Abstract
Background
Transmission-blocking vaccines (TBVs) target the sexual stages of malaria parasites to reduce or interrupt the transmission cycle in human and mosquito populations. The genetic diversity of TBVs candidate antigens, Pvs25 and Pvs28, in Plasmodium vivax could provide evidence for the development of TBVs.
Methods
Dry blood spots from P. vivax patients were collected from Dandong, Suining, Hainan, Nyingchi, Tengchong, and Yingjiang in China. The pvs25 and pvs28 genes were amplified and sequenced. The genetic diversity of pvs25 and pvs28 were analyzed using DNASTAR, MEGA6, and DnaSP 5.0 programs.
Results
A total of 377 samples were collected, among which 324 and 272 samples were successfully amplified in the pvs25 and pvs28 genes, respectively. Eight haplotypes were identified in Pvs25, for which the predominant mutation was I130T with 100% prevalence. A variety of 22 haplotypes in Pvs28 were identified. The number of GSGGE/D repeats of Pvs28 was a range of 4–8, among which, high (7–8) and low (4–5) copy numbers of tandem repeats were found in haplotypes H2 and H17, respectively. The nucleotide diversity of pvs28 (π = 0.00305 ± 0.00061) was slightly higher than that of pvs25 (π = 0.00146 ± 0.00007), thus they were not significantly different (P > 0.05). The Tajima's D value of pvs25 was positive whereas pvs28 was negative, which indicated that both genes were affected by natural selection.
Conclusion
The genetic diversity of pvs25 and pvs28 genes in China was relatively limited, which provided valuable information for TBVs design and optimization.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
There were an estimated 241 million malaria cases globally in 2020, an increase from 2019 and approximately 4.5 million cases were caused by Plasmodium vivax, which was a decline from 2000, but remains a serious public health concern [1]. Among the five human malaria species, P. vivax is not as harmful as Plasmodium falciparum, which causes malignant malaria globally, although it is the most widespread outside of Africa. P. vivax represents the most prevalent relapse form of malaria constitutes a major obstacle for elimination efforts. China was certified malaria free in June of 2021; however, the risk of malaria re-establishment caused by imported malaria still exists. Interrupting the spread of imported drug-resistant P. vivax remains one of the major challenges during the post-elimination phase.
Transmission-blocking vaccines (TBVs) target the sexual stages of malaria parasites to reduce or interrupt the transmission cycle in human and mosquito populations [2, 3]. TBVs are primarily mediated by antibodies to Plasmodium surface proteins and act on the mosquito midgut [4]. To date, effective target antigens of TBVs have been identified and demonstrate good immune-blocking activity [5]. Among these antigens, the surface proteins P25 and P28 are expressed on zygotes and mature ookinetes [6]. The most striking feature of these proteins is that they have four epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like and cysteine-rich domains [7]. Previous studies had shown that the P25 protein was expressed earlier than the P28 protein associated with parasite development in mosquitoes [8]. Among the TBVs candidate proteins, the P. vivax proteins Pvs25 and Pvs28 were most concerned. Antisera against both recombinant Pvs25 and Pvs28 can recognize the corresponding antigens expressed by the zygotes/ookinetes, thereby inhibiting the development of mosquito oocysts [9]. When these antisera were diluted with the blood of P. vivax infected chimpanzees, a significant reduction in the number of oocysts was observed; however, anti-Pvs25 antiserum achieved a significantly greater blockade compared to the anti-Pvs28 antiserum [9]. Pvs25 and Pvs28 antisera were also identified in the P. vivax isolates from Thailand, which could recognize the corresponding molecules expressed by the parasite and block its spread [10]. Pvs25 and Pvs28 were more polymorphic than the P. falciparum homologous products, but the antigenic polymorphism of Pvs25 was more limited than that of Pvs28 [11]. Pvs25 has been considered as the leading vivax malaria TBVs candidate. Additionally, although the Pvs28 was expressed later in mosquitoes, they were all conservative substitutions [11].
