Abstract
The South Eastern Desert (SED) of Egypt is one of the most promising areas in Egypt; it is widely explored for exploring the rare earth elements (REEs) and uranium-bearing ores. It is a main part of the Arabian-Nubian Shield (ANS). Therefore, the present study concerns with Sikait-Nugrus area as one of the most prolific sites in this region. The study provides a detailed geological, structural, and mineralogical investigation of the monzogranites to describe and characterize the various alteration types and sequence. For this purpose, remote sensing, geochemical and petrographical techniques were applied. The remote sensing technique helped in constructing a detailed geologic map of the study area to follow up strictly the alteration zone of the Sikait-Nugrus area. Petrographically, the granites predominates in the study area, they are described as slightly and highly altered monzogranites. The slightly altered one is composed mainly of quartz (~ 20–35%), alkali feldspar (~ 25–30%), plagioclase (~ 25–30%), and mica (~ 5–15%), while accessory minerals are represented by zircon and monazite. On the other hand, the portion of this granite close to the shearing zone is intensively altered and characterized by sericitization as the main alteration processes. This sheared portion is characterized by accessory minerals as, uranothorite, allanite, fluorite and Nb-minerals (ishikawaite). Minerlogically, the altered monzogranites are predominated by the following mineral groups: (1) radioactive minerals as uranyl silicates (soddyite, uranophane and kasolite), and thorium minerals (thorite and uranothorite), (2) Nb–Ta minerals (betafite, plumbobetafite, columbite, fergusonite, and aeschynite), (3) REE minerals (monazite, cheralite and xenotime), and (4) zircon and fluorite as accessory minerals. Geochemically, the recorded pattern of the REEs tetrad effect (M-type) for the highly altered samples indicate that these granites are highly evolved and affected by late stage of hydrothermal alteration and the effective water-rich alteration processes that connected to intensive physico-chemical changes. The total REE concentrations equal 241.8 and 249.75 ppm for the highly and slightly altered samples. A significant mass change (MC) was analyzed by the isocon technique (22.95 & 11.11) and volume change (VC) (1.8 &-7.99) for the highly and slightly altered samples, respectively. The mass balance calculations and the isocon diagrams revealed that some major oxides were removed from the slightly altered monzogranites and transformed later into highly altered monzogranites with increasing the alteration intensity due to the impacts of hydrothermal alteration processes. The studied area is virgin, where no detailed studies have been applied to this region. It is extendable to other parts of the Arabian-Nubian Shield in around the Red Sea in Egypt, Sudan, Saudi Arabia and Yemen. The applied technical workflow is also extendible to other surface analogues everywhere.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Introduction
In this work, “rare metals” refers to metals with a low natural availability. It is divided into four groups: fissionable elements (U and Th), rare earth elements (La–Lu), and trace elements (Nb, Ta, Mo, Ni, Co, Cu, Sn, and W) [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. According to [10] granite-hosted rare metal deposits are created either in the formed granite or accompanied with the hydrothermal alteration of magmatic rocks.
Weathering and hydrothermal alteration are two types of alteration that occur in rocks and affect their original characteristics. The classification relies on where the modifying fluids come from. Even though these phrases are frequently used interchangeably, the conditions under which these processes develop are different. In contrast to hydrothermal alteration, which occurs when hydrothermal fluids channel through parent rocks, weathering occurs in surface environments, according to [11, 12].
With the development of advanced satellite missions with higher spatial, spectral, radiometric and temporal resolutions, the remote sensing techniques are widely employed for mineral exploitation and geologic mapping, and their capabilities have increased [13,14,15]. Data of the satellite remote sensing (Landsat-8 OLI) was analyzed to trace the hydrothermal alterations in the form of iron-oxides, OH-bearing minerals and carbonate through the usage of the band ratio technique. Band ratio was broadly applied in geological and mineral alteration mapping in the central parts of the Eastern Desert of Egypt [16,17,18,19,20,21].
The GEOISO-Windows™ programme [22] was used in this study to calculate and visualize the mass balance/volume change by determining the absolute mobility of the components using [23] equations and [24, 25] isocon diagrams.
REE electron configurations cause irregular shapes of the normalized patterns, which can be attributed to the tetrad effect [26]. Mineral deposits, particularly those of precious and base metals, are frequently present along with hydrothermal alteration processes in acidic rocks [27,28,29,30,31].
The present study aims to differentiate and map the rock units using remote sensing techniques and characterize the highly and slightly altered monzogranites geochemically and mineralogically at Wadi Sikait, in the southern parts of the Eastern Desert.
Remote sensing data and geologic setting
Landsat-8 scene data for alteration mapping for Wadi Sikait area
To distinguish ferrugination, ferromagnesian, and OH-bearing minerals, three Landsat-8 band ratios were developed [18] (b4/b2, b5/b6, & b6/b7, Fig. 1a, b, c). The brighter regions signify the location of the target materials' dense concentration. Statistics and threshold values applied on the above-mentioned band ratios are summarized in (Table 1). Landsat-8 for delineating the hydrothermal alteration zones, colored composite images were for the aforementioned three image ratios (Fig. 1d), respectively. The image revealed that the Iron oxides (Ferrugination) appear in red and magenta color and are mainly concentrated in the monzogranites.
Landsat-8 ratios of the Wadi Sikait area in the Eastern Desert of Egypt: a Iron oxy-hydroxides minerals (Landsat-8 ratio b4/b2) red color shows anomalies after threshold is applied. b Ferromagnesian minerals B5/B6 ratio image, green color shows anomalies after threshold is applied. c OH-bearing and carbonate minerals (micas and clays) (Landsat-8 ratio b6/b7), blue color shows anomalies after threshold is applied. d Color composite of Landsat-8 ratio (b4/b2), (b5/b6), (b6/b7) in RGB
Geologic setting
Red Sea’s shorelines covers more than 2 million km2 of the Arabian Nubian Shield (ANS), which has been formed in the time interval 540–1100 Ma [32,33,34]. The Arabian Nubian Shield is thought to be formed because of the collision of East and West Gondwana plates during the Pan-African Orogeny; it is considered a northern extension of the Mozambique belt [8, 35,36,37,38]. The Red Sea rifting separates the Nubian Shield from the Arabian Shield, which is composed primarily of Pre-Cambrian basement complex in Egypt, Sudan, and Ethiopia [34, 39]. On the other bank, in Yemen, Saudi Arabia, and Jordan, some crystalline outcrops of the foundation rocks make up the Arabian Shield.
The Sikait-Nugrus region is exposed in the southern Eastern Desert and resembles the body of a fish with its head pointing towards the northwest and its tail extending towards the southeast [38, 40,41,42]. It is located on the Red Sea coast at about 70 km SW of Marsa Alam town.
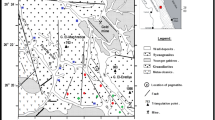
The study area represents the eastern part of Sikait-Nugrus area and lies between lat. 24° 38ʹ 36ʺ to 24° 39ʹ 21ʺ N and long. 34° 47ʹ 03ʺ to 34° 48ʹ 06ʺ E (Fig. 2a, b). From youngest to oldest the tectono-stratigraphic sequence is represented by the lamprophyre dykes, monzogranites, ophiolitic mélange, and psammitic gneisses [43]. The rocks are sheared, jointed, banded, hematized, and mylonitized; they also exhibit silicification and dipping by 50°–69° trending NNW-W.
a Landsat image showing the location of Wadi Sikait, and b a geological map of the study area, South Eastern Desert (SED), Egypt (modified after [42])
The ophiolitic mélange is primarily found in the eastern portion of the map region and is made up of blocks and fragments of ultramafic rocks that have been tectonically mixed together within a matrix with varying degrees of fineness. On the western side of Wadi Sikait, the mineralized zones of the psammitic gneiss consist of mélange matrix (composed of schists) containing considerable metagabbros, metaperidotites, and metapyroxenites fragments of various sizes [43,44,45]. These layered, highly foliated, featured, and folded matrixes are characterized by many rock schist types including tourmaline-garnetiferous-biotite, quartzo-feldspathic, sillimanite, and talc, schist [38].
On the western side of the plotted area, there are more monzogranite rocks. They are made mostly of quartz, biotite, feldspars, and plagioclase; they have grey to white pinkish in colour and is considered coarse to very coarse-grained. The rocks are jointed, blocky, weathered (Fig. 3a), sheared, mylonitic (Fig. 3b), and hematized (Fig. 3c) in some parts, while they are deformed and have a diagnostic gneissose structure (Fig. 3d) along their contacts with the oldest rocks. Sometimes, they are highly altered and become whitish with a considerable radioactive content (Fig. 3e, f). The quartz veins are striking E-W cutting all the aforementioned rocks and vary from 0.2 m to 1 m thick (Fig. 3g).
Field photographs in Wadi Sikait area indicating a General view of monzogranite showing blocky weathering, Looking NE, b Mylonitized in monzogranites at the contact with psammitic gneisses, looking S., c Hematization in monzogranites, looking W., d Gneissose structure in altered monzogranites, e Gradational contact between altered mineralized (whitish) and barren monzogranite (dark), Looking N., f Contact between altered mineralized (Whitish) and barren monzogranite (dark), Looking W., and g Quartz vein cutting monzogranite, Looking W
Materials and methods
On November 3, 2019, a terrain corrected and cloud-free single Landsat-8 L1T (terrain corrected) scene of UTM projection (path173/row 43), WGS-84 datum, zone 36 N was taken (Table 2). Band rationing, a form of image transformation, referring to processing multiple images from different bands into one single image. Theoretically, band rationing works because the effect of terrain and shadow is divided out in the calculations. Dividing the brightness values (DNs) at peaks/maxima and troughs/minima in a reflectance curve will elevate the DN values of specific geologic materials and may enhance the contrast between them. The choice of bands is based on their spectral reflectance and the absorption features of the mapped minerals. The data is processed using ENVI 5.3 software.
