Abstract
Background
Patients’ increasing needs and expectations require an overall assessment of hospital performance. Several international agencies have defined performance indicators sets but there exists no unanimous classification. The Impact HTA Horizon2020 Project wants to address this aspect, developing a toolkit of key indicators to measure hospital performance. The aim of this review is to identify and classify the dimensions of hospital performance indicators in order to develop a common language and identify a shared evidence-based way to frame and address performance assessment.
Methods
Following the PRISMA statement, PubMed, Cochrane Library and Web of Science databases were queried to perform an umbrella review. Reviews focusing on hospital settings, published January 2000–June 2019 were considered. The quality of the studies selected was assessed using the AMSTAR2 tool.
Results
Six reviews ranging 2002–2014 were included. The following dimensions were described in at least half of the studies: 6 studies classified efficiency (55 indicators analyzed); 5 studies classified effectiveness (13 indicators), patient centeredness (10 indicators) and safety (8 indicators); 3 studies responsive governance (2 indicators), staff orientation (10 indicators) and timeliness (4 indicators). Three reviews did not specify the indicators related to the dimensions listed, and one article gave a complete definition of the meaning of each dimension and of the related indicators.
Conclusions
The research shows emphasis of the importance of patient centeredness, effectiveness, efficiency, and safety dimensions. Especially, greater attention is given to the dimensions of effectiveness and efficiency. Assessing the overall quality of clinical pathways is key in guaranteeing a truly effective and efficient system but, to date, there still exists a lack of awareness and proactivity in terms of measuring performance of nodes within networks. The effort of classifying and systematizing performance measurement techniques across hospitals is essential at the organizational, regional/national and possibly international levels to deliver top quality care to patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Find the latest articles, discoveries, and news in related topics.Background
Addressing issues related to quality of care is one of the major concerns of healthcare systems [1]. It is a current topic on the agenda of policy makers at different levels and worldwide [2] because of a growing need to control costs and guarantee sustainability, reduce variability in healthcare delivery, ensure transparency and accountability, deliver effective, safe and person-centered care, improve patients’ clinical outcomes and their satisfaction [2, 4].
Scientific literature on the topic is wide and evidence is available on different aspects of quality of care. These lead to several perspectives such as, for example, area or level of care, type of organization, improvement strategies [2].. Despite the broad literature, disagreement persists on what the expression “quality of care” comprehends and there is no unanimous understanding of the term [2]. The definition of Donabedian, who defines quality as “the ability to achieve desirable objectives using legitimate means”, is perhaps the one that better describes the concept in healthcare [2]. Also, according to Donabedian, quality of care is referred to the whole process of care, where the goal is to maximize general patient welfare and health outcomes [2].. The internationally accepted definition of the Institute of Medicine also recalls health outcomes and gives importance to evidence and professional knowledge [5]. Moreover, this last definition and the one formulated by World Health Organization (WHO) in 2006 [5] encompass other characteristics of care delivery. Healthcare has to be safe, effective, patient-centered, timely, efficient, equitable, acceptable and accessible. Among these features, safety, effectiveness and patient-centeredness/responsiveness can be considered universally as core dimensions while others can be viewed as subdimensions [2]. This distinction is based on the framework (Health Care Quality Indicator (HCQI) project) formulated by the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) in 2006 with the intent to lead the development of indicators in order to compare quality at the international level [2]. Indicators are indirect measures that provide information about the dimensions of quality of care [2]. Measurement is important to assess quality and implement improvement actions in order to provide better healthcare and enhance health outcomes. The use of standardized indicators leads on one hand to a better assessment across all levels of healthcare, on the other, to the increase of transparency and trust by patients [5]. Quality is not a synonym of performance but it is an important component of healthcare systems’ performance. This latter concept is therefore wider than the one of quality and describes the extent to which health systems are able to reach their goals [2].
Monitoring healthcare providers’ performance is relevant worldwide, especially in settings such as hospitals, given their significant weight in terms of both health and economic effects. In 2003, WHO launched a project aimed at supporting hospitals in order to develop a framework for the assessment of their performance. The project – named PATH (Performance Assessment Tool for quality improvement in Hospital) – was aimed at identifying dimensions and indicators for assessing hospital performance [4]. However, despite the detection of a great number of hospital performance indicators, some gaps in their measurement as well as issues concerning the dimensions investigated still exist. For example, some dimensions are under-represented and some healthcare settings or clinical specialties are not well tracked [6].
