Abstract
Background
A group of 63708 Bangladeshi adults from a rural area were screened in 2011–12 for cardiovascular diseases (CVD) risk using a questionnaire based tool developed as part of the ‘WHO CVD-RISK Management Package for low-and medium resource setting’. In the current study participants who were found to be high risk and a sample of the not high risk participants from the screening were further characterized clinically and biochemically to explore the burden and determinants of CVD risk factors in a remote rural Bangladeshi population.
Methods
The high risk participants comprised all 1170 subjects who screened positive in 2011–12 and the not high risk group comprised 563 randomly sampled participants from the 62538 who screened negative. Socio-demographic, behavioral, anthropometric, clinical and biochemical data (glucose and lipids) were collected by standardized procedures. Body Mass Index (BMI) was classified following Asian BMI criteria. Data was analyzed using univariable and multivariable methods.
Results
On univariable analysis in high risk and not high risk participants respectively, age in years (M ± SD) was 50 ± 11 for both groups, ratio of male: female was 40:60 and 66:44, current smoking 28.5 % and 50.6 %; smokeless tobacco use 37.1 % and 34.8 %; overweight and obesity measured by body mass index (BMI) was 39.1 % and 20.5 %; high waist circumference (WC) 36.1 % and 11.9 %; high waist to hip ratio (WHR) 53.8 % and 26.3 %; and with high waist to height ratio (WHtR) 56.4 % and 28.4 %, existence of hypertension (HTN) was 15.8 % and 3.6 %, pre-HTN 43.8 % and 12.1 %, diabetes (DM) 14.0 % and 10.5 %, pre-DM 16.9 % and 12.1 % and dyslipidaemia 85.8 % and 89.5 %. In multivariable logistic regression analysis female sex, BMI, WC, WHR and WHtR, HTN and dyslipidaemia remain significantly more common among high risk participants (p < 0.05 and p < 0.001).
Conclusions
The prevalence of clinical and biochemical risk factors of CVDs are quite high even in this rural population and this may be related to the socioeconomic and cultural transition in Bangladeshi society. Surprisingly more of the high risk group was female and there were fewer smokers. Obesity and hypertension were more frequent in high risk participants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are now the major cause of death worldwide. It is estimated by World Health Organization (WHO) that 17.3 million people (31 % of all deaths) died from CVDs in 2012. Approximately 80 % of deaths occurred in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), predominately in people aged > 60 year [1]. Bangladesh is a LMIC where the emerging challenge in the health sector is non-communicable diseases (NCDs) and, among all NCDs, the foremost cause of death and disability is CVDs [1, 2]. As a whole CVDs and their known risk factors account for 13.4 % of disability adjusted life years (DALYs) lost in Bangladesh [3]. The number of people who are 60 years and above is expected to increase dramatically to 40.5 million by 2050 which would constitute 19 % of the total population of Bangladesh [4, 5]. If early prevention and long-term management measures are not adopted, this growing older population may suffer from multiple conditions due to various CVDs and therefore place a major burden on the Bangladeshi health system [3, 5].
Estimation of CVD risk is central for rational management and prevention of these disorders as well as for designing long-term policies and programs to combat the challenge. It is now known that many of the risk factors of CVDs like smoking, hypertension, dyslipidaemia, diabetes, physical inactivity and obesity are potentially modifiable by health counselling [6]. However, it is also known that the prevalence of these risk factors may vary substantially from population to population and even in various subgroups of the same population. Understanding of these variations is essential to design appropriate evidence based strategies to face the emerging problem.
To address this gap in knowledge a group of agreed 63708 Bangladeshi adults, living in a peripherally located area of Bangladesh, was screened (in 2011–12) using a WHO recommended tool, designed to estimate CVD risk in low resource settings [7]. The aim of this study was to describe and contrast the prevalence of CVD risk factors in the high risk and a sample of the not high risk members of the cohort. We also examined the association between socio-demographic, behavioral, anthropometric and clinical measures between these two groups of study participants. This study is expected to add to knowledge about the prevalence of established and emerging CVD risk factors in the Bangladeshi population.
