Abstract
Background
Agile concepts are not only beneficial for manufacturing sector but also for service sector such as healthcare. However, assessment of agility has been predominantly done in manufacturing enterprises. This study demonstrates a means to measure agility of a healthcare organization by assessing agility of a university dispensary. Its contribution to the knowledge base is twofold. First, it proposes a means to measure the agility of a healthcare organization and second, it identifies the attributes that prevent agile performance and outlines the suggestive measure to enhance its agile capabilities.
Method
A case study approach has been adopted and fuzzy logic has been employed to measure the agility of the case dispensary. At first, the measures of assessment which include four enablers, fifteen criteria and forty-five attributes have been identified from the literature and rated by the experts indicating the importance of the measures in the assessment. Then, the case dispensary has been assessed on those measures by collecting observed performance rating from decision makers. At last, Fuzzy logic has been applied on the performance rating data to analyze and interpret the agile capability of the dispensary.
Results
The findings suggest that transparent information flow, adequate salary and bonuses for caregivers, reading error in medical descriptions, in house/nearby pathology laboratory services, technical up-gradation of dispensary equipments and facilities, minimization of patient throughput time and adequate training programme for safety practices are the attributes that weakens agile capability of the University dispensary. The current agility of the dispensary was found to be ‘Agile’ which is average in relation to the agility labels.
Conclusion
Attributes such as transparent information flow, adequate salary and bonuses for caregivers, elimination of reading error in medical descriptions, in house/nearby pathology laboratory services, technical up-gradation of dispensary equipments and facilities, minimization of patient throughput time and adequate training programme for safety practices are extremely crucial for enhancing agile capability of a healthcare organization.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The term “Agility” came into existence in 1991 when a group of researchers at Iacocca Institute, Lehigh University conducted a study with 150 industry executives and referred the manufacturing practices observed during the study as agile practices [1]. Initially, agility was defined as using market knowledge and a virtual corporation to exploit profitable opportunities in a volatile market place [2]. Then it was referred as “the successful exploration of competitive bases (speed, flexibility, innovation pro-activity, quality and profitability) through the integration of reconfigurable resources and best practices in a knowledge-rich environment to provide customer- driven products and services in a fast changing market environment” [1]. Overtime, the definition went through further evolution and agility was defined as “the ability of an organization to respond rapidly to changes in demand both in terms of volume and variety” [3]. Another study translated agility to the power of moving quickly and having a quick resourceful and adaptable character [4]. Though the concept originated in manufacturing sector, it was found beneficial in service sectors as well; especially in healthcare sector [4]. Many studies and found that agile practices can help the healthcare organizations to meet the service demand which changes quickly and unpredictably and at the same time retain the competitive advantage over other players in the market [5, 6]. In addition, resilience and agility were found to be extremely crucial in healthcare [5]. Many studies in literature discussed how agility capabilities can help up-gradation of healthcare service quality [6]. Some studies also took an entirely different perspective by looking at agility as performance capability of an organization [7, 8]. As a result, the factors that drive agility of an organization have also been explored in the literature [9,10,11].
Acknowledging the importance of agility in healthcare, we continued our literature exploration in the context of how to assess agility of a healthcare organization. We found that assessment of agility has been predominantly done in manufacturing enterprises [12,13,14,15,16,17]. So far, agility of an organization has been assessed through several means such as index [13], system approach [12], graph theory [15], fuzzy data envelopment analysis [16, 17] and regression analysis [14]. Though a substantial amount of research endeavour has gone into assessment of agility in manufacturing enterprises, none of the studies has extended it to healthcare organizations. This leaves a gap in the existing literature as well as becomes the motivation behind this study. Here, we attempt to address the following research questions:
RQ1: How to measure agility of a healthcare organization?
RQ2: What are the attributes that influence agility of a healthcare organization?
RQ3: How to address those weak attributes to enhance agility?
Answer to these questions would help the researchers and managers in the field to identify the attributes that prevent agility of a healthcare organization and enforce suggestive measures to enhance its agile capabilities. Agile capability is referred as capability of an organization to prosper in a competitive environment and adapt quickly to the changing demands [18, 19].
