Abstract
Background
APETALA2/ethylene responsive factor (AP2/ERF) transcription factors are a plant-specific family of transcription factors and one of the largest families of transcription factors. Ethylene response factors (ERF) regulate plant growth, development, and responses to biotic and abiotic stress. In a previous study, the ERF2 gene was significantly upregulated in both resistant and susceptible tomato cultivars in response to Stemphylium lycopersici. The main purpose of this study was to systematically analyze the ERF family and to explore the mechanism of ERF2 in tomato plants resisting pathogen infection by the Virus-induced Gene Silencing technique.
Results
In this experiment, 134 ERF genes were explored and subjected to bioinformatic analysis and divided into twelve groups. The spatiotemporal expression characteristics of ERF transcription factor gene family in tomato were diverse. Combined with RNA-seq, we found that the expression of 18 ERF transcription factors increased after inoculation with S. lycopersici. In ERF2-silenced plants, the susceptible phenotype was observed after inoculation with S. lycopersici. The hypersensitive response and ROS production were decreased in the ERF2-silenced plants. Physiological analyses showed that the superoxide dismutase, peroxidase and catalase activities were lower in ERF2-silenced plants than in control plants, and the SA and JA contents were lower in ERF2-silenced plants than in control plants after inoculation with S. lycopersici. Furthermore, the results indicated that ERF2 may directly or indirectly regulate Pto, PR1b1 and PR-P2 expression and enhance tomato resistance.
Conclusions
In this study, we identified and analyzed members of the tomato ERF family by bioinformatics methods and classified, described and analyzed these genes. Subsequently, we used VIGS technology to significantly reduce the expression of ERF2 in tomatoes. The results showed that ERF2 had a positive effect on tomato resistance to S. lycopersici. Interestingly, ERF2 played a key role in multiple SA, JA and ROS signaling pathways to confer resistance to invasion by S. lycopersici. In addition, ERF2 may directly or indirectly regulate Pto, PR1b1 and PR-P2 expression and enhance tomato resistance to S. lycopersici. In summary, this study provides gene resources for breeding for disease resistance in tomato.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Tomatoes are susceptible to various diseases that severely affect yield and quality. Gray leaf spot caused by S. lycopersici is one of the most devastating fungal diseases worldwide in tomato. However, plants have developed an elaborate signaling network to resist the invasion of pathogens by activating the expression of a series of resistance genes. In addition, transcription factors (TFs) play essential roles in regulating the expression of specific resistance-related genes in various defense response pathways. Ethylene responsive factors (ERF) belong to a subfamily of the AP2/ERF superfamily in plants. The ERF family is defined by the presence of a conserved ERF domain consisting of 58 or 59 amino acids containing an N-terminal, a three-stranded β-sheet, and a C-terminal α-helix. This family is widely involved in the regulation of plant development as well as in responses to abiotic and biotic stresses. To date, some members of the ERF family have been studied. Previous studies have identified ERF genes (Pti4/5/6 gene) that could bind to pathogenesis-related Pto protein kinases [1]. For instance, the overexpression of Arabidopsis Pti4 could enhance resistance to Pseudomonas invasion by regulating the expression of GCC box-containing genes [2, 3]. At the same time, Pti5 was isolated in previous studies of its physical interaction with the serine-threonine kinase encoded by the Pto gene [1]. Furthermore, a previous study indicated that overexpression of tomato ERF2 could enhance basal resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato [4].
APETALA2/ethylene responsive factor (AP2/ERF) transcription factors are a plant-specific family of transcription factors and one of the largest families of transcription factors. These transcription factors have a significant impact on plant growth and physiological activities and even affect evolution [5]. The three subfamilies AP2, ERF, and RAV constitute the AP2 superfamily, which contains more ERF family members than other subfamilies. The AP2 gene was first isolated in Arabidopsis and found to regulate flower development [6], and then the AP2 domain was detected in bacterial and viral HNH endonucleases [7]. Subsequently, ERF was discovered in tobacco and found to be present in four ethylene response binding proteins isolated from tobacco, namely, ERF1, 2, 3 and 4 [8]. ERF family proteins contain only one conserved domain, AP2, with 60 to 70 amino acid residues, and ERF can be divided into two subfamilies, ERF and CBF/DREB, according to differences in conserved amino acid residues and binding sequences. The DNA binding domain of the ERF subfamily specifically binds to the cis-acting element GCC-box with a conserved sequence of AGCCGCC [9, 10]. The ability of ERF to exert a positive or negative influence on the functional expression of downstream genes is based on the nucleotides in the GCC-box environment [11]. The DREBA subfamily can recognize the drought-induced element DRE (TACCGACAT) and the low-temperature-induced element CRT (AGCCGAC) [12], participate in the ethylene signaling pathway, and help plants resist the effects of stress [13, 14].
Salicylic acid (SA), ethylene (ET), and jasmonic acid (JA) have been identified as signaling molecules that play key roles in various defense response pathways. The SA pathway is antagonistic to the ET/JA pathway; however, Pti4 and AtERF1 are induced by SA as well as by the JA/ET pathway [15, 16]. Moreover, studies have shown that Pti4, Pti5 and Pti6 could indirectly regulate the SA response by interacting with other TFs in Arabidopsis [3]. ERF TFs were shown to regulate the expression of PR genes by binding to GCC (AGCCGCC) box-containing genes in their promoter regions [17]. Previously, Pti4/5/6 was shown to interact with the Pto gene and bind the GCC box to activate the expression of PR genes in the plant defense response to pathogens [1].
In this study, PlantTFDB was used to identify and analyze the 134 ERF transcription factor families in tomatoes, including their physical and chemical properties, evolutionary grouping, conserved motifs, gene structure, chromosome positions, protein tertiary structure, and tissue-specific expression. To further examine the role of the ERF2 gene in the resistance to S. lycopersici in tomato, we used virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) to downregulate ERF2 gene expression in resistant tomato plants. In addition, we identified the potential signaling regulatory networks in which ERF2 participates in resistance to S. lycopersici. In this study, we aimed to identify the role of ERF2 in the response to S. lycopersici to provide a theoretical basis for cultivating resistant tomato varieties.
