimental systems, especially in vivo models.
Interleukin-20 receptor alpha (IL-20RA), located in chromosomal region 6q23, is a subunit of the IL-20RA/ IL-20RB receptor dimer for IL-10 family members including IL-19, IL-20, IL-22, IL-24 and IL-26 [137]. Studies have shown that IL-20RA is highly expressed in the skin, lung and reproductive organs targeted by the IL-10 family and has been reported to be involved in inflammatory diseases and tissue repair [138]. Studies demonstrated that IL-20RA promotes stemness features and increases the tumor-initiating ability of breast cancer cells via the JAK1-STAT3-SOX2 signaling pathway. Moreover, IL20RA promotes the chemoresistance of breast cancer cells and upregulates the expression of PD-L1 to compromise the activity of anti-cancer immune cells [139]. Furthermore, IL-20RA was highly expressed in the tumor tissue of colorectal cancer (CRC) and related to the advanced stage and poor patient prognosis. Further functional studies showed that knockdown of IL-20RA inhibited the growth and metastasis of CRC [140]. These functions are highly overlapping with those of B7-H3. Therefore, identification of IL-20RA as a possible binding partner for B7-H3 is an intriguing finding that warrants further validation and investigation. In a recent study, another putative binding partner for B7-H3 has been speculated. Angio-associated migratory cell protein (AAMP), ubiquitously expressed in glioma cells, immune cells, and glioma tissue was identified as interaction partner of B7-H3, using bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assay, co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP), and functional assays. Knockdown of AAMP reduced specifically the anti-proliferative effect of B7-H3 in Jurkat cells [141].
Development of B7-H3 targeting drugs for cancer treatment
The introduction of immune check point therapy, which targets the regulatory pathways of T cells in tumor microenvironment, has changed the paradigm of cancer treatment and improved patient survival significantly. Immune checkpoint blockade (e.g., anti-PD-1/ PD-L1 & anti-CTL4) enhances anticancer immune responses.
Despite the presence of the overwhelming evidence supporting the tumorigenic effects of B7-H3, there is so far no FDA approved therapeutics/drug targeting B7-H3. A lack of known receptor for B7-H3 makes this molecule difficult to target pharmacologically. It is foreseeable that a discovery of B7-H3 receptor will greatly accelerate the development of effective B7-H3 targeting drug. Nevertheless, due to its importance in cancer pathobiology, anti-B7-H3 approaches using different effector mechanisms including monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), CAR-T therapy, and Antibody Drug Conjugate (ADC) [142] have been explored (Fig. 6).
Another approach to target B7-H3 expressing tumor cells is targeted radioimmunotherapy (RIT). It is an attractive approach to selectively deliver and target therapeutic radionuclides to both localize and metastatic tumors while sparing normal tissues from the effects of radiation thereby minimizing toxicity [143]. In this regard, as B7-H3 is overexpressed in tumors but restricted in normal tissues, targeting B7-H3 with radionuclides would be particularly advantageous to minimize side effects. Several B7-H3 targeted RIT against preclinical and clinical models have been tested and encouraging results have shown [144, 145]. These studies indicated that targeted delivery of radioisotopes to malignant tissues is another approach to kill cancer cells while sparing normal tissues. B7-H3 targeted RIT combined with immunotherapy or chemotherapy or both would be particularly attractive and worthy of exploring this novel cancer therapeutics.
B7-H3 is a promising target for antibody-based immunotherapy as it is highly expressed on tumor cells, CSCs (critical for tumor metastasis and treatment failure or recurrence), tumor associated vasculature and stroma (involved in angiogenesis) [146]. The expression of B7-H3 and PDL-1, CTLA4 tend to be mutually exclusive. Moreover, the dramatic difference in the B7-H3 expression levels between tumor and normal tissues, provide a large therapeutic window, implying that successful targeting B7-H3 may selectively kill cancer cells and spare normal cells. Several studies have shown promising results using monoclonal antibodies and human-mice chimeric antibodies [147, 148] (Table 3). Furthermore, currently a number of clinical trials are evaluating the therapeutic efficacy of B7-H3 targeting strategies, alone or in combination with other checkpoint inhibitors [146]. There are several review articles extensively discussed targeting B7-H3 in tumor therapy, thus we recommend readers refer to them for additional information [4, 63, 149].
Conclusion and future perspectives
B7-H3 is a transmembrane immunoregulatory protein structurally related to the B7 family of proteins. B7-H3 is overexpressed in cancer cells and primarly localized on the cell membrane. B7-H3 has an inhibitory effect on the activation of T cells and possesses non-immune functions. Despite the lower expression of B7-H3 in the normal tissues, evidence suggest a possible link between B7-H3 and the risk of developing obesity and metabolic disorders such as diabetes mellitus.