Methods
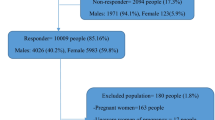
The original cohort was initiated in 2008 under the ‘BADAS-ORBIS Eye Care Project’. The project was designed to generate epidemiological data on the burden of diabetic retinopathy and associated risk factors from a rural population and study area (approx. 300 km from the capital) of Thakurgaon district of Bangladesh. The cohort had total n = 66701 participants who were aged between 31–74 years in 2008. In 2011–12, a screening program was run using a questionnaire based tool under the North Bengal Non-Communicable Disease Program (NB-NCDP) of Bangladesh University of Health Sciences (BUHS). The tool was developed as part of the ‘WHO CVD-RISK Management Package for low- and medium – resource settings’ and following the recommendations of the WHO [7]. The tool consists of a total of eight questions to screen for probable angina, heart attack, stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA). People who have pre-existing CVDs are known to be at high risk of experiencing another cardiovascular event [8]. It does not include measurement of any biochemical as well as a number of important clinical risk factors. Of 63708 BADAS-ORBIS participants who agreed to take part in NB-NCDP (95.5 % participation rate), 1733 were found to be at high risk for CVDs as assessed by the tool (paper submitted for publication). Detail screening methodology has been described in Fig. 1.
The current study was planned basing on our chain hospital [(i.e., Thakurgaon Swasthaseba Hospital TSH)] under the Health Care Development Project (HCDP) of Bangladesh Diabetes Somity (BADAS). To ensure uniformity in recruitment of participants and data collection, a team of 20 data collectors were given two weeks of intensive training on study protocol, questionnaire administration, techniques of examination [i.e., electrocardiography (ECG)] and evaluation. All interviewers were selected based on their competency, at least 12 years of education completed, and prior experience in conducting interviews, surveys and using the census method.
Among the 1733 participants of the present study, 1170 comprised of all the members of a high risk group identified by the 2011–12 survey using the WHO recommended 2002 tool. The remaining participants were recruited randomly from participants who were found to be negative on the WHO tool (n = 62538). From the screened negative group 1000 participants were approached and 563 (56.3 %) agreed to take part and provided data. From September 2011 to June 2012, using a structured, pretested, interviewer administrated questionnaire participants were interviewed to obtain information on (i) socio-demographic characteristics, (ii) three days dietary intake history including fruits and vegetables intake [consumption were assessed by a question that inquired number of serving (medium portions) of either fruits or any vegetables including green leafy per day], (iii) smoking status including type of smoking and/or smokeless tobacco use, past smoking history (iv) alcohol intake including local form of alcoholic beverages, (v) physical activity assessed by exact daily duration (minutes) of work related, commute related and leisure time related physical activity, and (vi) history of medicine intake for any chronic disease management.
Clinical measures
For health examination, the parameters included anthropometric and blood pressure measurements. Variables recorded were height (HT), weight (WT), waist circumference (WC), hip circumference (HC) and blood pressure (BP). To ensure data uniformity similar equipment were used by all data collectors. In addition all instruments were calibrated regularly before data collection. The health examination element involved measurement of HT by a portable, locally manufactured, stadiometer, standing upright on a flat surface machine; WT using modern electronic digital LCD weighing machines; WC and HC were measured using spring tapes and following standard procedures [8]. BP was measured in the right arm in both sitting and standing position using India Mart Ambala (Advanced Technocracy Inc, indiamart®, India) instruments. Measurement was done by auscultatory method on the day of interview. Prior to the measurement, 10 min rest was assured. Two readings were taken 5 min apart, and if the two reading varied more than 5 mm of Hg, a third reading was taken and the mean of the three readings was considered as final blood pressure of the individual and final data for data analysis. Hypertension was defined as a systolic blood pressure (SBP) of ≥140 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) of ≥90 mmHg [9].
Biochemical measures
Fasting samples were obtained from all individuals after an overnight fast of at least 8–10 h. With proper aseptic precaution, 8 ml of venous blood sample was collected from each participant to measure fasting blood glucose (FBG), total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), triglycerides (TG) and high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C). All participants other than those with known diabetes (n = 5) were then given a 75-g oral glucose solution (75 g of oral glucose in 250 mL of water) to drink. After 2 h, another 3 mL of venous blood was collected to determine 2-h post-oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). After collecting blood, samples were centrifuged on site within 3 h and plasma samples were then collected and were transferred using ice gel-packed cooling boxes from field to TSH to refrigerated and stored at −70 °C. From TSH, using dry ice, samples were shifted to the laboratory of the Bangladesh Institute of Research and Rehabilitation for Diabetes, Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders (BIRDEM) and stored at −70 °C until laboratory assays were carried out. Plasma glucose was measured by the glucose oxidase method using DimalesionRxL Max (Siemens AG, Erlangen, Germany). Quality control of the blood glucose measurement was checked by measuring the 2-h plasma glucose values in every 20th case. The intra-assay coefficient of variation was 1.08 % at a mean of 5.30 mmol/L, and the inter-assay coefficient of variation was 2.01 % at a mean of 5.39 mmol/L. TC, TG, HDL-C were analysed by enzymatic colorimetric method and LDL-C was estimated by Friedewald’s formula.