Results
Identification and analysis of the physical and chemical properties of ERF transcription factors
A total of 137 tomato ERF genes were confirmed with the SMART (http://smart.emblheidelberg.de/smart/batch.pl) and CDD (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/bwrpsb/bwrpsb.cgi) online tools. Genes without complete AP2/ERF domains were discarded. Finally, 134 transcription factors were screened. As shown in Supplementary Table 1, the longest sequence and the heaviest molecular weight were observed for Solyc04g071770.2.1, at 452 aa and 49,582.81, respectively; the shortest sequence and the lightest molecular weight were observed for Solyc10g080310.1.1, at 73 aa and 8382.60, respectively. The isoelectric point ranged from 4.09 (Solyc10g076380.1.1) to 10.08 (Solyc10g080310.1.1). The instability coefficient ranged from 21.51 (Solyc12g038450.1.1) to 86.25 (Solyc01g090340.2.1). Among the transcription factors, members Solyc03g093530.1.1, Solyc06g050520.1.1, Solyc06g063070.2.1, Solyc10g080310.1.1, Solyc10g080650.1.1, Solyc12g038440.1.1, and Solyc12g038450.1.1 all had instability coefficients below 40, indicating that they were more stable than the others. The total average hydrophilicity ranged from − 1.122 (Solyc06g068830.1.1) to − 0.303 (Solyc03g006320.1.1), indicating hydrophilic proteins.
Phylogenetic tree of ERF transcription factors
A total of 134 tomato ERF transcription factors and 122 Arabidopsis ERF genes were combined to construct a comprehensive phylogenetic tree. According to the grouping by conserved domain and the grouping of ERF family genes in Arabidopsis, the tomato and Arabidopsis ERF transcription factor genes in this experiment were divided into 12 groups (Fig. 1). Among these groups, groups A, B, C and D contained members of the CBF/DRBE ERF subfamily, corresponding to A6, A5, A1/A4 and A2 in the Arabidopsis group, respectively. There were no A3-subfamily genes in the ERF family of tomato, proving that there were no genes with a structure and function similar to those of AT2g40220.1 in tomato. In previous studies, 12 ERF genes were classified into group B6 in Arabidopsis thaliana [18, 19]. Based on motif analysis, B6 genes were divided into three groups. Therefore, in this experiment, B6 was divided into three groups (E, K, and L) as suggested by previous research, and there were no tomato ERF genes in group L. Groups F, G, H, I, and J corresponded to the B5, B2, B1, B3, and B4 groups in Arabidopsis, respectively. A total of 43 genes belonged to the CBF/DRBE subfamily, and 92 genes belonged to the ERF subfamily. Group I contained the most tomato ERF genes, with 35.
Conserved motif analysis and gene structural analysis of ERF transcription factors
To understand the specific distribution of conserved motifs of tomato ERF genes, 20 conserved motifs were identified by the online MEME analysis tool (http://meme-suite.org/). The logos of the 20 conserved motifs found are shown in the figure, and their position information in each subgroup is shown in Fig. 2A-a. On average, each member contained 4 motifs, and Solyc11g006050.1.1 had the largest number of motifs, which was 7 (Fig. 2A-b). The results showed that the conserved AP2 domains constituted by motifs 1, 2 and 3 were the most conserved in the sequences of tomato ERF transcription factors, which together with other conserved elements contributed to the diversity and identity of the genes. Among these transcription factors, 18 members of the C, B, D, E and H subgroups lacked motif 2. Similarly, most genes of subgroups B, D, J and I contain motif 15. Motif 5 was detected in groups C and B. Motif 6 appeared in members of subgroups C, D, and I and was conserved at the C-terminus of the protein sequence. In both groups F and K, motif 7 was identified as conserved at the N-terminus of the sequence. Motifs 8/9/12/16/20 were unique to the C/J/D/G/E group. Group I had the most members and, correspondingly, the most characteristic motif, motif 10/11/13/14/17. The results show that the members of the same subgroup are similar in rank and position, and the unique conserved motifs in different subgroups also enhance the support of the phylogenetic tree. The distribution of the conserved structural domain of the tomato ERF family is shown in Fig. 2A-c. Most of the ERF members have only AP2, a conserved structural domain with a length of approximately 60–70 amino acids. For example, Solyc05g052410.1.1 and Solyc08g081960.1.1, in addition to having AP2, also contain the H+-ATPase subunit H (NtpH) superfamily and Flavodoxin domain, respectively. The name of the Solyc02g077810.1.1 conserved domain is the same as that in the AP2 superfamily. The more closely related the members of an evolutionary branch are, the more closely related their conserved domains are, and the more similar their biological functions are. The dissimilarity in the arrangement of conserved domains among the members of the same subgroup may be caused by evolutionary or recombination mutations in the progeny.
The structure and chromosomal locations of ERF genes in tomato. A The structure of ERF genes in tomato. (a) Motif logo; (b) Distribution of conserved motifs on each ERF genes in tomato; (c) The position of the AP2 conserved domain on the ERF genes; (d) Distribution of exons and introns in the ERF genes. B Chromosomal locations of the tomato ERF genes. The scale was used to estimate the length of chromosomes, and the same set of tandem replication genes was marked with the same background color
To further study the gene structure of the ERF transcription factor family, a structural distribution map of introns and exons of 134 members was obtained through the Gene Structure Display Server (GSDS) analysis platform (http://gsds.cbi.pku.edu.cn/) (Fig. 2A-d). As shown in the figure, most members of the tomato ERF family contain only exons (107/134, 79.8%). This structural feature is similar to that in the Arabidopsis ERF family. In addition, no intron was found in the B, F, and K subgroups, and only one intron was found in the C, D, and I subgroups. The smaller number of intron-containing members than of non-intron-containing members in the tomato ERF family may be due to an increase in or a loss of introns during evolution.
