Abstract
Background
The members of the sucrose non-fermenting 1-related protein kinase 2 (SnRK2) family are specific serine/threonine protein kinases in plants that play important roles in stress signal transduction and adaptation. Because of their positive regulatory roles in response to adverse conditions, the genes encoding thes proteins are considered potential candidates for breeding of plants for disease resistance and genetic improvement. However, there is far less information about this kinase family, and the function of these genes has not been explored in Rosaceae.
Results
A genome-wide survey and analysis of the genes encoding members of the SnRK2 family were performed in pear (Pyrus bretschneideri) and seven other Rosaceae species. A total of 71 SnRK2 genes were identified from the eight Rosaceae species and classified into three subgroups based on phylogenetic analysis and structural characteristics. Purifying selection played a crucial role in the evolution of SnRK2 genes, and whole-genome duplication and dispersed duplication were the primary forces underlying the characteristics of the SnRK2 gene family in Rosaceae. Transcriptome data and qRT-PCR assay results revealed that the distribution of PbrSnRK2s was very extensive, including across the roots, leaves, pollen, styles, and flowers, although most of them were mainly expressed in leaves. In addition, under stress conditions, the transcript levels of some of the genes were upregulated in leaves in response to ABA treatment.
Conclusions
This study provides useful information and a theoretical introduction for the study of the evolution, expression, and functions of the SnRK2 gene family in plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
During growth and agricultural production, plants are frequently affected by various biotic and abiotic stresses such as waterlogging, salinity, and cold and drought stresses. Because of their immovable nature and inability to choose suitable environmental conditions, plants must change their characteristics to adapt to adverse environments. To cope with these stresses, plants have established a network of defense-related metabolic mechanisms by regulating the production of beneficial substances or the expressions of related genes over the long course of evolution [1]. As important adversity signal regulators, protein kinases and phosphorylation play essential roles in the process of recognizing and transmitting stress signals to different parts of cells [2]. The sucrose non-fermenting 1-related protein kinase 2 (SnRK2) family is a plant-specific serine/threonine (Ser/Thr) family of protein kinases that are particularly involved in adversity stress responses and play important roles in plant stress signal transduction [3,4,5]. Recent studies have shown that SnRK2s are involved in plant growth and development as well as in responses to stress signals such as osmotic stress, saline stress and ABA signaling [4, 6]. For example, SnRK2.6 and SnRK2.8 serve as regulators of carbohydrate metabolism and drought resistance response in Arabidopsis thaliana, respectively [7, 8], whereas SnRK2.4 and SnRK2.10 play essential roles in root growth and architecture under saline conditions in Arabidopsis [9]. Furthermore, in other species, overexpression of SnRK2.8 enhances the resistance to various adverse stresses in wheat (Triticum aestivum) [10], while ZmSAPK8, OsSAPK8, GhSnRK2.6, and MpSnRK2.10 are related to salt tolerance in maize (Zea mays), rice (Oryza sativa), cotton (Gossypium hirsutum), and apple (Malus domestica), respectively [11,12,13,14].
Similar to other SnRK family members, SnRK2 proteins possess a typical structure composed of structurally and functionally conserved domains. The amino acid sequence of SnRK2s can be divided into two regions: the highly conserved N-terminal catalytic domain, which is similar to that of SNF1/AMP kinases, and the relatively differentiated C-terminal regulatory domain, which is short [15]. In addition, earlier research found that the N-terminus of SnRK2 is a highly conserved kinase region, which is closely related to its kinase activity, and contains the highly conserved ATP-binding site (DXGXGNFGVAXL) and Ser/Thr kinase activity domain (KICDFGYSKSXXXHGXPK) [16]. It was also found that the C-terminus was composed of two subdomains (Domains I and II), which contain stretches of acidic patches of either glutamic acid or aspartic acid [16]. Domain I is a region shared by all members of the SnRK2 family that is located 20 amino acids away from the catalytic domain and is the necessary structural basis for independent ABA response to osmotic stress [17]. Domain II exists mainly in the members of the third subfamily and is the necessary structural basis for the response to ABA signals [17].
Differences in the functions of SnRK2 genes have been widely determined. In contrast to other protein kinases, SnRK2s are essential components and positive regulators of the ABA signaling pathway that are specific to plants. Based on the structural characteristics of the SnRK2 C-terminus and their response to ABA signals, SnRK2s were divided into three subfamilies [14]. Among them, members of Group I are rich in glutamic acid at the C-terminus and barely respond to ABA signals. In contrast, members of Group II and Group III are rich in aspartic acid; SnRK2s in Group II do not or weakly respond to ABA signals, whereas SnRK2s in Group III are strongly activated by ABA [4, 18]. Furthermore, the promoter region of SnRK2s usually contains cis-acting regulatory elements that are involved in stress responses, such as drought-responsive elements, ABA-responsive elements, and cold-responsive elements [6]. Previous research has shown that the kinase activity of SnRK2 is related to the reversible phosphorylation of key amino acid sites. For example, the kinase activity of NtOSAK is regulated by the phosphorylation of Ser154 and Ser158 within its activated ring in the tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) [19]. Furthermore, there are some differences in the kinase activity of SnRK2s because of their different phosphorylation sites. Regarding the SnRK2.6 gene in Arabidopsis, the phosphorylation sites Ser7, Ser18, Ser29, and Ser43 are mainly related to the regulation of self-phosphorylation, whereas Ser175 and Thr176 are primarily associated with kinase activity [20].
Because of the critical regulatory functions of SnRK2 genes in plant responses to various adversity stresses and developmental processes, the SnRK2 gene family has been widely studied in the model plant Arabidopsis as well as in non-model plants such as rice, maize, wheat, soybean (Glycine max), apple, and rubber (Hevea brasiliensis) [6, 15, 18, 21,22,23]. Compared with other species, the members of the SnRK2 gene family have not been extensively examined in Rosaceae. Pear (Pyrus bretschneideri) is a member of the Rosaceae family and a commercially important crop that is cultivated in temperate regions worldwide. In addition, the genome of the Chinese white pear (P. bretschneideri Rehd. cv. ‘Dangshansuli’) has been fully sequenced [24]. In recent years, the development of high-throughput sequencing technology has allowed genome sequencing in many organisms for genomic analysis. For example, genome sequences are available for seven other Rosaceae species, i.e., apple, strawberry (Fragaria vesca), peach (Prunus persica), Chinese plum (Prunus mume), black raspberry (Rubus occidentalis), cherry (Prunus avium), and European pear (Pyrus communis), which provides an opportunity to further analyze the SnRK2 gene family in Rosaceae. Therefore, the present study aimed to (1) annotate the full-length SnRK2 genes in Chinese white pear and seven additional Rosaceae fruit species; (2) infer their expansion, evolutionary history, and expression patterns; and (3) explore PbrSnRK2s responses to adversity stresses, as elicited by ABA stress, thereby providing valuable information for further investigation of SnRK2 gene functions in Rosaceae. These results will be useful for revealing the mechanisms of stress resistance in fruit trees and will lay a foundation for further investigations that will use genetic engineering for molecular breeding.