Methods
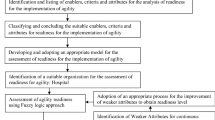
In order to answer the research questions, we conducted a case analysis in the University dispensary located in India. The dispensary caters to 5000 students and 2000 staff members in the campus and as the university is actively involved in student exchange programs from various counties and visiting professors from different geographical locations, the dispensary aspires to enhance its service dynamics, responsiveness and efficiency to world standards. Therefore, this study considers the University dispensary as a case to assess and recommend suggestive measures to improve its agility. Fuzzy logic has been used to measure the current agility level of the dispensary and identify the attributes that pose a challenge to its agile performance. Fuzzy logic is preferred over other methods because it can take the linguistic data as input, analyze it and then express the results back in linguistic terms. Linguistic expressions are vague to interpret and have very small difference in meaning; for instance “Very bad” and “Worst”. Conversion of linguistic expressions into numerical values is difficult, and poses a challenge in terms of consistency and reliability. Fuzzy logic addresses these challenges by converting the linguistic variables into corresponding fuzzy intervals; also known as membership function, perform fuzzy operation and then convert it back into linguistic terms with the help of Fuzzy Agility Measure Index (FAMI). Apart from this, fuzzy logic also identifies the obstacles of the phenomenon. Many studies in literature have used fuzzy logic to assess several phenomena. One among them is agility assessment in manufacturing companies [20,21,22]. In this context, studies have developed an agility index [23] and adopted multi-grade fuzzy to measure agility level of the manufacturing organization [24]. Taking cues from these studies, this study adopts fuzzy logic to assess agility of a healthcare organization. Here, we use triangular fuzzy which assigns a three point interval or membership function to each of the linguistic variables. For example: the linguistic term “Worst” is captured in fuzzy interval (0, 0.5, 1.5). The assessment involves three major steps. First, a list of agile enablers, criteria and attributes that influence agile performance of a healthcare organization is identified. Second, the above measures (agile enablers, criteria and attributes) are assessed in the case hospital by collecting the observed performance rating from the decision makers. Third, fuzzy mathematical calculations are performed on the above performance rating data and agility of the healthcare organization is determined. The details regarding each of these steps are discussed below. Apart from this, a pictorial representation of the framework is presented in Fig 1.
Step 1: identification of agile enablers, criteria and attributes
The first step, “identification of agile enablers, criteria and attributes” has been accomplished in this study by identifying a list of agile enablers, criteria and attributes from the literature, keeping the models for developed manufacturing organizations [1, 18, 20, 21, 25, 26] as reference. The list comprised of four enablers, fifteen criteria and forty-five attributes where each enabler branched out to a number of criteria and each criterion branched out to a set of attributes. The enablers, criteria and attributes put together constituted the measures of healthcare agility assessment and are presented in Table 1. Following the identification of these measures, five experts (E1, E2,…, E5) including three medical officers and two doctors from five different dispensaries in India were approached to capture the weightage of each enabler, criterion and attribute. The experts were asked to provide the weightage in terms of linguistic variables ranging from “Very low (VL)” to “Very High (VH)”. A sample question put forth to the experts to capture the weightage is given below.
Please mention how important is the following attribute for healthcare agility.
Decentralised organization structure
Very Low ( ) Low ( ) Fairly Low ( ) Medium ( ) Fairly High ( ) High ( ) Very High ( )
Team managed organization
Very Low ( ) Low ( ) Fairly Low ( ) Medium ( ) Fairly High ( ) High ( ) Very High ( )
For each of these linguistic variables from “Very low (VL)” to “Very High (VH)”, a corresponding fuzzy interval or membership function was assigned. For example: the linguistic variable “Very low (VL)” was assigned an interval (0, 0.05, 0.15) and “Very High (VH)” was assigned an interval (0.85, 0.95, 1.0). The intervals have been adopted from literature [20] and presented in Table 2. The linguistic weightage provided by the experts for enablers, criteria and attributes have been captured in Table 3, 4 and 5 respectively.
