Abstract
Background
The emergence and spread of multidrug resistance poses a significant risk to malaria control and eradication goals in the world. There has been no indigenous malaria cases reported in China since 2017, and China is approaching national malaria elimination. Therefore, anti-malarial drug resistance surveillance and tracking the emergence and spread of imported drug-resistant malaria cases will be necessary in a post-elimination phase in China.
Methods
Dried blood spots were obtained from Plasmodium falciparum-infected cases returned from Africa to China between 2012 and 2015, prior to anti-malarial drug treatment. Whole DNA were extracted and known polymorphisms relating to drug resistance of pfcrt, pfmdr1 gene, and the propeller domain of pfk13 were evaluated by nested PCR and sequencing. The haplotypes and prevalence of these three genes were evaluated separately. Chi-squared test and Fisher's exact test were used to evaluate differences among the different sub-regions of Africa. A P value < 0.05 was used to evaluate differences with statistical significance. The maps were created using ArcGIS.
Results
A total of 731 P. falciparum isolates were sequenced at the pfcrt locus. The wild type CVMNK was the most prevalent haplotype with prevalence of 62.8% and 29.8% of the isolates showed the triple mutant haplotype CVIET. A total of 434 P. falciparum isolates were successfully sequenced and pfmdr1 allelic variants were observed in only codons 86, 184 and 1246. Twelve haplotypes were identified and the prevalence of the wild type pfmdr1 NYD was 44.1%. The single mutant pfmdr1 in codons 86 and 184 was predominant but the haplotype NYY with single mutation in codon 1246 was not observed. The double mutant haplotype YFD was common in Africa. About 1,357 isolates were successfully sequenced of pfk13-propeller domain, the wild type was found in 1,308 samples (96.4%) whereby 49 samples (3.6%) had mutation in pfk13. Of 49 samples with pfk13 mutations, 22 non-synonymous and 4 synonymous polymorphic sites were confirmed. The A578S was the most common mutation in pfk13-propeller domain and three mutations associated with artemisinin resistance (M476I, R539T, P553L) were identified in three isolates.
Conclusion
This study provides evidence that could give insight into potential issues with anti-malarial drug resistance to inform national drug policy in China in order to treat imported cases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Historically, malaria was one of the most serious infectious diseases in China. China has made great contributions towards global malaria control in the past 40 years. In 2010, China launched the National Malaria Elimination Programme (NMEP) 2010–2020 with the goal to interrupt local malaria transmission by 2020. Over the following five years, malaria cases decreased dramatically and there has been no indigenous malaria case reported since 2017 [1]. Now, China has achieved malaria elimination nationwide and is ready for World Health Organization (WHO) certification. However, with increasing globalization, larger numbers of people entering or returning from malaria-endemic areas present challenges to malaria elimination in China [2]. According to the national malaria report, there were more than 2500 imported cases annually, including over 100 patients with severe symptoms and approximately 10 deaths in 2017 and 2018 [3].
Over the past 50 years, Plasmodium falciparum has developed resistance to all anti-malarial drugs that have been used, including chloroquine (CQ), amodiaquine, sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine (SP), quinine, piperaquine, and mefloquine. Recently, the emergence and spread of multidrug resistance, including artemisinin and partner drug resistance of P. falciparum in Southeast Asia, poses a significant risk to malaria control and eradication goals in the world. The WHO had implemented a strategy to eliminate P. falciparum from the six countries in the Greater Mekong Sub-region (GMS) by 2025 to respond to the threat of an untreatable multidrug-resistant parasite [4]. Several mutations in the P. falciparum gene encoding a kelch protein on chromosome 13 (pfk13) are associated with artemisinin resistance [5] and have arisen multiple times and spread in the GMS. Over 200 non-synonymous pfk13 mutations have been reported to date, of which nine validated variants (F446I, N458Y, M476I, Y493H, R539T, I543T, P553L, R561H, C580Y) and over 20 pfk13 variants are considered as candidate mutations [6]. Pfk13 mutations were detected predominantly in the GMS and were rare in Africa, but their profile was highly heterogeneous [5,6,7].