Until now, the genetic diversity of the pvs25 and pvs28 genes has been reported in malaria-endemic countries, including Mexico [12], Iran [13], Bangladesh [14], South Korea [15, 16], India [17], Myanmar [18], Thailand [10], and Yunnan Province in China [19]. In the present study, the genetic diversity of the TBVs candidate antigens, Pvs25 and Pvs28, was detected and analyzed in P. vivax isolates collected from six different locations in China.
Materials and methods
Study site
Blood samples were collected from Dandong, Suining, Nyingchi, Tengchong, Yingjiang, and Hainan Island. Dandong city in Liaoning Province is in northeastern China. Suining county in Jiangsu Province is located in central China. Nyingchi city in Tibet is located in western China. Tengchong and Yingjiang counties in Yunnan Province are located in southwestern China along the China-Myanmar border. Hainan Island is the southernmost part of China (Fig. 1).
Sample collection
P. vivax isolates were collected between 2009 and 2020 from six different geographic sites in China. Finger-prick blood was spotted on filter paper (Whatman™ 903, GE Healthcare, USA) and dried. All patients were diagnosed as P. vivax using a microscopic examination and reconfirmed using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) by amplifying the small-subunit rRNA gene of Plasmodium spp [20]. Written informed consent was obtained from the patients prior to blood collection. This study was approved by the Ethical Review Committee of National Institute of Parasitic Diseases, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention.
Genomic DNA extraction and amplification
Genomic DNA was extracted using QIAamp DNA Blood Mini Kits (Qiagen, USA) following the manufacturer’s instructions. The Salvador I (Sal-I) strain of P. vivax was used as the reference sequences for pvs25 and pvs28 genes. Nucleotide sequence of pvs25 and pvs28 were available in the GenBank databases under the accession numbers AF083502 and AF083503, respectively. The full-length target genes pvs25 and pvs28 were amplified by nested PCR using primer pairs: pvs25F (5′-CACTTAGCCAAAATGAACTC-3′) and pvs25R (5′-AAAGGACAAGCAGGATGATA-3′) for pvs25; pvs28F (5′-CTACCACAGCTTGCTGTTCC-3′) and pvs28R (5′-TGACATCATGAAGAAGGCG-3′) for pvs28. [11, 17]. Bidirectional sequencing of PCR products was performed by Oebiotech Technology Co., Ltd.
Data analysis
The nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences were analyzed using Bioedit and SeqMan in the DNASTAR package (DNASTAR, Madison, WI, USA). The difference of the amino acid substitutions and haplotype of Pvs25 and Pvs28 among different sites in China were statistically analyzed. All sequences were compared with the Sal-1 strain and the amino acid mutations were shown in bold in the results and tables. The haplotypes were determined based on the type of amino acid substitutions of the obtained sequences, and the number of GSGGE/D repeats was calculated by comparing the haplotypes with the reference sequences of Sal-I strain. The values of segregating sites (S), average number pair-wise nucleotide differences (K), haplotype diversity (Hd), and nucleotide diversity (π) were calculated using DnaSP (version 5.0) [21]. The Tajima’s D test [22] was analyzed to evaluate the neutral theory of natural selection using DnaSP. The number of synonymous (dS) and non-synonymous (dN) substitutions were estimated and compared using a Z-test with the program MEGA6 (P < 0.05). The Nei and Gojobori’ s method [23, 24] was used to test the null hypothesis of strict neutrality with the Jukes and Cantor correction.
Results
Polymorphism of Pvs25
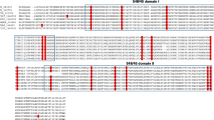
Pvs25 gene was successfully amplified in 324 P. vivax isolates, including seven from Dandong, 10 from Suining, 24 from Hainan, 24 from Nyingchi, 205 and 54 from Tengchong and Yingjiang, respectively. Compared to the reference Sal-I sequence, a variety of point mutations were found in pvs25 gene, which were all nonsynonymous. A total of 6 amino acid substitutions (D27N, Q87L, E97Q, T100S, I130T, and Q131K) in the Pvs25 protein were identified, which could be classified into 8 different haplotypes (Table 1; Fig. 1). A new amino acid substitution, D27N, was first detected in the first EGF-like domain (EGF-1). The amino acid substitutions of Q87L, E97Q, and T100S were found in the second EGF-like domain (EGF-2). The other two, I130T and Q131K, were detected in the third EGF-like domain (EGF-3). The amino acid substitution of I130T was a predominant variation with 100% prevalence in China (Table 1). Meanwhile, when compared the sequences of Chinese isolates using pv01 strain from Indonesia, both had 130 T mutation, which is common in Asia [19, 25]. Considering the geographical distribution, H5 (DQETTK) was the most common haplotype of Pvs25, accounting for 54.3% (Table 1). Two isolates from Tengchong showed the H2 (NQETTQ) and H8 (NQQTTK) haplotypes, respectively (Fig. 2). The H1 (DQETTQ) and H3 (DQQTTQ) were the most widely distributed haplotypes, both of which were found in all study sites. The haplotype H4 (DQESTQ) of Pvs25 was found in Yingjiang and Nyingchi each.
