Abstract
Background
We wished to evaluate the efficacy and safety of liposomal paclitaxel and docetaxel for induction chemotherapy (IC) for nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC).
Methods
A total of 1498 patients with newly-diagnosed NPC between 2009 and 2017 treated with IC plus concurrent chemotherapy were included in our observational study. Overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), locoregional relapse-free survival (LRFS), distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS) and grade-3–4 toxicities were compared between groups using propensity score matching (PSM).
Results
In total, 767 patients were eligible for this study, with 104 (13.6%) and 663 (86.4%) receiving a liposomal paclitaxel-based and docetaxel-based taxanes, cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil (TPF) regimen, respectively. PSM identified 103 patients in the liposomal-paclitaxel group and 287 patients in the docetaxel group. There was no significant difference at 3 years for OS (92.2% vs. 93.9%, P = 0.942), PFS (82.6% vs. 81.7%, P = 0.394), LRFS (94.7% vs. 93.3%, P = 0.981) or DMFS (84.6% vs. 87.4%, P = 0.371) between the two groups after PSM. Significant interactions were not observed between the effect of chemotherapy regimen and sex, age, T stage, N stage, overall stage, or Epstein–Barr virus DNA level in the subgroup multivariate analysis. The prevalence of grade-3–4 leukopenia and neutropenia in the liposomal-paclitaxel group was significantly lower than that of the docetaxel group (P < 0.05 for all).
Conclusions
Compared with docetaxel, liposomal paclitaxel has identical anti-tumor efficacy, but causes fewer and milder adverse reactions in IC for NPC.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Background
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a malignant disease arising from the nasopharyngeal epithelium. The incidence of NPC is particularly high in Southern China, where 50–80 cases per 100,000 persons are reported each year [1]. Because of the radiosensitive nature of NPC and the typically deep-seated location of the lesions, radiotherapy (RT) is the primary treatment for NPC [2]. Advances in radiation delivery have resulted in improved local control for NPC [3, 4]. However, prevention of distant metastasis in advanced NPC remains unsatisfactory and is the main cause of treatment failure [5, 6]. Several studies have shown that induction chemotherapy (IC) followed by definitive concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT) may be associated with reduced risk of distant metastases, which could improve clinical outcomes [7,8,9].
Studies have shown that taxanes, cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil (TPF) is the effective IC regimen for reducing the risk of treatment failure and improving overall survival (OS) in patients with high risk NPC [10,11,12]. In comparison with the standard cisplatin and fluorouracil (PF) regimen, regimens involving taxanes (microtubule-stabilizing drugs) have been used widely for the treatment of different types of malignancies for decades [13].
Docetaxel is a semi-synthetic taxane-based agent that has an enhanced ability to assemble tubulin in vitro [14]. Use of docetaxel has gradually superseded that of paclitaxel and occupied the dominant position in the last decade [15]. However, due to the undesirable water solubility of docetaxel, it is formulated with Tween 80 and ethanol. As a consequence, patients must be pre-medicated by corticosteroids for days to minimize the severe hypersensitivity reactions and fluid retention brought about by solvent-based docetaxel. “Liposomal paclitaxel” is a new paclitaxel drug encapsulated with liposomes which can reduce toxicities and improve bioavailability [16, 17]. Liposomal paclitaxel has comparable antitumor efficacy with that of conventional paclitaxel [18].
As an important agent in IC regimens, the toxicities of different taxane-based analogs affect the tolerance and compliance of patients considerably, thereby influencing IC efficacy. Under these circumstances, comparing the efficacy and toxicity of liposomal paclitaxel with that of docetaxel is important. We undertook a retrospective study to evaluate efficacy and toxicity of liposomal paclitaxel and docetaxel for the treatment of locally advanced NPC.
Methods
Patients
The study protocol was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Cancer Center of Sun Yat-sen University (Guangdong, China). Newly diagnosed patients treated in the Sun Yat-sen Cancer Center from 2009 to 2017 were identified. The inclusion criteria were: NPC confirmed by histology; age ≥ 18 years; in receipt of IC and CCRT; Karnofsky Performance Score > 70; availability of hematology data and results for Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) serology. Patients being treated under the IC regimen of taxanes and cisplatin (TP) or PF or adjuvant chemotherapy, patients with stage-II NPC, or those given conventional paclitaxel were excluded.
