Abstract
Background
The American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology (ABPN) and the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) require that residency programs allow at least 6 weeks of parental leave. The American Medical Association (AMA) recommends 12 weeks of paid parental leave. Despite these recommendations, there is little information about parental leave policies across U.S. neurology residencies. The objective of our study was to assess parental leave policies in U.S. adult neurology residencies and barriers to increasing the duration of leave.
Methods
We distributed an anonymous online survey to U.S. adult neurology program directors (PDs) to assess demographics, components and length of parental leave, perceived impact on residents’ clinical training and academic development, and barriers to increasing the length of leave.
Results
We contacted 163 PDs and received 54 responses (response rate of 33%). 87% reported policies for both childbearing and non-childbearing residents. The average maximal length of leave allowed without extension of training was 8.5 weeks (range 0–13) for childbearing and 6.2 weeks (range 0–13) for non-childbearing residents. Most PDs felt that parental leave had a positive impact on resident wellness and neutral impact on clinical competency, academic opportunities, and career development. The most common barriers to providing a 12-week paid policy were concerns about equity in the program (82%), staffing of clinical services (80%), and impact on clinical training (78%).
Conclusions
Although most programs in our study have parental leave policies, there is significant variability. Policies to improve parental leave should focus on addressing common barriers, such as additional solutions to staffing clinical services.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Parental leave is an increasingly important issue in graduate medical education. Paid parental leave has been associated with substantial health benefits for parents and children including reductions in infant mortality and numerous childhood illnesses, improvement in maternal mental health, and increases in rates of breastfeeding (the same degree of benefits are not associated with unpaid parental leave policies) [1].
The American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology (ABPN) recently updated its stance towards parental leave and requires that programs allow at least 6 weeks of parental leave without exhausting vacation time and nonclinical rotations and without mandatory extension of training [2]. Similarly, as of July 1, 2022, the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) mandates that all ACGME-accredited programs provide a minimum of 6 weeks of paid parental leave [3]. A New England Journal of Medicine editorial in 2019 and American Medical Association (AMA) guidelines from 2022 recommend that paid leave be at least 12 weeks [4, 5]. Though it is encouraging to see these recommendations, it is unclear whether neurology residencies are consistently incorporating these guidelines in practice.
We sought to understand and describe current parental leave policies in neurology residencies and analyze perceived barriers to increasing the duration of paid leave. These important questions have not been well addressed in neurology in the way that they have been in surgical subspecialties [6,7,8,9,10] and medical subspecialities including psychiatry [11] and pediatrics [12, 13]. Awareness of the most relevant barriers to increasing parental leave during neurology residency is critical to achieving better policies for trainees in our field, which could also lead to improved health outcomes for children and better experiences for the physician parent.
Methods
This study was determined to be exempt from IRB review per the Mass General Brigham institutional review board.
We created an online survey (Appendix A, supplementary material) to evaluate duration and composition of programs’ parental leave policies, program directors’ (PDs) perceptions of parental leave, perceived impact on residents, and perceived barriers to increasing duration of paid leave. Our survey was developed based on prior surveys used to evaluate parental leave policies in other medical and surgical specialities [7, 11, 14, 15]. Length of leave was measured in whole numbers from 0 to 12 weeks, with an option for greater than 12 weeks, and an option for “I’m not sure”. Childbearing leave was defined as leave for a resident who gave birth. Non-childbearing leave was defined as leave for a non-childbearing parent (either a partner of a childbearing parent, or adoption).
U.S. adult neurology PDs and their email addresses were identified via FREIDA, the American Medical Association’s online residency program database. 163 programs were contacted via email. There was no renumeration for participation. Data was collected via REDCap between 3/16/22 and 4/18/22. Survey responses were anonymous.
Statistical analysis
Descriptive statistics such as frequency counts and percentages were calculated. Spearman correlation was estimated to determine if length of leave correlated with program size. Logistic regression models were used to assess if the perceived impact of parental leave on residents (negative impact vs. neutral or positive impact), and perceived barriers (major or minor barriers vs. no barriers) were influenced by maximum length of leave, program size, percentage of females, average number of leaves per year, and program location.
Results
Program demographics
We received 54 responses, for a response rate of 33%. Most programs (50%) had between 6 and 10 residents per post-graduate year. Additional program demographics are shown in Table 1. Number of parental leaves per year are shown in Fig. 1.
Characterization of existing parental leave policies
47 (87%) programs have parental leave policies for both childbearing and non-childbearing residents, 4 (7%) programs have policies for childbearing residents only, and 3 (6%) programs have no policy or were not sure if they have a policy. Of the 47 programs with parental leave policies for both childbearing and non-childbearing residents, 30 (64%) stated the policy was the same for childbearing and non-childbearing residents, 16 (34%) stated it was different, and 1 (2%) program was not sure.