Mutations in P. falciparum CQ resistance transporter (pfcrt), located on the digestive vacuole membrane, were responsible for CQ resistance or treatment failure [8, 9]. Polymorphisms affecting amino acids at pfcrt residues 72–76 were observed in CQ-resistant field isolates, whereas pfcrt CVMNK haplotype was regarded as CQ-sensitive isolates [10, 11]. Polymorphisms in the P. falciparum multidrug-resistant 1 (pfmdr1) gene, encoding the plasmodial homologue of mammalian multidrug-resistant transporters, have previously been linked with anti-malarial drug resistance [12,13,14,15]. The mutations involving pfmdr1 codons N86Y, Y184F, S1034C, N1042D, and D1246Y have been proven to be associated with mefloquine, lumefantrine, amodiaquine, CQ, and artemisinin, as well [16, 17].
Artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT), which combines a fast-acting, rapidly eliminated artemisinin derivative with another slower-acting partner drug with a longer half-life, has been integral to the recent success of global malaria control. According to the current national malaria treatment policy in China, the first-line drugs to treat P. falciparum include three ACT (dyhidroartemisinin-piperaquine, artesunate-amadiquine, artesunate-piperaquine). Molecular surveillance of anti-malarial drug resistance markers is one of the tools to monitor and track the emergence and spread of drug resistance in imported malaria cases in China. This study collected the data of reported malaria cases from the national malaria case report system between 2012 and 2015, which were used to analyse malaria epidemiology in China. Dried blood spots were collected from P. falciparum-infected individuals returning from Africa in 2012–2015. The haplotypes of pfcrt, pfmdr1 and pfk13 genes were estimated by nested PCR and sequencing. The prevalence of different haplotypes of each gene was evaluated. The geographical distribution of the haplotypes of pfcrt, pfmrd1 and pfk13 genes in imported P. falciparum isolates from Africa were mapped.
Methods
Reported malaria cases
The data of all reported malaria cases, including indigenous and imported cases, were collected from the Chinese Infectious Disease Report System (CIDRS), a web-based reporting system between 2012 and 2015. Adhering to the ‘1-3-7’ strategy of the NMEP, a patient must be confirmed by microscope, rapid diagnostic test (RDT), or clinical test before the case was reported into the e-data system, and demographic data was recorded, including travel history, and/or imported source countries. According to the diagnostic criteria for malaria (WS 259-2015) in China, the clinically diagnosed cases were defined as patients with malaria-like symptoms and travel history to malaria-endemic areas but no parasites detected in blood examination. The epidemiology of imported malaria cases was analysed, and the main source countries were identified.
Sample collection and DNA extraction
Dried blood spots on filter paper (Whatman™ 903, GE Healthcare, USA) were obtained from P. falciparum-infected cases who returned from Africa to China in 2012–2015 prior to anti-malarial drug treatment. Whole DNA was extracted from dry blood spots using a QIAamp DNA mini kit (Valencia, CA, USA) as described by the manufacturer. Microscopic examination of Giemsa-stained thick smears or RDT (Malaria HRP2/pLDH (P.f/Pan), Wondfo, Guangzhou, China) was used for malaria diagnosis within 24 h before the case was reported. Nested polymerase chain reaction (PCR), amplifying the small-subunit rRNA gene of Plasmodium spp. [18] was used to confirm the positive samples and the species before anti-malarial drug resistance markers were sequenced. Only samples with mono-infection of P. falciparum were sequenced in this study and samples with multiple infections were excluded.
Nested PCR
The known polymorphisms relating to drug resistance at codons 72, 74, 75, 76 of the pfcrt gene and codons 86, 130, 184, 1034, 1042, 1109, 1246 of the pfmdr1 gene, and also mutations on the propeller domain of the pfk13 gene, were evaluated by nested PCR [5, 13, 19,20,21]. The primers for nested PCR, cycling conditions and sizes of PCR products are shown in Additional file 1. PCR products were purified using filter plates (Edge Biosystems, Gaithersburg, MD, USA) and directly sequenced and analysed on an ABI 3730XL automatic sequencer. The amplification products were analysed by 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis before sequencing. Bi-directional sequencing was used and all the products were sequenced twice using independently amplified PCR products. The target amplified fragments covering polymorphic sites were as follows: amino acid position 51–83 for pfcrt, amino acid position 69–228 and 1030–1282 for pfmdr1, and amino acid position 433–702 for pfk13-propeller.