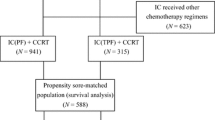
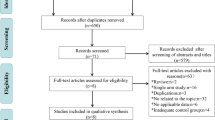
After the screening procedure, 767 individuals were chosen for the analysis. This cohort comprised 104 patients receiving liposomal paclitaxel and 663 patients receiving docetaxel.
Data collection
Using the medical records of patients, the following information was collected: demographics; diagnosis; tumor stage; imaging; EBV DNA results; regimen; chemotherapy dose; laboratory results at baseline and after each cycle of chemotherapy. Patients were followed up every 3 months in the first 2 years, and then every 6 months thereafter. Recurrence or metastasis was confirmed by pathology results or imaging (magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, abdominal ultrasound, whole-body bone scintigraphy, positron emission tomography–computed tomography). Our endpoints included overall survival (OS, the interval from the first day of hospitalization to death from any cause), progression-free survival (PFS, the interval from the first day of hospitalization to disease progression or death from any cause), locoregional relapse-free survival (LRFS) and distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS), which corresponded to the interval to first recurrence and distant metastasis, respectively. Hematologic and non-hematologic toxicities were graded under the instruction of the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events v4.0.
Induction chemotherapy and concurrent chemoradiotherapy
All patients received the TPF IC regimen: docetaxel (60 mg/m2, day-1) or liposomal paclitaxel (135 mg/m2, day-1), cisplatin (20–25 mg/m2/day, days 1–3), and 5-fluorouracil (500–800 mg/m2, 120 h of continuous intravenous infusion). All regimens were administered every 3 weeks over 2–4 cycles. RT was administered to the nasopharynx and neck using intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) or two-dimensional radiotherapy. IC was followed by concurrent cisplatin-based chemotherapy (80–100 mg/m2 every 3 weeks or 30–40 mg/m2 every week) [19, 20]. Five daily fractions of a total dose of 68–70 Gy at ≈2 Gy per fraction were prescribed per week. Other details of the IMRT plan were in accordance with the principles described previously [21,22,23].
Statistical analyses
The propensity score matching (PSM) method was adopted to adjust for potential confounders that may influence estimation of the treatment effect. Propensity scores were calculated by logistic regression at 1:3 ratios to balance the covariates of sex, age, T stage, N stage, and plasma levels of EBV DNA. The chi-squared test or Fisher’s exact test was used to compare the distribution of categorical factors between the docetaxel group and liposomal-paclitaxel group in the observational dataset and PSM dataset. Survival curves and survival outcomes were analyzed using the Kaplan–Meier method and log-rank tests. A multivariable Cox proportional hazards model was used for multivariable analysis, to calculate hazard ratios (HRs) and evaluate prognostic values. P < 0.05 (two-sided) was considered significant. SPSS v22.0 was used for all statistical analyses.
Results
Patient characteristics
From 2009 to 2017, 802 patients were initially considered to be qualified for this study. There were 35 patients receiving docetaxel that were switched to other chemotherapy regimens because of severe myelosuppression after one cycle of chemotherapy so we excluded these patients. Finally, after the screening procedure, 767 patients were involved in this study; 104 (13.6%) and 663 (86.4%) patients were treated with liposomal paclitaxel and docetaxel, respectively, in IC regimens. All patients have complete full radiotherapy in both groups. There were 61(58.7%) patients receiving a cumulative cisplatin dose (CCD) ≥200 mg/m2 in the liposomal group and 119(17.9%) patients receiving a CCD ≥200 mg/m2 in the docetaxel group. After PSM at a ratio of 1:3, a well-balanced cohort of 390 patients remained in the analysis (Fig. 1). Among them, 103 patients were in the liposomal-paclitaxel group and 287 patients in the docetaxel group. The median age was 44 (18–72) years, with 91 (23.3%) females and 299 (76.7%) males. Significant differences in potential prognostic factors were not observed in these two groups (P > 0.05 for all). The differences in patient characteristics between the liposomal-paclitaxel and docetaxel groups in the observational and propensity-matched datasets are shown in Table 1.
Survival outcomes
Among the original cohort of 767 patients, the median duration of follow-up was 21.5 months in the liposomal-paclitaxel group and 36.9 months in the docetaxel group, respectively. Overall, there was no significant difference in OS, PFS, LRFS and DMFS at 3 years between the two groups (OS: 92.2% vs. 93.9%, P = 0.887; PFS: 82.7% vs. 83.9%, P = 0.572; LRFS: 94.7% vs. 94.0%, P = 0.871; DMFS: 84.7% vs. 89.1%, P = 0.541) (Fig. 2a–d).