Classification criteria
Smokers included subjects who smoked cigarettes, bidis, or other forms of tobacco daily. Users of other forms of tobacco (mainly chewed tobacco and betel nut habit) were classified as non-smoked tobacco use. Less than 1 servings of fruits or less than 3 serving of vegetables daily were categorized as low dietary intake [10]. Those with no regular work-related or leisure-time physical activity were classified as having physical inactivity [11]. Asian BMI criteria was used to categorise and define underweight (less than 18 · 5 kg/m2), normal (18.5-23.0 kg/m2), overweight (23–27.5 kg/m2) and obesity (higher than 27.5 kg/m2) for both sexes [12]. Abdominal obesity was diagnosed when WHR was >0.90 in men and >0.80 in women or waist circumference was >95 cm in men and >80 cm in women according to the internationally harmonized definition of metabolic syndrome for South Asians [13] and WHtR for both sexes were ≥0.50 [14]. HTN were diagnosed if individual’s average systolic BP was ≥140 mmHg or diastolic BP was ≥90 mmHg, or if they were receiving treatment for HTN [14, 15]. Diabetes mellitus (DM) was defined as FBG ≥7.0 mmol/L and/or 2 h after 75-g oral glucose solution ≥11.1 mmol/L and pre-DM followed by the WHO guideline [16]. In addition, known DM was defined by the use of insulin or oral anti-diabetic medication(s) and self-reported DM. Dyslipidaemia was defined if serum total cholesterol high (≥200 mg/dl), triglycerides high (≥150 mg/dl), LDL cholesterol high (≥130 mg/dl) or HDL cholesterol low (<40 mg/dl in men and <50 mg/dl in women) according to the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel-3 (NCEP-ATP-3) guidelines [17]. Creatinine was defined high (>1.2 mg/dl). Income was classified according to the 2006 per capita Gross National Income (GNI) and according to World Bank (WB) calculations [18].
Verbal consent in presence of witnesses for all participants was obtained. The NB-NCDP study protocol was approved earlier from Human Research Ethical Committee (HREC) of the University of New South Wales (HREC ref: ≠HC12621), Sydney, Australia and the Ethics Review Committee of the Diabetic Association of Bangladesh (BADAS).
Statistical analysis
Percentages were used to describe the prevalence rates of risk factors for CVDs. Means and standard deviations (SD) were used for continuous variable and to summarize categorical data both the number and proportion for all the socio-demographic, behavioural, anthropometric, clinical and biochemical parameters of the study were used. Independent-sample t-tests (for continuous variables) and Pearson’s chi-square test (for categorical variable) were done as to perform intergroup comparison to examine the difference in the covariates between high risk and not high risk participants.
We examined the associations between socio-demographic, behavioural, anthropometric, clinical and biochemical measures among high risk and not high risk participants. To decide the final model of association for each individual with CVDs, a backward elimination approach of model building was used. We first fitted univariable logistic regression with all the predictors. Logistic regression models were also fitted with interaction terms between pairs of explanatory variables (e.g., age and gender, etc.). Variables those were significant at 15 % level in the univariable logistic regression models were included in a multivariable base model. For interaction terms, the criterion for significance to include in the base model was 5 % level. None of the interaction terms were significant and so was not included in the base model. From the base model, variables were excluded one by one based on their P-values (P > 0.05) to reach the final model. Following the development of final model with the backward elimination method, we checked for multi-collinearity by estimating a variance inflation factor (VIF) by fitting a multiple linear regression model with the binary outcome variable [19]. The model building was conducted manually, not using an automatic variable selection method. Data were analysed using Stata version 12.