Data analysis
The output sequence data were assembled, edited and aligned using Sequencher (version 5.1) software. All mutations were assessed by comparing each sequence to the 3D7 reference strain PF3D7_0709000 (pfcrt), PF3D7_0523000 (pfmdr1) and PF3DF_1343700 (pfk13) from PlasmoDB (http://www.plasmodb.org). The mixed alleles were determined according to the emergence of two chromatogram peaks at one nucleotide sited through the Mutation Surveyor (SoftGenetics LLC., version 5.1, State College, PA, USA). The prevalence of each haplotype was estimated by the number of the isolates carrying the specific haplotype and total samples with successful sequencing. R software (Version 4.0.2) and SAS software (SAS Institute Inc, Version 9.2, Cary, NC, USA) were used for data processing and statistical analysis. The Chi-squared test was used to evaluate differences among the different sub-regions but Fisher's exact test would be used if 25% of the cells had expected counts less than 5. A P value < 0.05 was used to evaluate differences with statistical significance. The maps were created by using ArcGIS 10.1 (Environmental Systems Research Institute, Inc, Redlands, CA, USA).
Results
Malaria epidemiology in China
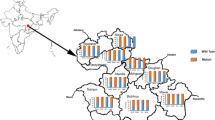
The reported malaria cases decreased to only thousands of cases in 2012–2015 compared with hundreds of thousands cases before 2010, when the NMEP had not been launched. A total of 42 counties in the entire country reported indigenous cases in 2012 which decreased to nine counties in 2015 (Additional file 2). The proportion of imported cases has remained at more than 90% since 2012, and 244 indigenous cases were reported in 2012 (Fig. 1). Since 2013, the number of indigenous cases has dropped below 100 and most cases were reported from Yunnan and Tibet province/autonomous region in southern China. In 2017, no indigenous cases were reported in the country for the first time. Nevertheless, the proportion of imported P. falciparum cases increased from 2012 (n = 1403, 57.3%) to 2015 (n = 1895, 61.6%).
Imported cases originated from four continents and more than 70% were from central and western Africa. The main source countries of imported malaria cases in China are shown in Table 1. Ghana, Angola, Equatorial Guinea, and Nigeria have been the major source countries for malaria imported into China.
Polymorphisms of pfcrt
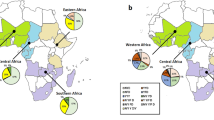
A total of 731 P. falciparum isolates collected from imported cases form Africa were successfully sequenced at the pfcrt locus. Five haplotypes of pfcrt were identified including the wild type CVMNK, mutant haplotypes CVMNT and CVIET, mixed mutant haplotypes CVMNK/T and CVM/I N/E K/T. The wild type CVMNK was the most prevalent haplotype (62.8%, 459/731). The highest prevalence of CVMNK was eastern Africa (75.4%, 43/57) followed by northern Africa (73.3%, 11/15) and central Africa (62.4%, 251/402) (Fig. 1). There was no significant difference among the sub-regions of Africa (P = 0.2216). The single mutant type K76T was detected in four isolates and the mixed mutant type of K/T76 were only detected once from all the isolates. However, 29.4% (215/731) of the isolates carried the triple mutations CVIET. Two mixed mutant haplotypes were confirmed including CVMNK/T and CVM/I N/E K/T with the prevalence of 0.1% (1/731) and 7.1% (52/731), respectively. The distribution of polymorphisms and prevalence of different haplotypes of pfcrt are shown in Table 2.