Several therapeutic agents have been tested to target B7-H3 and promising results were documented. Because of its tumor promoting functions and its special expression profile, many anti-B7-H3 therapeutic agents are under development by both academia and industry. Unfortunately, B7-H3 research and drug development have been hindered by the lack of understanding of the detailed mechanisms of action and the unknown receptor/functional binding partner. Exploring the receptor and binding partner for B7-H3, its localization in the cell, and the effect of posttranscriptional and posttranslational modifications on its functionality in cancer pathogenesis, its involvement in other diseases, and its function in normal physiology warrants further study to expand our understanding about B7-H3 and develop effective therapeutics.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- ADCC:
-
Antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity
- ADC:
-
Antibody drug conjugate
- B7-H3:
-
B7 homolog 3
- B7-H4:
-
B7 homolog 4
- BRD4:
-
Bromodomain-containing protein 4
- CAR-T:
-
Chimeric antigen receptor T cell
- CSC:
-
Cancer stem cells
- CTL4:
-
Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- GTEx:
-
Genotype-tissue expression
- HIF-1α:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha
- HPA:
-
Human protein atlas
- IL20RA:
-
Interleukin-20 receptor alpha
- MHC:
-
Major histocompatibility complex
- miRNA:
-
Micro RNA
- PD-1:
-
Programmed cell death protein 1
- PD-L1:
-
Programmed cell death ligand 1
- PTM:
-
Post-translational modifications
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- TNBC:
-
Triple-negative breast cancer
- TCR:
-
T cell receptor
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
References
Webster RM. The immune checkpoint inhibitors: where are we now? Nat Rev Drug Discovery. 2014;13(12):883.
Marin-Acevedo JA, Dholaria B, Soyano AE, Knutson KL, Chumsri S, Lou Y. Next generation of immune checkpoint therapy in cancer: new developments and challenges. J Hematol Oncol. 2018;11(1):1–20.
Ma X, Chan TA. Solving the puzzle of what makes immunotherapies work. Trends Cancer. 2022.
Flem-Karlsen K, Fodstad Ø, Tan M, Nunes-Xavier CE. B7–H3 in Cancer - Beyond Immune Regulation. Trends Cancer. 2018;4(6):401–4.
Picarda E, Ohaegbulam KC, Zang X. Molecular Pathways: Targeting B7–H3 (CD276) for human cancer immunotherapycancer immunotherapies against B7–H3. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22(14):3425–31.
Castellanos JR, Purvis IJ, Labak CM, Guda MR, Tsung AJ, Velpula KK, et al. B7–H3 role in the immune landscape of cancer. Am J Clin Experimen Immunol. 2017;6(4):66.
Greenwald RJ, Freeman GJ, Sharpe AH. The B7 family revisited. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:515–48.
Collins M, Ling V, Carreno BM. The B7 family of immune-regulatory ligands. Genome Biol. 2005;6(6):223.
Greaves P, Gribben JG. The role of B7 family molecules in hematologic malignancy. Blood. 2013;121(5):734–44.
Chapoval AI, Ni J, Lau JS, Wilcox RA, Flies DB, Liu D, et al. B7–H3: a costimulatory molecule for T cell activation and IFN-gamma production. Nat Immunol. 2001;2(3):269–74.
Oh Y, Park R, Kim SY, Park SH, Jo S, Kim TH, et al. B7–H3 regulates osteoclast differentiation via type I interferon-dependent IDO induction. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(11):971.
Hwang JY, Jeong JM, Kwon MG, Seo JS, Hwang SD, Son MH, et al. Olive flounder CD276 (B7–H3) a coinhibitory molecule for T cells: Responses during viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV) stimulation. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018;73:228–33.
Ling V, Wu PW, Spaulding V, Kieleczawa J, Luxenberg D, Carreno BM, et al. Duplication of primate and rodent B7–H3 immunoglobulin V- and C-like domains: divergent history of functional redundancy and exon loss. Genomics. 2003;82(3):365–77.
Sun J, Fu F, Gu W, Yan R, Zhang G, Shen Z, et al. Origination of new immunological functions in the costimulatory molecule B7–H3: the role of exon duplication in evolution of the immune system. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(9):e24751.
Zhang C, Chen Y, Li F, Yang M, Meng F, Zhang Y, et al. B7–H3 is spliced by SRSF3 in colorectal cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021;70(2):311–21.
Vigdorovich V, Ramagopal UA, Lazar-Molnar E, Sylvestre E, Lee JS, Hofmeyer KA, et al. Structure and T cell inhibition properties of B7 family member, B7–H3. Structure. 2013;21(5):707–17.
Sun Y, Wang Y, Zhao J, Gu M, Giscombe R, Lefvert AK, et al. B7–H3 and B7–H4 expression in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2006;53(2):143–51.