Distribution of tomato ERF transcription factors on chromosomes
The 134 ERF transcription factors in tomato showed an uneven distribution on 12 chromosomes (Fig. 2B). Chromosome 3 contained the most members, with 22 members. Chromosome 7 contained the fewest, with only five members. A total of 16, 9, 22, 11, 10, 10, 5, 12, 9, 9, 8, and 13 ERF genes were distributed sequentially on chromosomes 1–12 in tomato. A tandem repeat was defined as adjacent genes on the same chromosome within 100 kb. There were 20 pairs of genes in the tomato ERF family that exhibited tandem replication, and the number of tandemly replicated genes on chromosome 3 was the highest, at 4 pairs, including a total of 13 genes. Tandem replication led to the production of multiple gene clusters. The members of the ERF family accounted for 39.5% of the total, and 75% of the chromosomes of the tomato family exhibited tandem duplication.
Expression of the tomato ERF transcription factor family in different organs
To better understand the role of ERF genes in tomato development, we used previously published tomato RNA-seq data to draw a heat map of ERF tissue-specific expression (Fig. 3a). The results showed that the expression of most of the genes in the tomato ERF family was low in the bud, flower, leaf, root and fruit of tomato. The expression levels of Solyc06g063070.2.1, Solyc03g123500.2.1, and Solyc07g064890.1.1 in tomato seedlings were similar and higher than those of other genes. Solyc06g063070.2.1 had the highest expression level in flowers. The Solyc12g056590.1.1, Solyc07g064890.1.1, Solyc04g072900.1.1, and Solyc03g123500.2.1 genes were highly expressed in flowers. Solyc07g053740.1.1 had the highest expression in leaves. The Solyc10g006130.1.1, Solyc03g093540.1.1, Solyc03g093550.1.1, Solyc06g063070.2.1, Solyc03g093560.1.1, and Solyc05g052040.1.1 genes also had higher expression levels in leaves. Solyc06g063070.2.1 was also the most highly expressed gene in the root. The Solyc01g065980.2.1, Solyc07g053740.1.1, Solyc07g064890.1.1, Solyc04g054910.2.1, and Solyc09g075420.2.1 genes showed higher expression in the roots. During the fruit expansion period, the expression of some genes decreased with increasing fruit diameter, while that of others showed the opposite trend. The Solyc01g065980.2.1 gene had the highest expression level in fruits with a diameter of 1 cm. As the fruit gradually matured, the expression level of this gene decreased. The expression of the Solyc06g063070.2.1 gene showed an upward trend as the fruit matured, with the highest expression in the fruits with a diameter of 3 cm.
Expression pattern map of ERF genes in tomato. A Expression pattern of the ERF gene in different organs of tomato. B Comparison of differential expression of 18 ERF genes in tomato inoculated with S. lycopersici. Red triangles represent ERF2 gene. The colors from blue to red represent the range of the relative expression levels from low to high
Expression pattern of ERF transcription factors in tomato inoculation with S. lycopersici
In this study, we screened 18 ERF genes based on transcriptome data. These genes were grouped into two groups. The results showed that except for Solyc06g054630 and Solyc01g090340, the expression of 16 ERF genes retrieved in the RNA-seq data increased after inoculation (Fig. 3b). It is worth noting that in the first group, the difference was mainly shown in CK2 and SPI, while in the other group, it was shown in CK1 and RPI. This shows that these ERF genes play a positive role in tomato resistance to pathogen infection.
Phylogenetic analysis and sequence alignment of ERF2
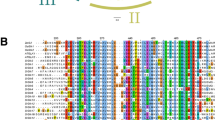
The coding sequence of ERF2 has one AP2/ERF domain, and this protein belongs to the ERF TF B-3 family (Fig. 4A-a). In addition, ERF2 is closely related to tomato ERF1 and A. thaliana AtERF1. The results indicated that ERF2 may have a similar function to other B-3 family members in plants. Analysis of the conserved protein sequence database revealed that ERF2 shares high similarity with other ERF proteins in terms of their whole putative protein sequences (Fig. 4A-b).
Sequence alignment, phenotype, and enzyme activity analysis of ERF2 in tomato. A Phylogenetic tree and sequence alignment of ERF2. (a) Phylogenetic tree of ERF2 and other ERF proteins; the phylogenetic tree was constructed via amino acid sequences of the AP2/ERF domain. (b) Alignment of ERF2 with other ERF proteins. ERF2 is composed of an ERF domain. The black and light-gray colors represent identical and conserved amino acids, respectively, and the darker blue colors represent greater percentages of the same amino acid. B Phenotypic and physiological changes after silencing of the ERF2 gene. (a) Silencing of ERF2 decreased disease resistance in tomato plants. The ERF2-silenced plants exhibited disease symptoms with lesions on leaves at 3 dpi, and only a hypersensitive reaction without disease symptoms was observed in TRV2 empty vector plants. (b) Histopathological observation of the accumulation of H2O2 and O2−. HR, hypersensitive reaction; Le, lesions. C, ROS content (a) and SOD (b), POD (c) and CAT (d) activities in tomato plants after inoculation with S. lycopersici at different time points. The data presented in (C) are the means ± SD from three independent experiments, and different letters above the columns indicate significant differences at the p < 0.05 level
ERF2- silenced plants showed impaired disease resistance to S. lycopersici
To investigate whether ERF2 influences tomato plant defense against S. lycopersici, we performed VIGS to downregulate ERF2 gene expression. In order to prevent interference with the expression of other ERF genes, the target fragment we selected is shown in Supplementary Figure 1. The results showed that disease symptoms were observed in the ERF2-silenced plants compared to the TRV2 empty vector plants after inoculation with S. lycopersici. In the ERF2-silenced plants, the lesions were aggravated, and perforations were observed. In contrast, only a hypersensitive reaction (HR) without disease symptoms was observed in the TRV2 empty vector plants (Fig. 4B-a). These results indicated that silencing the ERF2 gene in resistant tomato plants could impair resistance to S. lycopersici.
As shown in Fig. 4B-a, low levels of mycelial hyphae and a weak HR with necrotic lesions were observed in the ERF2-silenced plants. Nevertheless, strong HR symptoms without hyphal growth were observed in the TRV2::00 empty vector plants. Therefore, these results indicated that the HR was impaired in the ERF2-silenced plants compared to the TRV2::00 empty vector plants at 3 dpi with S. lycopersici.
