Abstract
Background
Previous studies have determined the epigenetic association between DNA methylation and pulmonary function among various ethnics, whereas this association is largely unknown in Chinese adults. Thus, we aimed to explore epigenetic relationships between genome-wide DNA methylation levels and pulmonary function among middle-aged Chinese monozygotic twins.
Methods
The monozygotic twin sample was drawn from the Qingdao Twin Registry. Pulmonary function was measured by three parameters including forced expiratory volume the first second (FEV1), forced vital capacity (FVC), and FEV1/FVC ratio. Linear mixed effect model was used to regress the methylation level of CpG sites on pulmonary function. After that, we applied Genomic Regions Enrichment of Annotations Tool (GREAT) to predict the genomic regions enrichment, and used comb-p python library to detect differentially methylated regions (DMRs). Gene expression analysis was conducted to validate the results of differentially methylated analyses.
Results
We identified 112 CpG sites with the level of P < 1 × 10–4 which were annotated to 40 genes. We identified 12 common enriched pathways of three pulmonary function parameters. We detected 39 DMRs located at 23 genes, of which PRDM1 was related to decreased pulmonary function, and MPL, LTB4R2, and EPHB3 were related to increased pulmonary function. The gene expression analyses validated DIP2C, ASB2, SLC6A5, and GAS6 related to decreased pulmonary function.
Conclusion
Our DNA methylation sequencing analysis on identical twins provides new references for the epigenetic regulation on pulmonary function. Several CpG sites, genes, biological pathways and DMRs are considered as possible crucial to pulmonary function.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Pulmonary function is determined as an important predictor of cardiovascular health [1] and mortality [2], which declines with increasing age after the third decade of lifetime [3]. Accelerated decline in pulmonary function has immense impact on individual and social economy [4]. Pulmonary function can be influenced by a variety of factors. Traditional epidemiologic studies have widely investigated the relationship of environmental factors, such as cigarette smoking [5] and air pollution [6] with pulmonary function. Besides, family-based study [7] and genome-wide association study (GWAS) [8] have estimated the heritability of pulmonary function ranging from 0.42 to 0.71, indicating genetic contribution to the variation of pulmonary function.
Currently, an increasing number of GWASs have smoothed the way for discovering human genetic variants linked to pulmonary function which are quantified by forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), forced vital capacity (FVC), and FEV1/FVC ratio [9]. Yet the reported nucleotide-level polymorphisms could explain a limited proportion of pulmonary function variation [10] (5.0% for FEV1, 3.4% for FVC, and 9.2% for FEV1/FVC) compared with the estimated heritability, suggesting that other gene-regulatory mechanisms such as epigenetics might also be at play. Epigenetics is the study of heritable phenotype alterations that do not involve changes in the DNA sequence [11], and the epigenetic changes include DNA methylation, histone modification and non-coding RNA. Previous epigenome-wide association studies (EWASs) have investigated the association between DNA methylation and pulmonary function among various ethnic population but only a limited amount of significant genomic sites have been revealed [4, 12,13,14]. Besides, expect one study based on monozygotic (MZ) twin design, most of previous studies were conducted based on general population, which could not control the genetic effect and early life milieu including intrauterine environment on epigenetic changes [15].
As the genetic makeup is perfectly matched within pair, the monozygotic twins serve as optimal and valuable samples for EWAS on complex diseases and phenotypes [16]. The genetic influences on epigenetic changes are cancelled out in the discordant MZ twins design, thus the differential DNA methylation triggered by environmental factors could be identified [17]. The Chinese population is different from the other ethnics of the world in terms of genetic background, environmental exposure and lifestyle. However, there is no EWAS of pulmonary function in the Chinese twins published present. Thereby, we performed an EWAS to identify the association between DNA methylation variants and pulmonary function among Chinese monozygotic twin pairs.
Materials and methods
Samples and study procedures
The discordant identical twin pairs are sub-sample of twins derived from Qingdao Twin Registry [18] conducted by Qingdao Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The details of sample recruitment have been described elsewhere [19]. A total of 68 twin pairs which were conducted DNA methylation sequencing using the reduced representation bisulfite sequencing (RRBS) were included in the sample. After excluded twin pairs with incomplete measurement of pulmonary function (n = 1) and participants with minimal absolute values of intra-pair difference in pulmonary function score (ΔFEV1 < 0.1, n = 7; ΔFVC < 0.1, n = 8, and ΔFEV1/FVC < 0.05, n = 23), complete monozygotic twin pairs who met the criteria were included in the study, including 60 twin pairs for FEV1(34 male and 26 female pairs), 59 twin pairs for FVC (34 male and 25 female pairs), and 44 twin pairs for FEV1/FVC (21 male and 23 female pairs). Informed written consents were obtained from all participants. Regional Ethics Committee of the Qingdao Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Institutional Review Boards has approved this study.
Pulmonary function including FEV1 and FVC (liters) was assessed by the electronic hand-held spirometer (Micro 0102). Trained investigators calibrated the spirometer before measurement every morning. Based on the standard procedure of spirometry, each participant performed two maneuvers in standing state twice, and best trial data were applied to further analysis. The ratio FEV1/FVC was calculated according to the above measurements.
DNA methylation analysis
The Cetyltrimethyl Ammonium Bromide was used to extract genomic DNA from whole blood. DNA methylation library was constructed using RRBS by Biomarker Technologies Corporation, Beijing, China (http://www.biomarker.com.cn/). Firstly, genomic DNA was digested with Mspl restriction enzyme. After digesting, the 5′ CG overhangs were repaired, and A-tails were added. Then the DNA was loaded on an agarose gel, and 230–380 bp long (including 100 bp adaptor) fragments were sort out for next bisulfite conversion using NEXTflex Bisulfite-Seq Kit (Bioo Scientific, Austin, TX, USA). After all, the bisulfite converted DNA was amplified with PCR. The reduced representation bisulfite sequencing was conducted using Illumina HiSeq X Ten (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, USA).