Deng J, Ma M, Wang D, Zhu H, Hua L, Sun S, et al. Expression and clinical significance of immune checkpoint regulator B7–H3 (CD276) in human meningioma. World Neurosurg. 2020;135:e12–8.
Qin X, Sun W, Wang C, Li M, Zhao X, Li C, et al. Mifepristone inhibited the expression of B7–H2, B7–H3, B7–H4 and PD-L2 in adenomyosis. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2021;19(1):114.
Saeednejad Zanjani L, Madjd Z, Axcrona U, Abolhasani M, Rasti A, Asgari M, et al. Cytoplasmic expression of B7–H3 and membranous EpCAM expression are associated with higher grade and survival outcomes in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2020;46:151483.
Ingebrigtsen VA, Boye K, Tekle C, Nesland JM, Flatmark K, Fodstad O. B7–H3 expression in colorectal cancer: nuclear localization strongly predicts poor outcome in colon cancer. Int J Cancer. 2012;131(11):2528–36.
Tran CN, Thacker SG, Louie DM, Oliver J, White PT, Endres JL, et al. Interactions of T cells with fibroblast-like synoviocytes: role of the B7 family costimulatory ligand B7–H3. J Immunol. 2008;180(5):2989–98.
Ulase D, Behrens HM, Kruger S, Zeissig S, Rocken C. Gastric Carcinomas with Stromal B7-H3 Expression Have Lower Intratumoural CD8+ T Cell Density. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):2129.
Purvis IJ, Velpula KK, Guda MR, Nguyen D, Tsung AJ, Asuthkar S. B7-H3 in medulloblastoma-derived exosomes; a novel tumorigenic role. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(19):7050.
Zhou WT, Jin WL. B7–H3/CD276: An Emerging Cancer Immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 2021;12:701006.
Guo L, Liu Z, Zhang Y, Quan Q, Huang L, Xu Y, et al. Association of increased B7 protein expression by infiltrating immune cells with progression of gastric carcinogenesis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(8):e14663.
Li S, Poolen GC, van Vliet LC, Schipper JG, Broekhuizen R, Monnikhof M, et al. Pediatric medulloblastoma express immune checkpoint B7–H3. Clin Transl Oncol. 2022;24(6):1204–8.
Lavoie RR, Gargollo PC, Ahmed ME, Kim Y, Baer E, Phelps DA, et al. Surfaceome Profiling of Rhabdomyosarcoma Reveals B7-H3 as a Mediator of Immune Evasion. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(18):4528.
Durlanik S, Fundel-Clemens K, Viollet C, Huber HJ, Lenter M, Kitt K, et al. CD276 is an important player in macrophage recruitment into the tumor and an upstream regulator for PAI-1. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):14849.
Digregorio M, Coppieters N, Lombard A, Lumapat PN, Scholtes F, Rogister B. The expression of B7–H3 isoforms in newly diagnosed glioblastoma and recurrence and their functional role. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2021;9(1):59.
Matsumura E, Kajino K, Abe M, Ohtsuji N, Saeki H, Hlaing MT, et al. Expression status of PD-L1 and B7–H3 in mesothelioma. Pathol Int. 2020;70(12):999–1008.
Xylinas E, Robinson BD, Kluth LA, Volkmer BG, Hautmann R, Kufer R, et al. Association of T-cell co-regulatory protein expression with clinical outcomes following radical cystectomy for urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2014;40(1):121–7.
Zong L, Zhang M, Wang W, Wan X, Yang J, Xiang Y. PD-L1, B7–H3 and VISTA are highly expressed in gestational trophoblastic neoplasia. Histopathology. 2019;75(3):421–30.
Amori G, Sugawara E, Shigematsu Y, Akiya M, Kunieda J, Yuasa T, et al. Tumor B7–H3 expression in diagnostic biopsy specimens and survival in patients with metastatic prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2021;24(3):767–74.
MacGregor HL, Sayad A, Elia A, Wang BX, Katz SR, Shaw PA, et al. High expression of B7–H3 on stromal cells defines tumor and stromal compartments in epithelial ovarian cancer and is associated with limited immune activation. J Immunother Cancer. 2019;7(1):357.
Yang J, Tian Z, Gao H, Xiong F, Cao C, Yu J, et al. Clinical significance and correlation of PD-L1, B7–H3, B7–H4, and TILs in pancreatic cancer. BMC Cancer. 2022;22(1):584.
Li H, Yang Z, Yang X, Zhang F, Wang J, Wu Z, et al. LINC01123 promotes immune escape by sponging miR-214-3p to regulate B7–H3 in head and neck squamous-cell carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(2):109.
Zhang W, Zhang L, Qian J, Lin J, Chen Q, Yuan Q, et al. Expression characteristic of 4Ig B7–H3 and 2Ig B7–H3 in acute myeloid leukemia. Bioengineered. 2021;12(2):11987–2002.