Accumulation of H2O2 and O2− was impaired in the ERF2-silenced plants
The accumulation of H2O2 and O2− can be used to evaluate the effects of disease resistance in tomato plants. At 3 dpi, H2O2 accumulation was too weak to observe in the TRV::ERF2 plants compared to the TRV::00 empty vector plants. H2O2 was observed earlier and was more abundant in the TRV::00 plants than in the TRV::ERF2 plants (Fig. 4B-b). Based on these results, we concluded that the downregulation of ERF2 gene expression could decrease resistance to S. lycopersici in tomato plants.
ROS content and SOD, POD and CAT activity assays
ROS production and enzyme activities were detected over a time course; therefore, leaves at 0, 1, 3 and 5 dpi were collected for determination of the ROS content and the SOD, POD and CAT activities. Inoculation with S. lycopersici caused the ROS content and SOD, POD and CAT activities to sharply increase at 3 dpi (Fig. 4C). In particular, in the ERF2-silenced plants, the ROS content and SOD, POD and CAT activities were lower than those in the control plants at 1, 3 and 5 dpi.
ERF2 may enhance disease resistance to S. lycopersici through SA and JA signaling pathways
To analyze the hormonal response to S. lycopersici infection, we performed liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) to measure the JA and SA contents in the ERF2-silenced and TRV::00 plants. For SA, the content in TRV2::ERF2 and TRV::00 plants peaked at 3 days, and the content of the latter was 4.7 times greater than that of the former. The JA levels of the ERF2-silenced plants were significantly lower than those of the TRV::00 plants after inoculation with S. lycopersici (Fig. 5A). These results indicated that ERF2 probably participates in both the SA and JA signaling pathways to improve disease resistance to S. lycopersici in tomato plants.
Expression of SA and JA, expression of related genes and predictive expression model. A SA (a) and JA (b) hormone levels in the ERF2-silenced plants. The data presented in (A) are the means ± SD from three independent experiments, and different letters above the columns indicate significant differences at the p < 0.05 level. B Silencing of ERF2 decreased the expression levels of the Pto and PR genes after infection with S. lycopersici. TRV::00, empty vector plants; TRV::ERF2, ERF2-silenced plants. The asterisks indicate significant differences in the expression levels between the silenced lines and the control lines (**p < 0.01; *p < 0.05, Student’s t-test). C Hypothetical model for the ERF2-mediated defense response to S. lycopersici
ERF2-silencing decreased the Pto and PR gene expression levels
Previous studies have shown that Pti4/5/6 interacts with Pto to regulate disease resistance. In addition, many studies have shown that ERF genes regulate the expression of PR genes to enhance plant resistance to disease [20, 21]. Here, qRT-PCR was used to identify the regulatory relationship between ERF2 and the defense genes Pto and PRs. As shown in Fig. 5B, the expression levels of the Pto, PR1b1 and PR1-P2 genes were significantly decreased in the ERF2-silenced plants compared to the TRV::00 plants after inoculation with S. lycopersici. Therefore, we proposed that ERF2 enhances disease resistance to S. lycopersici by directly or indirectly regulating the expression of the Pto and PR genes in tomato plants.
In particular, studies have indicated that the HR and the accumulation of ROS are stronger in resistant cultivars than in susceptible cultivars, leading to improved disease resistance [22]. Consistent with these previous studies, our studies showed that downregulating the gene expression of ERF2 decreased HR-induced cell death, the production of H2O2, and O2− in the ERF2-silenced plants compared to the TRV::00 plants. These results indicated that the accumulation of ROS was positively correlated with the HR in the disease resistance to S. lycopersici.
Many studies have shown that the regulation of PR gene expression by ERF TFs requires the combination of GCC-box or DRE/CRT cis-acting elements [23, 24]. In addition, studies have shown that different sequences on the GCC-box side affect the binding efficiency of ERFs, indicating that various ERFs may regulate different gene sets [25]. PR-P2 and PR1b are representative marker genes of the JA/ET- and SA-mediated defense signaling pathways. In particular, the tomato Pto gene could enhance defense responses after inoculation with P. syringae pv. tabaci [26]. The overexpression of the tomato Pto gene could activate the expression of PR gene resistance to Pseudomonas species, and EREBPs interacted with the Pto protein to regulate disease resistance [20]. Here, our studies showed that downregulation of ERF2 gene expression could decrease the Pto-mediated resistance to S. lycopersici. Furthermore, Pti4/5/6 TFs bind to the PR box to regulate gene expression. Similarly, our studies also showed that silencing the ERF2 gene decreased the gene expression of PR1b1 and PR-P2. Together, these results indicate that ERF2 may directly or indirectly regulate Pto, PR1b1 and PR-P2 expression and enhance tomato resistance to S. lycopersici. However, it remains to be determined whether ERF2 interacts with the Pto protein to regulate PR gene expression and enhance the resistance of tomato to S. lycopersici (Fig. 5C).
Furthermore, previous studies have also shown that SA and JA are important signaling molecules involved in PTI and ETI, regulating plant diseases and responses to abiotic stresses [27, 28]. In addition, the SA and JA/ET signaling pathways can induce defense responses, including the expression of most PR proteins [29,30,31]. Our data were consistent with previous findings that the SA and JA contents were decreased in ERF2-silenced plants compared to TRV::00 plants, suggesting that ERF2 involvement in the resistance of tomato plants to S. lycopersici may be dependent on the SA and JA signaling pathways.