In multivariate analysis, the following variables were considered in the Cox proportional hazards model: age, sex, T stage, N stage, overall stage, level of EBV DNA, and chemotherapy regimen. As shown in Table 2, application of liposomal paclitaxel was not associated with a higher risk of death (hazard ratio (HR), 1.017; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.361–2.868; P = 0.974), tumor progression (0.829; 0.429–1.603; 0.578), locoregional relapse (0.994; 0.301–3.288; 0.992) or distant metastasis (0.777; 0.353–1.708; 0.529) than application of docetaxel.
In the propensity score-matched cohort of 390 patients, the median duration of follow-up was 21.6 months in the liposomal-paclitaxel group and 36.9 months in the docetaxel group, respectively. Similar to the result in original cohort, application of liposomal paclitaxel resulted in similar survival to that observed with docetaxel at 3 years (OS: 92.2% vs. 93.9%, P = 0.942; PFS: 82.6% vs. 81.7%, P = 0.394; LRFS: 94.7% vs. 93.3%, P = 0.981; DMFS: 84.6% vs. 87.4%, P = 0.371) (Fig. 3a–d). In multivariate analysis, all clinical endpoints were also highly independent from the selection of chemotherapy regimen (OS: HR, 0.913; 95% CI, 0.302–2.762; P = 0.872; PFS: 0.746; 0.373–1.491; 0.407; LRFS: 1.027; 0.285–3.702; 0.967; DMFS: 0.694; 0.304–1.587; 0.387) (Table 2).
Acute toxicity
We evaluated acute toxicity during IC in the propensity score-matched cohort. No hypersensitivity reactions were observed in the liposomal-paclitaxel group. A liposomal paclitaxel-containing chemotherapy regimen was associated with a lower prevalence of grade-3–4 leukopenia significantly (grade 0–2: 96.1% vs. 70%; grade 3–4: 3.9% vs. 30.0%; P < 0.001) and neutropenia (grade 0–2: 78.6% vs. 53.0%; grade 3–4: 21.4% vs. 47.0%; P < 0.001) compared with the docetaxel-containing regimen. Intergroup differences in other acute toxicities such as anemia, as well as increases in levels of alanine transaminase, aspartate transaminase, and blood–urea–nitrogen were not significant (P > 0.05 for all) (Table 3).
Discussion
Distant metastasis is a critical issue in advanced NPC [5, 6]. There is increasing evidence that IC can facilitate eradication of micro-metastatic lesions and reduce the risk of distant metastasis [7,8,9], so IC is being used widely in clinical settings. Based on studies that have established its superiority over the standard PF regimen for lowering the prevalence of distant metastasis and improving OS prevalence, TPF has emerged as the effective IC regimen [10,11,12].
In comparison with the standard PF regimen, the TPF regimen includes taxanes, effective antitumor drugs used for the treatment of different types of malignancies for decades. Taxanes bind preferentially to microtubules, leading to stabilization, and are involved in the formation of mitotic spindles during the M phase of the cell cycle [24,25,26]. Taxanes also induce apoptosis and have anti-angiogenic properties [27]. Paclitaxel, a taxane plant product, is one of the most commonly used broad-spectrum anti-cancer agents and has been approved for the treatment various cancers. However, the poor aqueous solubility and serious side effects associated with commercial preparations of paclitaxel has triggered the development of alternative paclitaxel formulations [28].
Docetaxel is a semi-synthetic taxane-based agent [14] which has supplanted conventional paclitaxel as the most commonly used paclitaxel-type drug used clinically. Compared with conventional paclitaxel, docetaxel has linear pharmacokinetics, a longer plasma half-life, and longer intracellular retention [27]. The TAX 323 study was the first to demonstrate the benefits of adding docetaxel to cisplatin and 5-fuorouracil as an IC for locoregionally advanced head-and-neck cancer [29]. Subsequently, the TAX 324 study [30, 31] and GORTEC laryngeal study [32] also showed that TPF was significantly better than PF at improving survival, local control, and organ preservation, and was associated with manageable toxicity. In addition, a randomized phase-III study conducted by Sun et al. [33] showed that TPF could increase 3-year failure-free survival for NPC patients significantly.