Several field trips were taken in order to gather rock samples that would reflect the various geological units and mineralized varieties. Ten thin-sections and polished slabs were petrographically investigated and eleven representative samples were mineralogically studied. The petrographic examination was carried out using Olympus polarizing microscope. For estimating the heavy minerals content (fraction size 0.125–0.250 mm) using the bromoform, some representative samples were crushed and grinded then sieved and quartered. For a precise mono-mineralogical fractionation and identification, heavy minerals were collected under a binocular microscope. A scanning electron microscope ESEM model Prisma E, attached with an energy dispersive X-ray spectrometer (EDS) spot chemical analysis of minerals was used in the Nuclear Materials Authority (NMA) of Egypt. The analytical conditions were 25–30 kV accelerating voltages, 1–3 nm beam resolution and 60–120 s counting time. The thin sections were studied using plane polarized microscope (model OLYMPUS BX53) attached with digital camera. The major oxides and trace elements in a total of 11 samples were analyzed using coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) in Acme Lab, Vancouver, Canada. Detection limits for trace elements and major oxides were 0.01–0.5 ppm and 0.001 wt%–0.04 wt%, respectively. The analytical precision, as calculated from replicate analyses, was 0.5% for major oxides and varied from 2 to 20% for trace elements. The total silica (SiO2) was determined using a spectrophotometric method in NMA (Nuclear Materials Authority) labs.
Normative mineral abundances were estimated based on the main elemental analysis and a set plots were created using the igneous petrology software® GCDkit (S1). The isocon diagrams equations of [23,24,25], the GEOISO-Windows™ programme [22], and EASYGRESGRANT spreadsheet of [46] were used to carry out mass-balance modeling and calculate the volume changes in metasomatic systems.
Petrography and mineralogy
Petrography
Megascopically, the granite under consideration is medium–grained (about 2 mm in length) and characterized by pink to greyish-pink colors with equigranular texture and gneisossity. Microscopic examination classified this granite as slightly altered (Fig. 4) and highly altered (Fig. 5) monzogranites. The slightly altered one is composed mainly of quartz (~ 20–35%), alkali feldspar (~ 25–30%), plagioclase (~ 25–30%), and mica (~ 5–15%) (Fig. 4a). Quartz represents the main constituent occurring as anhedral elongated crystals, mostly showing undulose extinction (Fig. 4b). Perthite (K-feldspar) is present as patched of subhedral crystals and scattered microcline crystals of cross-hatched twinning (Fig. 4a). Plagioclase is found as euhedral to subhedral tabular oligoclase (An18) crystals that display its distinctive lamellar twining. Some crystals are zoned and characterized by selective alteration for the more sodic core, where sodium is replaced by potassium provided by hydrothermal solutions [47, 48]. Mica is represented by biotite and muscovite; biotite is the main mica mineral occurring as platy flakes exhibiting its characteristic interference colors (Fig. 4c). Accessory minerals are represented by zircon and monazite (Fig. 4d).
Photomicrographs of Wadi Sikait slightly altered monzogranite showing a Minute crystals of zircon (Zr) associating the essential minerals; quartz (Qz), oligoclase (Olig) and microcline (Mic), b Elongation and undulose extinction of quartz, c Foliated flakes of biotite (Bi) associating elongated quartz, and d Minute crystal of monazite (M) in quartz surrounded by glassy zone
Photomicrographs of Wadi Sikait highly altered monzogranite showing a Biotite and muscovite with inclusion of zircon, CN (crossed nicols), b Fine crystals of epidote associating biotite, CN, c Euhedral crystal of metamictized zircon dismissing its interference colors, d Anhedral crystal of pale brown tetragonal uranothorite, e Well-formed crystals of allanite (All) exhibiting its characteristic interference colors (3rd order), CN, f Euhedral crystal of violet or purple color fluorite (Fl) associated with Nb mineral, PPL, g Oval crystal of highly radioactive Nb-mineral (ishikawaite) associated with Zircon (Zr), CN, and h EDX and Back-scattered image for the Nb-mineral (ishikawaite)
On the other hand, the portion of this granite close to the shearing zone is intensively altered and characterized by yellowish color, where plagioclase is saussiritized and biotite is kinked. Some flakes of biotite are depleted in iron oxides and transformed to muscovite (muscovitization), and others are enriched by iron oxides and transformed to annite containing pleochroic halos enclosing very fine crystals of radioelements-bearing monazite and zircon (Fig. 5a). Occasionally, it is associated with fine crystals of secondary epidote (Fig. 5b).
The study of the sheared portion is enhanced by ESEM and EDX analyses to clarify the effect of tectonism in transformation and alteration and the role of hydrothermal solution in enriching the accessory minerals by the radioelements. In addition to zircon and monazite, this sheared portion is characterized by uranothorite, allanite, fluorite and Nb-minerals (ishikawaite) where the radioelements are incorporated in their structures by the circulation of the hydrothermal solutions. Zircon is intensively metamictized dismissing its interference colors (Fig. 5c). Uranothorite present as pale brown tetragonal crystals with masked interference colors associating zircon (Fig. 5d). The most prevalent accessory mineral, allanite comes in a variety of forms and is distinguished by its distinctive faint brown colour. It manifests as well-developed euhedral crystals that display their distinctive interference colours, (Fig. 5e). Presence of the radioelements in the crystal lattices is shown by radial cracks surrounding the crystals with disguised interference colors. Fluorite crystallizes at low temperatures (about 500 °C) and is found as a late-crystallizing mineral in felsic igneous rocks as a result of hydrothermal activity [49, 50]. Sometimes it is characterized by a violet or purple color and associated with Nb mineral (Fig. 5f). Nb-minerals are highly radioactive with the variable composition of Nb, U, and Th, and are surrounded by pleochroic hallos (Fig. 5g). They identified in the thin sections by opacity and kidney-shape and could be recognized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) supported by semi-quantitative energy dispersive spectrometry (EDS) as ishikawaite (Fig. 5h).
Mineralogy
After applying systematic heavy mineral separation steps, the obtained handpicked mineral grains were then subjected to mineralogical identification under the reflected light microscope. Using a quantitative energy depressive X-ray (EDX) unite and a scanning electron microscope, the concerned grains were examined. Detailed mineralogical studies have been performed upon the slightly altered and highly altered monzogranite indicating the presence of: (1) Radioactive minerals, (2) Nb–Ta minerals, (3) REE minerals, and )4) Accessory minerals.
Radioactive minerals
Uranium minerals (uranyl silicates)
Most uranyl complexes that are in contact with the free silicate ions may precipitate uranyl silicate due to their solubility in water. The ESEM data of the uranyl minerals showed the presence of soddyite, uranophane, and kasolite (uranyl silicate minerals) in the highly altered monzogranite. Uranyl ion U6+ (which is easily combined with cations such as Ca2+, Cu2+, and Pb2+ to create kasolite and uranophane as secondary uranium minerals) is formed when U4+ is oxidized in the oxidation zone [51].
Soddyite (UO2)2SiO4(H2O)2 is frequently mixed with curite in the oxidized uranium ores. It is confirmed by ESEM that it has 68% U by wt. and 28.7% Si by wt. (Fig. 6a).
Uranophane [Ca(UO2)2SiO3(OH)2.5(H2O)], is known as uranotile; it is the most abundant uranyl silicate. Uranophane occurs as idiomorphic crystals that are prismatic or acicular, sometimes reticulate, but more often in divergent clusters or tufts (200 μm in length). In the present study, uranophane occurs as clusters and has 76.4% U by wt., 9.8% Ca by wt., and 13.8% Si by wt. (Fig. 6b).
Kasolite [Pb(UO2) (SiO3) (OH)2], has been tentatively identified as fine-grained aggregates. It is found as patches on the mica surface in the highly altered monzogranite. ESEM and semi-quantitative EDX analyses show U concentration in kasolite (46 wt. %) and Pb (33 wt. %) (Fig. 6c).
Thorium mineral
Thorite (ThSiO4) is crystalline in the tetragonal form and isomorphous with Zr and hafnium. It is stated by the ESEM techniques in the highly and slightly altered monzogranite samples. The obtained ESEM data and its EDX reflect the chemical composition of the thorite (Th 69.7 wt. %) and Y (4.5 wt. %), (Fig. 6d) in the highly altered samples; while in the slightly altered samples the obtained data reflect the chemical composition of the thorite (Th 41 wt. %), U (8.7 wt. %), with traces of LREEs (Fig. 6e).
Uranothorite [(U, Th) SiO4] may carry by the substitution for Th by U. The EDX analyses show that uranothorite has Th (59 wt. %), and U (19.5 wt. %) (Fig. 6f).
Thorite behavior during low-temperature alteration is important for element mobility and redistribution. Here we describe the alteration of ThSiO4 by hydrothermal fluids: as primary ThSiO4 associated with Zr, Sn, and pyrite (Fig. 6g-j). Most crystals have undergone significant compositional alteration. The change is variously attributed to fluid infiltration along fissures and reprecipitation (Fig.S1).
Nb–Ta minerals
Betafite [(Ca,U)2(Ti,Nb,Ta)2O6(OH)], has rare earth elements in its chemical composition; it is one of the Rare Earth Oxides [52]. The analyses show that it is enriched in U (43.9–53 wt. %), Th (13.3–0 wt. %) Nb (17–16.2 wt. %), with traces of REEs (Fig. 7a, b) in the highly and slightly altered monzogranite respectively.
