Abstract
Background
Leaf color mutants have reduced photosynthetic efficiency, which has severely negative impacts on crop growth and economic product yield. There are different chlorophyll mutants in Arabidopsis and crops that can be used for genetic control and molecular mechanism studies of chlorophyll biosynthesis, chloroplast development and photoefficiency. Chlorophyll mutants in Brassica napus are mostly used for mapping and location research but are rarely used for physiological research. The chlorophyll-deficient mutant in this experiment were both genetically mapped and physiologically analyzed.
Results
In this study, yellow leaf mutant of Brassica napus L. mutated by ethyl methyl sulfone (EMS) had significantly lower chlorophyll a, b and carotenoid contents than the wild type, and the net photosynthetic efficiency, stomatal conductance and transpiration rate were all significantly reduced. The mutant had sparse chloroplast distribution and weak autofluorescence. The granule stacks were reduced, and the shape was extremely irregular, with more broken stromal lamella. Transcriptome data analysis enriched the differentially expressed genes mainly in phenylpropane and sugar metabolism. The mutant was mapped to a 2.72 Mb region on A01 by using BSA-Seq, and the region was validated by SSR markers.
Conclusions
The mutant chlorophyll content and photosynthetic efficiency were significantly reduced compared with those of the wild type. Abnormal chloroplasts and thylakoids less connected to the stroma lamella appeared in the mutant. This work on the mutant will facilitate the process of cloning the BnaA01.cd gene and provide more genetic and physiological information concerning chloroplast development in Brassica napus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Photosynthesis is crucial in crop production and provides energy and carbohydrates for plant vegetative and productive growth. Pigments capture light energy and convert it into the chemical energy ATP and NADPH, which are used for CO2 fixation to synthesize carbohydrates. The primary photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll (Chl.) in plants is responsible for light harvesting and drives electron transport in reaction centers [1]. Chl. biosynthesis begins with glutamate to Chl. a and Chl. b and includes 20 different enzyme reactions [2]. Most Chl. biosynthetic genes have been cloned and validated in plants [2, 3]. Furthermore, the expression of key plant Chl. biosynthetic genes is tightly and coordinately controlled by transcription factors, which respond to environmental factors, including light signals, hormonal levels and nutritional supplies [4]. Mutation of biosynthetic genes or associated transcription factors introduces Chl. content variation and malformed chloroplasts and impairs photosynthetic efficiency.
There are different chlorophyll mutants in Arabidopsis and crops that can be used for genetic control and molecular mechanism studies of Chl. biosynthesis, chloroplast development and photoefficiency. In Arabidopsis, more than 27 genes responsible for Chl. b synthesis starting from glutamyl-tRNA have been identified[2, 5]. More than 70 chlorophyll mutants exhibiting albino, chlorina, stripe, virescent, yellow–green and zebra leaves were identified in rice [6]. Jung et al. established T-DNA pools for rice mutants, and 189 lines showed a chlorophyll-deficient phenotype that segregated as a single recessive locus in the T2 generation[7]. Zhao et al. identified that HD domain-containing proteins affect chlorophyll biosynthesis and chloroplast development in the white stripe leaf3 mutant [8]. Zhang et al. identified an incompletely dominant gene located on chromosome 2BS flanked by the simple sequence repeat marker Xwmc25 responsible for yellow leaf color [9]. Transcriptome analysis of yellow leaf color in wheat indicated that DEGs were involved in Chl. biosynthesis, carotenoid biosynthesis, photosynthesis, and carbon fixation [10]. Chlorophyll deficiency was also detected in barley and wheat [11,12,13], maize [14,15,16,17], soybean [18,19,20,21,22] and cucumber [23, 24].