Polymorphism of Pvs28
A total of 272 P. vivax samples were successfully sequenced in pvs28 gene, including 6 from Dandong, 9 from Suining, 1 from Hainan, 5 from Nyingchi, 206 from Tengchong, and 45 from Yingjiang. Compared to the Sal-I sequence, a variety of 11 amino acid substitutions were identified, including M52L and A53V in EGF-1, T65K, A81T/V, G95N, L98I/S, and E105K in EGF-2, L116V, D125N, S131N, and T140S in EGF-3. Wild-type were only found in 8 isolates. Twenty-two haplotypes of Pvs28 were identified, which exhibited a greater polymorphic pattern than Pvs25 (Table 2; Fig. 1). The haplotype H9 was predominant, which accounted for 29%, with two amino acid substitutions at M52L and T140S. Moreover, H9 was the most widely distributed haplotype in five sites, except Hainan (Fig. 3). The haplotypes H5, H9, and H14 were associated with Nyingchi isolates (Fig. 1). Additionally, five haplotypes (H9, H11, H14, H17 and H19) were detected in Yingjiang, among which H19 was only found in this location. Two different types of amino acid substitutions were observed at A81T/V and L98I/S in Tengchong.
There was a range of 4–8 GSGGE/D repeats in Pvs28 (Table 2). One isolate with 7 copies of the GSGGE/D tandem repeats was found in the wild-type Pvs28. Samples from Dandong and Suining contained seven copies of the GSGGE/D tandem repeat, and were classified as haplotype H9. Both high (7–8) and low (4–5) copy numbers of tandem repeats were found in haplotypes H2 and H17, respectively, and both were found in Tengchong (Table 2; Fig. 3). A total of 215 (79.0%) isolates had six copies of the GSGGE/D tandem repeat at the end of the EGF-4 domain, which were consistent with the Sal-I strain.
Gene polymorphisms of pvs25 and pvs28
The genetic diversity of pvs25 and pvs28 genes were analyzed on both successfully sequenced samples (Tables 3, 4). The haplotype diversity (Hd) of Pvs25 and Pvs28 of all samples was 0.621 ± 0.021 and 0.485 ± 0.087, respectively. The average number of pvs25 nucleotide differences (K = 0.859) was lower than that of pvs28 (K = 1.679). The nucleotide diversity of pvs28 (π = 0.00305 ± 0.00061) was slightly higher; however, the difference was not significant compared to that of pvs25 (π = 0.00146 ± 0.00007) (P > 0.05). The number of dN in both Pvs28 and Pvs25 was higher than the number of dS. There was a positive Tajima’s D value for pvs25, which suggested that this gene was under balanced selection. In contrast, the Tajima's D value of pvs28 gene was negative, which was under purification selection. Both Tajima's D values deviate from 0, which indicated natural selection was likely to be involved. The K value of pvs25 gene ranged from 0.467 to 1.054, with a similar π value (Table 3); however, the values were not statistically significant (P > 0.05). The Tajima's D value of pvs28 gene in isolates form Yingjiang was negative, while Tengchong and Nyingchi were positive (Table 4). Only one haplotype was identified in sites of Dandong and Suining.