Results
Overall social and demographic characteristic of all the 1170 high risk participants and 563 not high risk participants are shown in the Table 1. High risk individuals differed from the not high risk participants with respect to gender and employment status (p < 0.001). Participants aged between 31–45 and 46–60 years comprised the largest number of high risk (80 %) participants compared to other age groups. Females were over-represented (60 %) in the high risk group. About three quarters of the participants (73 %) had low or poor educational knowledge (i.e., illiterate/only signature/gonoshikha and primary education) and almost 99 % were low and lower middle income group participants. Among high risk and not high risk group; 72.3 % and 54.4 % of the study participants respectively were from physically active group (i.e., house maker/farmer).
Prevalence of behavioural, anthropometric and other risk factors is shown in Table 2. Among all participants, rate of current smokers, past smokers and smoking 100 sticks in life time were 23.6 %, 22.6 % and 30.6 % respectively. Moreover regular betel nut chewing, occasionally and leaf format tobacco along with betel nut were 36.6 %, 18.5 % and 19.0 % respectively. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in total as BMI were 39.1 % and 20.5 % in high risk and not high risk participants respectively Except for physical activity and smokeless tobacco consumption all the anthropometric, behavioural and other risk factors were significantly higher among high risk group compared to not high risk individuals (p < 0.001).
Clinical and biochemical risk factors prevalence is shown in Table 3. In high risk and not high risk participants respectively: prevalence of HTN was 16.6 % and 3.7 %; pre HTN was 41.7 % and 11.9 %; pre-diabetes was 27.7 % and 21.7 %; all the lipid profile markers (i.e., serum cholesterol, TG, HDL and LDL) were high in an average 30 % for all participants and overall dyslipidaemia were 85.8 % and 89.5 %. The prevalence of self-reported DM among study participants was very low (only 5 individuals). With the exception of LDL and creatinine; all the clinical and biochemical risk markers were significantly higher among high risk compared with not high risk individuals (p < 0.001 and p < 0.05). Among all the study participants, 78.7 % had presence of at least two or more known risk (i.e., DM, HTN, dyslipidaemia or obesity), among them 91 % were female and 64.7 % were male.
In a multivariable logistic regression model the variable gender, fruits and vegetable intake pattern, smoking, BMI, WHR, WHtR, HTN and dyslipidemia were significantly associated to the participants CVD risk status (high risk/ not high risk) after adjusting for other variables.
Discussion
The study found a high prevalence of CVD risk factors even in a relatively traditional ruralFootnote 1 population in Bangladesh. A notable finding was that the proportion of females in the high risk group was almost twice the proportion in the low risk group. On multivariate analysis this nearly twofold association of female sex with high CVD risk status (OR 1.87, 95%ci 1.34-2.59) remained present. Usually males are reported to be more susceptible to CVDs [20] and thus the present finding of female predominance in this population needs further in-depth investigation.
A larger proportion of the high risk subjects in the present study are from lower socioeconomic and educational levels and they are homemakers and farmers. Again, this is in contrast to the usual notion that CVDs are more common among higher socioeconomic classes [11]. A majority of these people are active or very active and thus, unlike other studies on urban or urbanizing rural populations in Bangladesh [21–23], inactivity does not seem to be a major determinant of CVD high risk in this population.
Smoking is a well-known risk factor of CVDs [24] and high rates of smoking both in urban (42.3 %) [25] and rural (36.1 %) [26] populations in Bangladesh have been previously reported. In the present study even a higher proportion of smokers (50.6 %) has been found among the not high risk participants. There is the seemingly paradoxical finding of relatively lower (28.5 %) proportion of smokers among the high risk groups. However, given the fact that these people were identified (by the WHO Screening Tool) on the basis of cardiovascular symptoms and thus had already undergone some form of treatment, many of them may have quit smoking following medical advice. A similar paradox is seen regarding low fruits and vegetable intake which is known to be another risk factor for CVDs. A large proportion of subjects in both the groups had less than 1 servings/ day of fruits and less than 2 servings/ day of vegetable intake; however, the proportion of low intake was substantially higher for fruits and lower for vegetables in the high risk compared to the not high risk participants respectively (p < 0.001, Table 2). Again, advice from the health care providers and, additionally, support from families may have played a role in improving nutritional balance in the high risk group.