Oilseed rape, Brassica napus L., an amphidiploid species formed by the natural hybridization of two diploid progenitors, Brassica rapa (AA, 2n = 20) and Brassica oleracea (CC, 2n = 18), provides 13%–16% of vegetable oil for food and biofuel globally [25, 26]. Different locus mutations leading to chlorophyll deficiency in B. napus were identified. Zhu et al. mapped a chlorophyll-deficient mutant to C06, and 18 markers cosegregated with the mutant locus [27]. A dominant chlorophyll-deficient locus was mapped on chromosome C08 spanning a 0.9 cM interval with 22 genes in B. napus [28]. Chu et al., using iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomics analysis, identified 443 proteins related to photosynthesis, porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism, biosynthesis of secondary metabolites, and carbon fixation [29]. The Fv/Fm ratio, qP and electron transport rate in the chlorophyll b-deficient mutant were higher than those in the wild type according to chlorophyll fluorescence and thermoluminescence tests in the chlorophyll b-deficient mutant in B. napus [30]. A spontaneous mutant from Qingyou 10 caused by 2 recessive loci and one locus was mapped to A01 in B. napus [27]. The chlorophyll-deficient mutant Cr was introduced into male sterile lines, and the yellowish color was used as a phenotype marker to produce hybrid seeds [31].
In our research, we identified a chlorophyll-deficient mutant with yellow leaves by using ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS) treatment. The phenotype, photosynthetic characteristics, chloroplast anatomy and expression profile were investigated. Furthermore, the mutant locus was mapped on Chr. A01 by using BSA-Seq.
Results
The mutant showed reduced chlorophyll content and weak florescence
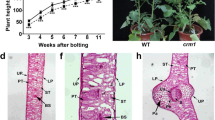
Compared with the wild type, the mutant leaf displayed a yellow color for the whole growth period (Fig. 1A, B). The mutant plants and seeds were smaller than those of the wild-type plants because of the reduced photosynthetic efficiency. Furthermore, only one-third of the mutant seeds germinated under the usual treatment. The F1 plants displayed a green leaf color, but the segregation did not fit the 3:1 ratio because of the impaired germination of the mutant seeds. The pigment content of the mutant was significantly lower than that of the wild type in fully expanded leaves (Table 1). Chlorophyll fluorescence kinetic tests indicated that the F0 and Fm in the mutant were weaker than those in the wild type, especially in the fully expanded leaf (Fig. 1C, D). There were no large differences in the remaining florescence characteristics between the mutant and wild type (Fig. 1E-H).
Phenotypic and chlorophyll fluorescence kinetics observations between the mutant type (Mut) and the wild type (WT) at the seedling stage. Note: A plants; B leaves. C to H show the fluorescence kinetics of Fo, Fm, Fv/Fm, ΦPSII, ETR, and Rfd, respectively. Top‚ WT; Bottom‚ Mut; Fo, initial fluorescence; Fm, maximum fluorescence; Fv/Fm, PSII maximum light energy conversion efficiency; Φ PSII, actual photochemical efficiency of PSII; ETR, apparent electron transfer efficiency; Rfd, fluorescence decay rate
The mutant had impaired chloroplast development
There were significant morphological and structural differences between the WT and the mutant. The chloroplasts in the WT were smooth and spindly in shape, with abundant and well-ordered thylakoids. The thylakoids were obviously connected by stromal lamella (Fig. 2 A, C). Compared with the WT, the chloroplast shape was less irregular and less connected between thylakoids (Fig. 2 B, D). Furthermore, there were more osmiophilic granules and smaller starch grains in the mutant than in the WT.
Chlorophyll and chlorophyll precursors were reduced in the mutant
The spectrophotometer method was used to determine the contents of chlorophyll and chlorophyll synthetic precursors in mutant and WT leaves. The mutant plant had significantly lower chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, total chlorophyll, and carotenoid contents than the wild type (Table 1). The contents of δ-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) and porphobilinogen (PBG) of chlorophyll synthetic precursors in the mutant were not significantly different from those in the WT. The contents of tetrapyrroles, such as protoporphyrin IX (Proto IX), magnesium protoporphyrin IX (Mg-proto IX), and prophytophyte chlorophyll (Pchlide), were significantly higher in the mutant than in the WT (Fig. 3). ALA and Pchlide were the early and later precursors in chlorophyll synthesis, respectively, suggesting that chlorophyll synthesis was impaired at the later step of Pchlide conversion into chlorophyll a.
The mutant had reduced photosynthetic ability
The net photosynthetic efficiency, stomatal conductance and transpiration rate were significantly reduced in the mutant, but the intercellular CO2 concentration was similar. The results indicate that the decrease in net photosynthetic efficiency was not due to a stomatal flaw, such as a decrease in stomatal conductance or an insufficient supply of CO2, but was instead due to the poor development of chloroplasts inside the mesophyll cells (Fig. 4).