Discussion
Ethylene is one of the most important hormones in plants, and its physiological functions affect plants through a series of physiological activities during their growth and development. Ethylene receptors regulate the downstream ERF and stimulate the expression of related genes through signal mediation [32]. The ERF family, a large family of transcription factors, is unique to plants. To date, ERF transcription factors have been identified in a variety of plant fruits. Its family members have conserved characteristics in each plant. Phylogenetic grouping also reveals similarities, but the number of genes varies: Arabidopsis has 122 genes [19], rice has 131 [18], corn has 133 [33], wheat has 104, apple has 51 [34], and Brassica napus has 286 [35]. In some species, individual subgroups do not exist, no lower plants contain singletons, and some higher plants contain singletons. All the groups studied belong to the dicotyledon or monocotyledon plant system, so it is speculated that the ERF transcription factor family completed differentiation before the split of dicotyledons and monocotyledons. Gene mutation, chromosome exchange and gene loss during the evolution of species are all reasons for the expression differences and functional diversity of the ERF family in different species.
In this experiment, 137 tomato ERF genes were obtained using a plant transcription factor database. In the detection of conserved domains, 134 genes met the requirements, so they were excavated and subjected to bioinformatic analysis. This experiment divided 134 ERF members into twelve groups based on the conserved domain of the genes. Sakuma divided Arabidopsis ERF members into A1-A6 (belonging to the DREB subfamily) and B1-B6 (belonging to the ERF subfamily). Nakano divided Arabidopsis ERF family members into two groups based on those of Sakuma, namely, the ten groups I-X and the class VI (VI-L) and class Xb (Xb-L) groups. This experiment adopted a grouping method similar to that of Nakamo. Group VI-L corresponds to group K, and the Xb-L group does not contain homologous tomato ERF genes. Genes in the same clade have the closest kinship and likely perform similar or complementary physiological functions. A preliminary understanding of the function of tomato ERF genes in the same clade or the same group can be obtained by understanding the function of the corresponding Arabidopsis ERF genes. The conserved domains involved in the regulation of plant growth and development in transcription factors always consist of different conserved motifs. In this study, motifs 1, 2, 3, 4, and 15 corresponded to the conserved part of the AP2 domain, and the most conserved elements were WLG and YRG. In addition to the conserved domain of AP2, transcription factors in the same subgroup also included one or more specific motifs, which may be related to different regulatory functions of ERF members, reflect the functional diversity of the ERF family, and have the potential to promote the interaction between nuclear localization and proteins [36]. The ERF family is largely free of introns, as has been demonstrated in several species [18, 35]. Taking Arabidopsis as an example, only a few more than 20 genes contain introns, which is similar to the conclusion of this study, and the introns are located in a conserved position, which verifies the reliability of grouping. The lack of introns may be due to the absence of intron transposons or intron loss during evolution. When plants complete evolution, gene replication often occurs, which expands and enriches the number and function of genes in the genome. The results of this study showed that 53 genes on 9 chromosomes exhibited tandem replication. This shows that the expansion of the ERF family mainly depends on tandem repeats. The homology modeling results of the tertiary structure of ERF proteins show that the tertiary structures of the proteins in the same subfamily are similar, and those of the genes in different subfamilies are different due to variable spatial angles. However, overall, the spatial structure of the AP2 domain is composed of three antiparallel β-sheets parallel to the β-sheet α-helix, which is the same as a previous conclusion [37].
Previous studies have shown that AP2/ERF proteins play an important role in the transcriptional regulation of various biotic stress responses. In addition, B-subfamily genes have been shown to be involved in resistance to various diseases [18], and B-3 subfamily members were reported to regulate plant disease resistance [38]. In this study, phylogenetic analysis showed that ERF2 belonged to the B-3 subfamily of the ERF protein family, and ERF2 showed a close relationship to ERF1 and AtERF1. Previous studies have demonstrated that ERF1 and AtERF1 play a role in disease resistance responses. In this study, our results showed that downregulating the gene expression of ERF2 impaired disease resistance to S. lycopersici, and obvious disease lesions were observed on the ERF2-silenced plants compared with the TRV::00 plants.
Conclusions
In this study, we identified and analyzed the members of the tomato ERF family by bioinformatics methods and then classified, described and analyzed these genes. A total of 134 ERF genes were divided into 12 branches, and genes in the same branch had similar gene structure. The expression of these genes in different organs of the tomato plant was specific. We found that ERF2 was an AP2/ERF TF that positively regulated tomato plant resistance to S. lycopersici by VIGS. Interestingly, ERF2 played a key role in multiple SA, JA and ROS signaling pathways to confer resistance to invasion by S. lycopersici. In addition, ERF2 may directly or indirectly regulate Pto, PR1b1 and PR-P2 expression and enhance tomato resistance to S. lycopersici. In summary, this study provides gene resources for breeding for disease resistance in tomato plants.
Methods
Plant materials
Tomato-resistant cultivars (cv. Motelle) were provided by the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. All tomato plants were grown in an artificial climate chamber with a light-dark (LD) cycle (16 h L: 8 h D), and the light condition was as follows: light intensity 40,000 Lx, temperature 24 °C, and relative humidity 60%; the dark condition was as follows: temperature 16 °C and relative humidity 50%. S. lycopersici was plated on potato dextrose agar (PDA) at approximately 28 °C for 2 weeks until spores were produced.
Identification of tomato ERF transcription factor family members
The protein sequences of tomato ERF transcription factor family genes were downloaded from PlantTFDB (http://planttfdb.cbi.pku.edu.cn). According to Pfam PF00847 of the tomato ERF transcription factor AP2 domain obtained from the Pfam database, all sequences were identified by using the online protein structure prediction tool SMART (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/), and genes without the AP2 domain were deleted. On the ExPASy website, the physical and chemical properties, such as protein length and molecular mass, of the protein amino acid sequences of all tomato ERF transcription factors screened were predicted.
Phylogenetic analysis of the tomato ERF transcription factor family
We introduced the sequences of the Arabidopsis ERF transcription factor family as a reference for tomato ERF grouping when constructing a phylogenetic tree of the tomato ERF transcription factor family. The 139 amino acid sequences of the Arabidopsis ERF transcription factor family were obtained from the PlantTFDB database. Duplicate genes and genes without conserved domains were excluded. Multisequence alignment of the conserved AP2 domains in the ERF family of tomato and Arabidopsis thaliana was performed using ClustalW, and the results were imported into MEGA 7.0 software to construct a rootless evolutionary tree of the ERF family. The algorithm used was the neighbor-joining (NJ) model, the bootstrap value for verification was set to 1000, and the model selection parameter was p-distance. The evolutionary tree was edited online with EvolView v3 (https://www.evolgenius.info/evolview) [39].