Results
Identification and classification of SnRK2 genes in Rosaceae
To investigate the SnRK2 gene family in Rosaceae, the protein sequences of SnRK2s from Arabidopsis and rice were used as queries. In addition, a Hidden Markov Model (HMM) search using the SnRK2 gene domain HMM profile (PF00069.1) was used to screen the Rosaceae genome. A total of 318 candidate SnRK2 genes were screened using these two strategies. Finally, the online program SMART (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/) was used to assess the Ser/Thr protein kinase catalytic domains, followed by the elimination of redundant sequences, incomplete gene sequences, and transcripts of the same gene. Subsequently, 71 nonredundant SnRK2 genes were identified in the Rosaceae genome. Among them, 10 SnRK2 proteins were identified in Chinese white pear (PbrSnRK2s), 14 in apple (MdSnRK2s), 8 in strawberry (FvSnRK2s), 7 in peach (PpeSnRK2s), 7 in Chinese plum (PmSnRK2s), 5 in black raspberry (RocSnRK2s), 7 in cherry (PavSnRK2s), and 13 in European pear (PcSnRK2s) (Fig. 1).
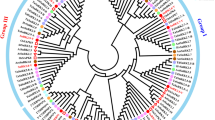
Phylogenetic analysis of SnRK2 proteins from Rosaceae, rice, and Arabidopsis. Full-length protein sequences were aligned with the integrated MUSCLE program and the phylogenetic tree was constructed by the maximum likelihood method using MEGA 6.0 and 1000 bootstrap replicates. Proteins clustered into three subgroups. The yellow, red, and green regions indicate the three subfamilies of the SnRK2 proteins
To classify and investigate the evolutionary relationships among SnRK2 genes, a phylogenetic tree was constructed using multiple sequence alignment of SnRK2 protein sequences from the eight Rosaceae species, Arabidopsis, and rice. The results of this analysis showed that the SnRK2 gene family was clustered into three well-supported clades (Groups I, II, and III; Fig. 1), which is consistent with the findings of a previous study performed in Arabidopsis and rice [15]. Among them, 22 members belonged to Group I, 25 to Group II, and 24 to Group III (Fig. 1).
Multiple sequence alignment of SnRK2 proteins
To gain insights into the structural features of PbrSnRK2 proteins, the amino acid sequences in all members and groups were aligned. Result of the amino acid sequence alignment showed that all members of SnRK2s had 54.87% sequence identity, of which the maximum and minimum percentage of amino acid sequence conserved was 79.78 and 29.33%, respectively (Table S1). Furthermore, the ratio of sequence conservation for subgroup I, II and III was 78.92, 64.5 and 65.17% respectively (Table S1). Previous studies in Arabidopsis had identified two conserved kinase regions and two functional subdomains within SnRK2, i.e. ATP-binding site, Ser/Thr kinase activity domain, Domain I and Domain II. To characterize the biological functions of PbrSnRK2 genes and their conserved domains in pear, multiple sequence alignment of PbrSnRK2 and AtSnRK2 proteins was performed. According to the result, the amino acid sites were very similar in these conserved regions of pear and Arabidopsis SnRK2 proteins. Specifically, members of PbrSnRK2 proteins have two conserved kinase domains in the N-terminal regions: an ATP-binding signature containing a lysine residue as an ATP-binding site, expected for the PbrSnRK2.5/2.6/2/9/2/10; and a Ser/Thr protein kinase active site signature, expected for the PbrSnRK2.8 (Fig. 2). In addition, the C-terminal of PbrSnRK2 contains two distinct domains (Domain I and Domain II), which is identical with the SnRK2 members identified in Arabidopsis lineages that showed divergent C-terminal domains. Together, the results manifest that SnRK2 gene family originated before the divergence of Rosaceae and Cruciferae. Additionally, the kinase domain regions are highly conserved during long-term evolution in SnRK2 proteins, which may have gone through purification choices. Furthermore, the conserved regions of several PbrSnRK2 proteins were lost, indicating that pseudogenezation or subfunctionalization might have been occurred during long-term evolution in pear.
Alignment of the amino acid sequences of PbrSnRK2s and AtSnRK2s. The serine/threonine protein kinase active site signature and the protein kinase ATP-binding region signature are indicated by a green box (a green pentacle) and red box (a red pentacle), respectively. Domain I and Domain II are marked by black boxes at the C-terminus
Structural and conserved motifs analysis of SnRK2 genes in pear
Analysis of the arrangement of introns and exons can provide valuable information regarding evolutions and functions of gene families [25]. To better understand the structural diversity of PbrSnRK2 genes, an exon/intron analysis was performed by aligning gene sequences with their corresponding coding domains from SnRK2 in pear and Arabidopsis. The number of exons identified in the members of the SnRK2 gene family ranged from 4 to 10 in pear and Arabidopsis (Fig. 3). Most members of the individual groups exhibited different number of exons/introns and varying lengths of the coding sequence in pear, which also supported the phylogenetic classification of the SnRK2 gene family. For example, SnRK2 genes in subgroup I in pear contained 9 exons. Most members of subgroup II included 5–6 exons, except PbrSnRK2.4, which contained 9 exons. In addition, subgroup III contained a number of exons (i.e., 7–8), except PbrSnRK2.10, which contained 4 exons (Fig. 2). In addition, the MEME tool was used to further investigate the conserved motifs of SnRK2 proteins. A total of 12 conserved motifs were identified, denominating motif 1–12. The SnRK2 genes of each subgroup shared similar conserved motifs, nevertheless those in subgroup II were disorganized. Based on the result of motif analysis, motif 1/4/6/8/9/10 were identified to be the basic regions of the SnRK2 domain, as they were detected in each group of the gene family (Fig. S1). For example, it contains 11 of 12 conserved motifs in subgroup I, and only motif 12 is lacked (Fig. S1). Group III contains one specific motifs, i.e. it contains two motifs 12, expected for PbrSnRK2.9 (Fig. S1). In total, the conservation and specificity of the number of exons and motifs in each subgroup support the close evolutionary relationship of PbrSnRK2 genes. This may result from the replication events in evolution process of the gene family, indicating that these subgroups originated via different evolutionary paths.