Discussion
The emergence of drug-resistant parasites is one major impediment to global malaria control and elimination [26]. The development of TBVs may play an important role in preventing the widespread global spread of drug-resistant parasites. Pvs25 and Pvs28 represent promising candidates for TBVs [27,28,29]. This study was firstly reporting the genetic diversity of the pvs25 and pvs28 genes of P. vivax isolates from different geographic sites in China.
The results showed that the polymorphism of Pvs25 appeared to be more limited than that of Pvs28, which was consistent with previous reports [13, 15, 17]. In addition, 6 and 11 amino acid substitutions were identified in the Pvs25 and Pvs28, respectively, and most of the amino acid substitutions were accumulated in the EGF-2 and EGF-3 domains. Different from previous studies in Yunnan Province of China [19], a new mutation D27N of Pvs25 was first detected in Tengchong. The haplotypes of Pvs25 were consistent with the variant isolates from Myanmar, Thailand, and India [10, 17, 18]. Compared with the Sal-I strain, a T100S mutation in the EGF-2 domain of Pvs25 and another D125N mutation in the EGF-3 domain of Pvs28 were first identified. In this study, the most significant variation in the Pvs28 was the number of GSGGE/D tandem repeats. Except 57 (21.0%) isolates identified in the tandem repeats of GSGGE/D ranged of 4–8, the left 215 (79.0%) isolates were same with the Sal-I strain. Different with other studies, four isolates containing 8 tandem repeats of GSGGE/D were first identified in Tengchong. Surprisingly, the haplotypes of Pvs28 were quite different between two close sites, Tengchong and Yingjiang of Yunnan Province. The causes might be the bias of samples sizes from two sites, as the samples size of Tengchong was almost four times of Yingjiang.
One of the major obstacles to vaccine development is the genetic polymorphisms in parasite populations. Different from antigens expressed in asexual parasites, TBVs candidate genes have limited polymorphism. [12, 30, 31]. Compared with Duffy binding protein (dbp: π = 0.0122 ± 0.0010) [32] and merozoite surface protein 1 (msp1: π = 0.1193 ± 0.0.0178) [33] in the blood stage of P. vivax, the nucleotide diversity of pvs25 (π = 0.00146 ± 0.00007) and pvs28 (π = 0.00305 ± 0.00061) were relatively lower in this study. In addition, the nucleotide diversity of the pvs25 and pvs28 genes was analogous to that reported in countries in Southeast Asia [18], which indicated that these two genes were relatively conserved in this region. The Tajima's D values for both pvs25 and pvs28 deviated from 0, suggesting that these antigens might be affected by natural selection. Therefore, it was speculated that the TBVs should play a similar blocking role in malaria control and elimination in Southeast Asia.
This study revealed the amino acid substitutions of these two vaccine candidate antigens in different geographic sites in China, and the genetic polymorphisms of pvs25 and pvs28 were similar to the findings from Thailand and Myanmar. These results gained insight into the genetic composition of the P. vivax population in Southeast Asia and provided useful information for the development of effective TBVs. Previous studies have shown that the specific amino acid substitutions in Pvs25 and Pvs28 can affect parasite fitness, resulting in reduced or altered vaccine efficacy in different geographical environments [34]. This is a major obstacle to vaccine efficacy. Thus, the analysis of the genetic diversity of these two antigens in different countries and regions had a great value for evaluating the efficacy of TBVs, as vaccines used in different regions of the world may require different formulations.
Conclusion
The key to vaccine design is to gain a comprehensive understanding of the genetic diversity of candidate antigens in different regions. P. vivax isolates from China demonstrated limited genetic diversity in the pvs25 and pvs28 genes, which could provide useful information for TBVs design and optimization.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets analyzed in this study are publicly available. DNA sequences of pvs25 and pvs28 genes were deposited in the NCBI database under GenBank accession number OP243722 to OP244045 and OP244076 to OP244347, respectively.
References
World Health Organization: World malaria report 2021. 2021.
Tsuboi T, Tachibana M, Kaneko O, Torii M. Transmission-blocking vaccine of vivax malaria. Parasitol Int. 2003;52(1):1–11.
Sauerwein RW. Malaria transmission-blocking vaccines: the bonus of effective malaria control. Microbes Infect. 2007;9(6):792–5.