Plumbobetafite [(Pb,U,Ca)(Nb,Ti)2O6(OH)] exists as small aggregates on the surfaces of quartz in the highly altered monzogranite. Its EDX indicated the presence of 51% U by wt., 16.9% Nb by wt., and 16.9% Pb by wt. (Fig. 7c).
Columbite [(Fe,Mn)(Nb,Ta)O4] is composed mainly of Nb (56.2–58 wt. %), Ta (9.1–11 wt. %), and Fe (26.9–23.4 wt. %) (Fig. 7d, e) in highly altered and slightly altered samples respectively.
Fergusonite has chemical formula [(Y,REEs)NbO4], where REE are the rare-earth elements in a solid solution with Y. Defining this mineral has been stated using the ESEM and has Nb (34.3–33.3 wt. %), Ta (5.4–2.6 wt. %), Y (29.7–25 wt. %), and REEs (19–29.5 wt. %) with U and Th traces (Fig. 7f, g) in highly altered and slightly altered samples respectively.
Aeschynite its general formula is [(Y,Ca,Fe)(Ti,Nb)2(O,OH)6]; its chemical composition, in the highly altered monzogranite, is Ti (13 wt. %), Nb (27 wt. %), Y (16 wt. %), Ta (4 wt. %), and U + Th (3 wt. %) (Fig. 7h).
REEs minerals
Monazite [(Ce,La,Th)PO4] is isostructural with Huttonite (ThSiO4), and Cheralite [(LREE,Th, Ca,U)(P,Si)O4] [53]. It is typically replaced by thorium in monazite. As a result of the complicated chemical compositions of the REEs minerals, isostructural minerals exhibit a variety of linked replacements in nature based on the pressure, temperature, and chemical compositions of the hydrothermal solutions and magma [54].
* The mechanisms of thorium substitution in monazite is as follows:
Thorium enters monazite via two paired substitutions: the cheralite (1) replacement and the huttonite exchange (2) [55].
Cheralite is usually the more prevalent of these two end members in natural monazite. In the highly altered samples, the EDX spectrum shows that these crystals range in composition from monazite to cheralite (Fig. 8a–c) due to the hydrothermal alteration effect.
Xenotime (HREE, Y, PO4) is a heavy rare earth element (HREE) phosphate, the principal host to economic HREE mineralization and a common accessory mineral in igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary rocks [56]. The existence of xenotime may be related to the abundance of the main component yttrium [57]. The EDX data shows that xenotime is composed of Y (35–17.6 wt. %), P (22–14 wt. %), HRREs (15–17 wt. %), Th + U (4–26.3 wt. %) and Fe (2.1–4.7 wt. %) (Fig. 8d, e) in highly altered and slightly altered samples respectively.
Accessory minerals
Zircon (ZrSiO4) was found as a solid solution with thorite as confirmed by EDX analyses Zr (50 wt. %), Hf (3 wt. %) with traces of U + Th (7 wt. %) (Fig. 8f). Some crystals contain inclusions of xenotime in the slightly altered monzogranite (Fig. 8g).
Fluorite (CaF2) exists in the form of fracture filling (Fig. 8h). The intimate association of purple fluorite with uranium minerals has been recognized in different deposits; this association is typical of epigenetic hydrothermal systems. The dark-blue/violet color of fluorite has been attributed to the effects of radioactivity, as postulated by many authors [49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58], which generates a disturbance in its crystal lattice rather than as a result of its chemical composition. Pi-Puig [59] concluded that the uranium-rich fluorite precipitated in the initial phases of mineralization from a reducing fluid, with low salinity (< 8% NaCl eq.) and an intermediate temperature (110–230 °C), and that the presence of organic compounds and sulfides (mainly pyrite) favored the simultaneous precipitation of uraninite (pitchblende variety) and fluorite.
Geochemistry
Major oxides
Eleven samples of altered monzogranites from Wadi Sikait were chemically analyzed to estimate major oxides, trace, and REEs using ICP-MS (Table 3). The altered samples are subdivided into slightly and highly altered rock samples. Four samples were chosen representatively from the slightly altered monzogranite, and seven samples from the highly altered ones. The altered monzogranite samples contained 73.4 –74.6 wt.% SiO2, 12.14–12.36 wt.% Al2O3, 3.3–2.12 wt.% Fe2O3, and 7.61–8.9 wt.% K2O + Na2O for the highly and slightly altered samples, respectively.
Trace elements
They were normalized to the primitive mantle [60]. It is indicated from the trace element patterns that the altered granites (Fig. 9) are effectively enriched in large ion lithospheric elements (Rb, Th, & U) and REEs (ƩREE + Y of 345 & 287.6 ppm) and depleted in Cu, Ni, Cr, and La. In addition, all samples had high Ga (38–31 ppm) contents for the highly and slightly altered samples.
Primitive mantle–normalized trace element for Wadi Sikait altered monzogranite using the primitive mantle values of [60]
Different alteration processes have affected the altered monzogranites under study along the fault plane. Their chemical analyses exhibit an increase in Th, U, Zr, Nb, and MREEs and depletion in L & HREEs for the highly altered samples; while in the slight one, there is an increase in Nb, U, Th, and LREEs and depletion in MREEs and HREEs (Fig. 10a, b).
REEs geochemistry
The two types of rocks (highly and slightly altered monzogranite) can be also distinguished by their chondrite normalized REE patterns. The altered granites show ‘seagull’ forms in chondrite-normalized REEs diagrams (Fig. 11). In the slightly altered samples, LREE and HREE are highly fractionated (LREE/HREE) (9.3); while in the highly altered there is less REE fractionation (LREE/HREE) (1.28). The total REE concentrations of 241.8 & 249.7 ppm, (La/Yb)N of 0.46–8.9, negative Ce anomaly (δCe) 0.98–0.96, and (negative Eu anomaly) δEu of 0.16–0.24 (in average) for the highly and slightly altered samples (Table 4). A weak REE fractionation, a strong negative Eu anomaly, and a weak negative Ce anomaly are all indicators of a weak REE fractionation [62,63,64]. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns demonstrate that the study samples were distinguished by LREE enrichment in the slightly altered samples and HREE in the highly altered, with strong negative Eu anomalies.
REE tetrad effects phenomenon in the altered monzogranites
The tetrad effect in highly evolved granitic systems is possibly caused by (1) fractional crystallization during igneous crystallization [71], (2) fluid–melt interaction during crystallization of the silicate melt [72, 73], (3) hydrothermal alteration during hydrothermal fluid–rock interaction [74], and (4) weathering after granite formation [75].
Masuda et al. [76] proposed two distinct categories of tetrad impacts. Both types are derived from each other and mirror themselves (M-type in solid samples as residue and W-type in the interacting fluids as extract). The labels “M” and “W” refer to REE patterns with upwards or downwards-curved tetrads respectively.
As suggested by [77] the development of the lanthanide tetrad effect (M-type) with pronounced negative Eu* in highly evolved granitic rocks implies the removal of a mirroring REE-pattern (W-type) with positive Eu*, corresponding to a coexisting high-temperature aqueous fluid. As a result, the majority of the granite facies under consideration exhibit steadily larger degrees of diversity in the REE fingerprints of silicate melts [78, 79].
The tetrad implication can be quantified using the techniques that proposed by [74, 77]. The TE1,3 values range from 1.17 to 1.02 in the highly and slightly altered monzogranite (Table 4).
According to the quantification approach suggested by [77] for the measurement of the 3rd and 4th tetrads which can be estimated as follows.
Then the tetrad implication TE1,3 = SQRT(t1 × t3).
Highly altered samples show convex tetrad implications of M-type in the 3rd and 4th tetrads, and the slightly altered ones have a flat HREE pattern based on the normalized REEs distribution patterns (Fig. 11). Rare earth elements in the highly altered granites are related to hydrothermal alteration during hydrothermal fluid–rock interaction.
Tetrad implications mechanism
Though the presence of tetrad impacts in geochemical operations, the primary procedure of this trait remain unknown [80]. Procedures like the melt/fluid interaction that is generally contributed to the hydrothermal activities and magmatic are the main aim of the present study. Yurimoto et al. [81] stated that the tetrad impacts of the normalized REEs distribution patterns may be attributed to the mineralization. REE3+ complexation by different ligands in various geological environments is considered a possible procedure for the tetrad implications. The outputs of this study show that in the hydrothermal F-rich and magmatic systems, REE-fluoride complex formation is an essential factor. Convex-type tetrad impacts are primarily caused by REE-Cl combination, whereas concave-type effects are caused by REE-F combination, according to thermodynamic modeling of Cl and F combination [82]. On the other hand, the activity of F-rich fluids in geological operations has been attributed to the M-type tetrad effects.
The late magmatic differentiates with deuteric alteration or substantial hydrothermal interactions have the greatest REEs tetrad impact. Additionally, the tetrad effect frequently occurs in conjunction with other altered geochemical action of numerous trace elements, which has been named by [83] as non-CHARAC (Charge & Radius Controlled) behavior. This activity is generally found in highly advanced magmatic systems that are abundant in elements like F, B, Li, and Cl, as well as in H2O, CO2, and other components [84]. This shows that an aqueous fluid system becomes increasingly important in the latter phases of acidic rocks crystallization.
Some researchers noticed the Co-existence of the W-shaped concave and M-shaped convex tetrad implications in many sites around the world such as Ti–rich bauxite in Iran [85], El Sela Eastern Desert, [86, 87], Qahr-Abad fluorite deposits in Iran [88], and the Eastern and Western Deserts of Egypt [10, 29]. The M-type tetrad impact is frequently noticed in the rare metal hydrothermal systems that produce granites [84]. The production of REE tetrad effects in granites is primarily governed by melt-fluid interaction in the late fractional crystallization phases [89]. The REE tetrad systems of these rocks were made by fractionation of the residual melt from a high-temperature aqueous fluid in the late phases of magma differentiation; just like the negative Eu anomalies were [90, 91].