This study is part of the IMPACT HTA (Improved Methods and ACtionable Tools for enhancing HTA) project. IMPACT HTA is a Horizon 2020 research project aimed at studying variations in costs and health outcomes and at improving economic evaluation regarding HTA (Health Technology Assessment) and health system performance measurement through the integration of clinical and economic data from different sources. The measurement of hospital performance and its link with organizational models is one of the core aspects of the project. Within the latter, the authors of this paper dealt with the identification and classification of the dimensions of hospital performance indicators, according to scientific evidence, with the double aim of synthesizing the available knowledge on the topic in a comprehensive manner and providing the basis for a possible common way of measuring hospital performance.
Methods
An umbrella review was performed with the aim of aggregating findings from reviews available on the topic. Indeed, an umbrella review allows to aggregate findings from reviews, making it possible to reassemble the fragmented knowledge concerning a specific topic. In other words, it provides a synthesis of the evidence described in several reviews that has been conducted on the same topic [7, 8].
Search strategy
To perform an umbrella review, PubMed, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science databases were queried through the following search string: ((((Indicator* OR standard OR benchmark*) AND (project* OR program OR tool* OR set OR model)) AND ((outcome OR output) OR (quality OR effectiveness OR safety OR appropriateness OR efficiency OR “patient satisfaction” OR efficacy OR equity OR accountability OR “patient centredness” OR “patient centeredness” OR “staff orientation” OR “staff satisfaction” OR access*))) AND (measure* OR assess* OR evaluate OR implement*)) AND (performance AND “hospital*”). The investigation was conducted in June 2019 and the articles retrieved were screened according to the inclusion/exclusion criteria previously stated and listed in the following paragraph.
Inclusion/exclusion criteria
The selection of the articles was conducted referring to previously defined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Only review articles focused on indicators of hospital performance, written in English or Italian, ranging from January 1st, 2000 to June 30th, 2019 and available in full text were considered. The included reviews had to classify the dimensions of hospital performance; articles analyzing only one dimension were maintained. Articles examining single indicators or lacking a classification in dimensions or reporting a classification only related to a single clinical setting or specialty were excluded.
Data synthesis
The selection of the articles followed the PRISMA statement [9]. Two researchers screened independently the results by title and abstract and finally by full text. Eventual disagreements were discussed between the researchers in order to find a solution and in case of persistent discordance a third researcher was involved in the decision. To synthetize the selected articles, a table was designed and the following information were extracted: authors, country, year of publication, title, objective, results, dimension/subdimension, indicators, definition of each indicator. A qualitative synthesis was performed to analyze the data. A quantitative synthesis was not carried out due to the heterogeneity of the data retrieved.
Quality appraisal
The quality of the studies selected was assessed using AMSTAR2 (A MeaSurement Tool to Assess systematic Reviews). AMSTAR2 allows to evaluate different aspects of reviews in order to define the quality of the studies. It enables researchers to carry out rapid and reproducible assessments to evaluate the published version of a review. The tool is composed of 16 domains in the form of questions that can be answered with ‘yes’; ‘partial yes’ or ‘no’. Seven out of 16 are the domains which can critically affect the validity of the review (in particular, domains 2, 4, 7, 9, 11, 13, and 15). The review is finally rated with a high, moderate, low or critically low overall confidence [10].
Reporting
The whole document has been produced bearing in mind the PRISMA statement indications [9].
Results
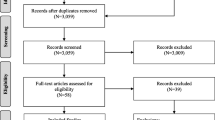
From the search, 222 records were identified in Web of Science, 333 in PubMed and 211 in Cochrane Library (Fig. 1). Duplicates removing was conducted through Mendeley software and a total number of 682 records was subsequently screened. A spreadsheet was compiled and, carefully reading the titles, 64 studies were assessed for eligibility. Six reviews were finally included in the qualitative synthesis.