Many policies were recently updated at the time of our survey: 20 (39%) within the past year, 20 (39%) two to five years ago, 2 (4%) five to ten years ago, 2 (4%) greater than 10 years ago, and 7 (14%) programs were not sure when their policies were last updated. 13 (25%) programs were in the process of revising their parental leave policies.
PDs were asked to identify everyone involved in scheduling a leave. Responsibility for scheduling an individual leave fell upon the trainee (73%), followed by chief residents (65%), and the PDs (59%). 100% reported that other neurology residents covered for those taking a parental leave. 14% utilized attending coverage, and 4% utilized fellow coverage. Only 10% had advanced practice providers (APPs) cover for the resident taking leave. 65% offered full pay and benefits for the duration of the parental leave, 22% offered full pay and benefits for a portion of leave and reduced pay for the remainder, 6% offered reduced pay throughout the leave, and the rest were not sure.
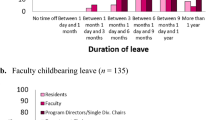
The average maximal length of leave allowed without extension of training was 8.5 weeks (range 0–13) for childbearing residents and 6.2 (range 0–13) for non-childbearing residents (Fig. 2). There was no correlation between length of leave and program size (r = 0.20, p = 0.18 and r = 0.16, p = 0.31 for childbearing and non-childbearing residents respectively).
Most programs did not require full use of vacation (51%) or elective time (59%). 16% required use of all vacation time, and only 2% required use of all elective time. 42% had policies for reducing clinical rotations to create a leave. Most programs (59%) did not require residents to make up call they missed as part of their leave.
Perceived impact of parental leave
The majority of PDs perceived that parental leave had a positive impact on resident wellness for both childbearing (70%) and non-childbearing residents (69%). Most responded that they perceived that parental leave had a neutral impact on clinical competency, academic opportunities, and career development for both childbearing and non-childbearing residents (Fig. 3). There were no statistical associations between these perceptions and program size, maximum length of leave, program location, percentage of females in the program, and average number of leaves per year.
Perceived impact of parental leave on childbearing and non-childbearing residents Bar graphs show PDs’ perceptions of the impact of parental leave on resident clinical competency, academic opportunities and career development, and well-being. Number of PDs is shown on the y-axis. A positive impact is shown in green, neutral impact is shown in gray, and negative impact is shown in red
Perceived barriers
The most common major and minor barriers to providing a 12-week paid policy were concerns about equity in the program and impact on other trainees (82%), staffing of clinical services (80%), and impact on clinical training (78%) (Fig. 4).
We assessed the impact of program size, maximum length of leave, program location, percentage of females in the program, and average number of leaves per year on each barrier. Programs with longer lengths of leave were less likely to find ACGME requirements a barrier (OR = 0.564 [0.407–0.782] for childbearing resident leave and 0.773 [0.632–0.946] for non-childbearing resident leave). Similarly, programs with longer lengths of leave were less likely to find ABPN requirements a barrier (OR = 0.666 [0.516–0.859] for childbearing residents and 0.803 [0.663–0.971] for non-childbearing residents). Programs with longer lengths of childbearing leave were also less likely to find local GME policy a barrier (OR = 0.805 [0.658–0.985]). This association was not seen for non-childbearing leave (OR = 0.990 [0.838–1.170]).
Discussion
In our study surveying neurology PDs on parental leave policies, 87% responded that they have policies for both childbearing and non-childbearing residents, 7% have policies for childbearing residents only, and 6% have no policy or were not sure if they have a policy. Of the programs with parental leave policies for both childbearing and non-childbearing residents, 64% have the same policy for childbearing and non-childbearing residents. These results are comparable to a study which surveyed internal medicine PDs in 2019 and found that 82% of programs had policies for childbearing leave and 69% had policies for non-childbearing leave [16]. A systematic review of parental leave in GME found that formal leave policies in graduate medical education have varied over time and ranged from 22% of programs [17] in 1986 to 90% more recently [18]. This increase is encouraging, but there is still room for improvement. All residency programs should have clearly written policies for both childbearing and non-childbearing residents. To promote equity, programs should also strive to have robust policies for both childbearing and non-childbearing residents.
The average maximal length of leave allowed without extension of training was 8.5 weeks (range 0–13) for childbearing residents and 6.2 (range 0–13) for non-childbearing residents of the programs surveyed. There was no association between program size and length of leave. Though these averages are in line with the minimum 6 weeks of leave as required by the ABPN and ACGME, they fall below the goal of a 12 week leave that is recommended by the Family Medical Leave Act [19] and the American Medical Association (AMA) [5]. For childbearing parents, 12 weeks or more of maternity leave is associated with numerous benefits including lower rates of postpartum depression, improved maternal mental health [20], and duration of breastfeeding [21]. Leave for non-childbearing parents is also important for promoting parent-child bonding [22, 23], and improving health outcomes for children [24].