Phylogenetic relationship of the intron/exon structure of SnRK2 genes from pear and Arabidopsis thaliana. a A phylogenetic tree constructed with CluxtalX2.0 using the full-length amino acid sequences of SnRK2 genes from pear and Arabidopsis. Bootstrap analysis was performed using 1000 replicates. The species in which SnRK2 proteins were functionally characterized are displayed as icons, and the different colors in the branches represent the different subfamilies. b The tangerine boxes, black lines, and light-green boxes in the gene structural diagram represent exons, introns, and UTRs, respectively. Gene models are drawn to scale, as indicated at the bottom
Physicochemical features of the SnRK2 genes in Rosaceae
To further study the functions of the SnRK2 proteins, we performed systematic analysis of the physicochemical properties of the SnRK2 proteins in Rosaceae. We found that the SnRK2 protein sequences ranged from 198 to 891 amino acids, and that most of them contained 220 to 402 amino acids. The isoelectric point of 87.3% of the SnRK2 proteins was acidic, which indicates that SnRK2 proteins from Rosaceae are rich in acidic amino acids. Moreover, the molecular weights of these proteins ranged from 30.09 to 85.3 kDa (Table 1). The negative and positive GRAVY scores of proteins reflect their hydrophobicity and hydrophilicity, respectively [26]. The grand average of the hydropathy scores of all SnRK2 proteins was negative in Rosaceae, which indicates that these proteins are hydrophilic. In addition, we found that the aliphatic index ranged from 80.76 to 94.08 for the SnRK2 proteins from Rosaceae, which indicated that all of them are thermally stable (Table 1).
Evolutionary expansion and synteny analysis of SnRK2 genes in Rosaceae
Several gene duplication patterns drive the evolution of protein-coding gene families, which include whole-genome duplication (WGD) or segmental duplication, tandem and segmental duplications, and rearrangements at the gene and chromosomal levels [27]. The origins of duplicated genes were explored in the SnRK2 gene family in eight Rosaceae genomes using the MCScanX package. Each member of the SnRK2 gene family was allocated to one of five different categories: WGD or segmental, singleton, proximal, tandem, or dispersed. Five types of duplication events contributed to the expansion of the SnRK2 gene family in Rosaceae: 50% WGD, 19.7% dispersed, 15.2% transposed, 9% proximal, and 6% tandem (Fig. 4). Among them, WGD events occurred in each of the Rosaceae species; in particular, 60% of the SnRK2 genes in Chinese white pear, 86% in apple, 57.1% in peach, and 50% in strawberry were duplicated and retained from WGD events compared with only 40% in black raspberry, 28.6% in Chinese plum, 28.6% in cherry, and 7.7% in European pear (Table S2). Hence, WGD may have impacted the evolution of the SnRK2 gene family in Chinese white pear, apple, peach and strawberry. In addition, the proportions of dispersed SnRK2 gene duplication events in black raspberry (40%), European pear (30%), peach (28.6%), strawberry (28.6%), cherry (28.6%), and apple (7%) were assessed (Table S2). Transposed events were 10% in pear, 37.5% in strawberry, 28.6% in Chinese plum, 28.6% in cherry and 15.4% in European pear. These results indicate that transposed, WGD, and dispersed events impacted the evolution of the SnRK2 gene family in Chinese plum and cherry. In black raspberry, WGD and dispersed events were the main forces, while dispersed and transposed events played key roles in the evolution of European pear.
To explore the evolutionary process of SnRK2 genes, an intra-genomic synteny map was constructed for each analyzed Rosaceae specie in the study. The result showed that PbrSnRK2 genes were distributed on 4 out of the 17 pear chromosomes, with 4 SnRK2 genes anchored on chromosome 15, and 2 syntenic pairs were identified (Fig. 5). Thirteen SnRK2 genes were assigned to 7 of the 17 chromosomes in apple, with 5 genes anchored to chromosome 15, and 9 syntenic pairs were identified. Furthermore, 7 SnRK2 genes were distributed on 5 of the 8 chromosomes in peach, with 3 genes anchored to chromosome 1, and 1 syntenic pair was identified (Fig. 5). Eight SnRK2 genes were assigned to 4 of the 7 chromosomes in strawberry, with 4 genes anchored to chromosome 5, and 2 syntenic pairs were identified (Fig. 5). In addition, 7 SnRK2 genes were located on Chr1, Chr2, Chr4, Chr6 and Chr8 in Chinese plum, of these, 3 genes were co-located on Chr2, and 1 syntenic pair was identified (Fig. S2). Five SnRK2 genes were located on Chr1, Chr2 and Chr5 in black raspberry, of these, 2 genes were co-located on Chr2 and Chr5, respectively, and 1 syntenic pairs was identified (Fig. S2). Seven SnRK2 genes were located on Chr1, Chr5, Chr6, Chr7 and Chr8 in cherry, of these, 3 genes were co-located on Chr1 and 1 syntenic pairs was identified (Fig. S2). Nine SnRK2 genes were located on Chr1, Chr2, Chr4, Chr8 and Chr15 in European pear, of these, 4 genes were co-located on Chr15 and 2 genes were co-located on Chr8, and 2 syntenic pairs were identified (Fig. S2).
Chromosomal localization and synteny of the SnRK2 genes in Rosaceae genomes. SnRK2 genes in Chinese white pear, apple, peach, and strawberry were mapped onto the different chromosomes. Chromosome number is indicated on the inner side in the inner circle, corresponding to different SnRK2 genes. Gene pairs with a syntenic relationship are joined by a line
Ks value and Ka/Ks ratio reveal dates and driving forces of evolution
Purifying selection (negative selection) is the process via which disadvantageous mutations are removed, whereas Darwinian selection (positive selection) accumulates new advantageous mutations and spreads them throughout the population [27]. To identify the selection process that drove the evolution of the SnRK2 gene family, the Ka value and Ka/Ks ratio of its paralogs were examined in the eight Rosaceae species based on coding sequences. We found that all values were < 1 in the studied Rosaceae species (Fig. 6a), implying that this family underwent a purifying selection pressure during its evolution in Rosaceae and that its evolution was very conservative.