Li Y, Cai Q, Shen X, Chen X, Guan Z. Overexpression of B7–H3 Is Associated With Poor Prognosis in Laryngeal Cancer. Front Oncol. 2021;11:759528.
Zhao B, Huang Z, Zhu X, Cai H, Huang Y, Zhang X, et al. Clinical significance of the expression of co-stimulatory molecule B7–H3 in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:819236.
Haydar D, Houke H, Chiang J, Yi Z, Ode Z, Caldwell K, et al. Cell-surface antigen profiling of pediatric brain tumors: B7–H3 is consistently expressed and can be targeted via local or systemic CAR T-cell delivery. Neuro Oncol. 2021;23(6):999–1011.
Nagai Y, Aso H, Ogasawara H, Tanaka S, Taketa Y, Watanabe K, et al. Anterior pituitary progenitor cells express costimulatory molecule 4Ig-B7-H3. J Immunol. 2008;181(9):6073–81.
Zhang G, Hou J, Shi J, Yu G, Lu B, Zhang X. Soluble CD276 (B7–H3) is released from monocytes, dendritic cells and activated T cells and is detectable in normal human serum. Immunology. 2008;123(4):538–46.
Nygren MK, Tekle C, Ingebrigtsen VA, Makela R, Krohn M, Aure MR, et al. Identifying microRNAs regulating B7–H3 in breast cancer: the clinical impact of microRNA-29c. Br J Cancer. 2014;110(8):2072–80.
Yu TT, Zhang T, Su F, Li YL, Shan L, Hou XM, et al. ELK1 Promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the progression of lung adenocarcinoma by upregulating B7–H3. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:2805576.
Zhang P, Yu S, Li H, Liu C, Li J, Lin W, et al. ILT4 drives B7–H3 expression via PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling and ILT4/B7-H3 co-expression correlates with poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. FEBS Lett. 2015;589(17):2248–56.
Zhao J, Lei T, Xu C, Li H, Ma W, Yang Y, et al. MicroRNA-187, down-regulated in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and associated with lower survival, inhibits cell growth and migration though targeting B7–H3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;438(2):439–44.
Zhao J, Meng Z, Xie C, Yang C, Liu Z, Wu S, et al. B7–H3 is regulated by BRD4 and promotes TLR4 expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019;108:84–91.
Hu X, Xu M, Hu Y, Li N, Zhou L. B7–H3, Negatively Regulated by miR-128, Promotes Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation and Migration. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2021;79(2):397–405.
Yang X, Feng KX, Li H, Wang L, Xia H. MicroRNA-199a inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion and activates akt/mtor signaling pathway by targeting B7–H3 in Cervical Cancer. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020;19:1533033820942245.
Zhao S, Wang Y, Yang N, Mu M, Wu Z, Li H, et al. Genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 screen reveals novel regulators of B7-H3 in tumor cells. J Immunother Cancer. 2022;10(6):e004875.
Chen Y, Wu Y, Yang H, Wang J, Kong J, Yu L, et al. DNA Methylation and mRNA Expression of B7-H3 Gene in Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Case-Control Study. Immunol Invest. 2022;51(7):2025–34.
Arigami T, Uenosono Y, Hirata M, Yanagita S, Ishigami S, Natsugoe S. B7‐H3 expression in gastric cancer: a novel molecular blood marker for detecting circulating tumor cells. Cancer science. 2011;102(5):1019–24.
Li Y, Zhang J, Han S, Qian Q, Chen Q, Liu L, et al. B7–H3 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasiveness of cervical cancer cells and is an indicator of poor prognosis. Oncol Rep. 2017;38(2):1043–50.
Xie C, Liu D, Chen Q, Yang C, Wang B, Wu H. Soluble B7–H3 promotes the invasion and metastasis of pancreatic carcinoma cells through the TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Sci Rep. 2016;6(1):1–9.
Baral A, Ye HX, Jiang PC, Yao Y, Mao Y. B7–H3 and B7–H1 expression in cerebral spinal fluid and tumor tissue correlates with the malignancy grade of glioma patients. Oncol Lett. 2014;8(3):1195–201.
Purvis IJ, Velpula KK, Guda MR, Nguyen D, Tsung AJ, Asuthkar S. B7-H3 in Medulloblastoma-Derived exosomes; a novel tumorigenic role. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(19):7050.
Lehmann BD, Paine MS, Brooks AM, McCubrey JA, Renegar RH, Wang R, et al. Senescence-associated exosome release from human prostate cancer cells. Can Res. 2008;68(19):7864–71.
Crispen PL, Sheinin Y, Roth TJ, Lohse CM, Kuntz SM, Frigola X, et al. Tumor cell and tumor vasculature expression of B7–H3 predict survival in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(16):5150–7.