Most programs did not require full use of vacation or elective time, and 42% had policies for reducing clinical rotations to create a leave. Constructing leaves in this manner is an important strategy to promote equity and wellness. It is critical for programs to develop policies that have a balanced approach toward constructing leave, without using vacation time, and using reductions of both elective time and some clinical rotations where possible.
Importantly, most PDs perceived that parental leave had a positive impact on resident wellness for both childbearing (70%) and non-childbearing residents (69%). A multi-center study which surveyed female residents found that increased duration of parental leave had a positive impact on resident wellness [25]. Improving resident wellness is an important reason in favor of further increasing the duration of parental leave in neurology residency. Most PDs responded that parental leave had a neutral impact on clinical competency, academic opportunities, and career development for both childbearing and non-childbearing residents. This contrasts with negative perceptions of parenthood in residency which have previously been reported18 and dispels common reasons that may be cited to not offer longer parental leave. Interestingly, there were no statistical associations (within the limitations of our study) between these perceptions and program size, maximum length of leave, program location, percentage of females in the program, and average number of leaves per year.
The most common major and minor barriers cited by PDs to providing a 12-week paid policy were concerns about equity in the program and impact on other trainees (82%) and staffing of clinical services (80%). Parental leave policies can be crafted in ways that mitigate potential inequities among other trainees in the program, and institutional financial backing can support additional solutions for staffing of clinical services. We recently reported our experience with the development of a 12-week paid parental leave policy in the Mass General Brigham neurology residency. In our article we highlight strategies for programs to minimize the impact of a parental leave on other trainees, including use of APPs and making intentional upfront scheduling changes [26]. Only 10% of programs in our survey reported that APPs participate in clinical coverage for a parental leave. Though there are financial constraints to utilizing APPs to fill in for a leave, they are a valuable and underutilized resource to minimize schedule disruptions and impact on other residents.
Impact on clinical training was another common barrier to providing a 12-week paid parental leave policy. We did not specifically include clinical competency metrics in this study, but data in other specialties suggest that overall parental leave does not have a measurable impact on clinical training. A study of physical medicine and rehabilitation residents showed no difference in board certification exam passing rates among individuals who took a medical or parental leave [27]. A study of ophthalmology residents who took parental leave found no differences in average scores on standardized assessments, research activity, ACGME milestone scores, or surgical volumes [28]. Additional studies in neurology residency are needed to understand if time away from neurology residency objectively impacts clinical training.
We found that programs with longer lengths of leave were less likely to consider ACGME, ABPN, or local GME requirements a barrier. Though these results are not surprising, they highlight the importance of educating PDs on these policies.
Our study has several limitations. Potential recall bias and a relatively low response rate may have skewed the results of the survey. It is also possible that those PDs who responded were more invested in parental leave policies and the results may be favorably biased. While we asked PDs about their perception of parental leave on wellness, academic opportunities, and career development, we did not look at objective measurements such as board examination scores, or clinical assessments. Because we did not obtain data on when leaves were taken in relation to completion of the survey, this study may also be limited by recency bias. PDs who had residents that took a parental leave years ago may have different recollections about the leave compared to PDs who had residents who took a more recent leave. Despite these limitations, we believe our study provides important insights on the current landscape of parental leave policies in neurology residency. These findings have value as more programs prioritize this issue and seek ways to augment parental leave.
In conclusion, there was variability in length and composition of leave among neurology residency programs. Overall PDs felt parental leave had a neutral impact on clinical competency, and academic opportunities, and a positive impact on well-being. Policies to improve parental leave should focus on addressing commonly perceived barriers, such as staffing of clinical services, and minimizing scheduling disruptions to promote equity among residents.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Burtle A, Bezruchka S. Population Health and paid parental leave: what the United States can learn from two decades of Research. Healthc (Basel) 2016;4.
Sica F, Centonze D, Buttari F. Fingolimod Immune effects Beyond its sequestration ability. Neurol Ther. 2019;8:231–40.
ACGME Institutional Requirements.
Weinstein DF, Mangurian C, Jagsi R. Parenting during Graduate Medical training - practical policy solutions to promote change. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:995–7.
Policies for Parental, Family and Medical Necessity Leave H-405.960. (Accessed 3/28/2023, at https://policysearch.ama-assn.org/policyfinder/detail/family%20leave?uri=%2FAMADoc%2FHOD.xml-0-3580.xml.).
Wallace CC, Edmunds RW, Bourne D, Wong L. Parenting in plastic surgery residency. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2022;149:1465–9.