Step 2: collection of observed performance rating on the measures
In the second step, a questionnaire was shared among five decision makers (D1, D2,…, D5) who are doctors in the case dispensary to provide an observed performance rating indicating where the dispensary stands in terms of each attribute. Here, the performance rating is collected for attributes alone because during fuzzy analysis, the attribute ratings are aggregated to criteria rating and criteria rating to enablers rating. The computations pertaining to this aggregation have been discussed in the sub section, “Details of fuzzy calculation steps”. The attribute rating was captured in linguistic variables ranging from “Worst (W)” to “Excellent (E)”. A sample question put forth to the decision makers is given below.
Please rate the dispensary indicating where it stands with respect to the attributes underlined below:
Decentralised organization structure
Worst ( ) Very poor ( ) Poor ( ) Fair ( ) Good ( ) Very Good ( ) Excellent ( )
Team managed organization
Worst ( ) Very poor ( ) Poor ( ) Fair ( ) Good ( ) Very Good ( ) Excellent ( )
For each of these linguistic variables from “Worst (W)” to “Excellent (E)”, a corresponding fuzzy interval or membership function was assigned. For example: the linguistic variable “Worst (W)” was assigned an interval (0, 0.5, 1.5) and “Excellent (E)” was assigned an interval (8.5, 9.5, 10). The intervals have been adopted from literature [20] and presented in Table 2. The performance rating provided by the decision makers is shown in Table 5.
Step 3: application of fuzzy calculations on the observed performance rating
In this step, fuzzy calculations are performed on the performance rating data collected in step 2. The details regarding the calculation are discussed in sub section “Details of fuzzy calculation steps” and the notations used are presented in Table 6.
Details of fuzzy calculation steps
At first, the fuzzy intervals assigned to the expert weightage in step 1 and performance ratings in step 2 are aggregated using average operation method. The decision for adopting this method has been taken following the literature [27]. An instance of ‘average fuzzy weightage’ and ‘average fuzzy performance rating’ calculation for the attribute “Decentralised organisation structure” (AM111) is shown below.
In the next step, the aggregate performance ratings of the attributes is translated into criteria rating and the criteria rating is translated into enabler rating using equation 1 and 2 respectively. Table 7 captures the criteria ratings and Table 8 captures the enabler ratings of the study. An instance of criteria rating calculation for “management structure of dispensary” O 11 (AM 11 ) and enabler rating calculation for “agility through management drivers” (AM 1 ) are demonstrated below.
After obtaining the ratings for criteria and enablers, the Fuzzy Agility Measure Index (FAMI) of the dispensary is calculated using equation 3. FAMI represents the overall agility of the dispensary and the calculation is shown below.
Euclidean distance method
Upon obtaining the FAMI, it is then converted back into linguistic terms using Euclidean distance method. Euclidean distance method is considered as the most intuitive method for humans to calculate perceived proximity [20, 22, 27]. In this method, five linguistic terms known as “natural language expression set of Agility Label (AL)” are adopted from literature [20] and for each agility label, the Euclidean distance (D) is calculated following equation 4. The minimum distance or D value is considered as the agility label of the organization in linguistic terms. Table 9 captures the linguistic agility labels and the corresponding fuzzy intervals. The calculation of Euclidean distance is shown below.
As the D value is minimum for the label “Agile”, the AL of the case dispensary was considered to be “Agile” in linguistic terms. Fig. 2 represents the agility label of the dispensary pictorially.