Structural analysis of the tomato ERF transcription factor family
Conserved motif analysis of the amino acid sequences of the tomato ERF family was performed online via MEME (http://meme-suite.org/). The maximum number of search motifs was set to 20, and the amino acid width was set to 6–50. The basic information on the conserved domain of the tomato ERF family was obtained from the Conserved Domains Database (CDD) of the NCBI, and the conserved domain was mapped by DOG 2.0 software (http://dog.biocuckoo.org/index.php) [40]. The GSDS (http://gsds.cbi.pku.edu.cn/) online analytical function was used to obtain the tomato ERF transcription factor family exon and intron genetic structure patterns. Coding sequence (CDS) and genome sequence information for the tomato ERF transcription factor family was obtained from SGN (https://solgenomics.net/).
Chromosome locations of the tomato ERF transcription factor family
After obtaining the location information of the ERF family on twelve tomato chromosomes from the SGN database, MapInspect software was used to complete the tomato ERF family chromosome location map (http://www.plantbreeding.wur.nl/UK/software_mapinspect.html). Tomato ERF genes with serial replication were identified.
Protein tertiary structural analysis of the tomato ERF transcription factor family
Through the online analysis software SWISS-MODEL (https://swissmodel.expasy.org/) [41], all genes of the tomato ERF transcription factor family were homologously modeled to analyze and predict the tertiary structure of ERF family proteins.
Analysis of the expression patterns of the tomato ERF transcription factor family
We obtained tomato Illumina RNA-seq data from SGN and NCBI (SRP097450). Fragments per kilobase of exon model per million mapped reads (FPKM) values were used to represent the expression levels of ERF genes. We selected the transcriptome data of genes belonging to the ERF transcription factor family. Using the Heinz variety as an example, using TBtools software (https://github.com/CJChen/TBtools) [42], log FPKM values with log10 as the base were calculated, a heat map was drawn, and then the ERF genes in tomato tissue were analyzed. Expression levels were also analyzed. The specific tissues included buds, flowers, leaves, roots, and fruits. Regarding the infection of pathogens, the expression profile of the ERF gene conformed to the standard of high probability value (p > 0.8).
VIGS vector construction and agroinfiltration
The specific primers designed by the SGN VIGS Tool were amplified to prevent interference with the expression of other ERF genes (https://vigs.solgenomics.net/). The PCR protocol was as follows: 94 °C for 10 min; 40 cycles of 5 s at 94 °C, 15 s at 65 °C, and 30 s/kb at 72 °C; and 72 °C for 10 min. The amplified 300 bp PCR product and TRV2 empty vector were digested with the restriction enzymes EcoRI and BamHI. Then, the target fragments were ligated into the TRV2 empty vector. The constructs were transformed into competent Escherichia coli DH5α, and single clones were cultured in liquid LB containing 50 μg/mL kanamycin. Once the recombinant plasmids were confirmed by sequencing, they were transformed into Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain GV3101 and shaken to optical density = 0.25 at 28 °C and 200 rpm. In addition, TRV-PDS (phytoene desaturase) was used as a control for evaluation of VIGS [43]. A. tumefaciens cells containing TRV1 were mixed with those containing TRV2-derived constructs or TRV2 empty vector at a volume ratio of 1:1. Briefly, 14-day-old Motelle plants were vacuum infiltrated with TRV-PDS, TRV-ERF2 and TRV-00 syringes containing approximately 0.5–1 mL of Agrobacterium cells and kept at 22 °C in a growth chamber with a 12-h photoperiod.
Pathogen inoculation and phenotypic observation
Tomato plants were inoculated with TRV-PDS, TRV-ERF2 and TRV-00 at the age of 4 weeks. The treatment group plants were inoculated with 250 mL conidia suspension (1 × 104 spores/mL), and the control group plants were sprayed with the same amount of sterilized water. Each of these groups contained 10 plants with the same growth potential. The plants were kept in a light culture chamber (light: 16 h, 28 °C; dark: 8 h, 25 °C) with a relative humidity of 80%. The disease status of plants was observed continuously after inoculation, and the leaves were collected at 0 and 3 days post inoculation (dpi). Furthermore, the photobleaching phenotype of the PDS gene acted as the positive control for evaluation of VIGS. The TRV2:00 empty vectors were included as controls.
Microscopic observation
At 0 and 3 dpi, 0.1% trypan blue (TB) staining was used to confirm the disease status of tomato plants infected with S. lycopersici [44]. Similarly, 0.1% 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (DAB) and 0.2% nitrotetrazolium blue chloride (NBT) were used to detect the accumulation of H2O2 and O2− in plant leaves, respectively [45, 46]. Finally, an optical microscope was used to record these images.
qRT-PCR analysis and physiological index determination
qRT-PCR was performed with three independent biological replicates using AceQ® qPCR SYBR® Green Master Mix (Vazyme, Nanjing, China) in a 20 μL volume on a qTOWER3G Real-time System (Analytik Jena AG, Germany). The qRT-PCR primers are listed in Supplementary Table 2. EF1α was used as an internal control for normalization of the data. Relative expression was calculated using the 2–△△CT method.
The activities of the main disease-resistance enzymes, including ROS, SOD, POD, and CAT, were determined using the ROS Assay Kit E004–1-1, SOD Assay Kit A001–3-2, POD Assay Kit A084–3 and CAT Assay Kit A007–1-1 (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, China) with the protocols provided by the manufacturer. The leaves we collected are random and they’re mixed together to extract total RNA. The leaves were collected at 10:00 AM on the 0, 1, 3 and 5 day after inoculation, and the collected samples were immediately used for analysis. All the treatment groups were carried out at the same time, and the whole experiment was repeated three times.
Assay of SA and JA contents
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was used to determine the levels of the endogenous hormones SA and JA [47]. The leaves of the plants were collected at 10:00 AM the 0, 1, 3 and 5 day after inoculation, and the collected samples were immediately used for analysis. The data for each group were obtained from 3 individual plants. Data of three independent experiments were used to analyze the SA and JA content.