Loos M, Hedderich DM, Friess H, Kleeff J. B7-h3 and its role in antitumor immunity. Clin Dev Immunol. 2010;2010:683875.
Kim NI, Park MH, Kweon S-S, Lee JS. B7–H3 and B7–H4 expression in breast cancer and their association with clinicopathological variables and T cell infiltration. Pathobiology. 2020;87(3):179–92.
Luo L, Chapoval AI, Flies DB, Zhu G, Hirano F, Wang S, et al. B7–H3 enhances tumor immunity in vivo by costimulating rapid clonal expansion of antigen-specific CD8+ cytolytic T cells. J Immunol. 2004;173(9):5445–50.
Picarda E, Ohaegbulam KC, Zang X. Molecular pathways: targeting B7–H3 (CD276) for human cancer immunotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22(14):3425–31.
Sun M, Richards S, Prasad DV, Mai XM, Rudensky A, Dong C. Characterization of mouse and human B7–H3 genes. J Immunol. 2002;168(12):6294–7.
Han S, Wang Y, Shi X, Zong L, Liu L, Zhang J, et al. Negative roles of B7–H3 and B7–H4 in the microenvironment of cervical cancer. Exp Cell Res. 2018;371(1):222–30.
Lu H, Shi T, Wang M, Li X, Gu Y, Zhang X, et al. B7–H3 inhibits the IFN-gamma-dependent cytotoxicity of Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cells against colon cancer cells. Oncoimmunology. 2020;9(1):1748991.
Si S, Wang L, Cao H, Xu Y, Zhan Q. Co-deficiency of B7–H3 and B7–H4 identifies high CD8 + T cell infiltration and better prognosis in pancreatic cancer. BMC Cancer. 2022;22(1):211.
Lee CC, Ho KH, Huang TW, Shih CM, Hsu SY, Liu AJ, et al. A regulatory loop among CD276, miR-29c-3p, and Myc exists in cancer cells against natural killer cell cytotoxicity. Life Sci. 2021;277:119438.
Long C, Li G, Zhang C, Jiang T, Li Y, Duan X, et al. B7–H3 as a Target for CAR-T Cell Therapy in Skull Base Chordoma. Front Oncol. 2021;11:659662.
Mao Y, Chen L, Wang F, Zhu D, Ge X, Hua D, et al. Cancer cell-expressed B7–H3 regulates the differentiation of tumor-associated macrophages in human colorectal carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2017;14(5):6177–83.
Miyamoto T, Murakami R, Hamanishi J, Tanigaki K, Hosoe Y, Mise N, et al. B7–H3 Suppresses Antitumor Immunity via the CCL2-CCR2-M2 Macrophage Axis and Contributes to Ovarian Cancer Progression. Cancer Immunol Res. 2022;10(1):56–69.
Li ZY, Wang JT, Chen G, Shan ZG, Wang TT, Shen Y, et al. Expression, regulation and clinical significance of B7–H3 on neutrophils in human gastric cancer. Clin Immunol. 2021;227:108753.
Meng F, Yang M, Chen Y, Chen W, Wang W. miR-34a induces immunosuppression in colorectal carcinoma through modulating a SIRT1/NF-kappaB/B7-H3/TNF-alpha axis. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021;70(8):2247–59.
Inamura K, Amori G, Yuasa T, Yamamoto S, Yonese J, Ishikawa Y. Relationship of B7–H3 expression in tumor cells and tumor vasculature with FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:7021–30.
Yim J, Koh J, Kim S, Song SG, Ahn HK, Kim YA, et al. Effects of B7–H3 expression on tumour-infiltrating immune cells and clinicopathological characteristics in non-small-cell lung cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2020;133:74–85.
Hanahan D. Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer cell. 2000;100(1):57–70.
Li Y, Yang X, Wu Y, Zhao K, Ye Z, Zhu J, et al. B7–H3 promotes gastric cancer cell migration and invasion. Oncotarget. 2017;8(42):71725.
Flem-Karlsen K, Fodstad Ø, Tan M, Nunes-Xavier CE. B7–H3 in cancer–beyond immune regulation. Trends in cancer. 2018;4(6):401–4.
Wang R, Ma Y, Zhan S, Zhang G, Cao L, Zhang X, et al. B7–H3 promotes colorectal cancer angiogenesis through activating the NF-κB pathway to induce VEGFA expression. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(1):1–15.
Yuan H, Wei X, Zhang G, Li C, Zhang X, Hou J. B7–H3 over expression in prostate cancer promotes tumor cell progression. J Urol. 2011;186(3):1093–9.
Chen Y-W, Tekle C, Fodstad O. The immunoregulatory protein human B7H3 is a tumor-associated antigen that regulates tumor cell migration and invasion. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2008;8(5):404–13.