The mutant locus was mapped on the A01 chromosome
BSA-Seq mapped the candidate gene at 2.72 Mb intervals between 3.36 and 6.07 Mb of chromosome A01 (Fig. 5A). Annotation in the candidate region was performed according to the B. napus cultivar Darmor-bzh reference genome (https://www.genoscope.cns.fr/brassicanapus/). A total of 502 genes were located in the candidate region, of which 277 genes contained mutated SNP sites that could cause changes in the protein sequence. SSR markers from 2.72 Mb were designed, and the mutant locus was mapped close to marker bna108 (Fig. 5 B).
Transcriptome analysis revealed DEGs related to the photosynthetic system
A total of 1273 differentially expressed genes were identified, of which 624 were upregulated and 649 were downregulated. Through KEGG analysis, it was found that the differentially expressed genes were mainly enriched in phenylpropane metabolism and sugar metabolism (Fig. 6). Among the differentially expressed genes related to the photosynthetic system, the expression of the BnaAnng22920D gene was severely reduced, and the expression levels of the BnaC02g42890D and BnaCnng19490D genes were both reduced to zero (Table 2). These genes encode the apoprotein Lhcb that binds to photosynthetic system I (PSI I), important constituent subunits of photosystem I reaction center subunit N (PSAN) and photosystem I reaction center subunit F (PSAF). The qRT–PCR results of the DEGs are shown in Fig. 7. The up- and downregulated genes are listed in supplementary files 2 and 3, respectively.
Discussion
In our study, we mapped the mutant locus in Chr. A01, and the plant leaf remained yellow throughout the growth stage. BnaC.ygl had yellow green leaves, but the color changed to green at later stages, and the mutant locus was mapped to Chr. C06 [27]. A single dominant leaf color mutant was mapped to Chr. C08 [28]. A yellow-virescent gene regulating chlorophyll biosynthesis was mapped to A03, which was controlled by a single recessive nuclear gene [39]. BnChd1-1, one of the two recessive loci involved in chlorophyll biosynthesis in B. napus, was mapped to A01 [40]. Compared with the former mapped leaf color mutant in B. napus, our mutant was mapped to A01, the same chromosome of BnChd1-1, but the BnaA01.cd leaf color was more obvious than that of the WT, and there was no curl up in the adult leaf. Brassica napus is an allotetraploid, and it is difficult to derive a phenotype mutant because there are more gene family members than in diploid crops. Currently, there are fewer leaf color mutants in B. napus than in rice; thus, our mutant line and work will enrich leaf mutant resources, which will facilitate chloroplast development research.
Chlorosis is a phenotype of yellowish or light green leaf color and can be a genetic mutation or a sign of nutritional deficiency. The genetic mutation causing chlorosis in B. napus might only occur in the seedling stage or during the whole growth stage. All chlorosis showed reduced Chl. content and impaired light energy absorption during photosynthesis. Chlorophyll synthesis starts from the precursor glutamyl-tRNA, branched at protoIX. Magnesium chelatase, the key enzyme in this pathway, inserts magnesium atoms into protoIX synthesis, the direct precursor of Chl. a and Chl. b. In our chlorophyll synthetic precursor test, the contents of δ-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) and porphobilinogen (PBG) showed no significant difference between the mutant and WT, but the contents of Proto IX, Mg-proto IX, and Pchlide were significantly higher in the mutant. The accumulation of Proto IX, Mg-proto IX, and Pchlide not only impairs chlorophyll synthesis but might also increase ROS production under light illumination, which would be toxic for chlorophyll development [41, 42]. In the mutant, the chloroplast structure was dramatically changed, including an oval shape, fewer stromal lamellae and thylakoids, and more osmiophilic granules. These changes occurred in senescent leaves. In the moth orchid leaf mutant, the green leaf sector with typical chloroplasts, including well-organized thylakoids and starch grains, but the yellow leaf area with poor developed plastids and more osimiophilic granules [43]. There are more grana in the yellow-white leaf at advanced senescence compared with leaf for 6 days regreening [44]. In rice early senescence 2 (es2) mutant, more osmiophilic granules (OG) were found in es2 compared to wild type [45]. The SEM observations indicate that the mutant chloroplasts from young leaves might be in the senescence state.