However, the main adverse effect of docetaxel is myelosuppression. Peng and colleagues showed that the prevalence of leukopenia and neutropenia using TPF was 28.1 and 45.0%, respectively [12]. A randomized phase-III study suggested that the most common grade-3 or − 4 adverse events during treatment in the TPF group were neutropenia (42%), leukopenia (41%) and stomatitis (41%) [33]. In our study, the prevalence of grade-3–4 leukopenia was 30.0% and that of neutropenia was 47.0% in the docetaxel-containing TPF regimen, a value that is consistent with that documented in previous studies.
Liposomal paclitaxel is a new paclitaxel drug encapsulated with liposomes. As new drug carriers, liposomes can improve the solubility of paclitaxel and prolong its action in vivo. Thus, liposomal formulations offer unsurpassed advantages, including the ability to carry a hydrophobic payload, ease of synthesis, favorable manufacturing control, and excellent biocompatibility [34,35,36]. As a result, liposomal paclitaxel can reduce toxicities, improve bioavailability [16, 17] and has comparable antitumor efficacy with conventional paclitaxel [18]. Huang and co-workers showed that liposomal paclitaxel exhibited a higher therapeutic index than clinical paclitaxel formulations [36].
Furthermore, hypersensitivity reactions are important adverse events in paclitaxel-based treatment, and can lead to death. Studies have shown that 8–14% of patients develop hypersensitivity reactions during paclitaxel-based chemotherapy [37, 38]. In our study, a hypersensitivity reaction was not observed, a result that is consistent with that in other studies [39,40,41]. The results shown above suggest that a liposomal paclitaxel-based TPF regimen is safe treatment for locally advanced NPC, especially for hypersensitive patients. In addition, the overall toxicity of liposomal paclitaxel was lower than that of free paclitaxel [42].
Su and colleagues showed that liposomal paclitaxel has the same anti-tumor efficacy as that of docetaxel and had greater safety for the treatment of breast cancer [43]. Lu and co-workers found that liposomal paclitaxel combined with capecitabine was, in general, well tolerated, and worth further study compared with docetaxel, cisplatin, and 5-fluorouracil in the treatment of gastric cancer [43, 44]. However, few studies have compared the efficacy and toxicity of liposomal paclitaxel with that of docetaxel.
This is the first study to show that application of liposomal paclitaxel results in comparable survival to that of docetaxel in NPC patients. Furthermore, consistent with other studies, patients in the liposomal-paclitaxel group were associated with a lower prevalence of grade-3–4 leukopenia and neutropenia in our study. Treatment goals for NPC are improvement of survival and reduction of treatment toxicity. Hence, selection of the treatment regimen should be based on drug efficacy and patient preference. Our study provides clinical evidence to support the use of a liposomal paclitaxel-based TPF regimen as an efficacious regimen for NPC.
Our study had three main limitations. First, as a retrospective study, there was an inevitable bias caused by selection. Second, data for hypersensitivity reactions due to docetaxel were not collected. Third, the OS value was limited because of the relatively short duration of follow-up; longer follow-up is needed to assess OS fully. Forth, liposomal paclitaxel patients were treated more recently and we did not include year of treatment in the PSM. In addition, 99% of the patients in our study were WHO III NPC and whether the results can be applied to western patients with WHO I/II NPC remains to be determined in future studies. Prospective studies are required to confirm our results.
Conclusions
The present study suggests that application of liposomal paclitaxel results in comparable survival with that of conventional docetaxel with a lower prevalence of grade 3–4 leukopenia and neutropenia. A liposomal paclitaxel-based TPF regimen could be an alternative treatment strategy to a docetaxel-based TPF regimen in patients with locally advanced NPC.
Abbreviations
- CCRT:
-
concurrent chemoradiotherapy
- CIs:
-
confidence intervals
- DMFS:
-
distant metastasis-free survival
- EBV:
-
Epstein–Barr virus
- HR:
-
hazard ratio
- IC:
-
induction chemotherapy
- IMRT:
-
intensity-modulated radiotherapy
- LRFS:
-
locoregional relapse-free survival
- NPC:
-
nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- OS:
-
overall survival
- PF:
-
cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil
- PFS:
-
progression-free survival
- PSM:
-
propensity score matching
- RT:
-
radiotherapy
- TP:
-
taxanes and cisplatin
- TPF:
-
taxanes, cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil
References
Wee JT, Ha TC, Loong SL, Qian CN. Is nasopharyngeal cancer really a "Cantonese cancer"? Chin J Cancer. 2010;29(5):517–26.