The six reviews retrieved range from 2002 to 2014. Their main characteristics and results are summarized in Table 1. All the studies report a classification of the indicators in diverse dimensions but not all of them specify the indicators included in each. The ones only describing the dimensions are three [1, 3, 6]. The review by Veillard et al. gives a deeper insight providing a definition of the dimensions and a precise definition of each indicator described [4]. A subclassification of the dimensions is proposed by two reviews: Ganjour et al. group the indicators according to the disease or intervention they refer to [11], while Veillard et al. specify each dimension according to specific and detailed characteristics [4].
The dimensions of performance indicators
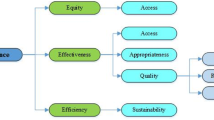
The dimensions in which the indicators of hospital performance have been classified are (Fig. 2): efficiency (6 studies; 100%) [1, 3, 4, 6, 11, 12], clinical effectiveness (5 studies; 83%) [1, 3, 4, 6, 12], patient-centeredness (5 studies; 83%) [1, 3, 4, 6, 12], safety (5 studies; 83%) [1, 3, 4, 6, 12], responsive governance (3 studies; 50%) [1, 3, 4], staff orientation (3 studies; 50%) [1, 3, 12], timeliness (3 studies; 50%) [1, 6, 12], equity (2 studies; 33%) [1, 6], utilization (2 studies; 33%) [1, 12]. All the other dimensions were described by only 1 (17%) article: acceptability [1], accessibility [1], appropriateness [1], care environment and amenities [1], continuity [1], competence or capability [1], expenditure or cost [1], improving health or clinical focus [1], resources and capacity [12], and sustainability [1]. The main findings of this work are summarized in the following paragraphs, while detailed information is presented in Table 2.
Efficiency
Efficiency has been explored by all the reviews included [1, 3, 4, 6, 11, 12]. It can be defined as the optimal allocation of available healthcare resources that maximize health outcomes for society [13]. Veillard et al. similarly refer to efficiency as hospital optimal use of inputs to yield maximal outputs, given the available resources [4]. The review by Gandjour et al. considers efficiency in terms of process (referring to specific clinical conditions) and structure [11]. Veillard et al. also provide a subclassification of the dimension, describing efficiency in terms of appropriateness of services, productivity, and use of capacity [4].
Clinical effectiveness
According to Veillard et al., clinical effectiveness is the appropriateness and competence which allows to deliver clinical care and services with the maximum benefit for all patients [4]. This study sub-classifies this dimension in appropriateness of care, conformity of processes of care, and outcomes of care and safety processes [4]. Simou et al., take into account mortality rates, readmissions, and survival [12].
Patient-centeredness
As reported by Veillard et al., this dimension concerns a set of indicators which pay attention to patients’ and families’ orientations. The main aim is to evaluate whether patients are placed at the center of care and service delivery [4]. Simou et al. provide patient centeredness indicators in terms of patients’ feedback [12].
Safety
Safety refers both to patients and professionals in terms of the ability to avoid, prevent and reduce harmful interventions or risks for them and for the environment [4, 12].
Responsive governance
Another aspect analyzed by three out of the six reviews is responsive governance [1, 3, 4]. Veillard et al. provide a definition of responsive governance which is described as the “degree of responsiveness to community needs, to ensure care continuity and coordination, to promote health and provide care to all citizens” and subclassify the related indicators into system integration and continuity and public health orientation [4]. The other two studies do not specify the set of indicators related to this dimension [1, 3].
Staff orientation
Staff orientation is reported by three studies [1, 3, 12]. This dimension is considered by Veillard et al. in terms of recognition of individual needs, health promotion and safety initiatives, behavioral responses [4]. Simou et al. address the issue through absenteeism, working environment satisfaction, overtime working, burnout and continuous education [12].
Timeliness
Timeliness [1, 6, 12] is assessed in terms of indicators only by Simou et al. and it refers to the time needed to be addressed to specific treatments [12].
Other dimensions
The other dimensions described are only addressed by one or two studies or only cited without specifying the related indicators. Just utilization and resource and capacity are described by Simou et al. [12]. The utilization dimension refers to the use of facilities and equipment, while the resources and capacity one analyzes the amount of personnel and equipment used.
Discussion
The present study aimed to identify and classify the dimensions of hospital performance indicators in order to make a contribution to the development of a common language and to identify a common evidence-based way to frame and address performance assessment. It is widely recognized that assessing hospital performance takes into account multiple aspects and dimensions, given the organizational and procedural complexity of such entities and the high number of stakeholders involved in their activities, likely to set different priorities as well as actual meanings to the term “performance” [14].