Data preprocessing
Our previous study has detailed the data preprocessing [20, 21]. In brief, the raw data were first trimmed and mapped to Genome Reference Consortium Human Build 37 (hg19) by Bismark [22]. The mapping output from Bismark was then imported to BiSeq (R package) [23] to detect the methylation level. To reduce bias, the coverage was restricted to 90% quantile, and CpG sites with beyond ten missing observations or average methylation beta value < 0.01 were removed. We used logit transformation to transform the beta value to M-value for conducting further differential methylation analyses.
Cell-type composition
Because the DAN sample extracted from the whole blood including distinct cell types which might result in false discoveries. We applied ReFACTor [24] method to control the cellular heterogeneity impact on DNA methylation. ReFACTor is based on principal component analysis and calculates the linear transformations of cell-type composition as principal component analysis components. We selected the top five components as covariates to control cell-type heterogeneity for the subsequent analyses.
Statistical analysis
Epigenome-wide association analyses
For single CpG analysis, linear mixed effect models were applied to regress methylation level on pulmonary function adjusting for cell-type composition and other confounding factors (FEV1: diastolic pressure; FVC: none; FEV1/FVC: diastolic and systolic pressure) as fixed effects and twin pairing variable as a random effect, based on the co-twin design as proposed by Tan et al. [16]. The smoking status of in-pair twins were almost consistent in sample. The number of smoking twins was 22 for FEV1 and FVC and 15 for FEV1/FVC, the number of non-smoking twins was 32 for FEV1, 31 for FVC, and 25 for FEV1/FVC, and the number of inconsistent smoking status twins was 6 for FEV1 and FVC, 4 for FEV1/FVC. We added the smoking status as fixed effects to control it. False discovery rate (FDR) [25] was calculated to solve multiplicity problem. We defined the significance of genome-wide as FDR < 0.05, and conducted these analyses by R software (version 4.1.0).
Genomic regions enrichment analysis
Genomic regions enrichment analysis was performed using Genomic Regions Enrichment of Annotations Tool (GREAT) to examine the enrichment of identified methylation sites (P < 0.05) in the functional significance of cis-regulatory regions [26]. GREAT is able to properly incorporate distal binding sites and control for false positives using a binomial test over the input genomic regions. Annotation of GREAT is based on Genome Reference Consortium Human Build 37 (hg19).
Detecting differentially methylated regions (DMRs)
Based on bisulfite-sequencing data with P-values from EWAS result, the significant differentially methylated regions (DMRs) for pulmonary function were identified using comb-p python library proposed by Petersen et al. [27]. This method first combined adjacent P-values as weighted according to the calculated auto-correlation, then performed Benjamini–Hochberg false discovery adjustment to find regions of significant enrichment. The documentation and implementation of comb-p python library are available at website [28] https://github.com/brentp/combined-pvalues. The analyses of DMRs were conducted by Python software (version 3.8.8).
Gene expression analyses
Weighted gene co-expression network analyses (WGCNA)
We used R software (version 4.1.0) to perform weighted correlation network analysis such as co-expression network analysis of gene expression data through WGCNA package [29,30,31]. In brief, we firstly constructed a gene co-expression network, and then used dynamic tree cut to identify modules. Next, we related modules to pulmonary function indices. Finally, we used DAVID [32, 33] tool to conduct the enrichment analysis of genes clustered in specific modules. The significant enriched terms were defined as a modified fisher exact P-value < 0.05.
Correlational analysis
We applied Spearman's rank correlation analyses by R software (version 4.1.0) to evaluate the correlation between the gene expression levels of genes where the top CpG sites and DMRs annotated and pulmonary function indices. Statistically significant was defied as P-value < 0.05.
Results
Descriptive statistics of basic characteristics are shown in Additional file 1: Table S1. The number of monozygotic twin pairs involved in our study was 60 for FEV1(34 male pairs), 59 for FVC (34 male pairs), and 44 for FEV1/FVC ratio (21 male pairs). The median age of participants was above 50 years old. The mean (standard deviation, SD) of pulmonary function was 1.98 (0.72) for FEV1, 2.33(0.83) for FVC, and 0.86(0.14) for FEV1/FVC. Most clinical indicators had considerably significant correlation, indicating that our discordant MZ twin design could benefit. And the insignificant intra-pair confounders would be added as covariates in our subsequent association analyses. We drew scatter plots with regression line to illustrate the relationship between intra-differences of pulmonary function (ΔFEV1, ΔFVC, ΔFEV1/FVC) and intra-differences of methylated values of top significant CpG sites (P value < 10−4, Δ methylated values of CpG sites at corresponding location) in MZ twin pairs (Additional file 2: Table S2, Additional file 3: Fig. S1, Additional file 4: Fig. S2, and Additional file 5: Fig. S3). The Δ methylation value of four CpG sites (f, h, i, j) were positively correlated with ΔFEV1, and the Δ methylation value of seven CpG sites (a, b, c, d, e, g, k) were negatively correlated with ΔFEV1. The Δ methylation value of eleven CpG sites (a, b, c, g, h, i, j, k, m, o, q) were positively correlated with ΔFVC, and the Δ methylation value of six CpG sites (d,e,f,l,n,p) were negatively correlated with ΔFVC. The Δ methylation value of two CpG sites (c,i) were positively correlated with ΔFEV1/FVC ratio, and the Δ methylation value of ten CpG sites (a,b,d,e,f,g,h,j,k,l) were negatively correlated with ΔFEV1/FVC ratio.