Availability of data and materials
The protein sequences of tomato ERF transcription factor family genes were downloaded from PlantTFDB (http://planttfdb.cbi.pku.edu.cn). All sequences were identified by using the online protein structure prediction tool SMART (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/). The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included with in the article and its Supplementary files.
References
Zhou J, Tang X, Martin GB. The Pto kinase conferring resistance to tomato bacterial speck disease interacts with proteins that bind a cis-element of pathogenesis-related genes. EMBO J. 1997;16:3207–18.
Wu K, Tian L, Hollingworth J, Brown DCW, Miki B. Functional analysis of tomato Pti4 in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2002;128:30–7.
Gu YQ, Wildermuth MC, Chakravarthy S, Loh YT, Yang C, He X, Han Y, Martin GB. Tomato transcription factors pti4, Pti5, and pti6 activate defense responses when expressed in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2002;14:817–31.
He P, Warren RF, Zhao T, Shan L, Zhu L, Tang X, Zhou JM. Overexpression of Pti5 in tomato potentiates pathogen-induced defense gene expression and enhances disease resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv tomato. Mol Plant Microbe. 2001;14:1453–7.
Riechmann JL, Heard J, Martin G, Reuber L, Jiang C, Keddie J, Adam L, Pineda O, Ratcliffe OJ, Samaha RR. Arabidopsis transcription factors: genome-wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes. Science. 2000;290:2105–10.
Jofuku KD, den Boer BG, Van Montagu M, Okamuro JK. Control of Arabidopsis flower and seed development by the homeotic gene APETALA2. Plant Cell. 1994;6:1211–25.
Magnani E, Siolander K, Hake S. From endonucleases to transcription factors: evolution of the AP2 DNA binding domain in plants. Plant Cell. 2004;16:2265–77.
Ohme-Takagi M, Shinshi H. Ethylene-inducible DNA binding proteins that interact with an ethylene-responsive element. Plant Cell. 1995;7:173–82.
Hao D, Ohme-Takagi M, Sarai A. Unique mode of GCC box recognition by the DNA-binding domain of ethylene-responsive element-binding factor (ERF domain) in plant. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:26857–61.
Yang R, Liu J, Lin Z, Sun W, Wu Z, Hu H, Zhang Y. ERF transcription factors involved in salt response in tomato. Plant Growth Regul. 2018;84:573–82.
Pirrello J, Prasad BCN, Zhang W, Chen K, Mila I, Zouine M, Latché A, Pech JC, Ohme-Takagi M, Regad F, Bouzayen M. Functional analysis and binding affinity of tomato ethylene response factors provide insight on the molecular bases of plant differential responses to ethylene. BMC Plant Biol. 2012;12:190.
Kizis D, Lumbreras V, Pages M. Role of AR2/EREBP transcription factors in gene regulation during abioticstress. FEBS Lett. 2001;498:187–9.
Xu ZS, Xia LQ, Chen M, Cheng XG, Zhang R, Li LC, et al. Isolation and molecular characterization of the Triticum aestivum L: ethylene- responsive factor 1 (TaERF1) that increases multiple stress tolerance. Plant Mol Biol. 2007;65:719–32.
Cheng MC, Liao PM, Kuo WW, Lin TP. The Arabidopsis ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR1 regulates abiotic stress-responsive gene expression by binding to different cis-acting elements in response to different stress signals. Plant Physiol. 2013;162:1566–82.
Gu YQ, Yang C, Thara VK, Zhou J, Martin GB. Pti4 is induced by ethylene and salicylic acid, and its product is phosphorylated by the Pto kinase. Plant Cell. 2000;12:771–86.
Onate-Sanchez L, Singh KB. Identification of Arabidopsis ethylene-responsive element binding factors with distinct induction kinetics after pathogen infection. Plant Physiol. 2002;128:1313–22.
Caarls L, Pieterse CMJ, Van Wees SCM. How salicylic acid takes transcriptional control over jasmonic acid signaling. Front Plant Sci. 2015;6:170.
Nakano T, Suzuki K, Fujimura T, Shinshi H. Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol. 2006;140:411–32.
Sakuma Y, Liu Q, Dubouzet JG, Abe H, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. DNA-binding specificity of the ERF/AP2 domain of Arabidopsis DREBs, transcription factors involved in dehydration- and cold-inducible gene expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;290:998–1009.
Li X, Xia B, Jiang Y, Wu Q, Wang C, He L, Peng F, Wang R. A new pathogenesis-related protein, LrPR4, from Lycoris radiata, and its antifungal activity against Magnaporthe grisea. Mol Biol Rep. 2010;37:995–1001.
El-Kereamy A, El-Sharkawy I, Ramamoorthy R, Taheri A, Errampalli D, Kumar P, Jayasankar S. Prunus domestica pathogenesis-related protein-5 activates the defense response pathway and enhances the resistance to fungal infection. PLoS One. 2011;6:e17973.
Hückelhoven R, Foder J, Preis C, Kogel KH. Hypersensitive cell death and papilla formation in barley attacked by the powdery mildew fungus are associated with H2O2 but not with salicylic acid accumulation. Plant Physiol. 1999;119:1251–60.
Vos IA, Moritz L, Pieterse CMJ, Van Wees SCM. Impact of hormonal crosstalk on plant resistance and fitness under multi-attacker conditions. Front Plant Sci. 2015;6:639–52.
Park CJ, Kim KJ, Shin R, Park JM, Shin YC, Paek KH. Pathogenesis-related protein 10 isolated from hot pepper functions as a ribonuclease in an antiviral pathway. Plant J. 2004;37:186–98.
Romero I, Vazquez-Hernandez M, Escribano MI, Merodio C, Sanchez-Ballesta MT. Expression profiles and DNA-binding affinity of five ERF genes in bunches of Vitis vinifera cv. Cardinal treated with high levels of CO2 at low temperature. Front Plant Sci. 2016;7:370–83.