Kaslow DC. Transmission-blocking vaccines. Chem Immunol. 2002;80:287–307.
Wu Y, Sinden RE, Churcher TS, Tsuboi T, Yusibov V. Development of malaria transmission-blocking vaccines: from concept to product. Adv Parasitol. 2015;89:109–52.
Grotendorst CA, Kumar N, Carter R, Kaushal DC. A surface protein expressed during the transformation of zygotes of Plasmodium gallinaceum is a target of transmission-blocking antibodies. Infect Immun. 1984;45(3):775–7.
Kaslow DC. Transmission-blocking vaccines: uses and current status of development. Int J Parasitol. 1997;27(2):183–9.
Kumar N, Carter R. Biosynthesis of two stage-specific membrane proteins during transformation of Plasmodium gallinaceum zygotes into ookinetes. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1985;14(2):127–39.
Hisaeda H, Stowers AW, Tsuboi T, Collins WE, Sattabongkot JS, Suwanabun N, Torii M, Kaslow DC. Antibodies to malaria vaccine candidates Pvs25 and Pvs28 completely block the ability of Plasmodium vivax to infect mosquitoes. Infect Immun. 2000;68(12):6618–23.
Sattabongkot J, Tsuboi T, Hisaeda H, Tachibana M, Suwanabun N, Rungruang T, Cao YM, Stowers AW, Sirichaisinthop J, Coleman RE, et al. Blocking of transmission to mosquitoes by antibody to Plasmodium vivax malaria vaccine candidates Pvs25 and Pvs28 despite antigenic polymorphism in field isolates. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2003;69(5):536–41.
Tsuboi T, Kaslow DC, Gozar MM, Tachibana M, Cao YM, Torii M. Sequence polymorphism in two novel Plasmodium vivax ookinete surface proteins, Pvs25 and Pvs28, that are malaria transmission-blocking vaccine candidates. Mol Med. 1998;4(12):772–82.
González-Cerón L, Alvarado-Delgado A, Martínez-Barnetche J, Rodríguez MH, Ovilla-Muñoz M, Pérez F, Hernandez-Avila JE, Sandoval MA, Rodríguez Mdel C, Villarreal-Treviño C. Sequence variation of ookinete surface proteins Pvs25 and Pvs28 of Plasmodium vivax isolates from Southern Mexico and their association to local anophelines infectivity. Infect Genet Evol. 2010;10(5):645–54.
Zakeri S, Razavi S, Djadid ND. Genetic diversity of transmission blocking vaccine candidate (Pvs25 and Pvs28) antigen in Plasmodium vivax clinical isolates from Iran. Acta Trop. 2009;109(3):176–80.
Tsuboi T, Kaneko O, Cao YM, Tachibana M, Yoshihiro Y, Nagao T, Kanbara H, Torii M. A rapid genotyping method for the vivax malaria transmission-blocking vaccine candidates, Pvs25 and Pvs28. Parasitol Int. 2004;53(3):211–6.
Han ET, Lee WJ, Sattabongkot J, Jang JW, Nam MH, An SS, Suh I, Lim CS. Sequence polymorphisms of Plasmodium vivax ookinete surface proteins (Pvs25 and Pvs28) from clinical isolates in Korea. Trop Med Int Health. 2010;15(9):1072–6.
Kang JM, Ju HL, Moon SU, Cho PY, Bahk YY, Sohn WM, Park YK, Cha SH, Kim TS, Na BK. Limited sequence polymorphisms of four transmission-blocking vaccine candidate antigens in Plasmodium vivax Korean isolates. Malar J. 2013;12:144.
Prajapati SK, Joshi H, Dua VK. Antigenic repertoire of Plasmodium vivax transmission-blocking vaccine candidates from the Indian subcontinent. Malar J. 2011;10:111.
Lê HG, Kang JM, Jun H, Lee J, Moe M, Thái TL, Lin K, Myint MK, Yoo WG, Sohn WM, et al. Genetic diversity and natural selection of transmission-blocking vaccine candidate antigens Pvs25 and Pvs28 in Plasmodium vivax Myanmar isolates. Acta Trop. 2019;198: 105104.