The Ks value is extensively used to evaluate the evolutionary dates of WGD or segmental duplication events. Previous studies have shown that the genome of pear and apple have undergone two genome-wide duplication events (ancient and recent). In Chinese white pear, the recent WGD event that is inferred to have occurred 30–45 MYA (Ks ~ 0.15–0.3) and the ancient WGD event that is inferred to take place ~ 140 MYA (Ks ~ 1.5–1.8) [24]. Furthermore, the recent WGD event that is inferred to have occurred 30–45 MYA (Ks ~ 0.2) and the ancient WGD event that is inferred to take place ~ 140 MYA (Ks ~ 1.6) in apple [28, 29]. To explore the evolutionary dates of the duplication events among the SnRK2 gene family members, Ks values were analyzed in the Rosaceae species. The results showed that the Ks values for the SnRK2 gene pairs ranged from 0.107 to 4.0487 in Rosaceae; moreover, the Ks values of WGD gene pairs PbrSnRK2.1–PbrSnRK2.2 (Ks, ~ 0.1028), PbrSnRK2.7–PbrSnRK2.8 (Ks, ~ 0.1363), PCP022180.1–PCP002062.1 (Ks, ~ 0.182), MD01G1035000–MD15G1321000 (Ks, ~ 0.1644), MD02G1166500–MD15G1279000 (Ks, ~ 0.1757), MD04G1054400–MD06G1046300 (Ks, ~ 0.1635), MD08G1187200–MD15G1373000 (Ks, ~ 0.1138), and MD08G1236500–MD15G1428500 (Ks, ~ 0.107) are close to the Ks peak corresponding to the recent WGD that was detected in pear genome, indicating that some SnRK2 genes were derived and retained from recent WGD events (30–45 MYA) [24]. Furthermore, other duplicated gene pairs (such as PbrSnRK2.5 and PbrSnRK2.6) possessed higher Ks values (2.26–4.0487), indicating that they might have stemmed from a more ancient duplication event (Fig. 6b).
Expressions of PbrSnRK2 genes in different tissues
To understand the expression patterns and functional properties of SnRK2 genes in different tissues, we constructed a heat map at the transcriptional level using MeV to depict the overall expression patterns of SnRK2 genes in pear based on the transcriptome data from pear root, stem, leaf, fruit, petal, sepal, ovary, bud, pollen, pollen tube and stop-growth pollen tube. The transcriptome data was obtained from previous studies conducted by our group [30,31,32]. The results showed that SnRK2 genes were expressed in most organizations of pear, i.e., three genes (PbrSnRK2.2/2.5/2.7) were exhibited high expression in fruits, two (PbrSnRK2.3/2.8) in leaves, and one (PbrSnRK2.4) in roots (Fig. S3). Furthermore, PbrSnRK2.1 and PbrSnRK2.6 were highly expressed in petal, PbrSnRK2.9 was highly expressed in bud, and PbrSnRK2.10 was highly expressed in ovary.
In addition, those PbrSnRK2 genes were also examined by qRT-PCR using gene-specific primers and in diverse pear tissues including root, stem, leaf, flower, fruit, PG, PT and style (Table S3). The results showed that SnRK2 genes have diverse expression patterns in different pear tissues, although some genes have the same expression pattern between the two methods, and some genes have different expression characteristics in different tissues. For example, PbrSnRK2.3 and PbrSnRK2.8 were also highly expressed in leaf, and PbrSnRK2.6 also exhibited high expression in the flower, which is consistent with transcriptome data (Figs. 7 and S3). PbrSnRK2.2, PbrSnRK2.4 and PbrSnRK2.7 were highly expressed in flower based on the data of qRT-PCR, nevertheless transcriptome data showed that PbrSnRK2.2, PbrSnRK2.4 and PbrSnRK2.7 were highly expressed in fruit, root and root, respectively (Figs. 7 and S3). PbrSnRK2.5 and PbrSnRK2.9 were highly expressed in leaf by qRT-PCR; PbrSnRK2.1 was highly expressed in PG, and PbrSnRK2.10 was highly expressed in style by qRT-PCR (Fig. 7). These results indicated that SnRK2 genes may play important roles in these pear tissues and respond to abiotic in different organizations. In addition, these genes may have different expression characteristics in different developmental stages of plant tissues.
Expression analyses of 10 PbrSnRK2 genes in different tissues. The relative transcript abundances of PbrSnRK2 genes were examined by qRT-PCR. Total RNA was extracted from roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, styles, pollen grains, and pollen tubes cultured for 5 h. Regarding each gene, the relative expression levels were obtained by normalization to that of pear Actin. The error bars indicate standard deviations. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation
Expression profiles of PbrSnRK2 genes under ABA treatment
Many studies have shown that SnRK2s play key roles in response to multiple abiotic stresses such as salinity, dehydration, and hyperosmotic stress [14]. Moreover, the members of the SnRK2 gene family are involved in the regulation of phytohormone pathway responses, particularly ABA signal transduction [4]. To explore the dynamic transcriptional changes in PbrSnRK2 genes in response to ABA treatment, the expression levels of these genes in leaves of pear were evaluated by qRT-PCR under ABA (50 μM) treatment at four time points: 0, 3, 6, and 9 h. The results showed that in response to exogenous ABA application, the SnRK2 genes exhibited different expression patterns. For example, eight genes (PbrSnRK2.1/2.2/2.3/2.4/2.6/2.7/2.8/2.9) were activated by ABA, whereas the expressions of two genes (PbrSnRK2.5/10) remained unchanged at each time point (Fig. 8). Among them, the expression levels of PbrSnRK2.1, PbrSnRK2.3, and PbrSnRK2.4 were significantly upregulated at 3 h after ABA treatment, and the expression pattern of PbrSnRK2.1 shows a wavy trend with ABA treatment (Fig. 8), whereas PbrSnRK2.4’s expression pattern shows a parabolic trend under ABA treatment. PbrSnRK2.7 and PbrSnRK2.9 showed similar expression patterns. Specifically, they were both significantly upregulated at 6 h after ABA treatment, and reached their peak value at 9 h after ABA treatment (Fig. 8). The expression levels of PbrSnRK2.2/2.6 were significantly upregulated at 9 h after ABA treatment. However, PbrSnRK2.8 was downregulated over time after ABA treatment (Fig. 8).