In Fig. 12a the degree of Eu negative anomaly increases in proportion to the degree of tetrad impact (TE1,3). Based on the depletion of elements including Ba, Sr, P, Eu, and Ti, [92, 93] hypothesized that the collected granite had undergone considerable plagioclase and K-feldspar fractionation and small fractionation of Fe-Ti, and oxides. In plagioclase and alkali feldspar matrices, strontium is a compatible element, but rubidium is incompatible with plagioclase and very mildly incompatible/compatible with alkali feldspar [94]. The Zr/Hf, TiO2, and CaO ratios likewise show that they are directly proportional to the level of the Eu anomaly (Fig. 12b, c).
Eu/Eu* vs. a tetrad effects, b CaO, c TiO2, and d Zr/Hf variation diagrams for the altered monzogranites. For denotations see Fig. 9
Since the pronounced negative Eu anomalies include many geochemical characteristics, such as the tetrad effect, it may be assumed that the feldspar fractionation that occurred during magmatic differentiation is what caused the Eu anomaly. In contrast to fractional crystallization, (Fig. 13a, b) suggests that the REE tetrad implication may be the result of a fluid-melt interaction. So, based on our results, it would appear that the REE tetrad impact, following the production of granitic magma in a system of magmatic-hydrothermal transition, is most likely what caused the Eu anomaly of the studied altered monzogranites.
a La/Nb, and b Zr/Hf vs. tetrad effects for the altered monzogranites. For denotations see Fig. 9
Discussion
Alteration geochemistry
Wadi Sikait altered monzogranites display a different degree of hydrothermal alteration as silicification, sericitization, and hematitization. Before discussing petrogenesis, it is important to consider how the fluid-rock and the hydrothermal alteration interaction could modify the fundamental geochemical compositions [95,96,97,98,99].
The substantial hydrothermal alteration may have an impact on the alkali elements (e.g., Na, Ba, Sr, Rb, and K), including:
-
i.
K alteration causes the loss of CaO and Na2O, while K2O enrichment, and the increased mobility of LILEs due to replacing the plagioclase by K-feldspar [100,101,102],
-
ii.
phyllic alteration indicates the enrichment of MgO, SiO2, and Fe2O3, and the depletion of K2O, Na2O and CaO [95, 103],
-
iii.
silicification happens not only due to adding SiO2 but also due to the loss of most other compositions such as K2O, CaO, Fe2O3, Al2O3, Ba, Sr, and MgO that result from replacing some minerals by the quartz [95], and
-
iv.
sericitization shows an increase in K2O, Pb, Rb, and LOI and a loss of Sr, Na2O, and CaO due to replacing the plagioclase by sericite [104].
Based on geological and petrographic research, the hydrothermally altered rocks in the study area exhibit widespread silicification, sericitization, and albitization. The chemical index of alteration (CIA = 100 × molar proportion [Al2O3/(Al2O3 + Na2O + K2O + CaO*)] of [68] is used to calculate the relative degree of alteration. CIA ratio indicates that the highly and slightly altered rocks (of average = 55–58) were impacted by a considerable change in chemical composition concerning the fresh rocks (of average = 56) [61].
According to Meyer and Hemley [105], Wadi Sikait altered monzogranites are presented on AKF ternary diagram, where K = K2O, F = Fe2O3 + MgO + MnO, and A = Al2O3–(K2O + Na2O). It shows that the study samples fall in sericite facies (due to sericitization processes) and propylitic field (Fig. 14a). The weathering trends are plotted on the (CaO + Na2O)–K2O–Al2O3 triangular diagram (Fig. 14b) [106, 107], the samples exhibit a relative enrichment in Al2O3 and K2O compositions due to the feldspars alteration into clays [108,109,110].
The K-Na variations diagram of [106] presents 5 trends: K-metasomatism, silicification, desilicification, Na-metasomatism, and argillation (Fig. 14c). Most samples lie in the argillation trend and K-metasomatism. The most diagnostic geochemical properties of Wadi Sikait samples shown considerable variations in the Ca, Na, Fe, and Mg content (Fig. 14d). Intensely altered samples have Na2O + CaO values in weight percent due to the gradual drop in Na2O and CaO that occurs as alteration intensity increases. This pattern is a sign of the production of muscovite and sericitization as well as the destruction of plagioclase.
Ishikawa et al. [113] developed the Ishikawa alteration index (AI) to rate the severity of chlorite and sericite alterations. AI = 100 x (K2O + MgO)/(CaO + Na2O + MgO + K2O) and the chlorite carbonate pyrite index (CCPI) = 100 × (Fe2O3 + MgO)/(K2O + Na2O + Mgo + Fe2O3) are two alteration indices used in the alteration box plot (Fig. 15). Sericite and chlorite replacement of sodic plagioclase as the primary processes tracked by the index. Following are some responses to these modification processes [114]:
The initial process is typically replacing the albite by sericite [115, 116]. Based on constant Al2O3, reaction (1) results in gaining K2O and losting Cao and Na2O, while reaction (2) results in gaining in MgO and FeO, and losing K2O. Based on the various diagrams (Fig. 15a) which applied the alteration indices of Ishikawa (AI), sericite–chlorite altered in the chlorite–carbonate–pyrite index (CCPI); F = (Fe2O3 + MgO + MnO), Á = Fe2O3 + Al2O3–(CaO + Na2O + K2O); and K = K2O, each alteration type has a diagnostic alteration trend [117].
On plotting the CCPI vs. (AI), it is indicated that samples of the Wadi Sikait altered monzogranite primarily follow the sericite alteration trend and to some extend the K-feldspar trend (Fig. 15a) because of their relatively high AI values. Also, they primarily indicate the K-gain for the slightly altered samples with little Fe-gain for the highly altered samples following the A’KF ternary phase diagram of [118] (Fig. 15b).
Mass-balance calculation
Alteration indices and mass balance approaches differ primarily in that they quantify chemical changes as opposed to taking into consideration mineralogical restrictions. Field observations are dependent on alteration; thus it is not always simple to apply them to mass balance findings. However, mass balance allows for the precise measurement of the quantities of Si, Fe, Mg, K, Na, and Ca that are absorbed by the fluid or leached from the rock [120]. Another distinction between indexing and mass balancing approaches is that the latter calls for the identification of a precursor as well as the analysis of a few trace immobile elements.
Understanding geological processes, particularly the mass losing or gaining elements in the hydrothermal solutions, can be done by using mass balance calculations [95, 121]. Gresens [23] Firstly proposed modeling the immobility/mobility in a solution system, while the immobile element concept was stated by [122, 123].
Chemical mass transfer calculations in the study area include comparing the geochemical compositions of (1) the unaltered monzogranite [61] (regarded as the initial parent rock composition, i.e. the fresh rock) and (2) The Wadi Sikait altered monzogranite (the highly and least altered) composition was calculated by averaging the bulk chemical compositions of 10 unaltered rocks, sampled within 11 samples from Wadi Sikait monzogranite. For estimating the mass balance, two methods were applied.
The Gresens mass transfer equation
These techniques calculate the mass changes (volume and density changes) brought on by modification [23, 124]. The hydrothermal alteration accompanied with the altered monzogranite mineralized zone in Wadi Sikait reveals the presence of chemical ion exchange among the hydrothermal fluid, and the host and wall rocks, resulting in the creation of new different alteration minerals and the formation of several zones based on the pH, Eh, temperature, and the host rock and fluid compositions [105, 125]. The hydrothermal alteration processes are usually accompanied by the gain and loss of some mineral components of the entire rock mass [126].
The geochemical composition of the hydrothermally unaltered and altered rocks differs because of the mineralogical and bulk chemical alterations. Its zonation shows a variation in the fluid composition through time due interaction between this fluid and its host rocks. The hydrothermal alteration accompanied with the altered rocks indicates that the occurrence of chemical ion exchange between the hydrothermal fluids and the wall rocks. The gain and loss of parts of the whole rock mass are often linked to the hydrothermal alteration processes [127].
Gresens [23] was the first to propose this method, in which the simultaneous decrease and increase in volume that occurs in the hydrothermal alteration process are eliminated, allowing an evaluation of the level of the elemental mass loss or gain. [24, 25] developed the equations of [23] by supposing that the immobile elements in the alteration operations have no mass transfer along the isocon trend.
Using [23] equations and [24] isocon diagrams, the GEOISO-Windows™ software of [22] is the most modern program that is applied to analyze and visualize the mass volume/balance change due to the final mobility of the components. According to [128], elements of the high field strength (HFS), particularly Zr, Ti, and Al, were proposed to be stationary or have a limited mobility in the alteration operations. The major oxides as well as the trace elements of the studied altered monzogranite at Wadi Sikait have a significant depletion and addition based on the mass balance estimations that plotted on the isocon and histograms (Fig. 16, Table 5).
According to [23], comparing the volume and composition of the altered and unaffected rocks can help scientists identify changes in elemental composition brought on by gains, losses, or dilution. Grant [24] enhanced the [23] equation and stated that the immobile elements should be presented along the isocon line with no mass transfer.
The highly altered monzogranite samples in Wadi Sikait have mainly enriched in SiO2, Al2O3, Fe2O3, MnO, K2O with U, Y, Nb, Zr, Hf and Rb and depletion in Na2O, MgO and Ni. While the samples of the least alteration type have enrichments in SiO2, Al2O3, with U, Zn, and Nb, and depletion in Fe2O3, MnO, MgO, Y, Zr, Hf and Pb (Table 5, Fig. 16).