Polymorphisms of pfmdr1
A total of 434 P. falciparum isolates were successfully sequenced and pfmdr1 allelic variants were observed in only codons 86, 184 and 1246. Twelve haplotypes were identified including six mixed mutant haplotypes. The prevalence of wild type pfmdr1 NYD was 44.0% (191/434). Comparing the prevalence of pfmdr1 wild type in the sub-regions of Africa, the region of highest prevalence was southern Africa and the lowest was eastern Africa (P < 0.05). Three single mutant haplotypes YYD, NFD, NYY, and three double mutant haplotypes of YFD, YYY, and NFY were observed. The Y184F of pfmdr1 was predominant mutation with a prevalence of 24.7% (107/434) and 34 mixed mutant haplotype of N Y/F D were confirmed (Table 2). The prevalence of two mixed mutant haplotype N/Y YD and N Y/F D was significant different among the sub-regions (P = 0.0015) whereas there were no significant difference of the other pfmdr1 haplotypes among the groups. The YYD haplotype was at low prevalence of 5.3% (23/434) and not identified in eastern Africa. The single mutant D1246Y variant was not detected and only one isolate carried double mutation NFY and the other was mixed mutant haplotype of N/Y Y D/Y. The YFD haplotype (12.7%, 55/434) was more prevalent compared to the other two haplotypes YYY (0.2, 1/434) and NFY (0.2, 1/434). The double mutant haplotype was more common in eastern Africa (25.0%, 5/20) followed by western Africa (18.3%, 13/71) and central Africa (13.2%, 34/257). (Fig. 1).
In addition, six mixed mutant haplotypes (N/Y YD, N Y/F D, Y Y/F D, N/Y F D, N/Y Y/F D, and N/Y Y D/Y) were identified with a combined prevalence of 10.37% (56/434) and the two most common mixed haplotypes were N Y/F D and N/Y Y/F D (Fig. 2 and Table 2).
Polymorphisms of pfk13
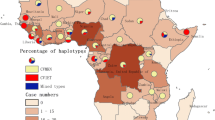
A total of 1,357 P. falciparum isolates from 33 African countries were successfully sequenced of pfk13-propeller domain. Twenty-six different mutant alleles were identified including 22 non-synonymous and four synonymous polymorphic sites (Table 3 and Fig. 3). A total of 49 isolates carried single pfk13 mutation with the prevalence of 3.6% (49/1,357). There were no pfk13 mutations isolated from northern and southern Africa. The prevalence of pfk13 mutations was highest in eastern Africa (9.5%, 4/42), followed by central Africa (4.5%, 38/839) and western Africa (1.9%, 7/370). The A578S variant, the most common mutation in pfk13 in Africa, was identified from 10 isolates (four from Equatorial Guinea, two from Angola, and one each from the Democratic Republic of Congo, Ghana, Guinea, and Uganda.) The Q613E variant was the second-most prevalent mutation, which was found in Angola, Democratic Republic of the Congo and Tanzania. Three mutations associated with artemisinin resistance were identified, including M476I, R539T and P553L. One isolate with R539T (0.1%, 1/1,357) and one with P553L (0.1%, 1/1,357) variant were found from Angola and another isolate with M476I mutation (0.1%, 1/1,357) was from Equatorial Guinea.
Discussion
This study was part of the national anti-malarial drug surveillance network and supported by the National Malaria Diagnosis Reference Laboratory Network and NMEP. China has set up a well-organized network for malaria diagnosis, treatment and surveillance covering national, provincial and county levels. Nevertheless, there are several challenges in the post-malaria elimination phase in China. One big challenge is how to maintain strong surveillance and response capacity after malaria elimination because thousands of imported malaria cases are reported in China annually. Plasmodium falciparum has developed resistance to all anti-malarial drugs, including ACT [22]. This study evaluated the prevalence of pfcrt, pfmdr1 and pfk13-propeller mutations of P. falciparum isolates imported from Africa and the geographical distribution of the prevalence of these three genes in imported African P. falciparum isolates was mapped as well.
CQ was a first-line anti-malarial drug to treat uncomplicated falciparum malaria in Africa from the 1940s, and was widely used because of its high efficacy, safety and low cost [23]. CQ resistance was first identified along the Thai-Cambodian border in the late 1950s [24, 25], and first reported in Africa in the 1970s [26]. In Africa, CQ was replaced by SP and ACT for uncomplicated malaria treatment between the late 1990s and early 2000s. The pfcrt mutations in codons 72–76 were considered to be the most reliable molecular marker for CQ resistance [19]. The prevalence of pfcrt mutations in Africa decreased significantly in contrast to the late 1990s. The reduction of prevalence of the pfcrt mutation and return of CQ sensitivity was also found in other studies in several malaria-endemic countries in Africa [27,28,29]. The termination of CQ use resulted in recovery of its efficacy. The most common haplotype of pfcrt was the wild type CVMNK with the prevalence of 62.8%, which was higher compared with that in the 1990s. Although only a few isolates were detected with single mutation at codon 76, the prevalence of triple mutant haplotype CVIET was 29.4%. In addition, 52 isolates with mixed triple mutant haplotypes CV M/I N/E K/T were identified. According to the published study, CQ resistance may have been caused by selective drug pressure, and multiple genomic background of the strains. Resistant mutations selected by anti-malarial drugs remove linked neutral variation as they sweep (increase in frequency) through a parasite population [30].