Epigenome-wide association analysis
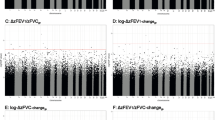
The results of EWAS for pulmonary function are shown in Table 1. In analysis of pulmonary function, 25 CpG sites with P value < 10−4 were identified for FEV1, and the top 25 CpG sites were located at 8 genes, among which 4 (50%) genes WDR90, DIP2C, PANX2, NUBP2 were associated with pulmonary function. For intra-pair difference in FVC, 56 CpG sites with a P value < 10−4 were found with 4 sites reaching a P value < 10−5. And the top CpG sites were located at 21 genes, among which 8 (38%) genes AP5B1, CYP26B1, GAS6, IL11, IRS1, IRS2, MAD1L1, NUAK1 were associated with pulmonary function. Intra-pair methylation difference of FEV1/FVC ratio identified 31 CpG sites with P value < 10−4. The CpG sites located at 11 genes and the most significant site was located at FENDRR and ENSG00000268388 (chr16: 86,528,639 bp, cor = − 1.93, P = 2.27 × 10−6). The Manhattan plots of pulmonary function for the P-values of each CpG site against its chromosomal location are illustrated in Fig. 1.
A total of 280 common CpG sites (P < 0.05) were found for FEV1, FVC, and FEV1/FVC. 794 common genes (P < 0.05) were found for FEV1, FVC, and FEV1/FVC, among which two genes reached the level of P < 1 × 10–3, including CHRNA4 and MAD1L1.
Biological pathway analysis
The number of genomic cis-regulatory regions related to one or more genes was 13,821, 14,901, and 17,929 for FEV1, FVC, and FEV1/FVC, respectively (Additional file 6: Fig. S4). The absolute distance of genomic regions to transcription start site was displayed in Additional file 7: Fig. S5 and Additional file 8: Fig. S6.
The analysis found 12 common functional clusters of biological process with very high statistical significance (binomial p-value < 1.07E−13) (Table 2), including negative regulation of phospholipid biosynthetic process, platelet-derived growth factor binding, potassium:chloride symporter activity, epithelial-mesenchymal cell signaling, decreased serum estradiol, low voltage-gated calcium channel activity, cAMP response element binding protein binding, activation of Cdc42 GTPase activity, ceramide signaling pathway, transcription regulation by bZIP transcription factor, mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 binding, and notch signaling pathway.
The MSiDB and PANTHER pathway, Human Phenotype, and Go enriched terms of FEV1, FVC, and FEV1/FVC are shown in Additional file 9: Table S3, Additional file 10: Table S4, and Additional file 11: Table S5, respectively.
Region-based analysis
By using comb-p, region-based analyses identified 13, 14, and 12 DMRs (FDR < 0.05) associated with FEV1, FVC, and FEV1/FVC ratio, respectively (Table 3). Interestingly, 4 significant FEV1 associated DMRs (from 41,207,271 to 41,207,436 bp and from 43,394,513 to 43,394,685 bp on chromosome 6; from 50,616,620 to 50,617,148 bp on chromosome 22; from 40,996,995 to 40,997,142 bp on chromosome 17), 2 significant FVC associated DMRs (from 179,554,269 to 179,554,550 bp on chromosome 5; from 39,719,381 to 39,719,533 bp on chromosome 4), and 1 significant FEV1/FVC ratio associated DMR (from 130,491,143 to 130,491,278 bp on chromosome 11) cover the corresponding top significant CpG sites in Table 1.
Of all DMRs, three DMRs (located at PRDM1, MPL, EPHB3) were related to more than one trait. Of the significant DMRs associated with pulmonary function, nine DMRs for FEV1 were annotated to PRDM1 on chromosome 6, MPL and ZNF496 on chromosome 1, CIDEB and LTB4R2 on chromosome 14, SLC6A5 on chromosome 11, EPHB3 on chromosome 3, HEMK1 on chromosome 22, CDKL4 on chromosome 2, and AOC2 on chromosome 17. Nine DMRs for FVC were annotated to RASGEF1C on chromosome 5, UBE2K on chromosome 4, RNA5SP207, PRDM1, and ATG5 on chromosome 6, FEM1A on chromosome 19, MPL on chromosome 1, EPHB3 on chromosome 3 and DRD5P2 on chromosome 2. And seven DMRs for FEV1/FVC ratio were annotated to RASGEF1C on chromosome 5, UBE2K on chromosome 4, RNA5SP207, PRDM1, and ATG5 on chromosome 6, FEM1A on chromosome 19, MPL on chromosome 1, EPHB3 on chromosome 3 and DRD5P2 on chromosome 2. In addition, four DMRs for FEV1, six DMRs for FVC, and five DMRs for FEV1/FVC ratio were located in the intergenic regions.
Figures 2, 3 and 4 display the methylation patterns for the significant DMRs for pulmonary function in Table 3, of which six DMRs (A, C, E, F, I, K) were positively and four DMRs (B, D, H, M) negatively associated with FEV1, and seven DMRs (A, C, F, G, H, J, L) were positively and five DMRs (B, E, K, M, N) negatively associated with FVC. One DMRs (K) was positively and seven DMRs (B, C, D, E, F, G, H) negatively associated with FEV1/FVC ratio.
Gene expression analysis
In the gene expression analyses, we included 12 twin pairs (7 male pairs) with median age of 53 years (ranging from 43 to 65), a median FEV1 of 2.05 (ranging from 1.04 to 3.81), a median FVC of 2.17 (ranging from 1.32 to 4.10), and a median FEV1/FVC of 0.97(ranging from 0.57 to 1.01).
Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA)
As shown in Additional file 12: Fig. S7, the genes clustered in lightsteelblue1 module (including 492 genes) were both positively correlated with FEV1 (r = 0.58, P = 0.003) and FVC (r = 0.51, P = 0.01). The genes clustered in this module were significantly enriched in positive regulation of protein secretion, positive regulation of cell division, growth factor activity, calcium ion binding, motile cilium, platelet degranulation, and phospholipase A2 activity. (Additional file 13: Table S6).
Moreover, the genes clustered in darkorange2 module (including 62 genes) were also both positively correlated with FEV1(r = 0.45, P = 0.03) and FVC (r = 0.53, P = 0.007). The genes clustered in this module were significantly enriched in extracellular region, negative regulation of exocytosis, and cell adhesion (Additional file 14: Table S7).