According to petrographic research, silicification processes may be associated with SiO2 enrichment, which may also be brought on by the more developed granites' increased the quartz amount as a free Si-bearing mineral. The enrichment of K in all samples could be related to K- metasomatism of these rocks. The change in redox potential of the fluids may have caused the Mn2+ to Mn4+ conversion, and it’s fixing as insoluble oxides and hydroxides may also have contributed to the Mn mass gain [129]. The enhanced Fe2O3 content may be attributed to the presence of hematite, goethite and pyrite that have been formed during the weathering processes in suitable pH-Eh conditions. Due to the sericitization processes, Al and Rb increase could be intimated to clay and sericite minerals. The depletion of Na could have produced due to the feldspar alteration and the release of Na into the alteration fluids. The Mg loss in the studied samples may be due to the alteration and destruction of the ferromagnesian minerals (such as micas and biotite). Y, Hf, and Zr are immobile and concentrated in the accessory minerals particularly in the xenotime, thorite, zircon, and uranothorite. U and Nb increments could be attributed to the presence of kasolite, uranophane, betafite, thorite, uranothorite, columbite, fergusonite, plumbobetafite, and aeschynite minerals.
Mass balance calculation
It is performed using the template of [46] which is based on the modified formula of [23], where the fresh monzogranite of [61] was used as the standard unaltered samples (Ci0), while highly and slightly altered samples were used as (Cia). The average concentrations were applied to reduce the implication of the compositional heterogeneity (e.g., [130, 131]).
An “isocon” is another solution for these models that exhibit no relative mass loss/gain. Plotting the elemental concentrations of the altered rock versus concentrations in the intact rock shows an isocon as a trend passing through the origin point. The mobility of the various elements is indicated by their positions on the plot relative to the isocon. Plotting the elemental concentrations of the original rock on the x-axis (marked Co) versus the elemental concentration of the altered rock on the y-axis (marked Ca). For each lithologic unit, one plot is given revealing the immobile elemental content and its increase/decrease in correlation with the isocon line.
The isocon lines are identified as the best-fit lines passing through the original point where the elements having relatively constant concentrations during the alteration process based on loss/gain ± 10% in correlation with the Ci0 both in the retrograde and prograde were chosen as immobile elements.
The isocon analysis states that there is an effective mass change (MC) (22.95 & 11.11) and volume change (VC) (1.8 & − 7.99) for the highly and slightly altered samples, respectively (Fig. 16, Table 5). Generally, some major oxides were lost from the slightly altered samples and transformed into the highly altered ones.
The graphical methods are primarily characterized by the clarity of their diagrams and their fast implementation [132]. The isocon method of [24] was applied to prove the chemical changes among the altered rocks and their accompanied intact rocks. All the calculations are applied following Grant’s approach [24]:
where CA and CF are the concentrations in the altered (A) and fresh (F) sample, respectively; and ΔC refer to the loss/gain of trace elements in ppm, or to the major elements in g/100 g of rock. Results are presented in Table 6.
It states that a large amount of Al, Fe, Si, and some Zr, Li dissolved in the fluid system (Fig. 17, Table 6). The elements Si, Al, Mg, Ca, and Sr exhibited strong mobility (∆Ci/C0 > 1.0) into the highly altered rocks during the hydrothermal alteration operations.
In terms of REEs and trace elements, most of the HREEs were migrated during a hydrothermal alteration into the highly altered samples, but LRREs were gained in the slightly altered ones. The highest gain in the highly altered samples was noticed in Zr (1194.91 ppm), Nb (882.86 ppm), U which is up to (331.79 ppm), Th (345.04 ppm), whereas in slightly altered one U which is up to (14.83 ppm), and Th (42.15 ppm).
Conclusion
The alteration zones in the altered monzogranites were identified by Landsat-image techniques and confirmed by field trips. The altered monzogranites were categorized into slightly and highly altered monzogranites. The petrographic investigations were comparable with these results. It is worthy to mention that severe alteration processes lead to chemical and mineralogical changes. The noticeable increments and decrements in most major oxides, trace and rare earth elements, accompanied by distinct mineral association confirmed these changes. The samples of Wadi Sikait highly altered monzogranite have mainly enrichments in SiO2, Al2O3, Fe2O3, MnO, K2O with U, Y, Nb, Zr, Hf and Rb and depletion in Na2O, MgO and Ni, while the samples of the slight alteration have enrichments in SiO2, Al2O3, with U, Zn, and Nb, and depletion in Fe2O3, MnO, MgO, Y, Zr, Hf and Pb. Highly altered samples show convex tetrad implications of M-type in the 3rd and 4th tetrads, and the slightly altered ones have a flat HREE pattern based on the normalized REEs distribution patterns. The total REE concentrations of 241.8 & 249.7 ppm, (La/Yb)N of 0.46–8.9, negative Ce anomaly (δCe) 0.98–0.96, and (negative Eu anomaly) δEu of 0.16–0.24 (in average) for the highly and slightly altered samples. The isocon analysis indicates that there was a significant mass change (MC) (22.95 & 11.11) and volume change (VC) (1.8 & − 7.99) for the highly and slightly altered samples, respectively. Generally, some major oxides were lost from the slightly altered samples and transformed into the highly altered ones, illustrating the effects of hydrothermal and water-rich alteration processes connected to vigorous physic-chemical changes. Minerlogically; the studied altered monzogranites demonstrated the presence of these mineralogical groups, (1) radioactive minerals as uranyl silicates (soddyite, uranophane, kasolite), thorium minerals (thorite, uranothorite), (2) Nb—Ta minerals (betafite, plumbobetafite, columbite, fergusonite, aeschynite), (3) REE minerals (monazite, cheralite, xenotime,) and (4) zircon and fluorite as accessory minerals (Table 7).
Availability of data and materials
I confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available in the article.
References
Arbuzov SI, Spears DA, Vergunov AV, Ilenok SS, Mezhibor AM, Ivanov VP, Zarubina NA (2019) Geochemistry, mineralogy and genesis of rare metal (Nb-Ta-Zr-Hf-Y-REE-Ga) coals of the seam XI in the south of Kuznetsk Basin, Russia. Ore Geol Rev 113:103073. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103073
Ibrahim ME, Saleh GM, Dawood NA, Aly GM (2010) Ocellar lamprophyre dyke bearing mineralization, Wadi Nugrus, Eastern Desert, Egypt: geology, mineralogy and geochemical implications. Chin J Geo Chem 29(383):392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-010-0470-6
Wang Y, Peng J, Wang L, Xu C, Dai B (2023) Micro-macro evolution of mechanical behaviors of thermally damaged rock: a state-of-the-art review. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.11.012
Yan T, Xu R, Sun S, Hou Z, Feng J (2024) A real-time intelligent lithology identification method based on a dynamic felling strategy weighted random forest algorithm. Pet Sci 21(2):1135–1148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petsci.2023.09.011
Ibrahim ME, Watanabe K, Saleh GM, Ibrahim WS (2015) Abu Rusheid lamprophyre dikes, South Eastern Desert, Egypt: as physical-chemical traps for REEs, Zn, Y, U, Cu, W, and Ag. Arab J Geosci 8:9261–9270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-1882-8
Baioumy H (2021) Geology of rare metals in Egypt-a review. Int J Mater Technol Innov 1(1):58–76
Saleh GM, Kamar MS, Mohamed GA, El Tohamy AM (2023) Petrochemistry, rare metals-bearing minerals and spectrometric exploration in Khour Abalea, Abu Rusheid area, Eastern Desert, Egypt. J Afr Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2023.105005
Saleh GM, Ali GM, El Tohamy AM (2023) Petrogenesis and geological implications of the trachytic rocks in the South Eastern Desert, Egypt: mineralogical, geochemical, and radioactivity insights. Appl Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1080/25726838.2023.2244771
Saleh GM, El Tohamy AM, Taher N, Ali GM (2023) Mineralogical, geochemical and radioactivity of Gabal Nasb Hebili, Arabian Nubian Shield, Egypt: implication for rare metals mineralization. J Afr Earth Sci 206:105041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2023.105041
Ibrahim ME, El-Kalioby BA, Aly GM, El Tohamy AM, Watanabe K (2016) Altered granitic rocks, Nusab El Balgum Area, Southwestern Desert, Egypt: mineralogical and geochemical aspects of REEs. Ore Geol Rev 70:252–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.04.016
Yildiz A, Kuscu M, Dumlupunar İ, Aritan AE, Bağci M (2010) The determination of the mineralogical alteration index and the investigation of the efficiency of the hydrothermal alteration on physicomechanical properties in volcanic rocks from Köprülü, Afyonkarahisar, W Turkey. Bull Eng Geol Environ 69:51–61
Ceryan S (2018) Weathering indices used in evaluation of the weathering state of rock material. In: Ceryan N (ed) Handbook of research on trends and digital advances in engineering geology. IGI Global, ABD, pp 132–186
Abrams MJ, Brown D, Lepley L, Sadowski R (1983) Remote sensing of porphyry copper deposits in Southern Arizona. Econ Geol 78:591–604