Choa G. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Some observations on the clinical features and technique of examination. Pac Med Surg. 1967;75(3):172–4.
Peng G, Wang T, Yang KY, Zhang S, Zhang T, Li Q, Han J, Wu G. A prospective, randomized study comparing outcomes and toxicities of intensity-modulated radiotherapy vs. conventional two-dimensional radiotherapy for the treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Radiother Oncol. 2012;104(3):286–93.
Zhang MX, Li J, Shen GP, Zou X, Xu JJ, Jiang R, You R, Hua YJ, Sun Y, Ma J, et al. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy prolongs the survival of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma compared with conventional two-dimensional radiotherapy: a 10-year experience with a large cohort and long follow-up. Eur J Cancer. 2015;51(17):2587–95.
Lee N, Xia P, Quivey JM, Sultanem K, Poon I, Akazawa C, Akazawa P, Weinberg V, Fu KK. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy in the treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: an update of the UCSF experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002;53(1):12–22.
Sun X, Su S, Chen C, Han F, Zhao C, Xiao W, Deng X, Huang S, Lin C, Lu T. Long-term outcomes of intensity-modulated radiotherapy for 868 patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: an analysis of survival and treatment toxicities. Radiother Oncology. 2014;110(3):398–403.
Hong RL, Ting LL, Ko JY, Hsu MM, Sheen TS, Lou PJ, Wang CC, Chung NN, Lui LT. Induction chemotherapy with mitomycin, epirubicin, cisplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin followed by radiotherapy in the treatment of locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19(23):4305–13.
Hui EP, Ma BB, Leung SF, King AD, Mo F, Kam MK, Yu BK, Chiu SK, Kwan WH, Ho R, et al. Randomized phase II trial of concurrent cisplatin-radiotherapy with or without neoadjuvant docetaxel and cisplatin in advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(2):242–9.
Bossi P, Orlandi E, Bergamini C, Locati LD, Granata R, Mirabile A, Parolini D, Franceschini M, Fallai C, Olmi P, et al. Docetaxel, cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil-based induction chemotherapy followed by intensity-modulated radiotherapy concurrent with cisplatin in locally advanced EBV-related nasopharyngeal cancer. Ann Oncol Med Oncol. 2011;22(11):2495–500.
Chen J, Qi J, Yu B, Peng XH, Wang F, Tan JJ, Chen QQ, Peng XY, Zeng FF, Liu X. A retrospective study to compare five induction chemotherapy regimens prior to radiotherapy in the reduction of regional lymph node size in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Med Sci Mon. 2018;24:2562–8.
Liu GY, Lv X, Wu YS, Mao MJ, Ye YF, Yu YH, Liang H, Yang J, Ke LR, Qiu WZ, et al. Effect of induction chemotherapy with cisplatin, fluorouracil, with or without taxane on locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a retrospective, propensity score-matched analysis. Cancer Commun (London, England). 2018;38(1):21.
Peng H, Tang LL, Chen BB, Chen L, Li WF, Mao YP, Liu X, Zhang Y, Liu LZ, Tian L, et al. Optimizing the induction chemotherapy regimen for patients with locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a big-data intelligence platform-based analysis. Oral Oncol. 2018;79:40–6.
Colevas AD, Posner MR. Docetaxel in head and neck cancer: a review. Am J Clin Oncol. 1998;21(5):482–6.
Verweij J, Clavel M, Chevalier B. Paclitaxel (TaxolTM) and docetaxel (TaxotereTM): not simply two of a kind. Ann Oncol. 1994;5(6):495–505.
Kelly CM, Green MC, Broglio K, Thomas ES, Brewster AM, Valero V, Ibrahim NK, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Booser DJ, Walters RS, et al. Phase III trial evaluating weekly paclitaxel versus docetaxel in combination with capecitabine in operable breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(9):930–5.
Sharma NK, Kumar V. Liposomal paclitaxel: recent trends and future perspectives. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res. 2015;31(1):205–11.
Yang T, Cui F-D, Choi M-K, Lin H, Chung S-J, Shim C-K, Kim D-D. Liposome formulation of paclitaxel with enhanced solubility and stability. Drug Delivery. 2007;14(5):301–8.