Li Y, Guo G, Song J, Cai Z, Yang J, Chen Z, et al. B7–H3 promotes the migration and invasion of human bladder cancer cells via the PI3K/Akt/STAT3 signaling pathway. J Cancer. 2017;8(5):816.
Ding M, Liao H, Zhou N, Yang Y, Guan S, Chen L. B7-H3-Induced Signaling in Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Lines with Divergent Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation Patterns. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:8824805.
Pouysségur J, Dayan F, Mazure NM. Hypoxia signalling in cancer and approaches to enforce tumour regression. Nature. 2006;441(7092):437–43.
Cheng R, Chen Y, Zhou H, Wang B, Du Q, Chen Y. B7–H3 expression and its correlation with clinicopathologic features, angiogenesis, and prognosis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. APMIS. 2018;126(5):396–402.
Cheng N, Bei Y, Song Y, Zhang W, Xu L, Zhang W, et al. B7–H3 augments the pro-angiogenic function of tumor-associated macrophages and acts as a novel adjuvant target for triple-negative breast cancer therapy. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021;183:114298.
Lai H, Sun Z, Yang J, Wu P, Guo Y, Sun J. B7–H3 modulates endothelial cell angiogenesis through the VEGF cytokine. Immunol Res. 2019;67(2):202–11.
Frezza C. Metabolism and cancer: the future is now. Br J Cancer. 2020;122(2):133-135.
Lim S, Liu H, da Madeira Silva L, Arora R, Liu Z, Phillips JB, et al. Immunoregulatory Protein B7-H3 Reprograms Glucose Metabolism in Cancer Cells by ROS-Mediated Stabilization of HIF1alpha. Cancer Res. 2016;76(8):2231–42.
DeBerardinis RJ, Lum JJ, Hatzivassiliou G, Thompson CB. The biology of cancer: metabolic reprogramming fuels cell growth and proliferation. Cell Metab. 2008;7(1):11–20.
Li Z, Liu J, Que L, Tang X. The immunoregulatory protein B7–H3 promotes aerobic glycolysis in oral squamous carcinoma via PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. J Cancer. 2019;10(23):5770–84.
<Decreased expression of B7-H3 reduces the glycolytic capacity.pdf>.
Yamato I, Sho M, Nomi T, Akahori T, Shimada K, Hotta K, et al. Clinical importance of B7–H3 expression in human pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer. 2009;101(10):1709–16.
Arigami T, Narita N, Mizuno R, Nguyen L, Ye X, Chung A, et al. B7–h3 ligand expression by primary breast cancer and associated with regional nodal metastasis. Ann Surg. 2010;252(6):1044–51.
<Aberrant expression of B7-H3 in gastric.pdf>.
Holohan C, Van Schaeybroeck S, Longley DB, Johnston PG. Cancer drug resistance: an evolving paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13(10):714–26.
Liu H, Tekle C, Chen YW, Kristian A, Zhao Y, Zhou M, et al. B7–H3 silencing increases paclitaxel sensitivity by abrogating Jak2/Stat3 phosphorylation. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011;10(6):960–71.
Zhou L, Zhao Y. B7–H3 Induces Ovarian Cancer Drugs Resistance Through An PI3K/AKT/BCL-2 Signaling Pathway. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:10205–14.
Reya T, Morrison S, Clarke M. Wiessman Il. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells Nature. 2001;414:105–11.
O’Brien CA, Kreso A, Jamieson CH. Cancer Stem Cells and Self-renewalCancer Stem Cells and Self-renewal. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16(12):3113–20.
Wang Y, Krivtsov AV, Sinha AU, North TE, Goessling W, Feng Z, et al. The Wnt/β-catenin pathway is required for the development of leukemia stem cells in AML. Science. 2010;327(5973):1650–3.
Maccalli C, Rasul KI, Elawad M, Ferrone S. The role of cancer stem cells in the modulation of anti-tumor immune responses. Semin Cancer Biol. 2018;53:189-200.
Batlle E, Clevers H. Cancer stem cells revisited. Nat Med. 2017;23(10):1124–34.
Vinogradov S, Wei X. Cancer stem cells and drug resistance: the potential of nanomedicine. Nanomedicine. 2012;7(4):597–615.
Liu Z, Zhang W, Phillips JB, Arora R, McClellan S, Li J, et al. Immunoregulatory protein B7–H3 regulates cancer stem cell enrichment and drug resistance through MVP-mediated MEK activation. Oncogene. 2019;38(1):88–102.
Zhang Y, He L, Sadagopan A, Ma T, Dotti G, Wang Y, et al. Targeting radiation-resistant prostate cancer stem cells by B7–H3 CAR T Cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2021;20(3):577–88.
Shi J, Zhao H, Lian H, Ke L, Zhao L, Wang C, et al. CD276 (B7H3) improve cancer stem cells formation in cervical carcinoma cell lines. Translational Cancer Research. 2021;10(1):65.