BSA-Seq mapped BnaA01.cd in A01, spanning a 2.72 Mb region, which included approximately 277 genes with SNPs. For candidate gene identification, more studies are needed for large population construction. The transcriptome data provide information about the leaf expression profile, which explains the phenotype and functional changes in the mutant. The DEGs were enriched in phenylpropane metabolism and the sugar synthetic system. The gene BnaAnng22920D, homologous to AT1G29930, encoding chlorophyll A/B-binding protein 1 (CAB1), was significantly downregulated. CAB1 binds chlorophyll from the LCHP complex [46], and CAB1 reduction leads to free chlorophyll degradation [47]. Furthermore, a reduction in the LCHP complex will indirectly influence thylakoid membrane structure and state transition. Two strongly downregulated genes, BnaC02g42890D and BnaCnng19490D, homologous to AT5G64040 and AT1G31330, encode the proteins PSAN and PSAF, respectively. PSAN functions in mediating the binding of the antenna complexes to the PSI reaction center and the core antenna, docking plastocyanin to the PSI complex [48]. PSAF participates in the efficiency of electron transfer from plastocyanin to P700 [49]. The above protein reduction will impair electron transfer and energy transition.
Conclusions
A mutant exhibiting chlorophyll deficiency was identified in B. napus, and the mutant locus was mapped on A01 in the 2.72 Mb region. The mutant chlorophyll content and photosynthetic efficiency were significantly reduced compared with those of the wild type. Abnormal chloroplasts and thylakoids less connected to the stroma lamella appeared in the mutant. This work on the mutant will provide more genetic and physiological information concerning chloroplast development in B. napus.
Methods
Plant materials
A chlorophyll-deficient mutant (B. napus chlorophyll deficient, BnaA01.cd) was screened from the EMS-mutated population. The mutant population was constructed from the inbreed line Zhongshuang11 (ZS11), and seeds were soaked in 1% EMS solution for 12 h. A mutant with yellow leaves was identified in the M2 generation and selfed for phenotype validation and crossing in the next generation. The inbred lines ZS11 and BnaA01.cd were used for phenotype comparison. Field growth was the same as usual.
Kinetic chlorophyll fluorescence imaging
Plants grown in climate chambers until the 7-leaf stage were used for fluorescence imaging. Chlorophyll fluorescence imaging was performed using a FluorCam PlantScreen™ phenotyping system (Photon Systems Instruments, Czech Republic). Actinic light at 150 μmol of photons·m−2·s−1 and saturating pulse intensity at 100% were applied to 16-h dark-adapted plants. The chlorophyll fluorescence levels of the wild-type and mutant plants were imaged based on the parameters F0, Fm, Fv/Fm, PSII, ETR and Rfd.
Transmission electron microscopy
Leaf samples of wild-type ZS11 and mutant BnaA01.cd from the bolting stage were prepared by transmission electron microscopy. Leaves were cut into 0.5 × 0.5 cm sections and fixed in 2.5% (w/v) glutaraldehyde in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) at 4 ºC for 4 h. Samples were further fixed in 1% OsO4 using the same buffer for 12 h. Ultrathin sections of the samples and transmission electron microscopy observations were performed according to Yi et al. [32].
Chlorophyll and precursor content determination
Fresh leaves of ZS11 and BnaA01.cd mutant plants were sampled from the bolting stage and used to measure chlorophyll content according to the method described by Wu et al. [33]. The same leaf was used for the 5 precursor content determinations. The precursor δ-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) content was extracted and measured following Dei [34]. The determination of bilirubin (PBG) was performed according to [35]. The Proto IX, Mg-Proto IX, and Pchlide precursors were extracted and measured according to the methods described by Rebeiz et al. [36].
Photosynthetic performance test
The leaves from the bolting stage were used for net photosynthetic efficiency, stomatal conductance, transpiration rate and intercellular CO2 concentration tests using an LI-6400 (LI-6400, Li-Cor, Lincoln, NE) according to the manual. Measurements were conducted at a saturating light intensity of 1,500 μmol photons m−2 s−1, with an air flow of 500 μmol air s−1 and a fixed flux of 400 μmol CO2 mol−1 air. Each genotype with 10 plants and 3 fully expanded leaves was measured for each plant on a sunny day at noon, and the mean value was used for data analysis.