Expression patterns of PbrSnRK2 genes under abiotic treatments. The relative transcript levels of PbrSnRK2.1–PbrSnRK2.10 were examined by qRT-PCR, and the samples were harvested at 0, 3, 6, and 9 h after foliar spraying in leaves from 3-month-old seedlings under 50 μM ABA stress treatments. Regarding each gene, the relative expression levels were obtained by normalization to that of pear Actin. The error bars indicate standard deviations. Asterisks indicate a significant difference (*P < 0.05) compared with 0 h at the different time points after ABA treatment. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation
Discussion
SnRK2 is a specific family of Ser/Thr protein kinases in plants that play important roles in the transduction of various signaling pathways, particularly in response to abiotic stress [4, 5]. With the completion of whole-genome sequencing in an increasing number of organisms, it has become possible to comprehensively analyze and study the functions of gene families from the genomic perspective. The members of the SnRK2 gene family have been identified and analyzed in many plant species [33, 34]; however, a comprehensive systematic investigation of this family remains limited in Rosaceae. Here, 71 SnRK2 genes were identified in Rosaceae and the same number of SnRK2 genes was identified in pear, compared with 10 in Arabidopsis. The SnRK2 gene families in Chinese white pear, apple, and European pear have more members compared with those in cherry, strawberry, and black raspberry. Recent genome-wide evidence revealed that pear and apple have undergone both a recent WGD event and an ancient WGD event; however, strawberry, peach, Chinese plum, black raspberry, and cherry did not undergo this event [27]. Our results, which showed that pear and apple experienced two WGD event (recent and ancient), also support the conclusion. Therefore, there is a possibility that WGD event lead to the number differentiation of SnRK2 genes detected in the investigated Rosaceae species. Moreover, these SnRK2 genes were classified into three subfamilies, subgroups I, II, and III, which is consistent with the classification of other SnRK2 genes [15, 16]. In addition, the conserved motif and exon-intron analysis also support the classification of SnRK2 genes in pear and Arabidopsis, regardless of the loss of exon-intron or motif in some PbrSnRK2 genes. We believe that the loss may be due to the structural polymorphism of the PbrSnRK2 genes in the long-term evolution process, simultaneously resulting in some functional differentiation.
To investigate the evolutionary process and history of SnRK2 genes in Rosaceae and to explore further their functions in response to various abiotic stresses, gene duplication events, gene syntenic relationships, and Ka/Ks values of SnRK2 genes were investigated in Rosaceae. Dispersed, tandem, proximal, transposed, and genome-wide duplications differentially contribute to the expansion of specific gene families in plant genomes [35]. The results of the synteny analysis performed here indicated that the SnRK2 genes in Chinese white pear, apple, peach and strawberry were derived primarily from WGD events. Dispersed duplications were the major drivers of SnRK2 gene family expansion in European pear. Furthermore, the expansion of the SnRK2 gene family underwent five types of duplication events, with WGD events accounting for 50% of the SnRK2 genes in Rosaceae. Among these events, four duplicated gene pairs, i.e., PbrSnRK2.1–PbrSnRK2.2, PbrSnRK2.7–PbrSnRK2.8, MD08G1236500–MD15G1428500, and MD08G1187200–MD15G1373000, had lower Ks values (0.12, 0.13, 0.11, and 0.11, respectively), suggesting that they resulted from a recent duplication event. However, the Ks values of other duplicated gene pairs, i.e., MD08G1187200–MD15G1321000 and PbrSnRK2.5–PbrSnRK2.6, and pm02088–pm004465, were > 3, which indicated that they resulted from a more ancient duplication event. This is similar to previous observation, i.e., > 90% of the increase in functional genes in the Arabidopsis lineage is due to expansion resulting from genome duplication events [36]. These results indicate that WGD events may play a key role in the expansion of the SnRK2 gene family and that SnRK2 genes function in response to various biological and abiotic stresses. This result is similar to previous observations in studies that analyzed the expansion of the Hsf and F-box gene family in pear [27, 37].
Purifying selection (negative selection) is the process via which deleterious mutations are eliminated. In contrast, Darwinian selection (positive selection) accumulates new advantageous mutations and spreads them across the population [38]. The Ka/Ks ratio was further calculated for exploring the selection process that drove the evolution of the SnRK2 gene family in Rosaceae. In this study, the Ka/Ks ratios of all paralogous genes were < 0.5. Previous studies have shown that the Ka/Ks ratio represents selection magnitude and direction measure: 1 indicates neutral evolution, < 1 indicates negative selection, and > 1 indicates positive selection [39]. These results indicate that negative selection may play a key role in the evolution of these SnRK2 genes.
Gene expression patterns can provide important clues for describing gene function. Therefore, information pertaining to the specific expressions of PbrSnRK2 genes was analyzed in various tissues using public RNA-Seq datasets and qRT-PCR. The results revealed that PbrSnRK2 genes exhibited diverse spatiotemporal expression patterns in different tissues of pear. For example, the qRT-PCR results showed that PbrSnRK2.3, PbrSnRK2.5, and PbrSnRK2.8 were preferentially expressed in leaves, implying that the proteins encoded by them possibly participate in leaf development and stomatal regulation in response to abiotic stress. The expression patterns of these genes were similar to those of AtSnRK2.3 in Arabidopsis, which was also highly expressed in leaves [40]. In addition, researchers have shown that AtSnRK2.3 is mainly involved in the water stress response of ABA signaling in leaves [41]. Conversely, PbrSnRK2.1, PbrSnRK2.2, PbrSnRK2.4, PbrSnRK2.7, PbrSnRK2.9, and PbrSnRK2.10 exhibited strong expression in germ cells such as flowers, pollen, and styles, thereby implying that their encoded proteins potentially participate in the reproductive growth of plants and adaptation to various adverse environments. The expression patterns of these genes were similar to those of AtSnRK2.7 and AtSnRK2.9 in Arabidopsis, which were also highly expressed in inflorescence [40]. Nevertheless, further studies are necessary to verify whether PbrSnRK2s play a key role in leaf development and the reproductive growth of plants in response to various abiotic stresses. Furthermore, previous studies have shown that SnRK2s exhibit widespread expressions in various tissues of Arabidopsis as well as are involved in seed germination and growth [42], regulation of primary metabolism [7] and stomatal aperture [43]. For example, AtSnRK2.2 is expressed in both seeding and cell suspension [44], and AtSnRK2.8 is mainly expressed in roots [45], whereas AtSnRK2.6 is highly expressed in stems and roots [7]. Furthermore, the expression patterns of SnRK2 genes have been reported in other species such as MpSnRK2.4, which is mainly expressed in fruit and may participate in fruit development in apple [23]; HbSnRK2.2, which is high expressed in leaf and flower tissues [15]; and StSnRK2.4, which is mainly expressed in shoot tissues and may be involved in responses to stress signaling [46].