Additionally, the genes clustered in ivory module (including 76 genes) were negatively correlated with FEV1/FVC (r = − 0.63, P = 0.001). The genes clustered in this module were significantly enriched in cytokine activity, extracellular region, intermediate filament, and so on (Additional file 15: Table S8).
The common genes and enrichment terms between methylation analysis and WGCNA
We detected the common genes and enrichment terms between the methylation analyses and WGCNA. We found DIP2C gene which included in lightsteelblue1 modules linked to FEV1, and ASB2 which included in darkorange2 modules associated with FVC. The common enrichment terms “platelet alpha granule lumen” was identified.
Correlation analysis
Significant correlations between gene expression levels and pulmonary function indices were identified, including SLC6A5 related to FEV1 (r = 0.454, P = 0.026), and GAS6 related to FVC (r = 0.533, P = 0.007).
Discussion
In this study, we detected the epigenetic variants of pulmonary function using EWAS based on monozygotic twin design. The number of CpG sites which was identified to reached the level of P < 1 × 10–4 was 25 for FEV1, 56 for FVC, and 31 for FEV1/FVC. And 12 significant pathways of interest for pulmonary function were highlighted by GREAT ontology enrichment analyses. Finally, we identified several DMRs related to pulmonary function, and of all DMRs, three (PRDM1, MPL, and EPHB3) were related to more than one trait. Two genes (DI92C and ASB2) and one enrichment terms (platelet alpha granule lumen) were overlapped between methylation analysis and WGCNA. Finally, two genes were found to be correlated to pulmonary function.
The genes DIP2C, WDR90, PANX2, NUBP2, AP5B1, CYP26B1, GAS6, IL11, IRS1, IRS2, MAD1L1, CAMTA1, CHRNA4, FENDRR, MUC2 associated with top CpG sites (Table 1) played important roles in pulmonary function. Most interestingly, DIP2C gene was not only identified to link to pulmonary function in our EWAS results, but further validated in the WGCNA. Moreover, DIP2C has been detected to related to pulmonary function in blood DNA in Koreans adults [34]. Mutations in DIP2C have been identified in lung cancer samples [35]. This demonstrated that DIP2C gene indeed plays an important role at the pulmonary disease. WDR90 was identified as required gene for ciliogenesis [36]. The lung ciliary-related proteins keeping the airways clear of mucus and dirt play a role in human pulmonary function. PANX2 was expressed in human airway epithelial cells and alveolar macrophages, which might have an impact on pulmonary function [37]. NUBP2 was found to express in distal lung epithelium, which might function in lung development of mice [38]. AP5B1 was identified as susceptibility loci for the combined eczema plus asthma phenotype, which might affect pulmonary function [39]. Cyp26b1 was an essential regulator of distal airway epithelial differentiation during lung development [40]. GAS6 promoted Axl-mediated survival in pulmonary endothelial cells [41]. IL-11 was suggested that could cause lung inflammation and airway obstruction [42]. IRS1 and IRS2 were found to mediate IL-4-induced migration of human airway epithelial cells, which influence pulmonary function [43]. MAD1L1 was identified as a genome-wide significant signals with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by GWAS [44]. CAMTA1 was a regulator of nuclear factor of activated T cells signaling, which was linked to pulmonary arterial hypertension [45]. FENDRR was long noncoding RNA exhibiting antifibrotic activity in pulmonary fibrosis [46]. Decreased expression of MUC2 has been observed in patients with COPD [47].
Pathway enrichment analyses showed lots of common significant pathways of pulmonary function using GREAT. The significant enrichment pathway include negative regulation of phospholipid biosynthetic process [48], platelet-derived growth factor binding [49], potassium:chloride symporter activity [50], epithelial-mesenchymal cell signaling [51], decreased serum estradiol [52], low voltage-gated calcium channel activity [53], cAMP response element binding protein binding [54], activation of Cdc42 GTPase activity [55], ceramide signaling pathway [56], transcription regulation by bZIP transcription factor [57], mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 binding [58], and notch signaling pathway [59].
The genomic region-based analyses found 39 DMRs locating at 23 genes (Table 3), of which PRDM1, MPL, LTB4R2, EPHB3 and SLC6A5 had certain biological function potentially linked to pulmonary function. Previous study found that NF-κB(p65) promotion of miR-99b could aggravate acute lung injury by PRDM1 down-regulation, and over-expressed PRDM1 inhibits acute lung injury in mice [60]. MPL was defined as an important gene in a novel VEGF–miR-1–Mpl–P-selectin effector pathway in lung Th2 inflammation and found as potential therapeutic targets for asthma [61]. LTB4R2, as one of pivotal leukotriene B4 receptors, was proposed as potential therapeutic targets in asthma [62]. EphB3 was expressed at human lung fibroblasts, which induce dephrin-B2 forward signal involved in several fibroblast functions [63]. SLC6A5, also named GLYT-2, encoded a sodium- and chloride-dependent glycine neurotransmitter transporter. The glycinergic inhibitory synaptic inputs played an important role in respiratory motoneurons, which could affect pulmonary function [64].
As additional validation, we integrated the methylation data with gene expression data. Genes clustered in lightsteelblue1 and darkorange2 modules were positively correlated with FEV1 and FVC in WGCNA, and some genes were in common with EWAS findings, including DIP2C discussed above and ASB2 involved in pulmonary function remained to be studied further. Additionally, SLC6A5 and GAS6 discussed above were positively correlated to pulmonary function. Moreover, the common enrichment terms between methylation analysis and WGCNA was platelet alpha granule lumen, which involved in pulmonary function remained to be studied further.