A very important finding in the present study is the prevalence of overweight and obesity (both general and central) in such a remote rural population. It is alarming that, irrespective of risk groups, both general (on the basis of BMI) and central (on the basis of WC, WHR and WHtR) obesity are quite high in this population. It is understandable that all these anthropometric measures are significantly more prevalent among the high risk group compared to the not high risk group. The finding was paralleled by the strong association (as revealed by OR) of all these measures with high risk on multivariable analysis. There is no recent study conducted in Bangladesh on a similar peripheral rural population. However, a few studies on populations close to urban areas report a prevalence of overweight as 17.2 % [27] and obesity as 24.4 % [28]. In these studies the rates of central obesity (with WC/WHR/WHtR as indicators) were reported to be 37.9 %, 69.8 % and 58.1 % [28]. There is evidence that abdominal and visceral fat deposits lead to pro-inflammatory profiles, dyslipidaemia, insulin resistance and other metabolic syndrome factors that promote atherosclerosis [29]. Abdominal obesity has also been shown as a risk factor in CVDs by various large scale epidemiological studies [30] mostly in Europe. Moreover, a recent study in Bangladesh has shown that after adjusting BMI, HTN and other confounding variables; WHR and WHtR showed better risk prediction for early CVDs [31]. Therefore in addition to BMI, these WC and WHR measures need to be considered as supplemental indices for re-defining obesity as well as risk factors for CVDs. These increasing trends of obesity indicators suggest that the transition in lifestyle among the rural population of Bangladesh may be rapidly producing adverse changes that could accelerate the CVDs burden.
Hypertension was found to be the single most important risk factor for CVDs in this study. A large proportion of the high risk participants were found to have either hypertension or pre-hypertension (Table 3) and these conditions were found to be associated with the increased CVDs risk by 6.85 and 8.10 times respectively after adjusting for some confounding variables (Table 4). The finding conforms with the reports or recent non-communicable disease surveillance in Bangladesh as well as the INTERHEART study [32, 33].
The proportion of diabetes and pre-diabetes is reasonably high in both the not high risk and high risk groups. For prevalence, although the two groups vary significantly, the differences are still not large and this is reflected in the lack of effect of glycemic status on CVD risk on multivariate analysis. The blood glucose values, both in high and not high risk participants (Table 3), are not particularly high and thus most of the diabetic subjects are probably in good control. This, in turn, may be due to the relatively organized diabetes care network in Bangladesh. Thus the effects of diabetes may have been offset by good control, particularly in the high risk participants.
A surprisingly high proportion of both high and not high risk participants were found to have dyslipidemia with at least on abnormal component of lipid profile (Total cholesterol, TG, HDL and LDL). The risk was mostly contributed by low HDL, borderline or high TG, high or very high LDL, and borderline or high cholesterol. Again, due to a scarcity of recent studies in similar settings it is difficult to compare previous data with the present study. Given the low intake of fat in this population the high prevalence of dyslipidemia needs further investigation.
Since there are no existing studies on such a remote rural population in Bangladesh it is difficult to directly compare the present data with previously generated data on Bangladeshi population. Several studies in Bangladesh from rural populations reported a prevalence of HTN 6.6 % - 19.1 % [27, 34–39], Pre DM and DM 8.6 % - 22.4 % and 1.7 % - 8.2 % [28, 35, 37, 40–42], dyslipidemia 4.8 % - 28.7 % and overweight/obesity 7.8 % - 24.4 % [28, 43–45]. The corresponding values for the urban population in Bangladesh were HTN 14.7 % - 44.80 % [23, 46–48], DM 6.1 % - 35.3 % [40, 45, 48] dyslipidemia 0.1 % - 64.0 % and overweight/obesity 20.9 % - 63.1 % [45, 48]. Our findings are consistent with the ranges provided in the aforementioned studies. The wide ranges in prevalence might occur due to variations in study quality, age group, selection of participants, risk factors diagnosis (self-reported and through measurement, measurement instruments etc.).
Study strengths and limitations
The strengths of the present study included large sample size and population-based design. However, the main weakness of this study is using the WHO recommended 2002 tool as it only identifies a subset of the high CVD risk participants (i.e. those who are at high risk because of existing CVD). It does not detect those who would be at high risk if all the relevant clinical and biochemical measures could be performed (BP, lipid profile, glucose abnormality) to calculate absolute risk. As we used this WHO tool during the 2011–2012 screening, it was to some extent focused on a clinical measure of cardiovascular disease. Therefore it is a possibility of overestimation of the prevalence of hypertensive disorders in the high risk participants when the average general population is considered. Also there is a possibility of differences in recall and reporting between men and women, with women perhaps being more likely to report symptoms. On the other hand, the exclusion of the persons with high propensity for subclinical CVDs may lead to some underestimation of the burden among the not high participants. Thus, it seems that the true prevalence of pre-hypertension and hypertension among adults in this population lies somewhere in between 16 % to 59.6 % and this needed to be explored through further studies with representative sampling. Similar works are required to estimate the burden of obesity and overweight (between 20 - 40 %) in this population. In contrast to these two risk factors the prevalence of dysglycemia and dyslipidemia do not differ significantly between the high and not high risk study participants and thus, the values may be considered to represent those of the general population.