Therefore, it is still difficult to assess the performance of hospitals concretely. The task is even more challenging if we consider the differences in the main characteristics of hospitals (e.g. dimension, ownership, degree of clinical focus, geographical location).
This review contributes in shedding light on the most common ‘clusters’ of hospital performance indicators. As predictable [15], the dimensions of effectiveness and efficiency are highly emphasized and these appear to be the most represented dimensions from our review. Alongside them, the dimensions of safety and patient-centeredness are also well represented in the included reviews. Interestingly, a number of further dimensions of performance emerges, held into account in a non-systematic way or only sporadically. This may provide an interesting picture of how performance is intended and understood concretely in our healthcare systems.
Clearly, the objective of healthcare organizations is to produce health, so clinical effectiveness is probably its most direct proxy. Effectiveness, however, must be consistent with efficiency, in the not less relevant challenge of ensuring organizational sustainability in the long run. The lively debate on conflicts emerging between clinical professionals and managerial teams testifies the challenging need of combining the perspectives of roles that tend to focus on different priorities [16].
Performing in terms of safety is strictly connected to clinical effectiveness. The capability of a hospital to preserve patients’ good health is the other side of the coin in assuring clinical quality. Clearly, a hospital should not only intervene to improve patients’ health, but it must do so in such a way as to avoid exposing them to potential sources of personal harm. Moreover, safety is also referred to staff, which is frequently directly exposed to numerous risks and requires a structured and solid organizational apparatus to preserve its health [17]. The dimension of patient-centeredness may be interpreted in a strictly interconnected way with that of responsive governance [18]. If, on the one hand, patient-centeredness may assume a ‘double face’, covering both the dimension of patient satisfaction as well as that of continuity of care, on the other, responsive governance seems related to the capability of the hospitals to monitor performance in an integrated manner (within its units and throughout different settings). The last topic surely needs an increasingly relevant focus in the years to come [19].
Indeed, in accordance with epidemiological patterns of developed countries, with ageing populations and the spread of multi-pathological chronic conditions, it is crucial to shift the conception of performance from a setting-oriented to a multi-setting oriented approach. Hospitals are by now one of the steps in patients’ clinical pathways and it is misleading to assess their contribution to their final status of health in a completely isolated way [20]. Indeed, although it is important to isolate the effects of a specific setting from the others, it makes little sense to think of performance as something that can be obtained without structured interconnections with the other settings of the system. In this sense, all the efforts in assessing the overall quality of clinical pathways are key in guaranteeing a truly effective and efficient system. As noted, however, only a limited percentage of the scientific evidence assessed in this study takes into account this perspective. This may suggest that, to date, there still exists an important lack of awareness and proactivity in terms of measuring performance of nodes within networks rather than of isolated monads.
Furthermore, the effects of possibly non-systematized ways of measuring performance are likely to exert heavy repercussions in a number of ways. These may include lack of transparent information to patients, career choices of professionals, access to public and private funds [21].
It is therefore clear that the effort of classifying and systematizing performance measurement techniques across hospitals is key at the organizational, regional/national and possibly international levels.
At the organizational level, the way in which performance is assessed is likely to have strong and direct effects on internal organizational and managerial equilibria, as well as on the overall strategy of the hospital. Depending on the choice of ‘key’ performance dimensions, some units or directorates are likely to be held more or less performing. This, in turn, can affect internal equilibria due to, for example, prestige and allocation of resources [22].
At the regional/national level this sort of assessment may have crucial effects on the access to resources. Not only in terms of monetary remunerations (due to patients’ choice of being assisted in a certain hospital or to, as is the case in some healthcare systems, the decision of regions to finance more or less large amounts of clinical activities within that hospital), but also in terms of their appeal to professionals and industries of health technologies [23].
At the international level, a common ground to assess performance would allow an indirect assessment of different healthcare systems. These are highly differentiated across countries and benchmarking efforts are frequently hindered by the lack of comparable data [24].
In this scenario, it is crucial to provide the basis for a possible common way of measuring hospital performance. This analysis provides a solid first step in this direction.