Many studies have shown that SnRK2 genes play a key role in response to various environmental stresses such as salinity, low temperature, and drought [34]. Moreover, SnRK2 genes play important roles in the regulation of phytohormones, particularly of ABA signal transduction [33]. In this study, the amino acid sequences of SnRK2 proteins were aligned in pear against those in Arabidopsis. The result showed that Domain I exists in each SnRK2 protein, which is consistent with previous study that Domain I is necessary in all SnRK2s and is needed for activation by osmotic stress [34]. Nevertheless, Domain II in subgroup III only exists in strong ABA-responsive kinases [34], and the results of verification assay accorded with this conclusion, i.e. PbrSnRK2.7 and PbrSnRK2.9 in subgroup III were strongly stimulated by ABA. Contrary to earlier reports, we found that PbrSnRK2.3 in the subgroup III was also strongly stimulated by ABA, and Domain II existed in PbrSnRK2.3, PbrSnRK2.7 and PbrSnRK2.9. Possible reason for these phenomenon is that SnRK2 gene family had expanded and displayed the structural diversity in a subgroup, which led to functional differentiation [47]. Furthermore, we also explored the dynamic expression levels of PbrSnRK2 genes in pear by treating the leaves with ABA. The results expanded our understanding of the functions of PbrSnRK2s in response to phytohormones and showed that all PbrSnRK2s but PbrSnRK2.5 and PbrSnRK2.10 were induced at different time points after ABA treatment. For example, PbrSnRK2.1, PbrSnRK2.3, and PbrSnRK2.4 were upregulated at 3 h after ABA treatment, similar to previous findings of StSnRK2.2, StSnRK2.4, GhSnRK2.7 and MpSnRK2.7 responding quickly to ABA treatment at 3 h in leaves [23, 46, 48]. PbrSnRK2.7, and PbrSnRK2.9 were upregulated at 6 h after ABA treatment, which is similar with the expression promotion of StSnRK2.3, HbSnRK2.5/2.7/2.8/2.9/2.10, MpSnRK2.1, and MpSnRK2.2 in leaves after ABA treatment [15, 23, 46]. Among them, the expression levels of PbrSnRK2.3, PbrSnRK2.7, and PbrSnRK2.9 were significantly induced at 9 h after ABA treatment. Moreover, PbrSnRK2.2, and PbrSnRK2.6 were also upregulated at 9 h after ABA treatment, similar with previous studies that HbSnRK2.9 responds to ABA treatment at 9 h in leaves [15]. In contrast, the expression levels of PbrSnRK2.8 was downregulated at 3 h after ABA treatment, and this gene similar to StSnRK2.1/2.5/2.7 expression pattern, which were downregulated significantly in leaves after ABA treatment [46]. These results indicate that the response of most SnRK2 genes to the various abiotic stresses is achieved via the ABA signaling pathway, which may be particularly involved in the regulation of salt stress and drought stress tolerance in pear. However, additional investigation is needed regarding the functional characterization of PbrSnRK2s. Furthermore, SnRK2 genes reportedly respond to various abiotic stresses in other species. Many of the SnRK2 genes (such as SAPK8, SAPK9, and SAPK10) were differentially regulated by ABA in different organs of rice [18]. The expression levels of TaSnRK2.7 and TaSnRK2.8 genes from wheat were induced in response to ABA treatment [4]. MpSnRK2.8, MpSnRK2.9, and MpSnRK2.10 exhibited strong responses to ABA application in apple [23]. In Arabidopsis, AtSnRK2.2, AtSnRK2.3, and AtSnRK2.6 are typically activated by ABA treatment, which can phosphorylate the ABA-responsive elements [20].
Conclusion
In this study, 71 SnRK2 genes were identified and characterized in eight Rosaceae species; among them, 10 SnRK2 proteins were identified in Chinese white pear. The structural characteristics of the encoded proteins and phylogenetic analysis showed that the SnRK2 gene family was clustered into three well-supported clades (Groups I, II, and III) and that most of the members of the PbrSnRK2 family had two conserved kinase domains in the N-terminal and C-terminal regions. In addition, synteny analyses revealed that SnRK2 genes underwent a purifying selection pressure during the evolution of Rosaceae and that WGD and dispersed duplication played key roles in the expansion of the SnRK2 gene family in Rosaceae. The relative expressions of the 10 SnRK2 genes varied among tissues and abiotic stresses, with prolonged ABA treatments showing that PbrSnRK2s are expressed in different tissues and respond to various abiotic stresses via the ABA signaling pathway. Our results represent a foundation for further studies that will dissect the structures and functions of the SnRK2 gene family in Rosaceae.
Methods
Identification of SnRK2 gene family members in Rosaceae
To identify the SnRK2 genes in Rosaceae species, multiple database searches were performed. The amino acid sequences of AtSnRK2s were downloaded from The Arabidopsis Information Resource (http://www.arabidopsis.org/, TAIR, 10) and the rice SnRK2 amino acid sequences were downloaded from Phytozome (http://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/pz/portal.html#, v9.1). These amino acid sequences were used as queries in BLAST algorithm-based searches against SnRK2 sequences. The genome sequence of pear (Pyrus bretschneideri, NJAU, v1.1) was downloaded from the Pear Genome Project (http://peargenome.njau.edu.cn/) [24]. Genome sequences of peach (Prunus persica, JGI, v2.1) and apple (Malus domestica, JGI, v1.1) were obtained from the Joint Genome Institute (JGI, http://www.jgi.doe.gov/). Genome sequences of strawberry (Fragaria vesca, GDR, v4.0), black raspberry (Rubus occidentalis, GDR, v3.0), European pear (Pyrus communis, GDR, v1.1) and sweet cherry (Prunus avium, GDR, v1.0) were obtained from the Genome Database for Rosaceae (GDR, http://www.Rosaceae.org/). In addition, the Chinese plum (Prunus mume, BUF, v1.0) genome sequence was downloaded from National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/assembly/GCF_000346735.1, v1.0). Furthermore, the seed alignment data for the SnRK2 domain (PF00069.25) obtained from the Pfam database were used to build an HMM file using the HMMER3 software package [49]. HMM searches were then performed against the local protein databases of Rosaceae using HMMER3. Finally, all obtained SnRK2 amino acid sequences were checked for the presence of SnRK2 family domains using Pfam (http://pfam.xfam.org) and SMART (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/); subsequently, sequences lacking the SnRK2 domain or with E-values of >e− 10 or redundant sequences were removed.