There were several strengths in the present study. The identical twin design used in our study to detect the epigenetic variation of pulmonary function could perfectly control over the genetic background to provide credible results. Moreover, this was one of the few pulmonary function EWA studies in Asian and the first in Chinese. As the genetic background and environmental exposures differ from ethnic populations, our study elucidated the underlying physiological mechanism of pulmonary function changes in Chinese adults. However, our studies also have some limitations. First, compared with other general case–control design, the sample size of our study was relatively small due to the difficulty of recruiting and identifying qualified MZ twin pairs. However, previous study has determined that the sample sizes of monozygotic twins just require roughly 1/4 of sample sizes in the ordinary case-only design to provide the sufficient power [65]. Second, the DNA sample was extracted from blood rather than the lung tissue. Although we know methylation is the characteristic of tissue-specificity, it was difficult to obtain the lung tissue of sample. Moreover, the mounting evidences have supported disease-associated methylation loci could be identified from peripheral samples [66]. Third, the non-shared environment for the individual siblings of MZ twins, such as occupational environment [67], residential environment [68], and mode of transport [69], could expose themselves to different levels of environmental pollutants, including particulate matter, nitrogen dioxide; volatile organic compounds, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and so on, which might directly affect pulmonary function [70,71,72,73], and cause different levels of DNA methylation [74,75,76,77,78] thereby indirectly influencing pulmonary function. However, due to the complicated causes of DNA methylation and the difficulty of monitoring for the external environmental exposure, we have not further analyzed the causes of DNA methylation. We will seek practical method to solve it in the future research.
Although these results could not immediately be applied as clinical predictors of disease in individuals, they are important from an aetiological perspective. Epigenetic studies complement genetic association studies to identify pulmonary function related genes. The EWAS and gene expression analysis identified candidate genes and pathways related to pulmonary function, which could help understand underlying mechanisms of pulmonary function and explore new molecular biological pathway of pulmonary functional decline in clinical.
Conclusion
In conclusion, our DNA methylation sequencing analysis on identical twins provides new references for the epigenetic regulation on pulmonary function. Several CpG sites, genes, biological pathways and DMRs were considered as possible crucial to pulmonary function. All findings point important clues to further explore of pulmonary function.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request.
References
Sin DD, Wu L, Man SF. The relationship between reduced lung function and cardiovascular mortality: a population-based study and a systematic review of the literature. Chest. 2005;127(6):1952–9.
Beaty TH, Cohen BH, Newill CA, Menkes HA, Diamond EL, Chen CJ. Impaired pulmonary function as a risk factor for mortality. Am J Epidemiol. 1982;116(1):102–13.
Weiss ST. Lung function and airway diseases. Nat Genet. 2010;42(1):14–6.
Bolund ACS, Starnawska A, Miller MR, Schlunssen V, Backer V, Borglum AD, Christensen K, Tan Q, Christiansen L, Sigsgaard T. Lung function discordance in monozygotic twins and associated differences in blood DNA methylation. Clin Epigenet. 2017;9(132):1–13.
Allinson JP, Hardy R, Donaldson GC, Shaheen SO, Kuh D, Wedzicha JA. Combined impact of smoking and early-life exposures on adult lung function trajectories. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;196(8):1021–30.
Havet A, Hulo S, Cuny D, Riant M, Occelli F, Cherot-Kornobis N, Giovannelli J, Matran R, Amouyel P, Edme JL, Dauchet L. Residential exposure to outdoor air pollution and adult lung function, with focus on small airway obstruction. Environ Res. 2020;183:109161.
Klimentidis YC, Vazquez AI, de Los CG, Allison DB, Dransfield MT, Thannickal VJ. Heritability of pulmonary function estimated from pedigree and whole-genome markers. Front Genet. 2013;4:174.
Yamada H, Yatagai Y, Masuko H, Sakamoto T, Iijima H, Naito T, Noguchi E, Hirota T, Tamari M, Hizawa N. Heritability of pulmonary function estimated from genome-wide SNPs in healthy Japanese adults. Respir Investig. 2015;53(2):60–7.
Yao TC, Du G, Han L, Sun Y, Hu D, Yang JJ, Mathias R, Roth LA, Rafaels N, Thompson EE, et al. Genome-wide association study of lung function phenotypes in a founder population. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;133(1):248–55.
Shrine N, Guyatt AL, Erzurumluoglu AM, Jackson VE, Hobbs BD, Melbourne CA, Batini C, Fawcett KA, Song K, Sakornsakolpat P, et al. New genetic signals for lung function highlight pathways and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease associations across multiple ancestries. Nat Genet. 2019;51(3):481–93.
Dupont C, Armant DR, Brenner CA. Epigenetics: definition, mechanisms and clinical perspective. Semin Reprod Med. 2009;27(5):351–7.
Lee MK, Hong Y, Kim SY, London SJ, Kim WJ. DNA methylation and smoking in Korean adults: epigenome-wide association study. Clin Epigenet. 2016;8:103.
Lee MK, Hong Y, Kim SY, Kim WJ, London SJ. Epigenome-wide association study of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and lung function in Koreans. Epigenomics. 2017;9(7):971–84.
Imboden M, Wielscher M, Rezwan FI, Amaral AFS, Schaffner E, Jeong A, Beckmeyer-Borowko A, Harris SE, Starr JM, Deary IJ, et al. Epigenome-wide association study of lung function level and its change. Eur Respir J. 2019;54:1.
Tan Q, Christiansen L, Thomassen M, Kruse TA, Christensen K. Twins for epigenetic studies of human aging and development. Ageing Res Rev. 2013;12(1):182–7.
Tan Q, Christiansen L, von Bornemann HJ, Christensen K. Twin methodology in epigenetic studies. J Exp Biol. 2015;218(Pt 1):134–9.
Li W, Christiansen L, Hjelmborg J, Baumbach J, Tan Q. On the power of epigenome-wide association studies using a disease-discordant twin design. Bioinformatics. 2018;34(23):4073–8.
Duan H, Ning F, Zhang D, Wang S, Zhang D, Tan Q, Tian X, Pang Z. The Qingdao Twin Registry: a status update. Twin Res Hum Genet. 2013;16(1):79–85.
Xu C, Zhang D, Tian X, Wu Y, Pang Z, Li S, Tan Q. Genetic and environmental basis in phenotype correlation between physical function and cognition in aging chinese twins. Twin Res Hum Genet. 2017;20(1):60–5.