BSA-Seq and SSR mapping
A cross was made between Z300 (line with normal green leaf) and the BnaA01.cd to create F1 plants which were subsequently selfed to create a F2 population with 322 plants. The yellow and green leaf bulks were prepared from the segregated F2 population, each containing 15 plants with distinctive leaf color. The two parents and two DNA bulks were sent to GENOSEQ (Wuhan, China) for BSA-Seq. Sequence library construction and SNP calling were performed as described by Zhao et al. [37].
Based on the BSA-Seq interval, 64 SSR primer pairs were developed to confirm the BSA-Seq mapped region. The SSR loci were searched by the Tandem repeats finder [38] with a maximum of 6-bp motifs and a minimum of 3 repeats, and the polymorphic SSR primers are provided in supplementary file 1. The test was performed by standard PCR with primer pair-specific annealing temperature followed by PAGE gel electrophoresis.
RNA extraction and transcriptome analysis
The yellow and green leaves from mutant and wild-type plants at the bolting stage were sampled for RNA extraction and cDNA library construction, with two biological repeats. The leaves were kept in liquid nitrogen for immediate RNA extraction. Total RNA was extracted using TRIzol Reagent and treated with RNase-free DNase I. cDNA library construction and sequencing on the Illumina HiSeq 4000 platform were performed by Biomarker Technologies (Beijing, China). After the removal of low-quality reads, the clean reads were aligned to the B. napus reference genome. Fragments per kilobase million (FPKM) values were calculated to estimate gene expression levels. FDR < 0.001 and fold change ≥ 4 were used to assess the significance of differences in gene expression. qRT–PCR primers were designed using Primer Premier 5 and synthesized by Sangon Biotech (Shanghai) Co. qRT–PCR was performed using a Bio–Rad CFX96 Real-time System with SYBR® Green PCR Supermix (CA, USA) in triplicate. BnActin7 was used as a control. Each reaction included 10 µl SYBR ® Green PCR Supermix, 0.4 µL primer F, 0.4 µL primer R, 7.2 µL ddH2O, and 2 µL cDNA template.
Availability of data and materials
All data are presented in the main manuscript and the additional supporting files.
The Kanehisa laboratory have provided us permission of The KEGG pathway database from www.kegg.jp/feedback/copyright.html [50]. KOBAS software was used to test the statistical enrichment of differential expression genes in KEGG pathways [51]. ZS11 was kindly provided by Dr. Jiaqin Shi, oil crop research institute, CAAS, Wuhan, China.
References
Tanaka A, Tanaka R. Chlorophyll metabolism. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2006;9(3):248–55.
Nagata N, Tanaka R, Satoh S, Tanaka A. Identification of a vinyl reductase gene for chlorophyll synthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana and implications for the evolution of Prochlorococcus species. Plant Cell. 2005;17(1):233–40.
Beale SI. Green genes gleaned. Trends Plant Sci. 2005;10(7):309–12.
Kobayashi K, Masuda T. Transcriptional control for the chlorophyll metabolism. Adv Bot Res. 2019;91:133–61.
Nagata N, Tanaka R, Tanaka A. The major route for chlorophyll synthesis includes [3,8-divinyl]-chlorophyllide a reduction in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2007;48(12):1803–8.
Kurata N, Miyoshi K, Nonomura K, Yamazaki Y, Ito Y. Rice mutants and genes related to organ development, morphogenesis and physiological traits. Plant Cell Physiol. 2005;46(1):48–62.
Jung KH, Hur J, Ryu CH, Choi Y, Chung YY, Miyao A, Hirochika H, An GH. Characterization of a rice chlorophyll-deficient mutant using the T-DNA gene-trap system. Plant Cell Physiol. 2003;44(5):463–72.
Zhao SL, Long WH, Wang YH, Liu LL, Wang YL, Niu M, Zheng M, Wang D, Wan JM. A rice White-stripe leaf3 (wsl3) mutant lacking an HD domain-containing protein affects chlorophyll biosynthesis and chloroplast development. J Plant Biol. 2016;59(3):282–92.