Xu X, Wang L, Xu H-Q, Huang X-E, Qian Y-D, Xiang J. Clinical comparison between paclitaxel liposome (Lipusu®) and paclitaxel for treatment of patients with metastatic gastric cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(4):2591–4.
Al-Sarraf M, LeBlanc M, Giri PG, Fu KK, Cooper J, Vuong T, Forastiere AA, Adams G, Sakr WA, Schuller DE, et al. Chemoradiotherapy versus radiotherapy in patients with advanced nasopharyngeal cancer: phase III randomized intergroup study 0099. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16(4):1310–7.
Lee AW, Ngan RK, Tung SY, Cheng A, Kwong DL, Lu TX, Chan AT, Chan LL, Yiu H, Ng WT, et al. Preliminary results of trial NPC-0501 evaluating the therapeutic gain by changing from concurrent-adjuvant to induction-concurrent chemoradiotherapy, changing from fluorouracil to capecitabine, and changing from conventional to accelerated radiotherapy fractionation in patients with locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer. 2015;121(8):1328–38.
Lee A, Lau K, Hung W, Ng W, Lee M, Choi C, Chan C, Tung R, Cheng P, Yau T. Potential improvement of tumor control probability by induction chemotherapy for advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Radiother Oncol. 2008;87(2):204–10.
Lin S, Lu JJ, Han L, Chen Q, Pan J. Sequential chemotherapy and intensity-modulated radiation therapy in the management of locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: experience of 370 consecutive cases. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:39.
Yu Z, Luo W, Zhou QC, Zhang QH, Kang DH, Liu MZ. Impact of changing gross tumor volume delineation of intensity-modulated radiotherapy on the dose distribution and clinical treatment outcome after induction chemotherapy for the primary locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Ai zheng = Aizheng = Chinese journal of cancer. 2009;28(11):1132–7.
Kampan NC, Madondo MT, McNally OM, Quinn M, Plebanski M: Paclitaxel and its evolving role in the Management of Ovarian Cancer. Biomed Res Int 2015, 2015:413076.
Rowinsky EK, Donehower RC. Paclitaxel (taxol). N Engl J Med. 1995;332(15):1004–14.
Goldspiel BR. Clinical overview of the taxanes. Pharmacotherapy. 1997;17(5 Pt 2):110s–25s.
Crown J, O'Leary M. The taxanes: an update. Lancet (London, England). 2000;355(9210):1176–8.
Nehate C, Jain S, Saneja A, Khare V, Alam N, Dubey RD, Gupta PN. Paclitaxel formulations: challenges and novel delivery options. Curr Drug Deliv. 2014;11(6):666–86.
Posner MR, Hershock DM, Blajman CR, Mickiewicz E, Winquist E, Gorbounova V, Tjulandin S, Shin DM, Cullen K, Ervin TJ, et al. Cisplatin and fluorouracil alone or with docetaxel in head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(17):1705–15.
Vermorken JB, Remenar E, van Herpen C, Gorlia T, Mesia R, Degardin M, Stewart JS, Jelic S, Betka J, Preiss JH, et al. Cisplatin, fluorouracil, and docetaxel in unresectable head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(17):1695–704.
Lorch JH, Goloubeva O, Haddad RI, Cullen K, Sarlis N, Tishler R, Tan M, Fasciano J, Sammartino DE, Posner MR. Induction chemotherapy with cisplatin and fluorouracil alone or in combination with docetaxel in locally advanced squamous-cell cancer of the head and neck: long-term results of the TAX 324 randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12(2):153–9.
Pointreau Y, Garaud P, Chapet S, Sire C, Tuchais C, Tortochaux J, Faivre S, Guerrif S, Alfonsi M, Calais G. Randomized trial of induction chemotherapy with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil with or without docetaxel for larynx preservation. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009;101(7):498–506.
Sun Y, Li WF, Chen NY, Zhang N, Hu GQ, Xie FY, Sun Y, Chen XZ, Li JG, Zhu XD, et al. Induction chemotherapy plus concurrent chemoradiotherapy versus concurrent chemoradiotherapy alone in locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a phase 3, multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(11):1509–20.
Hong SS, Choi JY, Kim JO, Lee MK, Kim SH, Lim SJ. Development of paclitaxel-loaded liposomal nanocarrier stabilized by triglyceride incorporation. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016;11:4465–77.
Crosasso P, Ceruti M, Brusa P, Arpicco S, Dosio F, Cattel L. Preparation, characterization and properties of sterically stabilized paclitaxel-containing liposomes. J Controlled Release. 2000;63(1–2):19–30.