Moreover our sample of CVDs may not be representative of all parts of Bangladesh as it is one of the remote areas in the North where people survive with a below average GDP rate. However, the demographic characteristics of the study area were similar with respect to sex ratio, per-capita income, household size, literacy rate, life expectancy, occupation, and marital status to those in other rural areas of Bangladesh and similar as national average [49], and the study proved helpful in understanding CVDs risk score and CVD risk factors prevalent among the rural population. A random measurement error would bias the association towards null, particularly for smoking, physical activity and for dietary intake; these biases could influence the overall study findings. However, we used an average of three day dietary recall methods to minimize the recall bias. We also used yearly physical activity history on parallel with weekly pattern, to control and minimize random measurement error. The recall bias would be non-differential and might have further pooled the association towards null. Lastly, we did not include family history of CVDs in our detailed questionnaire. It is possible that some other risk factors that play a role in CVDs in the rural environment are yet to be explored.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the present study showed that the prevalence of clinical and biochemical risk factors of CVDs are quite high, even in a remote rural Bangladeshi population. This may be related to the socioeconomic and cultural transition in Bangladeshi society. Surprisingly, more of the high risk group was female and there were fewer smokers. Obesity and hypertension were more frequent in high risk participants. In particular, central obesity is common despite the high level of physical activity. Public health strategies to address overweight and obesity are needed. The data also shows that the most important biochemical risk factors of CVDs are not addressed by the WHO CVD Risk Screening Tool for Low – and Medium-Resource settings.
Notes
Most of the existing research conducted in Bangladeshi rural settings has been in rural areas adjacent to urban spaces, whereas a traditional rural area is one geographically and behaviorally distinct from urban influences.
References
World Health Organization (WHO): Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs). Fact Sheet N 317. January 2015. Available at this website: http://wwwwhoint/mediacentre/factsheets/fs317/en/indexhtml (Updated January, 2015 and accessed on 5/01/2015) 2015.
Ghaffar A, Reddy KS, Singhi M. Burden of non-communicable diseases in South Asia. Br Med J. 2004;328(7443):807–10.
El-Saharty S, Ahsan KZ, Koehlmoos TL, Engelgau MM. Tackling Noncommunicable Diseases in Bangladesh: Now is the Time. : Direstion in Development. Washington, DC: World Bank. doi:10.1596/978-0-8213-9920-0. License: Creative Commons Attribution CC BY 3.0. World Bank Publications; 2013.
Streatfield PK, Karar ZA. Population challenges for Bangladesh in the coming decades. J Health Popul Nutr. 2008;26(3):261.
Bleich SN, Koehlmoos TL, Rashid M, Peters DH, Anderson G. Noncommunicable chronic disease in Bangladesh: Overview of existing programs and priorities going forward. Health Policy. 2011;100(2):282–9.
Hussain SM, Oldenburg B, Wang Y, Zoungas S, Tonkin AM. Assessment of Cardiovascular Disease Risk in South Asian Populations. International journal of vascular medicine 2013, 2013;1-10. (http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/786801).
World Health Organization (WHO). Cardiovascular Disease Programme. WHO CVD-risk management package for low-and medium-resource settings. 20 Avenue Appia, 1211 Geneva 27, Switzerland. Printed in France: World Health Organization; 2002.
Hoffbrand B. Treat Obesity Seriously. A Clinical Manual. Postgrad Med J. 1982;58(684):671.
Ong KL, Cheung BM, Man YB, Lau CP, Lam KS. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension among United States adults 1999–2004. Hypertension. 2007;49(1):69–75.
World Health Organization (WHO). Diet, nutrition and the prevention of chronic diseases: report of a joint WHO/FAO expert consultation, vol. 916. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization: Diamond Pocket Books (P) Ltd.; 2003.
Gupta R, Deedwania PC, Sharma K, Gupta A, Guptha S, Achari V, et al. Association of educational, occupational and socioeconomic status with cardiovascular risk factors in Asian Indians: a cross-sectional study. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e44098.