Reilly G, Tipton C, Liberman P, Berkenstock M. Attitudes toward parental leave and breastfeeding during ophthalmology residency. Can J Ophthalmol 2021.
Sandler BJ, Tackett JJ, Longo WE, Yoo PS. Pregnancy and parenthood among surgery residents: results of the First Nationwide Survey of General surgery Residency Program directors. J Am Coll Surg. 2016;222:1090–6.
Reid DBC, Shah KN, Lama CJ, Kosinski LR, Daniels AH, Eberson CP. Parenthood among orthopedic surgery residents: Assessment of Resident and Program Director perceptions on training. Orthopedics. 2021;44:98–104.
Tang AL, Miller A, Hauff S, et al. Maternity and paternity leave in otolaryngology residency training in the United States. Laryngoscope. 2019;129:1093–9.
Leandre FM, Sudak DM, Ginory A. Are Psychiatry Programs providing adequate parental leave to their residents? Acad Psychiatry 2021:1–5.
Ben-Zion S, Lehmann A, Price L, Burnett HQ, Michelson CD. The Use of Parenting Electives in Pediatric Residency. Acad Pediatr. 2022;22:513–7.
Powell WT, Dundon KMW, Frintner MP, Kornfeind K, Haftel HM. Parenthood, parental benefits, and Career goals among Pediatric residents: 2008 and 2019. Pediatrics 2021;148.
MacDonald SM, Raman JD. Widely Variable Parental Leave Practices for Urology Residency Programs in the United States. Urology. 2021;153:81–6.
Sharpe EE, Ku C, Malinzak EB, et al. A cross-sectional survey study of United States residency program directors’ perceptions of parental leave and pregnancy among anesthesiology trainees. Can J Anaesth. 2021;68:1485–96.
Stack SW, Finn KM, Kisielewski M, Law KL, Milne CK, Best JA. Parental leave policies in Residency: A National Survey of Internal Medicine Program directors. Acad Med. 2022;97:1021–8.
Sayres M, Wyshak G, Denterlein G, Apfel R, Shore E, Federman D. Pregnancy during residency. N Engl J Med. 1986;314:418–23.
Humphries LS, Lyon S, Garza R, Butz DR, Lemelman B, Park JE. Parental leave policies in graduate medical education: a systematic review. Am J Surg. 2017;214:634–9.
Family and Medical Leave Act. (Accessed 4/27/23, at https://www.dol.gov/agencies/whd/fmla.).
Dagher RK, McGovern PM, Dowd BE. Maternity leave duration and postpartum mental and physical health: implications for leave policies. J Health Polit Policy Law. 2014;39:369–416.
Whitney MD, Holbrook C, Alvarado L, Boyd S. Length of Maternity leave impact on Mental and Physical Health of Mothers and Infants, a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Matern Child Health J 2023.
Yang YT, Wallington SF, Morain S. Paid leave for fathers: policy, practice, and Reform. Milbank Q. 2022;100:973–90.
Huerta MC, Adema W, Baxter J, et al. Fathers’ leave and fathers’ involvement: evidence from four OECD Countries. Eur J Soc Secur. 2014;16:308–46.
DOL Policy Brief. Paternity leave: why parental leave for fathers is so important for working families. (Accessed 4/27/2023, at https://www.dol.gov/sites/dolgov/files/OASP/Paternity-Leave.pdf.).
Stack SW, McKinney CM, Spiekerman C, Best JA. Childbearing and maternity leave in residency: determinants and well-being outcomes. Postgrad Med J. 2018;94:694–9.
Conway SE, Vaswani PA, Budhu JA, et al. Development and impact of a progressive parental leave policy in a neurology residency. Neurology; 2022.
McDeavitt JT, Appelbaum NP, Raddatz MM, Driscoll SW, Kinney CL. Taking leave during Residency: types of absences and subsequent delays and variations in Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Medical Board Pass Rates. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2022;101:S30–4.
Huh DD, Wang J, Fliotsos MJ, et al. Association between parental leave and Ophthalmology Resident Physician performance. JAMA Ophthalmol; 2022.
Acknowledgements
Harvard Catalyst for statistical support.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SC contributed to conception and design of the study, acquisition, and analysis of data, and drafting a significant portion of the manuscript and figures. WW contributed to analysis of data. SP contributed to conception and design of the study, acquisition and analysis of data, and drafting a significant portion of the manuscript and figures.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was determined to be exempt from IRB review per the Mass General Brigham institutional review board. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
Author SC has nothing to report. Author WW has nothing to report. Author SP has nothing to report.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Conway, S.E., Wang, W. & Prasad, S. Barriers to increasing paid parental leave in U.S. neurology residencies: a survey of program directors. BMC Med Educ 24, 387 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05333-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05333-1