The study presents some limitations, hereby presented. No quantitative synthesis of the studies was conducted as there was high heterogeneity among the reviews included and therefore among their results. The dimensions were described by all the studies but only half of them specified the respective indicators and the list presented is not comprehensive of all the possible indicators. The overall quality of the review was assessed to be ‘critically low’ as the reviews did not meet the quality criteria stated by the AMSTAR2 tool, even though it has to be pointed out that this tool does not fit completely the needs of a review centered on organizational/management topics. Despite these limitations, the proposed review represents, so far, the first attempt to synthetize the available knowledge on the topic in a comprehensive manner and with a strict methodology. The inclusion of only reviews was aimed at providing stronger evidence.
Quality assessment
All the included reviews, assessed for quality through AMSTAR2 tool, have been rated as critically low (Annex 1). All the reviews did not meet 11 out of 16 domains of the AMSTAR2 scale. Five out of those 11 domains are critical and are referred to: (7) justification for the exclusion of studies which were not included in the review; (9) assessment of the risk of bias (RoB) in individual studies which were included in the review; (11) use of appropriate methods for statistical combination of results if meta-analysis was performed; (13) taking into account RoB in individual studies when interpreting/discussing the results of the review; (15) adequate investigation of publication bias if quantitative synthesis was performed and discussion of its likely impact on the results of the review.
Conclusions
The assessment of the overall quality of clinical pathways is key in guaranteeing a truly effective and efficient system. The effort of a deeper understanding of what quality really means and which are the related dimensions is not new and in 2006 a framework aimed at the development of indicators to compare quality at the international level was settled by OECD [2]. Quality is made of different dimensions [2] thus, measuring quality means measuring those dimensions through the use of specific indicators. According to OECD, some dimensions, such as safety, effectiveness and patient-centeredness/responsiveness, can be considered universally as core dimensions when dealing with quality in healthcare [2]. Nevertheless, although some clusters of indicators may appear rather intuitive and universally monitored (although – even here – it should be assessed what is actually measured within each cluster), some clusters appear incredibly subject to interpretations or even overlooked. Therefore, the effort of clustering indicators into shared categories is fundamental to guarantee a systematic, reproducible, comparable, and universally shared evaluation but it also sheds light on the existing gaps concerning this evaluation and systematization. Further studies should provide guidance in covering this gap, as well as in highlighting how all the less frequently assessed dimensions of performance may be integrated within overall hospital assessments.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
Abbreviations
- AMSTAR2:
-
A MeaSurement Tool to Assess systematic Reviews
- HCQI:
-
Health Care Quality Indicator
- HTA:
-
Health Technology Assessment
- IMPACT HTA:
-
Improved Methods and ACtionable Tools for enhancing HTA
- OECD:
-
Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development
- PRISMA:
-
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
- PATH:
-
Performance Assessment Tool for quality improvement in Hospital
- RoB:
-
Risk of Bias
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
Beyan OD, Baykal N. A knowledge based search tool for performance measures in health care systems. J Med Syst. 2012;36(1):201–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-010-9459-2.
Busse R, Klazinga N, Panteli D, Quentin W. Improving healthcare quality in Europe. Characteristics, effectiveness and implementation of different strategies. WHO-European Observatory on Health Systems and Policies and OECD: United Kingdom; 2019.
Groene O, Skau JK, Frølich A. An international review of projects on hospital performance assessment. Int J Qual Health Care. 2008;20(3):162–71. https://doi.org/10.1093/intqhc/mzn008.
Veillard J, Champagne F, Klazinga N, Kazandjian V, Arah OA, Guisset AL. A performance assessment framework for hospitals: the WHO regional office for Europe PATH project. Int J Qual Health Care. 2005;17(6):487–96. https://doi.org/10.1093/intqhc/mzi072.
Handbook for national quality policy and strategy. a practical approach for developing policy and strategy to improve quality of care. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
Copnell B, Hagger V, Wilson SG, Evans SM, Sprivulis PC, Cameron PA. Measuring the quality of hospital care: an inventory of indicators. Intern Med J. 2009;39(6):352–60. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1445-5994.2009.01961.x.
Grant MJ, Booth A. A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Inf Libr J. 2009;26(2):91–108. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x.
Fusar-Poli P, Radua J. Ten simple rules for conducting umbrella reviews. Evid Based Ment Health. 2018;21(3):95–100. https://doi.org/10.1136/ebmental-2018-300014.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, The PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed1000097.
Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G, et al. AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ. 2017;358:j4008. Published 2017 Sep 21. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.j4008.
Gandjour A, Kleinschmit F, Littmann V, Lauterbach KW. An evidence-based evaluation of quality and efficiency indicators. Qual Manag Health Care. 2002;10(4):41–52. https://doi.org/10.1097/00019514-200210040-00008.
Simou E, Pliatsika P, Koutsogeorgou E, Roumeliotou A. Developing a national framework of quality indicators for public hospitals. Int J Health Plann Manag. 2014;29(3):e187–206. https://doi.org/10.1002/hpm.2237.
HTA Glossary. INAHTA, HTAi and other partner organizations. 2006. http://htaglossary.net/efficiency. Accessed 7 May 2020.
Lega F, DePietro C. Converging patterns in hospital organization: beyond the professional bureaucracy. Health Policy. 2005;74(3):261–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healthpol.2005.01.010.
Braithwaite J, Matsuyama Y, Manninon R, Johnson J. Healthcare reform, quality and safety. Perspectives, participants, partnerships and prospects in 30 countries. Farnham (UK): Ashgate publishing; 2015.
Rivers PA, Woodard B, Munchus G. Organizational power and conflict regarding the hospital-physician relationship: symbolic or substantive? Health Serv Manag Res. 1997;10(2):91–106. https://doi.org/10.1177/095148489701000110.
Ancarani A, Di Mauro C, Giammanco MD. Hospital safety climate and safety behavior: a social exchange perspective. Health Care Manag Rev. 2017;42(4):341–51. https://doi.org/10.1097/HMR.0000000000000118.
Gabutti I, Mascia D, Cicchetti A. Exploring "patient-centered" hospitals: a systematic review to understand change. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017;17(1):364. Published 2017 May 22. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-017-2306-0.
Rathert C, Wyrwich MD, Boren SA. Patient-centered care and outcomes: a systematic review of the literature. Med Care Res Rev. 2013;70(4):351–79. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077558712465774.
Gabutti I, Cicchetti A. Translating strategy into practice: a tool to understand organizational change in a Spanish university hospital. An in-depth analysis in hospital clinic. Int J Healthc Manag. 2020;13(2):142–55.
Anema HA, Kievit J, Fischer C, Steyerberg EW, Klazinga NS. Influences of hospital information systems, indicator data collection and computation on reported Dutch hospital performance indicator scores. BMC Health Serv Res. 2013;13:212. Published 2013 Jun 12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6963-13-212.
Maniadakis N, Kotsopoulos N, Prezerakos P, Yfantopoulos J. Measuring intra-hospital clinic efficiency and productivity: an application to a Greek University general hospital. Eur Res Stud J. 2008;11(1–2):95–109.
Ghaferi AA, Osborne NH, Dimick JB. Does voluntary reporting bias hospital quality rankings? J Surg Res. 2010;161(2):190–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2009.07.033.
Medin E, Häkkinen U, Linna M, et al. International hospital productivity comparison: experiences from the Nordic countries. Health Policy. 2013;112(1–2):80–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healthpol.2013.02.004.
Acknowledgements
The authors of this review want to thank Dr. Pasquale Cacciatore, Dr. Adriano Grossi and Dr. Ilda Hoxhaj, essential components of the IMPACT HTA project working group of Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore.
The preliminary findings of this work were orally presented at the 12th European Public Health Conference in Marseille, France (20-23 November 2019). The abstract of the presentation could be accessed at the following link: https://academic.oup.com/eurpub/article/29/Supplement_4/ckz185.617/5624593
Funding
The publication was supported by IMPACT HTA project, a European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme. The funding body has no direct involvement in any aspect of the study design; collection, analysis and interpretation of the data; in the writing of the manuscript. The views expressed in the article are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MLS, SB, CdW, IG designed the study under the supervision of AC. EC, AMP carried out databases search and EC, ADP, AMP conducted data extraction. IG, MLS, EMF, EC prepared the manuscript that was reviewed by AC, CdW, SB. All authors approved the final version of the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Carini, E., Gabutti, I., Frisicale, E.M. et al. Assessing hospital performance indicators. What dimensions? Evidence from an umbrella review. BMC Health Serv Res 20, 1038 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-020-05879-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-020-05879-y