World Health Organization (WHO). Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. (WHO Expert Consultation). Lancet. 2004;363(9403):157.
Alberti K, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA, et al. Harmonizing the Metabolic Syndrome A Joint Interim Statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation. 2009;120(16):1640–5.
Ashwell M, Gibson S. Waist to height ratio is a simple and effective obesity screening tool for cardiovascular risk factors: analysis of data from the British National Diet and Nutrition Survey of adults aged 19–64 years. Obesity facts. 2009;2(2):97–103.
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo Jr JL, et al. The seventh report of the joint national committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure: the JNC 7 report. Jama. 2003;289(19):2560–71.
Consultation W. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications, vol. 1: Part. 1999.
Lung NH, Institute B. Third report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (Adult Treatment Panel III): final report. Circulation. 2002;106(25):3143.
Haque AN. By the numbers: The middle-income matrix. 2007.
Allison P: Logistic regression using SAS: Theory and application. Second Edition. Cary, NC: SAS Institute. In., Second Edition edn: Inc; 2012.
6th International Congress of Nutrition, Edinburgh, August 1963. [not specified]: 6th International Congress of Nutrition, Edinburgh, August 1963.; 1963, August. :219 pp.; 1963.
Zaman MM, Choudhury SR, Ahmed J, Numan SM, Islam MS, Yoshiike N. Non-biochemical risk factors for cardiovascular disease in general clinic-based rural population of Bangladesh. Journal of epidemiology / Japan Epidemiological Association. 2004;14(2):63–8.
Salim MA, Begum M, Mahmood M, Banerjee SK, Siddiqe MA, Haque KS. Association of major risk factors (diabetes mellitus and hypertension) in acute coronary syndrome in Bangladeshi population. Circulation. 2010;122(2):e157.
Ahsan SA, Haque KS, Salman M, Bari AS, Nahar H, Ahmed MK, et al. Detection of ischaemic heart disease with risk factors in different categories of employees of University Grants Commission. Univ Heart J. 2009;5(1):20–3.
Villablanca AC, McDonald JM, Rutledge JC. Smoking and cardiovascular disease. Clin Chest Med. 2000;21(1):159–72.
Kabir MA, Goh KL, Kamal SM, Khan MM. Tobacco smoking and its association with illicit drug use among young men aged 15–24 years living in urban slums of Bangladesh. PLoS ONE [Electronic Resource]. 2013;8(7):e68728.
Kamal SMM, Islam MA, Raihan MA. Differentials of tobacco consumption and its effect on illicit drug use in rural men in Bangladesh. Asia Pacific Journal of Public Health. 2011;23(3):349–62.
Karim A, Das D, Salahuddin M, Marjan G, Islam M, Shaha A, et al. Prevalence of Microalbuminuria and Overt Proteinuria in Hypertension and Their Relations with Renal Function in a Rural Population of Bangladesh. Bangladesh Journal of Medicine. 2014;24(2):59–64.
Bhowmik B, Munir SB, Diep LM, Siddiquee T, Habib SH, Samad MA, et al. Anthropometric indicators of obesity for identifying cardiometabolic risk factors in a rural Bangladeshi population. Journal of Diabetes Investigation. 2013;4(4):361–8.
Després J-P, Lemieux I. Abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome. Nature. 2006;444(7121):881–7.
Canoy D, Boekholdt SM, Wareham N, Luben R, Welch A, Bingham S, et al. Body Fat Distribution and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in Men and Women in the European Prospective Investigation Into Cancer and Nutrition in Norfolk Cohort A Population-Based Prospective Study. Circulation. 2007;116(25):2933–43.
Ge W, Parvez F, Wu F, Islam T, Ahmed A, Shaheen I, et al. Association between anthropometric measures of obesity and subclinical atherosclerosis in Bangladesh. Atherosclerosis. 2014;232(1):234–41.
NCD B. Risk Factor Survey 2010. Dhaka: WHO; 2011.
Joshi P, Islam S, Pais P, et al. RIsk factors for early myocardial infarction in south asians compared with individuals in other countries. JAMA. 2007;297(3):286–94.
Islam MR, Khan I, Attia J, Hassan SMN, McEvoy M, D’Este C, et al. Association between hypertension and chronic arsenic exposure in drinking water: A cross-sectional study in Bangladesh. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2012;9(12):4522–36.