Clark RN (1999) Spectroscopy of rocks and minerals, and principles of spectroscopy. In: Rencz AN (ed) Manual of remote sensing, Volume 3, remote sensing for the earth sciences. John Wiley and Sons, New York, pp 3–58
Wang M, Wu Y, Song B, Xu W (2024) Point load strength test power index of irregular sandy dolomite blocks. Rock Mech Rock Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-023-03733-1
Abdeen MM, Thurmond AK, Abdelsalam M, Stern B (2001) Application of ASTER band-ratio images for geologic mapping in arid regions; The Neoproterozoic Allaqi Suture. Egypt Geol Soc Am 33:1–289
Tolba A, Kamel M (2014) Lithological discrimination of Neoproterozoic basement rocks based on Landsat ETM+ image processing techniques and petrographic studies of Gabal Gassuss, Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. Al Azhar Bull Sci 25(1):9–28
Abdel Ghani IM (2020) The application of Landsat-8 imagery and airborne Gamma-ray spectrometric data for lithological mapping of Gabal Nuqara area, Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. J North Basic Appl Sci (JNBAS) 5(1):47–69
Li X, Fan G (2024) On strain localization of aeolian sand in true triaxial apparatus. Acta Geotech. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-024-02273-4
He M, Dong J, Jin Z, Liu C, Xiao J, Zhang F, Deng L (2021) Pedogenic processes in loess-paleosol sediments: Clues from Li isotopes of leachate in Luochuan loess. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 299:151–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2021.02.021
Awad H, Zakaly M, Nastavkin V, El Tohamy AM, El-Taher A (2020) Radioactive mineralizations on granitic rocks and silica veins on shear zone of El-Missikat area, Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. Appl Radiat Isot. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2020.109493
Coelho J (2006) GEOISO—a Windows™ program to calculate and plot mass balances and volume changes occurring in a wide variety of geologic processes. Comput Geosci 32(9):1523–1528
Gresens RL (1967) Composition-volume relationships of metasomatism. Chem Geol 2:47–65
Grant JA (1986) The isocon diagram; a simple solution to Gresens’ equation for metasomatic alteration. Econ Geol 81(8):1976–1982
Grant JA (2005) Isocon analysis: a brief review of the method and applications. Phys Chem Earth A B C 30(17):997–1004
Abedini A, Azizi RM, Calagari AA, Cheshmehsari M (2017) Rare earth element geochemistry and tetrad effects of the Dalir phosphatic shales, northern Iran. Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie Abhandlungen 286:169–188. https://doi.org/10.1127/njgpa/2017/0693
Ibrahim ME, El- Kalioby BA, Aly GM, Qurany EA, El Tohamy AM (2016) Rare metals mineralization in altered granites at Nusab El Balgum area, south Western Desert, Egypt. Annals Geol Surv Egypt V.XXXIII:151–173
Yang L, Yang D, Zhang M, Meng S, Wang S, Su Y, Long Xu (2024) Application of nano-scratch technology to identify continental shale mineral composition and distribution length of bedding interfacial transition zone - a case study of Cretaceous Qingshankou formation in Gulong Depression, Songliao Basin, NE China. Geoenergy Sci Eng 234:212674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoen.2024.212674
El Mezayen AM, Heikal MA, El-Feky MG (2019) Petrology, geochemistry, radioactivity, and M-W type rare earth element tetrads of El Sela altered granites, south eastern desert. Egypt Acta Geochim 38:95–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-018-0274-7
Kamar MS, Moghazy NM, Saleh GM (2021) Pan-African rare metals bearing pegmatites in Wadi Ghadir, South Eastern desert, Egypt: the geochemical evolution and implications for mineralization. SN Appl Sci 3:427. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-021-04414-w
Su F, He X, Dai M, Yang J, Hamanaka A, Yu Y, Li J (2023) Estimation of the cavity volume in the gasification zone for underground coal gasification under different oxygen flow conditions. Energy 285:129309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2023.129309
Lasheen ES, Rashwan MA, Osman H, Alamri S, Khandaker MU, Hanfi MY (2021) Radiological hazard evaluation of some Egyptian magmatic rocks used as ornamental stone: petrography and natural radioactivity. Materials 14:7290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14237290
Liang S, Zhao Z, Li C, Yin Y, Li H, Zhou J (2024) Age and petrogenesis of ore-forming volcanic-subvolcanic rocks in the Yidonglinchang Au deposit, Lesser Xing’an Range: implications for late Mesozoic Au mineralization in NE China. Ore Geol Rev 165:105875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2024.105875
Khaleal FM, Saleh GM, Lasheen ES, Alzahrani AM, Kamh SZ (2022) Exploration and petrogenesis of corundum-bearing pegmatites: a case study in MigifHafafit Area, Egypt. Front Earth Sci 10:869828. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2022.869828
Alharshan GA, Kamar MS, Lasheen ES, Ene A, Uosif MA, Awad HA, Issa SM, Zakaly HM (2022) Distribution of radionuclides and radiological health assessment in Seih-Sidri area, southwestern Sinai. Int J Environ Res Publ Health 19:10717. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191710717
Xiao D, Liu M, Li L, Cai X, Qin S, Gao R, Li G (2023) Model for economic evaluation of closed-loop geothermal systems based on net present value. Appl Therm Eng 231:121008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2023.121008
Liu W, Zhou H, Zhang S, Zhao C (2023) Variable parameter creep model based on the separation of viscoelastic and viscoplastic deformations. Rock Mech Rock Eng 56(6):4629–4645. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-023-03266-7
Saleh GM, Khaleal FM, Lasheen ER (2022) Geochemistry and paleoweathering of metasediments and pyrite-bearing quartzite during the neoproterozoic era, Wadi Ibib-Wadi Suwawrib, south Eastern Desert, Egypt. Arab J Geosci 15:51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-09141-5
Khaleal FM, David RL, Mohamed SK, Gehad MS, El Saeed RL (2023) Critical raw material resources in Nugrus-Sikait area, South Eastern Desert, Egypt: geological and geochemical aspects. J Afr Earth Sci 197:104782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2022.104782
El Tohamy AM (2019) Mineralogy and geochemistry of the sikait U-Au-bearing lamprophyre dyke, south eastern desert, Egypt. Arab J Geosci 12:237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4394-0
El Tohamy AM, Kamar MS, Ismail AM (2023) Petrological and geochemical characteristics of Wadi Sikait Lamprophyre Dykes, South Eastern Desert, Egypt: implications for petrogenesis and crustal contamination. Middle East J Appl Sci 13:233–256. https://doi.org/10.36632/mejas/2023.13.2.19.ISSN:2077-4613
Kamar MS, El Tohamy AM, Mira HI, Ismail AM (2022) Geology and environmental impact assessment of psammitic gneiss and lamprophyre dykes at Wadi Sikait, South Eastern Desert, Egypt. In: 11st International Conference on chemical and environmental engineering ICEE, 2305. 012001. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2305/1/012001
Saleh GM (1997) The potentiality of uranium occurrences in Wadi Nugrus area, South Eastern Desert, Egypt. Ph.D. Thesis mans. Univ., 171.
Abdel-Hakeem M, El-Tahir M, Zeid EA (2023) Genetic implications of Th/U, Th/K, and U/K ratios for U mineralizations: a case study from El-Missikat and El-Erediya shear zones, Eastern Desert, Egypt. Geochem Trans 24:3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12932-023-00083-3
Xi Z, Xiaoming Z, Jiawang G, Shuxin L, Tingshan Z (2023) Karst topography paces the deposition of lower Permian, organic-rich, marine–continental transitional shales in the southeastern Ordos Basin, northwestern China. AAPG Bull. https://doi.org/10.1306/11152322091
Lȫpez-Moro FJ (2012) EASYGRESGRANT-a microsoft excel spread- sheet to quantify volume changes and to perform mass-balance modeling in metasomatic systems. Comput Geosci 39:191–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2011.07.014
Du C, Bai X, Li Y, Tan Q, Zhao C, Luo G, Yang S (2024) Storage, form, and influencing factors of karst inorganic carbon in a carbonate area in China. Sci China Earth Sci 67(3):725–739. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-023-1249-9
Basavarajappa HT, Maruthi NE (2018) Petrochemical characteristics and hyperspectral signatures on corundum bearing precambrian litho-units of Varuna area, Mysuru district, Karnataka, India. Int J Creative Res Thoughts 6:998–1009
Deer WA (2013) An introduction to the rock-forming minerals. The Mineralogical Society, London
Yu J, Zhu Y, Yao W, Liu X, Ren C, Cai Y, Tang X (2021) Stress relaxation behaviour of marble under cyclic weak disturbance and confining pressures. Measurement 182:109777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109777
Cebron F, Ildefonse P, Sichere MC (1993) New mineralogical data on uranophane and ßuranophane: synthesis of uranophane. Mineral Mag 57:301–308
Warr LN (2021) IMA–CNMNC approved mineral symbols. Mineral Mag 85(3):291–20
Bowles JW, Jobbins EA, Young BR (1980) A re-examination of cheralite. Mineral Mag 43:885–888
Förster HJ (1998) The chemical composition of REE-Y-Th-U-rich accessory minerals in peraluminous granites of the Erzgebirge-Fichtelgebirge region, Germany, part I: the monazite-(Ce)-brabantite solid solution series. Am Miner 83:259–272. https://doi.org/10.2138/am-1998-3-409
Skrzypek E, Kato T, Kawakami T, Sakata S, Hattori K, Hirata T, Ikeda T (2018) Monazite behaviour and time-scale of metamorphic processes along a low-pressure/high-temperature field gradient (Ryoke belt, SW Japan). J Petrol 59(6):1109–1144