The pfmdr1 gene was associated with resistance to multiple anti-malarial drugs [12,13,14]. The pfmdr1 N86Y and pfcrt K76T variants have been shown to be in strong linkage disequilibrium, which is associated with CQ, mefloquine, lumefantrine, quinine, and dihydroartimisinin resistance in vitro [31,32,33]. This study identified pfmdr1 mutations in only codons 86, 184 and 1246 and total 12 haplotypes, including six mixed mutant haplotypes, were detected. The predominant mutation of Y184F had prevalence of 24.7% (107/434). The single mutant haplotype of pfmdr1 N86Y was at low prevalence of 5.3% (23/434), lower than another study with the prevalence of 31.0% in 2012 and 8.2% in 2016 [34]. The single mutant type NYY was not detected in this study, suggesting that NYY was rare in Africa compared with previous data [35]. In addition, the single mutant haplotype YYD and NYD was common in Africa while prevalence of the double mutant haplotype YFD, YYY and NFY was not significantly different among the different sub-regions (P > 0.05). This difference might be caused by the diversity of drug pressure and transmission intensity among the countries or regions in Africa.
Mutations in pfk13-propeller domain were first confirmed to be associated with artemisinin resistance in 2014 [20]. Until now, nine validated variants and over 20 candidates or associated mutations of pfk13 have been identified [6]. Forty-nine out of 1,357 isolates showed pfk13-propeller mutations with prevalence of 3.6% (49/1,357) in this study. The non-synonymous mutations in pfk13 are rare in Africa and their profile is diverse [6, 36,37,38]. A total of 22 non-synonymous and four synonymous polymorphic sites were identified in this study (Table 3). C580Y and F446I mutations, which are the most common mutations in GMS, and the predominant mutation in southern China, respectively [39], were not detected in imported African isolates in this study. Three mutations in pfk13-propeller domain, including M476I, R539T and P553L associated with artemisinin resistance, were observed in three isolates in this study. Another pfk13 mutation, M579I was identified from one isolate from Equatorial Guinea, which was reported to be associated with artemisinin resistance in Africa [40]. Nevertheless, this mutation was not observed in this study. The presence of C580Y mutation was detected in three patients (2.7%, 3/113) from migrant Chinese workers returning from Ghana in 2013, but this needed further characterization [41]. Previous studies reported that R539T mutation was identified from a population returning to China from Africa [42]. In this study, although one isolate carried the R539T variant, there was no evidence to prove this was an artemisinin-resistant isolate because there was no treatment failure outcome associated with the variant. The A578S variant, which is the most common mutation in pfk13 in Africa, was identified from 10 isolates (four from Equatorial Guinea, two from Angola, and one each from the Republic of Congo, Ghana, Guinea, and Uganda). A578S is comprised of two tightly linked SNPs and might be involved in artemisinin resistance in Africa [43]. Recently, the de novo emergence and clonal expansion of pfk13 R561H lineage has been reported in Rwanda and this mutation has been confirmed as a mediator of artemisinin resistance in vitro [44]. Another more recent study reported that pfk13 R561H occurred in 4.5% (3/66) of the isolates collected in southern Rwanda in 2019 [45]. Interestingly, an imported malaria case from Rwanda to China was detected with R561H mutation [46] and one isolate from southeast Tanzania carried this mutation too [47]. Therefore, molecular marker surveillance could provide early warning and evidence for efficacy of anti-malarial drugs to treat imported cases. China has set up an anti-malarial drug surveillance network that is responsible for implementing an integrated drug efficacy study (iDES) of anti-malarial drugs for national policy and molecular surveillance in the entire country.