Sequence alignment and phylogenetic and structural analyses
Multiple sequence alignment of SnRK2 proteins in pear and Arabidopsis was performed using DNAMAN software. The program SCANPROSITE (http://www.prosite.expasy.org/scanprosite/) was used to detect the protein kinase conserved domains. Phylogenetic trees were constructed based on the SnRK2 amino acid sequences from Arabidopsis, rice, and Rosaceae species using the maximum likelihood method in MEGA6.0 (http://www.megasoftware.net/) [50], with amino acid sequences aligned using MUSCLE. The bootstrap test was performed with 1000 replicates, and p-distance and pairwise deletion option parameters were selected. Furthermore, based on the cDNA sequences and their corresponding genomic DNA sequences, the structures of the SnRK2 genes were analyzed using the Gene Structure Display Server v2.0 (http://gsds.cbi.pku.edu.cn/). The conserved motifs of SnRK2 protein were identified using the Multiple Expectation-Maximization for Motif Elicitation (MEME) tool version 5.0.5 (http://meme-suite.org/tools/meme) using full-length amino acid sequences [51].
Chromosomal location, synteny analysis, and calculation of the Ka and Ks values
The information of chromosomal localization of SnRK2 genes was obtained from genome annotation documents [24]. A method similar to that developed for PGGD (http://chibba.agtec.uga.edu/duplication/) was then performed for synteny analysis [52]. Initially, BLASTP was used to search for potential homologous gene pairs (E < 1 e− 6) across multiple genomes. Subsequently, MCScanX was used to identify syntenic chains using homologous pairs as input [53]. In addition, MCScanX was used to identify tandem, whole-genome/segmental, proximal, and dispersed duplications in the SnRK2 gene family. The data were then plotted using Circos software [54]. The Ka and Ks substitution rates of syntenic gene pairs were identified by the MCScanX downstream analysis tools. The mean Ks values of orthologous SnRK2 gene pairs among Rosaceae species were calculated using all homologous gene pairs located in the same syntenic block. KaKs Calculator 2.0 was used to confirm the Ka and Ks values [27].
Plant treatments and qRT-PCR assays
To examine the expression patterns of PbrSnRK2 genes in response to abiotic stresses, the leaves of 3-month-old pear seedlings were sprayed with 50 μM ABA solutions. Samples were harvested from leaves at 0, 3, 6, and 9 h after treatment. All samples were frozen immediately in liquid nitrogen and maintained at − 80 °C for total RNA extraction. Total RNA was isolated independently from roots, stems, leaves of 3-month-old pear seedlings, flowers (8-year-old pear tree), ripening fruits (8-year-old pear tree), styles (8-year-old pear tree), pollen grains (8-year-old pear tree), and pollen tubes (8-year-old pear tree) cultured for 5 h as well as samples for ABA treatment using the RNA Extraction Kit (Invitrogen™ TRIzol® Reagent, Thermo Scientific, Nanjing, China), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Subsequently, the first-strand cDNA was synthesized using M-MLV reverse transcriptase (TaKaRa, Biotech, Shanghai, China). Specific primers for PbrSnRK2s and the housekeeping Actin gene Pbr035825.1 in pear were designed using Primer Premier 5.0 (Table S3), and we used the program Primer Search-Paired against the pear genome to verify the specificity of these primers. Three biological and three technical replicates were used for qRT-PCR assays, and each PCR reaction included 10 μL of LightCycler 480 SYBRGREEN I Master Mix (Roche, Basel, Switzerland), 100 ng of cDNA, and 200 nM of each primer in a final volume of 20 μL. All reactions were conducted using the CFX96 Real-Time System (Roche), Relative expression levels were calculated using the 2–ΔΔCt method and normalized to the PbrSnRK2 genes. The results were analyzed using Office 2010, and statistical analyses were performed with SPSS17.0 using Duncan’s multiple-range test at a significance level (P) of < 0.05.
Availability of data and materials
All data and materials used in this study are publicly available.
Abbreviations
- SnRK2:
-
Sucrose non-fermenting 1-related protein kinase 2
- WGD:
-
Whole-genome duplication
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- PGDD:
-
Plant genome duplication database
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time PCR
- PG:
-
Pollen grain
- PT:
-
Pollen tube
- HMM:
-
Hidden Markov Model
References
Viswanathan C, Karen S, Zhu J. Molecular genetic perspectives on cross-talk and specificity in abiotic stress signalling in plants. J Exp Bot. 2004;55(395):225–36.
Umezawa T, Sugiyama N, Takahashi F, Anderson JC, Ishihama Y, Peck SC, Shinozaki K. Genetics and Phosphoproteomics reveal a protein phosphorylation network in the Abscisic acid signaling pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana. Sci Signal. 2013.
Hardie DG. Plant protein serine/threonine kinases: classification and functions. Annu Rev Plant Phys. 1999;50(1):97–131.
Kulik A, Wawer I, Krzywińska E, Bucholc M, Dobrowolska GY. SnRK2 protein kinases-key regulators of plant response to abiotic stresses. OMICS. 2011;15(12):859–72.
Fujita Y, Yoshida T, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. Pivotal role of the AREB/ABF-SnRK2 pathway in ABRE-mediated transcription in response to osmotic stress in plants. Physiol Plantarum. 2012;147(1):15–27.
Huai JL, Wang M, He J. Cloning and characterization of the SnRK2 gene family from Zea mays. Plant Cell Rep. 2008;27(12):1861–8.
Zheng Z, Xu X, Crosley RA, Greenwalt SA, Sun Y, Blakeslee B, Wang L, Ni W, Sopko MS, Yao C. The protein kinase SnRK2.6 mediates the regulation of sucrose metabolism and plant growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2010;153(1):99–113.
Kim MJ, Park MJ, Seo PJ, Song JS, Kim HJ, Park CM. Controlled nuclear import of the transcription factor NTL6 reveals a cytoplasmic role of SnRK2.8 in the drought-stress response. Biochem J. 2012;448(3):353–63.
McLoughlin F, Galvan-Ampudia CS, Julkowska MM, Caarls L. Does Dvd: the Snf1-related protein kinases SnRK2.4 and SnRK2.10 are involved in maintenance of root system architecture during salt stress. Plant J. 2012;72(3):436–49.
Zhang H, Mao X, Zhang J, Chang X, Jing R. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms and association analysis of drought-resistance gene TaSnRK2.8 in common wheat. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2013;70(1):174–81.