Gysi A, Williams-Jones A, Harlov D (2015) The solubility of xenotime-(Y) and other HREE phosphates (DyPO4, ErPO4 and YbPO4) in aqueous solutions from 100 to 250°C and psat. Chem Geol 401:83–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2015.02.023
Sallam OR, Mira HI, El Tohamy AM, Abd Elhadi AA (2021) Mineralogy and geochemistry of uraniferous sandstones in fault zone, Wadi El Sahu area, southwestern Sinai, Egypt: implications for provenance. Weather Tecton Setting 95:830–845
Raslan MF (2009) Mineralogical and geochemical characteristics of uranium-rich fluorite in El-Missikat mineralized granite, Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. Geologija 52:213–220
Pi-Puig T, Solé J, Alba-Aldave L (2023) Uranium in fluorite, a case study: the La Azul fluorspar deposit, Taxco, Guerrero, Mexico. Minerals 13(12):1495. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13121495
Sun SS, McDonough WF (1989) Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders AD, Norry MJ (eds) Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, pp 313–345
Kamar MS (2021) Geochemical and mineralogical studies of the Mylonite Xenoliths and Monzogranite rocks at Wadi Abu Rusheid, South Eastern Desert, Egypt: insights on the genesis of mineralization. Acta Geol Sinica 95(5):1551–1567. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-6724.14743
Gougazeh M, Bamousa A, Hasan A (2018) Evaluation of granitic rocks as feldspar source: Al Madinah, western part of Saudi Arabia. J Taibah Univ Sci 12(1):21–36
Kharbish S, Eldosouky AM, Amer O (2022) Integrating mineralogy, geochemistry and aeromagnetic data for detecting Fe–Ti ore deposits bearing layered mafic intrusion, Akab El-Negum, Eastern Desert, Egypt. Sci Rep 12:15474. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-19760-x
Ren C, Yu J, Liu X, Zhang Z, Cai Y (2022) Cyclic constitutive equations of rock with coupled damage induced by compaction and cracking. Int J Min Sci Technol 32(5):1153–1165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2022.06.010
Taylor Y, McLennan SM (1985) The continental crust: its composition and evolution, 1st edn. Blackwell, Oxford, UK
Bau M, Dulski P (1996) Comparative study of yttrium and rare-earth element behaviours in fluorine-rich hydrothermal fluids. Contrib Miner Petrol 119:213–223
Cox R, Lowe DR, Cullers RL (1995) The influence of sediment recycling and basement composition on evolution of mudrock chemistry in the Southwestern United States. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59:2919–2940. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(95)00185-9
Nesbitt HW, Young GM (1982) Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites. Nature 199:715–717
Fedo CM, Nesbitt HW (1995) Young GM (1995) Unraveling the effects of potassium metasomatism in sedimentary rocks and paleosols, with implications for paleoweathering conditions and provenance. Geology 23:921–924
Zen E (1986) Aluminium enrichment in silicate melts by fractional crystallisation: Some mineralogic and petrologic constraints. J Petrol 27:1095–1117
Zhao J-X, Cooper JA (1993) Fractionation of monazite in the development of V-shaped REE patterns in leucogranite systems: evidence from a muscovite leucogranite body in central Australia. Lithos 30:23–32
Boulvais P, Ruffet G, Cornichet J, Mermet M (2007) Cretaceous albitization and dequartzification of Hercynian peraluminous granite in the Salvezines Massif (French Pyrénées). Lithos 93:89–106
Zhao Z-H, Bao Z-W, Qiao Y-L (2010) A peculiar composite M- and W-type REE tetrad effect: evidence from the Shuiquangou alkaline syenite complex, Hebei Province. China Chin Sci Bull 55:2684–2696
Monecke T, Dulski P, Kempe U (2007) Origin of convex tetrads in rare earth element patterns of hydrothermally altered siliceous igneous rocks from the Zinnwald Sn-W deposit, Germany. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 71(2):335–353
Takahashi Y, Yoshida H, Sato N, Hama K, Yusa Y, Shimizu H (2002) W- and M type tetrad effects in REE patterns for water–rock systems in the Tono uranium deposit, Central Japan. Chem Geol 184:311–335
Masuda A, Kawakami O, Dohmoto Y, Takenaka T (1987) Lanthanide tetrad effects in nature: two mutually opposite types W and M. Geochem J 21:119–124. https://doi.org/10.2343/geochemj.21.119
Irber W (1999) The lanthanide tetrad effect and its correlationwith K/ Rb, Eu/Eu*, Sr/Eu, Y/Ho and Zr/Hf of evolving peraluminous granitesuites. Geochemica et Cosmochimica Acta 63:489–508
Martins I, Mateus A, Cathelineau M, Boiron MC, Ribeiro da Costa I, Dias da Silva Í, Gaspar M (2022) The lanthanide “tetrad effect” as an exploration tool for granite-related rare metal ore systems: examples from the Iberian Variscan belt. Minerals 12:1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12091067
Yu H, Wang H, Lian Z (2022) An assessment of seal ability of tubing threaded connections: a hybrid empirical-numerical method. J Energy Resour Technol. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4056332
Veksler IV, Dorfman AM, Kamenetsky M, Dulski P, Dingwell DB (2005) Partitioning of lanthanides and Y between immiscible silicate and fluoride melts, fluorite and cryolite and the origin of the lanthanide tetrad effect in igneous rocks. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69:2847–2868
Yurimoto H, Duke EF, Papike JJ, Shearer CK (1990) Are discontinuous chondrite normalized REE patterns in pegmatitic granite systems the results of monazite fractionation? Geochim Cosmochim Acta 54:2141–2145
Monecke T, Kempe U, Trinkler M, Thomas R, Dulski P, Wagner T (2011) Unusual rare earth element fractionation in a tin-bearing magmatic-hydrothermal system. Geology 39:295–298
Bau M (1996) Controls on the fractionation of isovalent trace elements in magmatic and aqueous systems: evidence from Y/Ho, Zr/Hf, and lanthanide tetrad effect. Contrib Miner Petrol 123:323–333
Monecke T, Kempe U, Monecke J, Sala M, Wolf D (2002) Tetrad effect in rare earth element distribution patterns: a method of quantification with application to rock and mineral samples from granite-related rare metal deposits. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 66:1185–1196. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7037(01)00849-3
Abedini A, Calagari AA, Azizi RM (2018) The tetrad-effect in rare earth elements distribution patterns of titanium-rich bauxites: evidence from the Kanigorgeh deposit, NW Iran. J Geochem Explor 186:129–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2017.12.007
El-Feky M (2011) Mineralogical, REE-geochemical and fluid inclusion studies on some uraniumoccurrences, Gabal Gattar, Northeastern Desert, Egypt, China. J Geochem 30:430–443
El Dabe MM, Ismail AM, Metwaly M, Taalab SA, Hanfi MY, Ene A (2022) Hazards of radioactive mineralization associated with pegmatites used as decorative and building material. Materials 15:1224
Azizi RM, Abedini A, Alipour S, Niroomand S, Sasmaz A, Talaei B (2017) Rare earth element geochemistry and tetrad effects in fluorites: a case study from the Qahr-Abad deposit, Iran. Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie-Abhandlungen 383:255–273. https://doi.org/10.1127/njgpa/2017/0639
Zhao ZH, Bao ZW, Lee SG (2008) A composite M- With W-type of REE tetrad effect in a north China alkaline complex. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 72:95–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-010-231-3
Lee HM, Lee JI, Lee JJ, Kim J, Choi SW (2013) The A-type Pirrit Hills granite, West Antarctica: an example of magmatism associated with the break-up of the Gondwana supercontinent. Geosci J 16:421–433
Li WS, Ni P, Wang GG, Yang YL, Pan JY, Wang XL, Chen LL, Fan MS (2020) A possible linkage between highly fractionated granitoids and associated W mineralization in the Mesozoic Yaogangxian granitic intrusion, Nanling region, South China. J Asian Earth Sci 193:104314
Lee SG, Asahara Y, Tanaka T, Lee SR, Lee T (2012) Geochemical significance of the Rb-Sr, La-Ce and Sm-Nd isotope systems in A-type rocks with REE tetrad patterns and negative Eu and Ce anomalies: the Cretaceous Muamsa and Weolaksan granites, South Korea. Chemie Erde 73:75–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2012.11.008
Lee HM, Lee SG, Kim H, Lee JI, Lee MJ (2021) REE tetrad effect and Sr-Nd isotope systematics of A-type pirrit hills granite from West Antarctica. Minerals 11:792. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11080792
Frost DC, Frost BR, Beard JS (2016) On silica-rich granitoids and their eruptive equivalents. Am Min 101:1268–1284
Zhang Y, Gao JF, Ma DS, Pan J (2018) The role of hydrothermal alteration in tungsten mineralization at the Dahutang tungsten deposit, South China. Ore Geol Rev 95:1008–1027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.04.006
Ballouard C, Poujol M, Mercadier J, Deloule E, Boulvais P, Baele J-M, Cuney M, Cathelineau M (2018) Uranium metallogenesis of the peraluminous leucogranite from the Pontivy-Rostrenen magmatic complex (French Armorican Variscan belt): the result of long term oxidized hydrothermal alteration during strike-slip deformation. Miner Dep 53:601–628
Stefano C, Anna G, Marco L, Fabio S (2019) Mineralogical-chemical alteration and origin of Ignimbritic stones used in the Old Cathedral of Nostra Signora di Castro (Sardinia, Italy). Stud Conserv 64(7):397–422. https://doi.org/10.1080/00393630.2018.1565016
Babazadeh S, D’Antonio M, Cottle JM, Ghalamghash J, Raeisi D (2021) Constraints from geochemistry, zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf-Nd isotopic compositions on the origin of Cenozoic volcanic rocks from central Urumieh-Dokhtar magmatic arc. Iran Gondwana Res 90:27–46