Limitations
This study only evaluated the prevalence of molecular markers associated with anti-malarial drug resistance of imported cases from Africa and the treatment outcome was not analysed. All imported malaria cases will be treated according to national anti-malarial drug policy (Additional file 3). The iDES, as one component of routine surveillance systems, will be considered in the malaria elimination phase to provide evidence for updating the guidelines of anti-malarial drug treatment in China, especially for imported malaria cases. In addition, although mixed haplotypes were identified in some samples, the multiplicity of infection of the samples was not tested in this study.
Conclusion
This study provides evidence to give insight into potential issues with anti-malarial drug resistance to inform national anti-malarial drug policy in China to treat imported cases.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets analysed in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Feng J, Zhang L, Huang F, Yin JH, Tu H, Xia ZG, et al. Ready for malaria elimination: zero indigenous case reported in the People’s Republic of China. Malar J. 2018;17:315.
Feng X, Levens J, Zhou XN. Protecting the gains of malaria elimination in China. Infect Dis Poverty. 2020;9:43.
Zhang L, Feng J, Zhang SS, Xia ZG, Zhou SS. The progress of national malaria elimination and epidemiological characteristics of malaria in China in 2017. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis. 2018;36:201–9 (in Chinese).
WHO. Strategy for malaria elimination in the GMS (2015–2030). Geneva: World Health Organization; 2015.
Ashley EA, Dhorda M, Fairhurst RM, Amaratunga C, Lim P, Suon S, et al. Spread of artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:411–23.
WHO. Artemisinin resistance and artemisinin-based combination therapy efficacy. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018.
Roper C, Alifrangis M, Ariey F, Talisuna A, Menard D, Mercereau-Puijalon O, et al. Molecular surveillance for artemisinin resistance in Africa. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14:668–70.
Lakshmanan V, Bray PG, Verdier-Pinard D, Johnson DJ, Horrocks P, Muhle RA, et al. A critical role for PfCRT K76T in Plasmodium falciparum verapamil-reversible chloroquine resistance. EMBO J. 2005;24:2294–305.
Picot S, Olliaro P, Monbrison FD, Bienvenu AL, Price RN, Ringwald P. A systematic review and meta-analysis of evidence for correlation between molecular markers of parasite resistance and treatment outcome in falciparum malaria. Malar J. 2009;8:89.
Awasthi G, Prasad GBKS, Das A. Population genetic analyses of Plasmodium falciparum chloroquine receptor transporter gene haplotypes reveal the evolutionary history of chloroquine-resistant malaria in India. Int J Parasitol. 2011;41:705–9.
Awasthi G, Satya Prasad GB, Das A. Pfcrt haplotypes and the evolutionary history of chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium falciparum. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2012;107:129–34.
Holmgren G, Hamrin J, Svard J, Martensson A, Gil JP, Bjorkman A. Selection of pfmdr1 mutations after amodiaquine monotherapy and amodiaquine plus artemisinin combination therapy in East Africa. Infect Genet Evol. 2007;7:562–9.
Dahlström S, Ferreira PE, Veiga MI, Sedighi N, Wiklund L, Mårtensson A, et al. Plasmodium falciparum multidrug resistance protein 1 and artemisinin-based combination therapy in Africa. J Infect Dis. 2009;200:1456–64.
Vinayak S, Alam MT, Sem R, Shah NK, Susanti AI, Lim P, et al. Multiple genetic backgrounds of the amplified Plasmodium falciparum multidrug resistance (pfmdr1) gene and selective sweep of 184F mutation in Cambodia. J Infect Dis. 2010;201:1551–60.
Ferreira PE, Holmgren G, Veiga MI, Uhlen P, Kaneko A, Gil JP. PfMDR1: mechanisms of transport modulation by functional polymorphisms. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e23875.
Sidhu AB, Uhlemann AC, Valderramos SG, Valderramos JC, Krishna S, Fidock DA. Decreasing pfmdr1 copy number in Plasmodium falciparum malaria heightens susceptibility to mefloquine, lumefantrine, halofantrine, quinine, and artemisinin. J Infect Dis. 2006;194:528–35.