Feng H, Zheng L, Zhu X, Wang G, Pan Y, Li Y, Yang Y, Lin Y, Cui L, Cao Y. Genetic diversity of transmission-blocking vaccine candidates Pvs25 and Pvs28 in Plasmodium vivax isolates from Yunnan Province, China. Parasit Vectors. 2011;4:224.
Snounou G, Viriyakosol S, Zhu XP, Jarra W, Pinheiro L, do Rosario VE, Thaithong S, Brown KN. High sensitivity of detection of human malaria parasites by the use of nested polymerase chain reaction. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993;61(2):315–20.
Rozas J, Sánchez-DelBarrio JC, Messeguer X, Rozas R. DnaSP, DNA polymorphism analyses by the coalescent and other methods. Bioinformatics. 2003;19(18):2496–7.
Tajima F. Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics. 1989;123(3):585–95.
Nei M, Gojobori T. Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol Biol Evol. 1986;3(5):418–26.
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30(12):2725–9.
Escalante AA, Cornejo OE, Freeland DE, Poe AC, Durrego E, Collins WE, Lal AA. A monkey’s tale: the origin of Plasmodium vivax as a human malaria parasite. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102(6):1980–5.
Breman JG. The ears of the hippopotamus: manifestations, determinants, and estimates of the malaria burden. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2001;64(1–2 Suppl):1–11.
Malkin EM, Durbin AP, Diemert DJ, Sattabongkot J, Wu Y, Miura K, Long CA, Lambert L, Miles AP, Wang J, et al. Phase 1 vaccine trial of Pvs25H: a transmission blocking vaccine for Plasmodium vivax malaria. Vaccine. 2005;23(24):3131–8.
Wu Y, Ellis RD, Shaffer D, Fontes E, Malkin EM, Mahanty S, Fay MP, Narum D, Rausch K, Miles AP, et al. Phase 1 trial of malaria transmission blocking vaccine candidates Pfs25 and Pvs25 formulated with montanide ISA 51. PLoS ONE. 2008;3(7): e2636.
Saul A, Hensmann M, Sattabongkot J, Collins WE, Barnwell JW, Langermans JA, Wu Y, Long CA, Dubovsky F, Thomas AW. Immunogenicity in rhesus of the Plasmodium vivax mosquito stage antigen Pvs25H with Alhydrogel and Montanide ISA 720. Parasite Immunol. 2007;29(10):525–33.
Barry AE, Schultz L, Buckee CO, Reeder JC. Contrasting population structures of the genes encoding ten leading vaccine-candidate antigens of the human malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum. PLoS ONE. 2009;4(12): e8497.
Escalante AA, Lal AA, Ayala FJ. Genetic polymorphism and natural selection in the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Genetics. 1998;149(1):189–202.
Cole-Tobian J, King CL. Diversity and natural selection in Plasmodium vivax Duffy binding protein gene. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2003;127(2):121–32.
Putaporntip C, Jongwutiwes S, Sakihama N, Ferreira MU, Kho WG, Kaneko A, Kanbara H, Hattori T, Tanabe K. Mosaic organization and heterogeneity in frequency of allelic recombination of the Plasmodium vivax merozoite surface protein-1 locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99(25):16348–53.
Saxena AK, Singh K, Su HP, Klein MM, Stowers AW, Saul AJ, Long CA, Garboczi DN. The essential mosquito-stage P25 and P28 proteins from Plasmodium form tile-like triangular prisms. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006;13(1):90–1.
Acknowledgements
We thank all the participants who provided blood samples for this study.
Funding
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (No. 18ZR1443400).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FH conceived and designed the study. SW conducted the laboratory work and data analysis. SL, PT, and XG collected the blood samples. HL provided technique support for the data collection and analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Ethical Review Committee of National Institute of Parasitic Diseases, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. Research involving human participants, human material, or human data have been performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Informed written consent and/or assent with parental consent was obtained from all patients.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Tian, P., Li, S. et al. Genetic diversity of transmission-blocking vaccine candidate antigens Pvs25 and Pvs28 in Plasmodium vivax isolates from China. BMC Infect Dis 22, 944 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-022-07931-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-022-07931-0