Wang C, Li Y, Jia L, koo Kim J, Li J, Deng P, et al. CD276 expression enables squamous cell carcinoma stem cells to evade immune surveillance. Cell Stem Cell. 2021;28(9):1597-e7.
McHugh D, Gil J. Senescence and aging: Causes, consequences, and therapeutic avenues. J Cell Biol. 2018;217(1):65–77.
Muñoz-Espín D, Serrano M. Cellular senescence: from physiology to pathology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(7):482–96.
Kumari R, Jat P. Mechanisms of cellular senescence: cell cycle arrest and senescence associated secretory phenotype. Front Dev Biol. 2021;9:645593.
Wang L, Lankhorst L, Bernards R. Exploiting senescence for the treatment of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022;22(6):340–55.
Lan L, Holland JD, Qi J, Grosskopf S, Vogel R, Györffy B, et al. Shp2 signaling suppresses senescence in Py MT-induced mammary gland cancer in mice. EMBO J. 2015;34(11):1493–508.
Pare R, Yang T, Shin J-S, Lee CS. The significance of the senescence pathway in breast cancer progression. J Clin Pathol. 2013;66(6):491–5.
Acosta JC, Gil J. Senescence: a new weapon for cancer therapy. Trends Cell Biol. 2012;22(4):211–9.
Wang R, Sun L, Xia S, Wu H, Ma Y, Zhan S, et al. B7–H3 suppresses doxorubicin-induced senescence-like growth arrest in colorectal cancer through the AKT/TM4SF1/SIRT1 pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(5):1–17.
Lim S, Liu H, Da Silva LM, Arora R, Liu Z, Phillips JB, et al. Immunoregulatory Protein B7–H3 reprograms glucose metabolism in cancer cells by ros-mediated stabilization of HIF1αB7-H3 regulates glucose metabolism in cancer cells. Can Res. 2016;76(8):2231–42.
Shi T, Ma Y, Cao L, Zhan S, Xu Y, Fu F, et al. B7–H3 promotes aerobic glycolysis and chemoresistance in colorectal cancer cells by regulating HK2. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(4):1–12.
Picarda E, Galbo PM Jr, Zong H, Rajan MR, Wallenius V, Zheng D, et al. The immune checkpoint B7-H3 (CD276) regulates adipocyte progenitor metabolism and obesity development. Science advances. 2022;8(17):eabm7012.
Fang C, Li S, Xu R, Guo H, Jiang R, Ding S, et al. Soluble B7–H3 (sB7-H3) is over-expressed in the serum of type 1 diabetes patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018;143:332–6.
Sharma B, Prabhakaran V, Desai A, Bajpai J, Verma R, Swain P. Post-translational modifications (PTMs), from a cancer perspective: an overview. Oncogen. 2019;2:12.
Sun R, Kim AMJ, Lim S-O. Glycosylation of immune receptors in cancer. Cells. 2021;10(5):1100.
Benicky J, Sanda M, Brnakova Kennedy Z, Grant OC, Woods RJ, Zwart A, et al. PD-L1 Glycosylation and its impact on binding to clinical antibodies. J Proteome Res. 2020;20(1):485–97.
Hsu J-M, Li C-W, Lai Y-J, Hung M-C. Posttranslational modifications of PD-L1 and their applications in cancer therapy. Can Res. 2018;78(22):6349–53.
Huang Y, Zhang H-L, Li Z-L, Du T, Chen Y-H, Wang Y, et al. FUT8-mediated aberrant N-glycosylation of B7H3 suppresses the immune response in triple-negative breast cancer. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):1–18.
Chen J-T, Chen C-H, Ku K-L, Hsiao M, Chiang C-P, Hsu T-L, et al. Glycoprotein B7–H3 overexpression and aberrant glycosylation in oral cancer and immune response. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2015;112(42):13057–62.
An Y, Zhang W, Liu T, Wang B, Cao H. The intratumoural microbiota in cancer: new insights from inside. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021;1876(2):188626.
Pham F, Moinard-Butot F, Coutzac C, Chaput N. Cancer and immunotherapy: a role for microbiota composition. Eur J Cancer. 2021;155:145–54.
Park EM, Chelvanambi M, Bhutiani N, Kroemer G, Zitvogel L, Wargo JA. Targeting the gut and tumor microbiota in cancer. Nat Med. 2022;28(4):690–703.
Lina TT, Gonzalez J, Pinchuk IV, Beswick EJ, Reyes VE. Helicobacter pylori elicits B7H3 expression on gastric epithelial cells: Implications in local T cell regulation and subset development during infection. Clin Oncol Res. 2019;2(5):10.31487/j.cor.2019.05.05.
Peuker K, Strigli A, Tauriello DVF, Hendricks A, von Schonfels W, Burmeister G, et al. Microbiota-dependent activation of the myeloid calcineurin-NFAT pathway inhibits B7H3- and B7H4-dependent anti-tumor immunity in colorectal cancer. Immunity. 2022;55(4):701-17 e7.