Zhang LL, Liu C, An XY, Wu HY, Feng Y, Wang H, Sun DJ. Identification and genetic mapping of a novel incompletely dominant yellow leaf color gene, Y1718, on chromosome 2BS in wheat. Euphytica. 2017;213(7):1–11.
Wu HY, Shi NR, An XY, Liu C, Fu HF, Cao L, Feng Y, Sun DJ, Zhang LL. Candidate Genes for Yellow Leaf Color in Common Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and Major Related Metabolic Pathways according to Transcriptome Profiling. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(6):1594.
Yaronskaya E, Ziemann V, Walter G, Averina N, Borner T, Grimm B. Metabolic control of the tetrapyrrole biosynthetic pathway for porphyrin distribution in the barley mutant albostrians. Plant J. 2003;35(4):512–22.
Mueller AH, Dockter C, Gough SP, Lundqvist U, von Wettstein D, Hansson M. Characterization of Mutations in Barley fch2 Encoding Chlorophyllide a Oxygenase. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012;53(7):1232–46.
Falbel TG, Staehelin LA. Characterization of a Family of Chlorophyll-Deficient Wheat (Triticum) and Barley (Hordeum-Vulgare) Mutants with Defects in the Magnesium-Insertion Step of Chlorophyll Biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 1994;104(2):639–48.
Guan HY, Xu XB, He CM, Liu CX, Liu Q, Dong R, Liu TS, Wang LM. Fine Mapping and Candidate Gene Analysis of the Leaf-Color Gene ygl-1 in Maize. PLoS ONE. 2016;11(4):1–19.
Li TC, Yang HY, Lu Y, Dong Q, Liu GH, Chen F, Zhou YB. Comparative transcriptome analysis of differentially expressed genes related to the physiological changes of yellow-green leaf mutant of maize. PeerJ. 2021;9(1):e10567.
Greene BA, Staehelin LA, Melis A. Compensatory Alterations in the Photochemical Apparatus of a Photoregulatory, Chlorophyll-B-Deficient Mutant of Maize. Plant Physiol. 1988;87(2):365–70.
Bazzaz MB. New Chlorophyll Chromophores Isolated from a Chlorophyll-Deficient Mutant of Maize. Photobioch Photobiop. 1981;2(4–5):199–207.
Campbell BW, Mani D, Curtin SJ, Slattery RA, Michno JM, Ort DR, Schaus PJ, Palmer RG, Orf JH, Stupar RM. Identical Substitutions in Magnesium Chelatase Paralogs Result in Chlorophyll-Deficient Soybean Mutants. G3-Genes-Genom Genet. 2015;5(1):123–31.
Shiroshita Y, Yuhazu M, Hase Y, Yamada T, Abe J, Kanazawa A. Characterization of chlorophyll-deficient soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] mutants obtained by ion-beam irradiation reveals concomitant reduction in isoflavone levels. Genet Resour Crop Ev. 2021;68(3):1213–23.
Du HY, Qi MZ, Cui XP, Cui YM, Yang H, Zhang JY, Ma YJ, Zhang SS, Zhang X, Yu DY. Proteomic and functional analysis of soybean chlorophyll-deficient mutant cd1 and the underlying gene encoding the CHLI subunit of Mg-chelatase. Mol Breeding. 2018;38(6):71.
Sakowska K, Alberti G, Genesio L, Peressotti A, Delle Vedove G, Gianelle D, Colombo R, Rodeghiero M, Panigada C, Juszczak R, et al. Leaf and canopy photosynthesis of a chlorophyll deficient soybean mutant. Plant Cell Environ. 2018;41(6):1427–37.
Zhang H, Zhang D, Han S, Zhang X, Yu D. Identification and gene mapping of a soybean chlorophyll-deficient mutant. Plant Breeding. 2011;130(2):133–8.
Gao ML, Hu LL, Li YH, Weng YQ. The chlorophyll-deficient golden leaf mutation in cucumber is due to a single nucleotide substitution in CsChlI for magnesium chelatase I subunit. Theor Appl Genet. 2016;129(10):1961–73.