Cravedi P, Sharma SK, Bravo RF, Islam N, Tchokhonelidze I, Ghimire M, et al. Preventing renal and cardiovascular risk by renal function assessment: insights from a crosssectional study in low-income countries and the USA. BMJ open. 2012;2(5):e001357.
Bhowmik B, Diep LM, Munir SB, Rahman M, Wright E, Mahmood S, et al. HbA(1c) as a diagnostic tool for diabetes and pre-diabetes: the Bangladesh experience. Diabet Med. 2013;30(3):e70–7.
Van Minh H, Ng N, Juvekar S, Razzaque A, Ashraf A, Hadi A, et al. Peer Reviewed: Self-Reported Prevalence of Chronic Diseases and Their Relation to Selected Sociodemographic Variables: A Study in INDEPTH Asian Sites, 2005. Preventing chronic disease 2008;5(3).(http://www.cdc.gov/pcd/issues/2008/jul/2007_0115.htm).
Zaman MM, Ahmed J, Choudhury SR, Numan SM, Parvin K, Islam MS. Prevalence of ischemic heart disease in a rural population of Bangladesh. Indian Heart J. 2007;59(3):239–41.
Hypertension Study G. Prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension among the elderly in Bangladesh and India: a multicentre study. Bull World Health Organ. 2001;79(6):490–500.
Akter S, Rahman MM, Abe SK, Sultana P. Prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes and their risk factors among Bangladeshi adults: a nationwide survey. Bull World Health Organ. 2014;92(3):204–13.
ICDDR B. Type 2 diabetes and pre-diabetic conditions among adults aged 27-50 years in Matlab: a hidden public health burden. Health and Science Bulletin 2009;7(2):13-18.
Sayeed MA, Mahtab H, Khanam PA, Ahsan KA, Banu A, Rashid ANMB, et al. Diabetes and Impaired Fasting Glycemia in the Tribes of Khagrachari Hill Tracts of Bangladesh. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(5):1054–9.
Parr JD, Lindeboom W, Khanam MA, Perez Koehlmoos TL. Diagnosis of chronic conditions with modifiable lifestyle risk factors in selected urban and rural areas of Bangladesh and sociodemographic variability therein. BMC Health Serv Res. 2011;11:309.
Zaman MM, Yoshiike N, Rouf MA, Syeed MH, Khan MR, Haque S, et al. Cardiovascular risk factors: distribution and prevalence in a rural population of Bangladesh. J Cardiovasc Risk. 2001;8(2):103–8.
Saquib N, Khanam MA, Saquib J, Anand S, Chertow GM, Barry M, et al. High prevalence of type 2 diabetes among the urban middle class in Bangladesh. BMC public health. 2013;13(1):1032.
Moni MA, Rahman MA, Haque MA, Islam MS, Ahmed K. Blood pressure in relation to selected anthropometric measurements in senior citizens. Mymensingh medical journal : MMJ. 2010;19(2):254–8.
Das PK, Rahaman F, Kamal M. Complications of acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in hypertensive patients a prospective observational study in CCU of chittagong medical college hospital, Bangladesh. Journal of Clinical Hypertension. 2012;14(Suppl 1):155.
Sayeed S, Banu A, Khanam PA, Alauddin S, Makbul S, Begum T, et al. Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrom in Three Urban Communities of Dhaka City. Ibrahim Medical College Journal. 2008;2(2):44–8.
Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics (BBS). Bangladesh Population and Housing Census 2011, in Community Report, Thakurgaon Zila, Dhaka. 2012.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all participants in this study. Also acknowledge important contribution of the field workers and Thakurgaon Swasthoseba Hospital to make this work possible.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Bangladesh University of Health Sciences (BUHS) and Dr KM Maqsudur Rahman Trust.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
KF, NZ, AHM and LA developed the concept. KF oversaw all aspects of the study design, field training, supervision and monitoring data collection, statistical analysis, interpretation of analysis, and drafted the manuscript. ZZ performed the biochemical analysis. KF, NZ, ZZ AHM, BR, and LA – all authors read, provide critical revision of the article for important intellectual content and approved the final manuscript.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Fatema, K., Zwar, N.A., Zeba, Z. et al. Clinical and biochemical characterization of high risk and not high risk for cardiovascular disease adults in a population from peripheral region of Bangladesh. BMC Public Health 15, 559 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-015-1919-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-015-1919-7