Hashiguchi M, Kobori H, Ritprajak P, Kamimura Y, Kozono H, Azuma M. Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cell-like transcript 2 (TLT-2) is a counter-receptor for B7–H3 and enhances T cell responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2008;105(30):10495–500.
Leitner J, Klauser C, Pickl WF, Stöckl J, Majdic O, Bardet AF, et al. B7–H3 is a potent inhibitor of human T-cell activation: no evidence for B7–H3 and TREML2 interaction. Eur J Immunol. 2009;39(7):1754–64.
Yan R, Yang S, Gu A, Zhan F, He C, Qin C, et al. Murine b7–h3 is a co-stimulatory molecule for T cell activation. Monoclonal Antibodies in Immunodiagnosis and Immunotherapy. 2013;32(6):395–8.
Husain B, Ramani SR, Chiang E, Lehoux I, Paduchuri S, Arena TA, et al. A platform for extracellular interactome discovery identifies novel functional binding partners for the immune receptors B7–H3/CD276 and PVR/CD155. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2019;18(11):2310–23.
Cao S, Peterson SM, Müller S, Reichelt M, McRoberts Amador C, Martinez-Martin N. A membrane protein display platform for receptor interactome discovery. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2021;118(39):e2025451118.
Wu J, Yang S, Yu D, Gao W, Liu X, Zhang K, et al. CRISPR/cas9 mediated knockout of an intergenic variant rs6927172 identified IL-20RA as a new risk gene for multiple autoimmune diseases. Genes Immun. 2019;20(2):103–11.
Rutz S, Wang X, Ouyang W. The IL-20 subfamily of cytokines—from host defence to tissue homeostasis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14(12):783–95.
Gao W, Wen H, Liang L, Dong X, Du R, Zhou W, et al. IL20RA signaling enhances stemness and promotes the formation of an immunosuppressive microenvironment in breast cancer. Theranostics. 2021;11(6):2564.
Yu D, Yang X, Lin J, Cao Z, Lu C, Yang Z, Zheng M, Pan R, Cai W. Super-Enhancer Induced IL-20RA Promotes Proliferation/Metastasis and Immune Evasion in Colorectal Cancer. Front Oncol. 2021;11:724655.
Ciprut S, Berberich A, Knoll M, Pusch S, Hoffmann D, Furkel J, et al. AAMP is a binding partner of costimulatory human B7-H3. Neuroonco Adv. 2022;4(1):vdac098.
Tang X, Zhao S, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Yang M, et al. B7–H3 as a novel CAR-T therapeutic target for glioblastoma. Mol Ther-Oncol. 2019;14:279–87.
Milenic DE, Brady ED, Brechbiel MW. Antibody-targeted radiation cancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3(6):488–99.
Wang G, Wu Z, Wang Y, Li X, Zhang G, Hou J. Therapy to target renal cell carcinoma using 131I-labeled B7–H3 monoclonal antibody. Oncotarget. 2016;7(17):24888–98.
Kasten BB, Arend RC, Katre AA, Kim H, Fan J, Ferrone S, et al. B7-H3-targeted (212)Pb radioimmunotherapy of ovarian cancer in preclinical models. Nucl Med Biol. 2017;47:23–30.
Kontos F, Michelakos T, Kurokawa T, Sadagopan A, Schwab JH, Ferrone CR, et al. B7–H3: An Attractive Target for Antibody-based Immunotherap. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27(5):1227–35.
Tyagi A, Ly S, El-Dana F, Yuan B, Jaggupilli A, Grimm S, et al. Evidence supporting a role for the immune checkpoint protein B7–H3 in NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity against AML. Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology. 2022;139(18):2782–96.
Bendell JC, Doi T, Patel MR, Piha-Paul SA, Sen S, Shimizu T, et al. A phase I/II, two-part, multicenter, first-in-human study of DS-7300a in patients with advanced solid malignant tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:15_suppl, TPS3646-TPS3646.
Kontos F, Michelakos T, Kurokawa T, Sadagopan A, Schwab JH, Ferrone CR, et al. B7–H3: An attractive target for antibody-based Immunotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27(5):1227–35.
Funding
This research was in part funded by China Medical University Ying-Tsai Scholar Fund CMU109-YT-04 (to M.T.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This manuscript was conceived by AAG and MT, written by AAG, AT, and MT, and revised by AAG, AT, MZ, JL, OF, and MT. MT supervised development of this paper as the principal investigator. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to particiapte
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Getu, A.A., Tigabu, A., Zhou, M. et al. New frontiers in immune checkpoint B7-H3 (CD276) research and drug development. Mol Cancer 22, 43 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-023-01751-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-023-01751-9