Burnham M, Phatak SC, Peterson CE. Graft-Aided Inheritance Study of a Chlorophyll Deficient Cucumber. P Am Soc Hortic Sci. 1966;89(9):386–92.
Lohani N, Jain D, Singh MB, Bhalla PL. Engineering Multiple Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Canola Brassica napus. Front Plant Sci. 2020;11(3):1–26.
Song JM, Guan ZL, Hu JL, Guo CC, Yang ZQ, Wang S, Liu DX, Wang B, Lu SP, Zhou R, et al. Eight high-quality genomes reveal pan-genome architecture and ecotype differentiation of Brassica napus. Nat Plants. 2020;6(1):34–45.
Zhu LX, Zeng XH, Chen YL, Yang ZH, Qi LP, Pu YY, Yi B, Wen J, Ma CZ, Shen JX, et al. Genetic characterisation and fine mapping of a chlorophyll-deficient mutant (BnaC.ygl) in Brassica napus. Mol Breeding. 2014;34(2):603–14.
Wang YK, He YJ, Yang M, He JB, Xu P, Shao MQ, Chu P, Guan RZ. Fine mapping of a dominant gene conferring chlorophyll-deficiency in Brassica napus. Sci Rep-Uk. 2016;6(1):31419.
Chu P, Yan GX, Yang Q, Zhai LN, Zhang C, Zhang FQ, Guan RZ. iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomics analysis of Brassica napus leaves reveals pathways associated with chlorophyll deficiency. J Proteomics. 2015;113:244–59.
Guo JW, Gu JK, Zhao YR, Du LF. Changes of photosystem II electron transport in the chlorophyll-deficient oilseed rape mutant studied by chlorophyll fluorescence and thermoluminescence. J Integr Plant Biol. 2007;49(5):698–705.
Zhao Y, Wang ML, Zhang YZ, Du LF, Pan T. A chlorophyll-reduced seedling mutant in oilseed rape, Brassica napus, for utilization in F-1 hybrid production. Plant Breeding. 2000;119(2):131–5.
Yi B, Zeng FQ, Lei SL, Chen YN, Yao XQ, Zhu Y, Wen J, Shen JX, Ma CZ, Tu JX, et al. Two duplicate CYP704B1-homologous genes BnMs1 and BnMs2 are required for pollen exine formation and tapetal development in Brassica napus. Plant J. 2010;63(6):925–38.
Wu ZM, Zhang X, He B, Diao LP, Sheng SL, Wang JL, Guo XP, Su N, Wang LF, Jiang L, et al. A chlorophyll-deficient rice mutant with impaired chlorophyllide esterification in chlorophyll biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 2007;145(1):29–40.
Dei M. Benzyladenine-Induced Stimulation of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid Accumulation under Various Light Intensities in Levulinic Acid-Treated Cotyledons of Etiolated Cucumber. Physiol Plantarum. 1985;64(2):153–60.
Rawal R, Kharangarh PR, Dawra S, Tomar M, Gupta V, Pundir CS. A comprehensive review of bilirubin determination methods with special emphasis on biosensors. Process Biochem. 2020;89:165–74.
Rebeiz CA, Mattheis JR, Smith BB, Rebeiz CC, Dayton DF. Chloroplast Biogenesis - Biosynthesis and Accumulation of Protochlorophyll by Isolated Etioplasts and Developing Chloroplasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975;171(2):549–67.
Zhao B, Wang B, Li ZH, Guo T, Zhao JW, Guan ZL, Liu KD. Identification and characterization of a new dwarf locus DS-4 encoding an Aux/IAA7 protein in Brassica napus. Theor Appl Genet. 2019;132(5):1435–49.
Benson G. Tandem repeats finder: a program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999;27(2):573–80.
Zhao CJ, Liu LJ, Safdar LB, Xie ML, Cheng XH, Liu YY, Xiang Y, Tong CB, Tu JX, Huang JY, et al. Characterization and Fine Mapping of a Yellow-Virescent Gene Regulating Chlorophyll Biosynthesis and Early Stage Chloroplast Development in Brassica napus. G3-Genes Genom Genet. 2020;10(9):3201–11.