Li W, Zhang D, Wang W, Wu Y, Mohammadnejad A, Lund J, Baumbach J, Christiansen L, Tan Q. DNA methylome profiling in identical twin pairs discordant for body mass index. Int J Obes (Lond). 2019;43(12):2491–9.
Wang W, Li W, Jiang W, Lin H, Wu Y, Wen Y, Xu C, Tian X, Li S, Tan Q, Zhang D. Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis of cognitive function in middle and old-aged Chinese monozygotic twins. J Psychiatr Res. 2021;136:571–80.
Krueger F, Andrews SR. Bismark: a flexible aligner and methylation caller for Bisulfite-Seq applications. Bioinformatics. 2011;27(11):1571–2.
Hebestreit K, Dugas M, Klein HU. Detection of significantly differentially methylated regions in targeted bisulfite sequencing data. Bioinformatics. 2013;29(13):1647–53.
Rahmani E, Zaitlen N, Baran Y, Eng C, Hu D, Galanter J, Oh S, Burchard EG, Eskin E, Zou J, Halperin E. Sparse PCA corrects for cell type heterogeneity in epigenome-wide association studies. Nat Methods. 2016;13(5):443–5.
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J Roy Stat Soc: Ser B (Methodol). 1995;57(1):289–300.
McLean CY, Bristor D, Hiller M, Clarke SL, Schaar BT, Lowe CB, Wenger AM, Bejerano G. GREAT improves functional interpretation of cis-regulatory regions. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28(5):495–501.
Pedersen BS, Schwartz DA, Yang IV, Kechris KJ. Comb-p: software for combining, analyzing, grouping and correcting spatially correlated P-values. Bioinformatics. 2012;28(22):2986–8.
Brent P, Roy L. Combining p-values using modified stouffer-liptak for spatially correlated results (probes). https://github.com/brentp/combined-pvalues. Accessed 21 April 2021.
Langfelder P, Horvath S. WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008;9:559.
Langfelder P, Horvath S. Fast R functions for robust correlations and hierarchical clustering. J Stat Softw. 2012;46:11.
Wang W, Jiang W, Hou L, Duan H, Wu Y, Xu C, Tan Q, Li S, Zhang D. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis of expression data of monozygotic twins identifies specific modules and hub genes related to BMI. BMC Genomics. 2017;18(1):872.
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Kir J, Liu D, Bryant D, Guo Y, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC, Lempicki RA. DAVID Bioinformatics Resources: expanded annotation database and novel algorithms to better extract biology from large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:W169-175.
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang J, Gao W, Lane HC, Lempicki RA. DAVID: database for annotation, visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 2003;4(5):P3.
Terzikhan N, Sun F, Verhamme FM, Adams HHH, Loth D, Bracke KR, Stricker BHC, Lahousse L, Dupuis J, Brusselle GG, O’Connor GT. Heritability and genome-wide association study of diffusing capacity of the lung. Eur Respir J. 2018;52:3.
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G, Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y, Jacobsen A, Sinha R, Larsson E, et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal. 2013;6(269):pl1.
Hamel V, Steib E, Hamelin R, Armand F, Borgers S, Fluckiger I, Busso C, Olieric N, Sorzano COS, Steinmetz MO, et al. Identification of Chlamydomonas central core centriolar proteins reveals a role for human WDR90 in ciliogenesis. Curr Biol. 2017;27(16):2486–98.
Ransford GA, Fregien N, Qiu F, Dahl G, Conner GE, Salathe M. Pannexin 1 contributes to ATP release in airway epithelia. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2009;41(5):525–34.
Schnatwinkel C, Niswander L. Nubp1 is required for lung branching morphogenesis and distal progenitor cell survival in mice. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(9):e44871.
Pividori M, Schoettler N, Nicolae DL, Ober C, Im HK. Shared and distinct genetic risk factors for childhood-onset and adult-onset asthma: genome-wide and transcriptome-wide studies. Lancet Respir Med. 2019;7(6):509–22.
Daniel E, Barlow HR, Sutton GI, Gu X, Htike Y, Cowdin MA, Cleaver O. Cyp26b1 is an essential regulator of distal airway epithelial differentiation during lung development. Development. 2020;147(4):dev181560.
Healy AM, Schwartz JJ, Zhu X, Herrick BE, Varnum B, Farber HW. Gas 6 promotes Axl-mediated survival in pulmonary endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2001;280(6):L1273-1281.
Ng B, Dong J, D’Agostino G, Viswanathan S, Widjaja AA, Lim WW, Ko NSJ, Tan J, Chothani SP, Huang B, et al. Interleukin-11 is a therapeutic target in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sci Transl Med. 2019;11:511.
White SR, Martin LD, Abe MK, Marroquin BA, Stern R, Fu X. Insulin receptor substrate-1/2 mediates IL-4-induced migration of human airway epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009;297(1):L164-173.
Allen RJ, Guillen-Guio B, Oldham JM, Ma SF, Dressen A, Paynton ML, Kraven LM, Obeidat M, Li X, Ng M, et al. Genome-wide association study of susceptibility to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;201(5):564–74.
Kang K, Peng X, Zhang X, Wang Y, Zhang L, Gao L, Weng T, Zhang H, Ramchandran R, Raj JU, et al. MicroRNA-124 suppresses the transactivation of nuclear factor of activated T cells by targeting multiple genes and inhibits the proliferation of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(35):25414–27.
Huang C, Liang Y, Zeng X, Yang X, Xu D, Gou X, Sathiaseelan R, Senavirathna LK, Wang P, Liu L. Long noncoding RNA fendrr exhibits antifibrotic activity in pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2020;62(4):440–53.
Ballester B, Milara J, Cortijo J. Mucins as a new frontier in pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Med. 2019;8(9):1447.
Chen H, Li Z, Dong L, Wu Y, Shen H, Chen Z. Lipid metabolism in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019;14:1009–18.