Huang ST, Wang YP, Chen YH, Lin CT, Li WS, Wu HC. Liposomal paclitaxel induces fewer hematopoietic and cardiovascular complications than bioequivalent doses of Taxol. Int J Oncol, 1117. 2018;53(3):1105.
Aoyama T, Takano M, Miyamoto M, Yoshikawa T, Soyama H, Kato K, Ishibashi H, Iwahashi H, Nakatsuka M, Yajima I, et al. Is there any predictor for hypersensitivity reactions in gynecologic cancer patients treated with paclitaxel-based therapy? Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2017;80(1):65–9.
Ratanajarusiri T, Sriuranpong V, Sitthideatphaiboon P, Poovoravan N, Vinayanuwat C, Parinyanitikul N, Angspatt P, Thawinwisan W, Tanasanvimon S. A difference in the incidences of hypersensitivity reactions to original and generic Taxanes. Chemotherapy. 2017;62(2):134–9.
Chen G, Sheng L, Du X. Efficacy and safety of liposome-paclitaxel and carboplatin based concurrent chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced lung squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2018.
Zhang Q, Huang XE, Gao LL. A clinical study on the premedication of paclitaxel liposome in the treatment of solid tumors. Biomed Pharmacother. 2009;63(8):603–7.
Wang HY, Zhang XR. Comparison of efficacy and safety between liposome-paclitaxel injection plus carboplatin and paclitaxel plus carboplatin as first line treatment in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Zhongguo yi xue ke xue yuan xue bao Acta Academiae Medicinae Sinicae. 2014;36(3):305–8.
Wang RH, Cao HM, Tian ZJ, Jin B, Wang Q, Ma H, Wu J. Efficacy of dual-functional liposomes containing paclitaxel for treatment of lung cancer. Oncol Rep. 2015;33(2):783–91.
Su W, Zhang S, Li C, Hao X, Zhang J. Efficacy and safety analysis of paclitaxel liposome and docetaxel for the neoadjuvant chemotherapy of breast cancer. Zhonghua zhong liu za zhi [Chinese journal of oncology]. 2015;37(5):379–82.
Lu M, Wang T, Wang J. Effects of paclitaxel liposome and capecitabine in the treatment of advanced gastric cancer by clinical observation. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2016;54(9):693–7.
Acknowledgments
We kindly thank the editor and reviewers for careful review and valuable comments, which have led to a significant improvement of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the National Key R&D Program of China (2016YFC0902003, 2017YFC1309003, 2017YFC0908500), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81425018, 81672868, 81602371, 81572848, 81772877, 81372814, 81773103), Sun Yat-sen University Clinical Research 5010 Program, Sci-Tech Project Foundation of Guangzhou City (201707020039), National Key Basic Research Program of China (2013CB910304), Special Support Plan of Guangdong Province (2014TX01R145), Sci-Tech Project Foundation of Guangdong Province (2014A020212103, 2012B031800255, 2014A020212528), Guangzhou Science and Technology Planning Project (2014 J4100181), Health & Medical Collaborative Innovation Project of Guangzhou City (201400000001), National Science & Technology Pillar Program during the Twelfth Five-year Plan Period (2014BAI09B10), PhD Start-up Fund of Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2016A030310221), Cultivation Foundation for Junior Teachers in Sun Yat-sen University (16ykpy28), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities. The funding bodies had no role in the design of the study, the collection, analysis, and interpretation of the data, or in the writing of the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HQM, LG, and LQT carried out the study concepts; SLL, XSS, and XYL participated in study design; SLL, XSS, XYL, YJL, JJY, CL, YFW, SSG, LTL, HJX, QNT, and ZCY participated in data acquisition; SLL, XSS and XYL participated in quality control of data and algorithms; SLL and XSS participated in data analysis and interpretation; SLL, XSS and XYL participated in statistical analysis; SLL, QYC and HXL participated in manuscript preparation; SLL, QYC and HXL participated in manuscript editing; HQM, LG and LQT participated in Manuscript review. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This retrospective study was approved by the Clinical Research Committee of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center. Patients were required to provide written informed consent before enrolling in the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, SL., Sun, XS., Li, XY. et al. Liposomal paclitaxel versus docetaxel in induction chemotherapy using Taxanes, cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil for locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. BMC Cancer 18, 1279 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-5192-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-5192-x