Thilmony RL, Chen Z, Bressan RA, Martin GB. Expression of the tomato Pto gene in tobacco enhances resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv. Tabaci expressing avrPto. Plant Cell. 1995;7:1529–36.
Divi UK, Rahman T, Krishna P. Brassinosteroid-mediated stress tolerance in Arabidopsis shows interactions with abscisic acid, ethylene and salicylic acid pathways. BMC Plant Biol. 2010;10:151–65.
Ton J, Flors V, Mauch-Mani B. The multifaceted role of ABA in disease resistance. Trends Plant Sci. 2009;14:310–7.
Van Loon LC, Rep M, Pieterse CMJ. Significance of inducible defense-related proteins in infected plants. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2006;44:135–62.
Beckers GJM, Spoel SH. Fine-tuning plant defence signaling: salicylate versus jasmonate. Plant Biol. 2006;8:1–10.
Mur LA, Kenton P, Atzorn R, Miersch O, Wasternack C. The outcomes of concentration-specific interactions between salicylate and jasmonate signaling include synergy, antagonism, and oxidative stress leading to cell death. Plant Physiol. 2006;140:249–62.
An FY, Zhao Q, Ji YS, Li WY, Jiang ZQ, Yu XC, Zhang C, Han Y, He WR, Liu YD, Zhang SQ, Ecker JR, Guo HW. Ethylene-induced stabilization of ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE3 and EIN3-LIKE1 is mediated by proteasomal degradation of EIN3 binding F-box 1 and 2 that requires EIN2 in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2010;22:2384–401.
Zhuang J, Deng DX, Yao QH, Zhang J, Xiong F, Chen JM, Xiong AS. Discovery,phylogeny and expression patterns of AP2-like genes in maize. Plant Growth Regul. 2010;62:51–8.
Zhuang J, Yao QH, Xiong AS, Zhang J. Isolation,phylogeny and expression patterns of AP2-like genes in Apple (Malus×domestica Borkh). Plant Mol Biol Report. 2011;29:209–16.
Owji H, Hajiebrahimi A, Seradj H, Hemmati S. Identification and functional prediction of stress responsive AP2/ERF transcription factors in Brassica napus by genome-wide analysis. Comput Biol Chem. 2017;71:32–56.
Liu L, White MJ, MacRae TH. Transcription factors and their genes in higher plants functional domains, evolution and regulation. Eur J Biochem. 1999;262:247–57.
Allen MD, Yamasaki K, Ohme-Takagi M, Tateno M, Suzuki M. A novel mode of DNA recognition by a β-sheet revealed by the solution structure of the GCC-box binding domain in complex with DNA. EMBO J. 1998;17:5484–96.
Gutterson N, Reuber TL. Regulation of disease resistance pathways by AP2/ERF transcription factors. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2004;7:465–71.
Subramanian B, Gao S, Lercher MJ, Hu S, Chen WH. Evolview v3: a webserver for visualization, annotation, and management of phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:270–5.
Ren J, Wen LP, Gao XJ, Jin CJ, Xue Y, Yao XB. DOG 1.0: illustrator of protein domain structures. Cell Res. 2009;19:271–3.
Waterhouse A, Bertoni M, Bienert S, Studer G, Tauriello G, Gumienny R, Heer FT, Beer TAP, Rempfer C, Bordoli L, Lepore R, Schwede T. SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46:296–303.
Chen CJ, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas HR, Frank MH, He YH, Xia R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant. 2020;13:1194–202.
Liu Y, Schiff M, Dinesh-Kumar SP. Virus-induced gene silencing in tomato. Plant J. 2002;31:777–86.
Wang X, Hadrami AE, Adam LR, Daayf F. Differential activation and suppression of potato defence responses by Phytophthora infestans isolates representing US-1 and US-8 genotypes. Plant Pathol. 2008;57:1026–37.
Rao MV, Davis KR. Ozone-induced cell death occurs via two distinct mechanisms in Arabidopsis: the role of salicylic acid. Plant J. 1999;17:603–14.
Kumar D, Yusuf MA, Singh P, Sardar M, Sarin NB. Histochemical detection of superoxide and H2O2 accumulation in brassica juncea seedlings. Bio-Protocol. 2014;4:e1108.
Llugany M, Martin SR, Barceló J, Poschenrieder C. Endogenous jasmonic and salicylic acids levels in the cd-hyperaccumulator Noccaea (Thlaspi) praecox exposed to fungal infection and/or mechanical stress. Plant Cell Rep. 2013;32:1243–9.
Acknowledgements
We thank all the colleagues in our laboratory for providing useful discussions and technical assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by the Open Project of the Key Laboratory of Biology and Genetic Improvement of Horticultural Crops (Northeast Region), Ministry of Agriculture; the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32002059); the Heilongjiang Natural Science Foundation of China (LH2020C10); the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFD0101900) and the Fellowship of China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2020 M681068); the “Young Talents” Project of Northeast Agricultural University (18QC08). The funders had no role in study design, collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript, but just provide the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Experiments were designed by JFL and JBJ. HHY and YGS wrote the original manuscript, revised and edited it. Experiments were performed by HHY, YGS, and HXW. YGS and HXW analyzed the family genes and visualized their structures. TTZ and XYX was responsible for supervising. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ information
Laboratory of Genetic Breeding in Tomato, Key Laboratory of Biology and Genetic Improvement of Horticultural Crops (Northeast Region), Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, College of Horticulture and Landscape Architecture, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin 150030, China.
Huanhuan Yang, Yaoguang Sun, Hexuan Wang, Tingting Zhao, Xiangyang Xu, Jingbin Jiang and Jingfu Li
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table S1.
Identification and Analysis of Physical and Chemical Properties of ERF
Additional file 2: Figure S1.
The target fragment for SlERF2 gene silencing was designed by the SGN VIGS tool.
Additional file 3: Table S2.
Primers used in the text
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, H., Sun, Y., Wang, H. et al. Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of the ERF2 gene family in response to disease resistance against Stemphylium lycopersici in tomato. BMC Plant Biol 21, 72 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-021-02848-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-021-02848-3