McGowan SE, Lansakara TI, McCoy DM, Zhu L, Tivanski AV. Platelet-derived growth factor-alpha and neuropilin-1 mediate lung fibroblast response to rigid collagen fibers. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2020;62(4):454–65.
Zhao KQ, Xiong G, Wilber M, Cohen NA, Kreindler JL. A role for two-pore K(+) channels in modulating Na(+) absorption and Cl(-) secretion in normal human bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012;302(1):L4–12.
Hewlett JC, Kropski JA, Blackwell TS. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions and emerging therapeutic targets. Matrix Biol. 2018;71–72:112–27.
Stamatiou R, Paraskeva E, Papagianni M, Molyvdas PA, Hatziefthimiou A. The mitogenic effect of testosterone and 17beta-estradiol on airway smooth muscle cells. Steroids. 2011;76(4):400–8.
Zhou C, Wu S. T-type calcium channels in pulmonary vascular endothelium. Microcirculation. 2006;13(8):645–56.
Barlow CA, Shukla A, Mossman BT, Lounsbury KM. Oxidant-mediated cAMP response element binding protein activation: calcium regulation and role in apoptosis of lung epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006;34(1):7–14.
Li B, Wang R, Wang Y, Stief CG, Hennenberg M. Regulation of smooth muscle contraction by monomeric non-RhoA GTPases. Br J Pharmacol. 2020;177(17):3865–77.
Petrache I, Berdyshev EV. Ceramide signaling and metabolism in pathophysiological states of the lung. Annu Rev Physiol. 2016;78:463–80.
Asada R, Kanemoto S, Kondo S, Saito A, Imaizumi K. The signalling from endoplasmic reticulum-resident bZIP transcription factors involved in diverse cellular physiology. J Biochem. 2011;149(5):507–18.
Qian F, Deng J, Wang G, Ye RD, Christman JW. Pivotal role of mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2 in inflammatory pulmonary diseases. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2016;17(4):332–42.
Xu K, Moghal N, Egan SE. Notch signaling in lung development and disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;727:89–98.
Zhao J, Xie F, Chen R, Zhang Z, Dai R, Zhao N, Wang R, Sun Y, Chen Y. Transcription factor NF-kappaB promotes acute lung injury via microRNA-99b-mediated PRDM1 down-regulation. J Biol Chem. 2020;295(52):18638–48.
Takyar S, Vasavada H, Zhang JG, Ahangari F, Niu N, Liu Q, Lee CG, Cohn L, Elias JA. VEGF controls lung Th2 inflammation via the miR-1-Mpl (myeloproliferative leukemia virus oncogene)-P-selectin axis. J Exp Med. 2013;210(10):1993–2010.
Gelfand EW. Importance of the leukotriene B4-BLT1 and LTB4-BLT2 pathways in asthma. Semin Immunol. 2017;33:44–51.
Lagares D, Ghassemi-Kakroodi P, Tremblay C, Santos A, Probst CK, Franklin A, Santos DM, Grasberger P, Ahluwalia N, Montesi SB, et al. ADAM10-mediated ephrin-B2 shedding promotes myofibroblast activation and organ fibrosis. Nat Med. 2017;23(12):1405–15.
Berger AJ. Development of synaptic transmission to respiratory motoneurons. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2011;179(1):34–42.
Li W, Baumbach J, Mohammadnejad A, Brasch-Andersen C, Vandin F, Korbel JO, Tan Q. Enriched power of disease-concordant twin-case-only design in detecting interactions in genome-wide association studies. Eur J Hum Genet. 2019;27(4):631–6.
Liang S, Li Z, Wang Y, Li X, Yang X, Zhan X, Huang Y, Gao Z, Zhang M, Sun C, et al. Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis reveals epigenetic pattern of SH2B1 in Chinese monozygotic twins discordant for autism spectrum disorder. Front Neurosci. 2019;13:712.
Saraga DE, Volanis L, Maggos T, Vasilakos C, Bairachtari K, Helmis CG. Workplace personal exposure to respirable PM fraction: a study in sixteen indoor environments. Atmos Pollut Res. 2014;5(3):431–7.
Vardoulakis S, Giagloglou E, Steinle S, Davis A, Sleeuwenhoek A, Galea KS, Dixon K, Crawford JO. Indoor exposure to selected air pollutants in the home environment: a systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(23):8972.
Cepeda M, Schoufour J, Freak-Poli R, Koolhaas CM, Dhana K, Bramer WM, Franco OH. Levels of ambient air pollution according to mode of transport: a systematic review. Lancet Public Health. 2017;2(1):e23–34.
Forbes LJ, Kapetanakis V, Rudnicka AR, Cook DG, Bush T, Stedman JR, Whincup PH, Strachan DP, Anderson HR. Chronic exposure to outdoor air pollution and lung function in adults. Thorax. 2009;64(8):657–63.
Manisalidis I, Stavropoulou E, Stavropoulos A, Bezirtzoglou E. Environmental and health impacts of air pollution: a review. Front Public Health. 2020;8:14.
Cakmak S, Dales RE, Liu L, Kauri LM, Lemieux CL, Hebbern C, Zhu J. Residential exposure to volatile organic compounds and lung function: results from a population-based cross-sectional survey. Environ Pollut. 2014;194:145–51.
Mu G, Fan L, Zhou Y, Liu Y, Ma J, Yang S, Wang B, Xiao L, Ye Z, Shi T, et al. Personal exposure to PM2.5-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and lung function alteration: results of a panel study in China. Sci Total Environ. 2019;684:458–65.
Shi Y, Zhao T, Yang X, Sun B, Li Y, Duan J, Sun Z. PM2.5-induced alteration of DNA methylation and RNA-transcription are associated with inflammatory response and lung injury. Sci Total Environ. 2019;650(Pt 1):908–21.
Wang M, Zhao J, Wang Y, Mao Y, Zhao X, Huang P, Liu Q, Ma Y, Yao Y, Yang Z, et al. Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis reveals significant impact of long-term ambient air pollution exposure on biological functions related to mitochondria and immune response. Environ Pollut. 2020;264:114707.