Dokomajilar C, Nsobya SL, Greenhouse B, Rosenthal PJ, Dorsey G. Selection of Plasmodium falciparum pfmdr1 alleles following therapy with artemether-lumefantrine in an area of Uganda where malaria is highly endemic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50:1893–5.
Snounou G, Viriyakosol S, Zhu XP, Jarra W, Pinheiro L, do Rosario VE, et al. High sensitivity of detection of human malaria parasites by the use of nested polymerase chain reaction. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993;61:315–20.
Djimde A, Doumbo OK, Cortese JF, Kayentao K, Doumbo S, Diourte Y, et al. A molecular marker for chloroquine-resistant falciparum malaria. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:257–63.
Ariey F, Witkowski B, Amaratunga C, Beghain J, Langlois AC, Khim N, et al. A molecular marker of artemisinin-resistant Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Nature. 2014;505:50–5.
Basco LK, Ringwald P. Molecular epidemiology of malaria in Cameroon. X. Evaluation of PFMDR1 mutations as genetic markers for resistance to amino alcohols and artemisinin derivatives. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2002;66:667–71.
White NJ. Antimalarial drug resistance. J Clin Invest. 2004;113:1084–92.
Flegg JA, Metcalf CJE, Gharbi M, Venkatesan M, Shewchuk T, Hopkins Sibley C, et al. Trends in antimalarial drug use in Africa. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2013;89:857–65.
Harinasuta T, Suntharasamai P, Viravan C. Chloroquine-resistant falciparum malaria in Thailand. Lancet. 1965;2:657–60.
Montgomery R. Chloroquine-resistant falciparum malaria in South-East Asia, with a report of a case from Thailand. J R Army Med Corps. 1964;110:172–4.
Young MD, Moore DV. Chloroquine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1961;10:317–20.
Lu F, Zhang M, Culleton RL, Xu S, Tang J, Zhou H, et al. Return of chloroquine sensitivity to Africa? Surveillance of African Plasmodium falciparum chloroquine resistance through malaria imported to China. Parasit Vectors. 2017;10:355.
Mita T, Kaneko A, Lum JK, Bwijo B, Takechi M, Zungu IL, et al. Recovery of chloroquine sensitivity and low prevalence of the Plasmodium falciparum chloroquine resistance transporter gene mutation K76T following the discontinuance of chloroquine use in Malawi. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2003;68:413–5.
Frosch AE, Laufer MK, Mathanga DP, Takala-Harrison S, Skarbinski J, Claassen CW, et al. Return of widespread chloroquine-sensitive Plasmodium falciparum to Malawi. J Infect Dis. 2014;210:1110–4.
Escalante AA, Smith DL, Kim Y. The dynamics of mutations associated with anti-malarial drug resistance in Plasmodium falciparum. Trends Parasitol. 2009;25:557–63.
Sidhu AB, Verdier-Pinard D, Fidock DA. Chloroquine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum malaria parasites conferred by pfcrt mutations. Science. 2002;298:210–3.
Duraisingh MT, Cowman AF. Contribution of the pfmdr1 gene to antimalarial drug-resistance. Acta Trop. 2005;94:181–90.
Wurtz N, Fall B, Pascual A, Fall M, Baret E, Camara C, et al. Role of Pfmdr1 in in vitro Plasmodium falciparum susceptibility to chloroquine, quinine, monodesethylamodiaquine, mefloquine, lumefantrine, and dihydroartemisinin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58:7032–40.
Zhang T, Xu X, Jiang J, Yu C, Tian C, Li W. Surveillance of antimalarial resistance molecular markers in imported Plasmodium falciparum malaria cases in Anhui, China, 2012–2016. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2018;98:1132–6.
Amor A, Toro C, Fernandez-Martinez A, Baquero M, Benito A, Berzosa P. Molecular markers in Plasmodium falciparum linked to resistance to anti-malarial drugs in samples imported from Africa over an eight-year period (2002–2010): impact of the introduction of artemisinin combination therapy. Malar J. 2012;11:100.
de Laurent ZR, Chebon LJ, Ingasia LA, Akala HM, Andagalu B, Ochola-Oyier LI, et al. Polymorphisms in the K13 gene in Plasmodium falciparum from different malaria transmission areas of Kenya. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2018;98:1360–6.