Fuzzy performance importance index (FPII)
Fuzzy Performance Importance Index (FPII) calculation is performed to identify the attributes that pose a challenge to the phenomenon which in this study is agile capability. The FPII computation consists of two steps: first is the calculation of FPII following equation 5 and second is the development of a ranking score for each attribute following centroid method shown in equation 6. An instance of FPII and ranking score calculation for attribute “Decentralised organisation structure (AM111)” is shown below following the equations.
where, \( {W}_{ijk}\kern0.5em =\kern0.5em \left(1,\kern0.5em 1,\kern0.5em 1\right)\kern0.5em -\kern0.5em {N}_{ijk} \)
After obtaining the ranking scores, the dispensary management was consulted to decide the threshold. The reason behind consulting the management to set the threshold is that the management has to take a decision on how high the agile capability of the dispensary will be raised going further. If the management is not ready to aim high, then it is more likely that they would choose a lower threshold whereas it reverses if the management is fully in for it. In this study, after management consultation, ‘1.1’ was set as the threshold and the attributes below 1.1 was identified as weak attributes. As a result, seven attributes viz. transparent information flow, adequate salary and bonuses for caregivers, medical descriptions reading error, in house/nearby pathology laboratory services, technical up-gradation of dispensary equipments and facilities, minimization of patient throughput time and adequate training programme for safety practices were found to be the critical or weak for the university dispensary. Table 10 captures the FPII and ranking score of the attributes and Table 11 presents the suggestive measures for the critical attributes.
Statistical validation of fuzzy results
Applicability of fuzzy logic approach in assessment of healthcare agility has been statistically validated following the literature [28]. To accomplish this step, a feedback session was conducted with 5 caregivers and 5 patients of the case dispensary. Among the care givers, 3 were doctors and 2 were senior nurses on duty at the dispensary. Similarly the 5 patients chosen for the feedback session were the patients who visited the dispensary frequently in last one year. The above respondents were selected randomly from the pool of caregivers and patients. The decision for going with 5 caregivers and 5 patients was based on literature [29]. The respondents were asked to rate the agile criteria of the dispensary in a Likert’s scale ranging from 0–10. The maximum and minimum mean rating was found to be 5.8 and 7.8 respectively which confirmed the FAMI range obtained in fuzzy calculation. Table 12 shows the rating of the respondents and the mean scores. Following this, a t-test was performed on the mean rating to examine whether the ‘assessment of agility using fuzzy logic is accepted or not’. At first, the test value was assigned as ‘10’ which indicates that the null Hypothesis (H0) is “H0: 100% of the feedback opinions favoured the assessment results of agility” at 95% confidence interval”. The significance of two tailed t-test (p-value) was found to be less than 0.05 and as a result, the null hypothesis was rejected at 95% level of confidence. Then, the test value was lowered to 9, 8 and 7 in subsequent attempts and the significance (p-value) converged towards 0.05 between 7.1 and 7.19. This indicated that the null hypothesis can’t be rejected for test value between 7.1 and 7.19. Statistically, this result translated into “71% of the feedback opinions favoured the assessment results of agility” at 95% confidence interval. In summary, it was established that assessment of agility using fuzzy logic can be adopted with a success rate of 71%.
Results and discussions
The case analysis brings forth two essential insights. First, the current agility level of the dispensary is “Agile” which is average in relation to the Agility Labels (AL). Second seven attributes viz. transparent information flow, adequate salary and bonuses for caregivers, medical descriptions reading error, in house/nearby pathology laboratory services, technical up-gradation of dispensary equipments and facilities, minimization of patient throughput time and adequate training programme for safety practices need the attention of the management to enhance the dispensary’s agility. Though, this study deals with only one healthcare organization, the means of assessment and the findings regarding the critical attributes can be extended to other healthcare organizations. Moreover, it delineates the framework for healthcare agility assessment which would help both management and researchers in the field to extend and enrich it further.
In the context of university dispensary, the study recommends that the managers should conduct group meetings, circulate the minutes, review the caregiver’s feedback and discuss the management plan with all caregivers. This kind of communication would help the frontline employees to remain updated with information and plan the workflows accordingly. In addition, the management should link the incentive system to innovative and creative performances of the employees and introduce bonus for the staff on duty in festive occasions. This step would motivate the employees to be proactive and flexible while discharging the duty. Apart from this, “error in reading the medical description by the pharmacists/nurses” and “absence of in house pathology laboratory service” were found to be another set of challenges before dispensary agility. The management can address these issues by providing printed medical descriptions instead of handwritten ones and setting up a pathology laboratory inside the dispensary premises. In addition, technical up-gradation of the equipments and reduction of patient throughput time were also found to be crucial for the agile capability of the dispensary. The management should upgrade the medical equipments and allocate more doctors in peak hours. Apart from this, frequent training programs on fire safety practices and installation of smoke detectors and automatic water sprinklers would help enhance the agile performance of the dispensary. The suggestive measures recommended to the management are presented in Table 11.