Ren M, Wang W, Huang Z, Li S, Wu Q, Yu H, Yuan G, Sargent P (2022) Effect of alteration on the geochemistry and mechanical properties of granite from Pingjiang, Hunan Province, China. Environ Earth Sci 81(60):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10197-z
Li XC, Fan HR, Santosh M, Hu FF, Yang KF, Lan TG (2013) Hydrothermal alteration associated with Mesozoic granite-hosted gold mineralization at the Sanshandao deposit, Jiaodong Gold Province, China. Ore Geol Rev 53:403–421
Bonnetti C, Liu X, Mercadier J, Cuney M, Riegler T, Yu C (2020) Evolution of the uranium mineralisation in the Zoujiashan deposit, Xiangshan ore field: implications for the genesis of volcanic-related hydrothermal U deposits in South China. Ore Geol Rev 122:103514
Bonnetti C, Liu X, Mercadier J, Cuney M, Wu B, Li G (2021) Genesis of the volcanic-related Be-U-Mo Baiyanghe deposit, West Junggar (NW China), constrained by mineralogical, trace element and U-Pb isotope signatures of the primary U mineralisation. Ore Geol Rev 128:103921
Dana C, Agangi A, Takahashi R, Idrus A, Lai CK, Nainggolan NA (2022) Element mobility during formation of the Ruwai Zn-Pb-Ag skarn deposit, Central Borneo, Indonesia. Resour Geol 72(1):e12290. https://doi.org/10.1111/rge.12290
Manalo PC, Imai A, Takahashi R, Sato H, Subang L, De Los SM (2020) Lithogeochemistry of hydrothermally-altered host rocks by multiple mineralizations in the Mankayan Mineral District, Philippines. J Geochem Explor 218:106612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2020.106612
Meyer C, Hemley JJ (1967) ll rock alteration. Geochem Hydrotherm Ore Depos 1:166
Cuney M, Leroy J, Valdiviezo PA, Daziano C, Gamba M (1989) Geochemistry of the uranium mineralized Achala granitic complex, Argentina: comparison with Hercynian peraluminous leucogranites of western Europe. Metallog Uranium Depos 20:1–12
Le Maitre RW, Bateman P, Dubek A, Keller J, Lameyre J (1989) A classification of igneous rocks and glossary of terms: recommendations of the International Union of Geological sciences subcommisson on the systematics of igneous rocks. Black-well Scientific Publications, Oxford
Harlaux M, Romer R, Mercadier J, Morlot C, Marignac C, Cuney M (2018) 40 Ma of hydrothermal W mineralization during the Variscan orogenic evolution of the French Massif Central revealed by U-Pb dating of wolframite. Miner Dep 53:21–51
Legros H, Richard A, Tarantola A, Kouzmanov K, Mercadier J, Vennemann T, Marignac C, Cuney M, Wang RC, Charles N, Bailly L, Lespinasse MY (2019) Multiple fluids involved in granite-related W-Sn deposits from the world-class Jiangxi province (China). Chem Geol 508:92–115
Codeço M, Weis P, Trumbull R, Hinsberg V, Pinto F, Lecumberri-Sanchez P, Schleicher A (2021) The imprint of hydrothermal fluids on trace-element contents in white mica and tourmaline from the Panasqueira W-Sn–Cu deposit, Portugal. Miner Dep 56:481–508
Nesbitt HW, Young GM (1984) Prediction of some weathering trends of plutonic and volcanic rocks based up on thermodynamic and kinetic consideration. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 48:1523–1534
Nesbitt HW, Young GM (1989) Formation and diagenesis of weathering profiles. J Geol 97:129–147
Ishikawa Y, Sowaguch T, Lwaya S, Horiuchi M (1976) Delineation of prospecting targets for kuroko deposits based on modes of volcanism of underlying dacites and alteration halos. Min Geol 26:105–117
Ferry JM (1979) Reaction mechanisms, physical conditions and mass transfer during hydrothermal alteration of mica and feldspar in granitic rocks from south-central Maine, USA. Contrib Miner Petrol 68:125–139
Date J, Watanabe Y, Saeki Y (1983) Zonal alteration around the Fukazawa Kuroko deposits, Akita Prefecture, Northern Japan. In: Hiroshi O (eds) The Kuroko and Related volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits. Geoscience World, USA
Eastoe CJ, Solomon M, Walshe JL (1987) District-scale alteration associated with massive sulfide deposits in the Mount Read Volcanics, Western Tasmania. Econ Geol 82:1239–1258
Milani L, Lehmann J, Naydenov KV, Saalmann K, Nex PA, Kinnaird JA, Friedman IS, Woolrych T, Selley D (2019) Geology and mineralization of the Cu-rich Mumbwa district, a potential IOCG-type system at the eastern margin of the Pan-African Hook batholith, Zambia. J Afr Earth Sci 158:103513
Bonnet AL, Corriveau L (2007) Alteration vectors to metamorphosed hydrothermal systems in gneissic terrains. In: Goodfellow WD (ed) Mineral deposits of Canada: a synthesis of major deposit-types, district metallogeny, the evolution of geological provinces, and exploration methods, 5. Mineral Deposits Division, Special Publication, Geological Association of Canada, Special Publication, St. John’s, pp 1035–1049
Large RR, Gemmell JB, Paulick H, Huston DL (2001) The alteration box plot: a simple approach to understanding the relationship between alteration mineralogy and lithogeochemistry associated with VHMS deposits. Econ Geol 96:957–972
Mathieu L (2018) Quantifying hydrothermal alteration: a review of methods. Geosciences 8(7):245. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8070245
Zhang Y, Liu NQ, Pan JY, Xiang XK, Jiang QX, Jiang CQ, Jiang YY, Ding WK (2018) The superposition of alkaline by acidic hydrothermal alteration and its formation mechanism at Dahutang tungsten deposit, South China. Science Press, Beijing, p 116
Maclean WH (1988) Rare earth element mobility at constant inter-REE ratios in the alteration zone at the Phelps Dodge massive sulphide deposit, Matagami. Quebec Mineralium Deposita 23(4):231–238. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00206399
Maclean WH (1990) Mass change calculations in altered rock series. Miner Deposita 25(1):44–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326382
Babcock RS (1973) Computational models of metasomatic processes. Lithos 6:279–290
Kumral M, Abdelnasser A, Budakoglu M (2016) Geochemistry of hydrothermal alteration associated with cenozoic intrusion-hosted Cu-Pb-Zn mineralization at Tavşanlı Area, Kütahya, NW Turkey. Minerals 6:13
Middelburg JJ, Van der Weijden CH, Woittiez JW (1988) Chemical processes affecting the mobility of major, minor and trace elements during weathering of granitic rocks. Chem Geol 68:253–273
Hagag W, Abdelnasser A (2021) High resolution mapping of alteration zones in Daghbag and Bakriya gold occurrences (Central Eastern Desert, Egypt) using field, mineralogical-geochemical, and remote sensing data. Arab J Geosci 14:1344
Barton MD, Ilchik RP, Marikos MA (1991) Metasomatism. Rev Mineral Geochem 26:321–349
Abbas A (2020) Auriferous, uraniferous and REEs mineralized marl of Middle Um Bogma formation, Southwestern Sinai, Egypt. IOSR J Appl Geol Geophys. 8(2):12–36
Oliver NH, Cleverley JS, Mark G, Pollard PJ, Fu B, Marshall LJ, Rubenach MJ, Williams PJ, Baker T (2004) Modeling the role of sodic alteration in the genesis of iron oxide-copper-gold deposits, eastern mount Isa Block, Australia. Econ Geol 99:1145–1176. https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.99.6.1145
Mrozek SA, Chang Z, Spandler C, Windle S, Raraz C, Paz A (2020) Classifying skarns and quantifying metasomatism at the Antamina deposit, Peru: insights from whole-rock geochemistry. Econ Geol 115:177–188. https://doi.org/10.5382/econgeo.4698
Durand C, Oliot E, Marquer D, Sizun JP (2015) Chemical mass transfer in shear zones and metacarbonate xenoliths: a comparison of four mass balance approaches. Eur J Mineral 27:731–754. https://doi.org/10.1127/ejm/2015/0027-2475
Acknowledgements
I am grateful to Prof/Daniel S. Alessi the Editor-in-Chief and the anonymous reviewers for allowing us to reconstruct our manuscript in much better version. My sincere thanks and gratitude are due to the late Prof. Dr. M. El Ahmady Ibrahim, for his help offered during the fieldwork as well as for suggesting the research point. I would like to express my thanks to Prof. Dr. Mohamed S. Kamar Head of the Abu Rashid—Halayeb project, Nuclear Materials Authority (NMA), Egypt, for his help offered during the fieldwork as well as his kind and continued guidance at critical stages during all steps of the present work. Many thanks to Prof. Dr. Gehad M. Saleh, professor of geology and vice chairman of the Nuclear Materials Authority (NMA) for his revisions and critical comments. Special thanks to Prof. Dr. Ehab Korany for his fruitful help in petrography. I would like to express my thanks to Prof. Dr. Mohamed Galal El Feky, Prof. Dr. Ismail Abdel Ghani and Ass. Prof. Yasser Salman for their helpful comments and suggestions.
Funding
The author reported that there is no funding associated with the work featured in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Amira M. El Tohamy: Conceptualization, methodology, software, data curation, writing-original draft preparation, writing- reviewing and Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
I certify that this paper is unique, that it has not been published anywhere in any form or language (in part or in whole), and that it has not been submitted for consideration at the same time in other journals. I also state clearly that results are presented accurately, honestly, and without fabrication, falsification, or data modification (including image-based manipulation).
Competing interests
There is no financial or non-financial conflict of interests that is directly or indirectly related to the current work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
El Tohamy, A.M. Hydrothermal alteration processes in monzogranite: a case study from the Eastern Desert of Egypt: implications from remote sensing, geochemistry and mineralogy. Geochem Trans 25, 6 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12932-024-00089-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12932-024-00089-5