Kiaco K, Teixeira J, Machado M, do Rosario V, Lopes D. Evaluation of artemether-lumefantrine efficacy in the treatment of uncomplicated malaria and its association with pfmdr1, pfatpase6 and K13-propeller polymorphisms in Luanda, Angola. Malar J. 2015;14:504.
Kamau E, Campino S, Amenga-Etego L, Drury E, Ishengoma D, Johnson K, et al. K13-propeller polymorphisms in Plasmodium falciparum parasites from sub-Saharan Africa. J Infect Dis. 2015;211:1352–5.
Huang F, Takala-Harrison S, Jacob CG, Liu H, Sun X, Yang H, et al. A single mutation in K13 predominates in Southern China and is associated with delayed clearance of Plasmodium falciparum following artemisinin treatment. J Infect Dis. 2015;212:1629–35.
Lu F, Culleton R, Zhang M, Ramaprasad A, von Seidlein L, Zhou H, et al. Emergence of indigenous artemisinin-resistant Plasmodium falciparum in Africa. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:991–3.
Feng J, Li J, Yan H, Feng X, Xia Z. Evaluation of antimalarial resistance marker polymorphism in returned migrant workers in China. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59:326–30.
Yang C, Zhang H, Zhou R, Qian D, Liu Y, Zhao Y, et al. Polymorphisms of Plasmodium falciparum k13-propeller gene among migrant workers returning to Henan Province, China from Africa. BMC Infect Dis. 2017;17:560.
Maiga-Ascofare O, May J. Is the A578S single-nucleotide polymorphism in K13-propeller a marker of emerging resistance to artemisinin among Plasmodium falciparum in Africa? J Infect Dis. 2016;213:165–6.
Uwimana A, Legrand E, Stokes BH, Ndikumana JM, Warsame M, Umulisa N, et al. Emergence and clonal expansion of in vitro artemisinin-resistant Plasmodium falciparum kelch13 R561H mutant parasites in Rwanda. Nat Med. 2020;26:1602–8.
Bergmann C, van Loon W, Habarugira F, Tacoli C, Jäger JC, Savelsberg D, et al. Increase in Kelch 13 polymorphisms in Plasmodium falciparum, Southern Rwanda. Emerg Infect Dis. 2021;27:294–6.
Wang X, Ruan W, Zhou S, Huang F, Lu Q, Feng X, Yan H. Molecular surveillance of Pfcrt and k13 propeller polymorphisms of imported Plasmodium falciparum cases to Zhejiang Province, China between 2016 and 2018. Malar J. 2020;19:59.
Bwire GM, Ngasala B, Mikomangwa WP, Kilonzi M, Kamuhabwa AAR. Detection of mutations associated with artemisinin resistance at k13-propeller gene and a near complete return of chloroquine susceptible falciparum malaria in Southeast of Tanzania. Sci Rep. 2020;10:3500.
Acknowledgements
We thank all the participants who provided blood samples for this study.
Funding
The study was one component of the National Anti-malarial Drug Resistance Surveillance Network, which was supported by the National Malaria Elimination Programme of China. Mapping and part of the sequencing work were supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (No. 18ZR1443400).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FH, XNZ conceived and designed the study. FH, HY and YWC conducted the laboratory work; FH, JBX carried out the data analysis. SSZ, ZGX, RA, and PR provided technique support for the data analysis and reviewing the manuscript. FH drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Ethical Review Committee of National Institute of Parasitic Diseases, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests. PR is a staff member of WHO. The author alone is responsible for the views expressed in this publication and they do not necessarily represent the decisions, policy or views of WHO.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table S1.
Primer sequences and nested PCR amplification conditions for pfcrt, pfmdr1 and pfk13 genes in Plasmodium falciparum.

Additional file 2: Fig. S1.
Indigenous malaria case distribution at county level in China, 2012–2015.
Additional file 3.
Anti-malarial drug policy of China.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, F., Yan, H., Xue, JB. et al. Molecular surveillance of pfcrt, pfmdr1 and pfk13-propeller mutations in Plasmodium falciparum isolates imported from Africa to China. Malar J 20, 73 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-021-03613-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-021-03613-5