Conclusions
In conclusion, this study suggests that agile concepts are beneficial for healthcare organizations both in terms of meeting the service demand which changes quickly and unpredictably and retaining its competitive advantage over other players in the field. In this context, assessment of agility plays a crucial role because it helps to understand how flexible, accommodative and responsive is the healthcare organization at present and what prevents it from being more flexible and accommodative. According to our findings transparent information flow, adequate salary and bonuses for caregivers, elimination of medical descriptions reading error, in house pathology laboratory services, technical up-gradation of medical equipments, minimization of patient throughput time and adequate training programme for safety practices are imperative for healthcare agility. However, generalizability of these findings can be obtained by replicating the study in other healthcare organizations. Therefore, we propose that future research should replicate the study in large multi-speciality hospitals in different geographical locations. Apart from this, we suggest future research to explore the cause and effect paradigm for each of the attributes discussed in the study. This would help extend the current study and enrich the body of knowledge with new insights.
References
Yusuf YY, Sarhadi M, Gunasekaran A. Agile manufacturing: the drivers, concepts and attributes. Int J Prod Econ. 1999;62(1–2):33–43.
Naylor JB, Naim MM, Berry D. Legality: integrating the lean and agile manufacturing paradigms in the total supply chain”. Int J Prod Econ. 1999;62:107–18.
Christopher M. The agile supply chain: competing in volatile markets”. Ind Mark Manage. 2000;29(1):37–44.
Kitzmiller R, Hunt E, Sproat SB. Adopting best practices: “Agility” moves from software development to healthcare project management. CIN - Comp Inform Nurs. 2006;24(2):75–84.
Pipe TB, Buchda VL, Launder S, Hudak B, Hulvey L, Karns KE, Pendergast D. Building personal and professional resources of resilience and agility in the healthcare workplace. Stress Health. 2012;28(1):11–22.
Teoh SY, Cai S. The process of strategic, agile, innovation development: a healthcare systems implementation case study. J Glob Inf Manage. 2015;23(3):1–22.
Sherehiy B, Karwowski W, Layer JK. A review of enterprise agility: concepts, frameworks, and attributes”. Int J Ind Ergon. 2007;37(5):445–60.
Sherehiy B, Karwowski W. The relationship between work organization and workforce agility in small manufacturing enterprises”. Int J Ind Ergon. 2014;44(3):466–73.
Alexopoulou N, Nikolaidou M, Martakos D. Exploring the business process agility issue: an experience report. Int J Inf Syst Model Des. 2013;4(1):25–41.
Burwitz M, Schlieter H, Esswein W. Agility in medical treatment processes-a model-based approach. In Modellierung. 2012;201:267–79.
Teoh SY, Chen X. Towards a strategic process model of governance for agile information technology implementation: a healthcare information technology study in China. J Glob Inf Manag. 2013;21(4):17–23.
Saleeshya PG, Subash Babu A, Vishnu AS. A model to assess the agility of manufacturing organizations: systems approach and application. Int J Prod Qual Manage. 2011;8(3):247–64.
Azevedo SG, Carvalho H, Cruz–Machado V. Agile index: automotive supply chain. World Acad Sci, Eng Technol, Int J Mech, Aerosp, Ind, Mechatronic Manuf Eng. 2011;5(7):1433–9.
Saleeshya PG, Babu AS. A combined AHP- and DEA-based approach to measure agility of manufacturing systems. Int J Bus Syst Res. 2012;6(4):431–55.
Dong H, Li CL. Agile supply chain performance evaluation of automobile manufacturing based on regression analysis. Appl Mech Mater. 2013;397–400:2662–6.