Alhamdow A, Essig YJ, Krais AM, Gustavsson P, Tinnerberg H, Lindh CH, Hagberg J, Graff P, Albin M, Broberg K. Fluorene exposure among PAH-exposed workers is associated with epigenetic markers related to lung cancer. Occup Environ Med. 2020;77(7):488–95.
Li J, Zhu X, Yu K, Jiang H, Zhang Y, Wang B, Liu X, Deng S, Hu J, Deng Q, et al. Exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and accelerated DNA methylation aging. Environ Health Perspect. 2018;126(6):067005.
Cho Y, Song MK, Kim TS, Ryu JC. DNA methylome analysis of saturated aliphatic aldehydes in pulmonary toxicity. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):10497.
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TW: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing—original draft. WW and WL: Methodology, Software, Formal analysis. HD, CX and XT: Validation, Investigation, Resources. DZ: Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing—review &editing. All authors reviewed the draft for intellectual content, and approved submission of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Informed written consents were obtained from all participants. Regional Ethics Committee of the Qingdao Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Institutional Review Boards has approved this study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors have declared no conflicts of competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table S1.
Descriptive statistics of basic characteristicsof the sample.
Additional file 2: TableS2.
Descriptive statistics of intra-pair difference of FEV1, FVC, FEV1/FVCratio and some significant methylated value of CpG sites.
Additional file 3: Figure S1.
Scatter plots with regression lineshowing the association of Δ methylated value of CpG sites and Δ FEV1. The Δmethylation value of four CpG sites (f, h, i, j) were positively correlatedwith ΔFEV1, and the Δ methylation value of seven CpG sites (a,b,c,d,e,g,k) werenegatively correlated with ΔFEV1.
Additional file 4: Figure S2.
Scatter plot with regression line showing the association of Δ methylatedvalue of CpG sites and Δ FVC. The Δ methylation value of eleven CpG sites(a,b,c,g,h,i,j,k,m,o,q) were positively correlated with ΔFVC, and the Δmethylation value of six CpG sites (d,e,f,l,n,p) were negatively correlatedwith ΔFVC.
Additional file 5: Figure S3.
Scatter plots with regression line showing the association of Δ methylatedvalue of CpG sites and Δ FEV1/FVC. The Δ methylation value of two CpG sites(c,i) were positively correlated with ΔFEV1/FVC ratio, and the Δ methylation valueof ten CpG sites (a,b,d,e,f,g,h,j,k,l) were negatively correlated withΔFEV1/FVC ratio.
Additional file 6: Figure S4.
Number of associated genes per region for FEV1 (a), FVC (b), and FEV1/FVC (c). The number of genomiccis-regulatory regions related with one or more genes was 13,821 for FEV1,14,901 for FVC, and 17,929 for FEV1/FVC.
Additional file 7: Figure S5.
Binned by orientation and distance to transcription start site FEV1 (a),FVC (b), and FEV1/FVC (c). Thenumber of FEV1 genomic regions whose distance to the TSS was <-500, -500 to-50, -50 to -5, -5 to 0, 0 to 5, 5 to 50, 50 to 500, >500 kb was 478, 3691,3732, 1666, 2440, 5817, 6066, and 632, respectively. The number of FVC genomicregions whose distance to the TSS was <-500, -500 to -50, -50 to -5, -5 to0, 0 to 5, 5 to 50, 50 to 500, >500 kb was 549, 4046, 4054, 1816, 2666,6306, 6425, and 673, respectively. The number of FEV1/FVC genomic regions whosedistance to the TSS was <-500, -500 to -50, -50 to -5, -5 to 0, 0 to 5, 5 to50, 50 to 500, >500 kb was 610, 4826, 4673, 2537, 3125, 7458, 7530, and 840,respectively.
Additional file 8: Figure S6.
Binned by absolute distance to transcription start site for FEV1 (a), FVC(b), and FEV1/FVC (c). Thenumber of FEV1 genomic regions whose absolute distance to the TSS was 0 to 5, 5to 50, 50 to 500, >500 kb was 4106, 9549, 9757, 1110, respectively. Thenumber of FVC genomic regions whose absolute distance to the TSS was 0 to 5, 5to 50, 50 to 500, >500 kb was 4482, 10360, 10471, 1222, respectively. Thenumber of FEV1/FVC genomic regions whose absolute distance to the TSS was 0 to5, 5 to 50, 50 to 500, >500 kb was 5662, 12131, 12356, 1450, respectively.
Additional file 9: Table S3.
Significantfunctional clusters biological process related to FEV1 by GREAT using binomialtest.
Additional file 10: Table S4.
Significantfunctional clusters biological process related to FVC by GREAT using binomialtest
Additional file 11: Table S5.
Significantfunctional clusters biological process related to FEV1/FVC by GREAT usingbinomial test.
Additional file 12: Figure S7.
Relationships of consensus module eigengenes and external traits. Each row inthe table corresponds to a consensus module, and each column to a sample ortrait. Numbers in the table report the correlations of the corresponding moduleeigengenes and traits, with the P-valuesprinted below the correlations in parentheses. The table is color coded bycorrelation according to the color legend. The genes clustered inlightstellblue1 module and darkorange2 module are the positively correlatedwith FEV1 and FVC, and the genes clustered in ivory module is negativelycorrelated with FEV1/FVC.
Additional file 13: Table S6.
The results ofenrichment analysis for genes clustered in lightsteelblue1 module by DAVID tool.
Additional file 14: Table S7.
The results ofenrichment analysis for genes clustered in darkorange2 module by DAVID tool
Additional file 15: Table S8.
The results ofenrichment analysis for genes clustered in ivory module by DAVID tool.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, T., Wang, W., Li, W. et al. Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis of pulmonary function in middle and old-aged Chinese monozygotic twins. Respir Res 22, 300 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-021-01896-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-021-01896-5