Zhao H, Yu L, Huai ZX, Wang XH, Ding GD, Chen SS, Li P, Xu FS. Mapping and candidate gene identification defining BnChd1-1, a locus involved in chlorophyll biosynthesis in Brassica napus. Acta Physiol Plant. 2014;36(4):859–70.
op den Camp RGL, Przybyla D, Ochsenbein C, Laloi C, Kim CH, Danon A, Wagner D, Hideg E, Gobel C, Feussner I, et al. Rapid induction of distinct stress responses after the release of singlet oxygen in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2003;15(10):2320–32.
Kim CH, Apel K. Singlet oxygen-mediated signaling in plants: moving from flu to wild type reveals an increasing complexity. Photosynth Res. 2013;116(23):455–64.
Tsai CC, Wu YJ, Sheue CR, Liao PC, Chen YH, Li SJ, Liu JW, Chang HT, Liu WL, Ko YZ, et al. Molecular Basis Underlying Leaf Variegation of a Moth Orchid Mutant (Phalaenopsis aphrodite subsp formosana). Front Plant Sci. 2017;8:1333.
Zavaleta-Mancera HA, Thomas BJ, Thomas H, Scott IM. Regreening of senescent Nicotiana leaves II. Redifferentiation of plastids. J Exp Bot. 1999;50(340):1683–9.
Yang SL, Fang GN, Zhang AP, Ruan BP, Jiang HZ, Ding SL, Liu CL, Zhang Y, Jaha N, Hu P, et al. RiceEARLY SENESCENCE 2, encoding an inositol polyphosphate kinase, is involved in leaf senescence. Bmc Plant Biol. 2020;20(1):393.
Kusaba M, Ito H, Morita R, Iida S, Sato Y, Fujimoto M, Kawasaki S, Tanaka R, Hirochika H, Nishimura M, et al. Rice NON-YELLOW COLORING1 is involved in light-harvesting complex II and grana degradation during leaf senescence. Plant Cell. 2007;19(4):1362–75.
Peng G, Xie XL, Jiang Q, Song S, Xu CJ. Chlorophyll a/b binding protein plays a key role in natural and ethylene-induced degreening of Ponkan (Citrus reticulata Blanco). Sci Hortic-Amsterdam. 2013;160:37–43.
Haldrup A, Naver H, Scheller HV. The interaction between plastocyanin and photosystem I is inefficient in transgenic Arabidopsis plants lacking the PSI-N subunit of photosystem I. Plant J. 1999;17(6):689–98.
Haldrup A, Simpson DJ, Scheller HV. Down-regulation of the PSI-F subunit of photosystem I (PSI) in Arabidopsis thaliana - The PSI-F subunit is essential for photoautotrophic growth and contributes to antenna function. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(40):31211–8.
Kanehisa M, Araki M, Goto S, Hattor M, Hirakawa M, et al. KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:D480–4.
Mao X, Cai T, Olyarchuk JG, Wei L. Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the KEGG Orthology (KO) as a controlled vocabulary. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:3787–93.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the reviewers and editors for their constructive review and suggestions for this paper.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31971902, 32001509), and The R&D Key Project of ShanXi Province: High quality and yield ornamental rapeseed germplasm innovation and breeding (2020NY-057).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.Z.L. and J.M.Y. designed this research. N. L., Y.M.G., and X.K.P. performed the experiments, analyzed the data.Y.M.G.undertook the formal identification of the plant material. N.L. wrote the main manuscript. J.N.L. provided experimental materials. J.M.Y. provided experimental conditions. Q.Y. Z. provided suggestions for the article. All authors reviewed the manuscript. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.
Experimental research on plants (either cultivated or mutant) including collection of plant material complied with the IUCN Policy Statement on Research Involving Species at Risk of Extinction and the Convention on the Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora.
Permissions of collecting Plant Brassica napus L.(wild-type ZS11 and mutant BnaA01.cd) were obtained from Oil Crops Research Institute of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, and these specimens should be deposited in College of Agricultural and Biotechnology of Southwest University.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1. Table S1.
Polymorphic SSR primers in the BSA-Seq region.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, N., Gao, Y., Zhou, Q. et al. Genetic mapping and physiological analysis of chlorophyll-deficient mutant in Brassica napus L. BMC Plant Biol 22, 244 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-022-03630-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-022-03630-9