Aravind Raj S, Sudheer A, Vinodh S, Anand G. A mathematical model to evaluate the role of agility enablers and criteria in a manufacturing environment. Int J Prod Res. 2013;51(19):5971–84.
Khalili-Damghani K, Taghavifard M. A three-stage fuzzy DEA approach to measure performance of a serial process including JIT practices, agility indices, and goals in supply chains. Int J Serv Oper Manage. 2012;13(2):147–88.
Gunasekaran A. Agile manufacturing: enablers and an implementation framework. Int J Prod Res. 1998;36(5):1223–47.
Gunasekaran A. Design and implementation of agile manufacturing systems. Int J Prod Econ. 1999;62(1):1–6.
Lin CT, Chiu H, Tseng YH. Agility evaluation using fuzzy logic. Int J Prod Econ. 2006;101:353–68.
Vinodh S, Devadasan SR. Twenty criteria based agility assessment using fuzzy logic approach. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. 2011;54:1219–31.
Vinodh S, Aravindraj S. Benchmarking agility assessment approaches: a case study. BIJ. 2015;22(1):2–17.
Lin CT, Chiu H, Chu PY. Agility index in the supply chain. Int J Prod Econ. 2006;100(2):285–99.
Vinodh S, Devadasan SR, Vasudeva Reddy B, Ravichand K. Agility index measurement using multi-grade fuzzy approach integrated in a 20 criteria agile model. Int J Prod Res. 2010;48(23):7159–76.
Gunasekaran A, Yusuf YY. Agile manufacturing: a taxonomy of strategic and technological imperatives. Int J Prod Res. 2002;40(6):1357–85.
Vinodh S, Kumar UV, Girubha JR. Thirty-criteria-based agility assessment: a case study in an Indian pump manufacturing organisation. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. 2012;63(9-12):915–29.
Vinodh S, Devadasan SR, Vimal KEK, Kumar D. Design of agile supply chain assessment model and its case study in an Indian automotive components manufacturing organization. J Manuf Syst. 2013;32:620–31.
Vinodh S. Assessment of sustainability using multi-grade fuzzy approach. Clean Techn Environ Policy. 2011;13(3):509–15.
Khatwani G, Singh SP, Trivedi A, Chauhan A. Fuzzy-TISM: a fuzzy extension of TISM for group decision making. Glob J Flex Syst Manag. 2015;16(1):97–112.
Funding
Not applicable. This study has not been funded by any government or non government agencies.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable. The data pertaining to the study primarily includes the weightage provided by the experts (E1, E2,…, E5) on the measures and observed performance rating by the decision makers (D 1 , D 2 ,…, D 5 ) on agile attributes. A sample of questions put forth to the experts, decision makers are mentioned inside the paper under section “Step 1: Identification of agile enablers, criteria and attributes” and “Step 2: Collection of observed performance rating on the measures”. The data or response collected in the form of linguistic expressions e.g. Very Low, Low, Medium and High is shared in Table 6 in the main paper.
Authors’ contributions
“SM carried out the agility assessment study in the university dispensary, participated in its design and coordination and drafted the manuscript. RP conceived of the study, participated in the design of the study, caregivers’ opinions captured, performed the statistical analysis and helped to draft the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.”
Competing interests
The authors of this manuscript do not have any financial or non-financial competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable. The manuscript does not contain any individual person’s identifiable data.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical clearance for this research was granted by the institutional ethics committee of Amrita School of Business, Coimbatore, India (Ref No. EC/AL/001/2017). In addition, prior to the data collection, a request letter was issued from the University seeking the permission of the dispensary management to allow the researchers to collect data. The dispensary management countersigned the above letter indicating its permission to the employees’ to participate in the study. The letter was produced before each participant of the study including the experts and dispensary employees and a verbal informed consent was obtained from those who were willing to participate in the study.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Suresh, M., Patri, R. Agility assessment using fuzzy logic approach: a case of healthcare dispensary. BMC Health Serv Res 17, 394 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-017-2332-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-017-2332-y