Ying S, Zhang D, Li H, Liu Y, Shi Y, Song Y, Wang TY, Li Y. Cloning and characterization of a maize SnRK2 protein kinase gene confers enhanced salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep. 2011;30(9):1683–99.
Sun SJ, Qi GN, Gao QF, Wang HQ, Yao FY, Hussain J, Wang YF. Protein kinase OsSAPK8 functions as an essential activator of S-type anion channel OsSLAC1, which is nitrate-selective in rice. Planta. 2016;243(2):489–500.
Su Y, Wang Y, Zhen J, Zhang X, Chen Z, Li L, Huang Y, Hua J. SnRK2 homologs in Gossypium and GhSnRK2.6 improved salt tolerance in transgenic upland cotton and Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol Rep. 2017;35(4):442–56.
Shao Y, Zhang X, Van Nocker S, Gong X, Ma F. Overexpression of a protein kinase gene MpSnRK2.10 from Malus prunifolia confers tolerance to drought stress in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana and apple. Gene. 2019;692:26–34.
Guo D, Li HL, Zhu JH, Wang Y, Peng SQ. Genome-wide identification, characterization, and expression analysis of SnRK2 family in Hevea brasiliensis. Tree Genet Genomes. 2017;13(4):86.
Wei Z, Cheng YH, Chi Z, Shen XJ, You QB, Wei G, Xiang L, Song XJ, Zhou XA, Jiao YQ. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the GmSnRK2 family in soybean. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(9):1834.
Yoshida R, Umezawa T, Mizoguchi T, Takahashi S, Takahashi F, Shinozaki K. The regulatory domain of SRK2E/OST1/SnRK2.6 interacts with ABI1 and integrates Abscisic acid (ABA) and osmotic stress signals controlling Stomatal closure in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(8):5310–8.
Kobayashi Y, Yamamoto S, Minami H, Kagaya Y, Hattori T. Differential activation of the rice sucrose nonfermenting1-related protein kinase2 family by hyperosmotic stress and abscisic acid. Plant Cell. 2004;16(5):1163–77.
Burza AM, Pekala I, Sikora J, Siedlecki P, Malagocki P, Bucholc M, Koper L, Zielenkiewicz P, Dadlez M, Dobrowolska G. Nicotiana tabacum osmotic stress-activated kinase is regulated by phosphorylation on Ser-154 and Ser-158 in the kinase activation loop. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(45):34299–311.
Tian X, Ren R, Zhang YY, Pang Y, Yan C, Gong X, Yuan H, Li W, Di M, Qi H. Molecular mechanism for the inhibition of a critical component in the Arabidopsis thaliana abscisic acid signal transduction pathways, SnRK2.6, by the protein phosphatase ABI1. J Biol Chem. 2011;287(1):794–802.
Zhang H, Mao X, Jing R, Chang X, Xie H. Characterization of a common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) TaSnRK2.7 gene involved in abiotic stress responses. J Exp Bot. 2011;62(3):975–88.
Monks DE, Aghoram K, Courtney PD, De Wald DB, Dewey RE. Hyperosmotic stress induces the rapid phosphorylation of a soybean phosphatidylinositol transfer protein homolog through activation of the protein kinases SPK1 and SPK2. Plant Cell. 2001;13(5):1205–19.
Shao Y, Qin Y, Zou Y, Ma F. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of the SnRK2 gene family in Malus prunifolia. Gene. 2014;552(1):87–97.
Wu J, Wang ZW, Shi ZB, Zhang S, Ming R, Zhu SL, Khan MA, Tao ST, Korban SS, Wang H, et al. The genome of the pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.). Genome Res. 2013;23(2):396–408.
Chen G, Chen Q, Qi K, Xie Z, Yin H, Wang P, Wang R, Huang Z, Zhang S, Wang L, et al. Identification of shaker K+ channel family members in Rosaceae and a functional exploration of PbrKAT1. Planta. 2019;250(6):1911–25.
Chen G, Li X, Qiao X, Li J, Wang L, Kou X, Wu X, Wang G, Yin H, Wang P, et al. Genome-wide survey and expression analysis of the SLAC/SLAH gene family in pear (Pyrus bretschneideri) and other members of the Rosaceae. Genomics. 2019;111:1097–107.
Qiao X, Li M, Li LT, Yin H, Wu JY, Zhang SL. Genome-wide identification and comparative analysis of the heat shock transcription factor family in Chinese white pear (Pyrus bretschneideri) and five other Rosaceae species. BMC Plant Biol. 2015;15(1):12.
Velasco R, Zharkikh A, Affourtit J, Dhingra A, Cestaro A, Kalyanaraman A, Fontana P, Bhatnagar SK, Troggio M, Pruss D. The genome of the domesticated apple (Malus× domestica Borkh.). Nat Genet. 2010;42(10):833–9.
Fawcett JA, Maere S. Van dP, Y.: plants with double genomes might have had a better chance to survive the cretaceous-tertiary extinction event. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2009;106(14):5737–42.
Zhou H, Yin H, Chen J, Liu X, Zhang S. Gene-expression profile of developing pollen tube of Pyrus bretschneideri. Gene Expr Patterns. 2016;20(1):11–21.
Li Q, Qiao X, Yin H, Zhou Y, Dong H, Qi K, Li L, Zhang S. Unbiased subgenome evolution following a recent whole-genome duplication in pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.). Horticulture Res. 2019;6(34):1–12.
Chen G, Li X, Chen Q, Wang L, Qi K, Yin H, Qiao X, Wang P, Zhang S, Wu J, et al. Dynamic transcriptome analysis of root nitrate starvation and re-supply provides insights into nitrogen metabolism in pear (Pyrus bretschneideri). Plant Sci. 2018;277:322–33.
Chen S, Jia H, Wang X, Shi C, Li J. Hydrogen sulfide positively regulates abscisic acid signaling through persulfidation of SnRK2.6 in guard cells. Mol Plant. 2020;13(5):732–44.
Lin Z, Li Y, Zhang Z, Liu X, Wang P. A RAF-SnRK2 kinase cascade mediates early osmotic stress signaling in higher plants. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):1–10.
Maher C, Stein L, Ware D. Evolution of Arabidopsis microRNA families through duplication events. Genome Res. 2006;16(4):510–9.
Maere S, De Bodt S, Raes J, Casneuf T, Van Montagu M, Kuiper M, Van de Peer Y. Modeling gene and genome duplications in eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2005;102(15):5454–9.
Wang G, Yin H, Qiao X, Tan X, Gu C, Wang B, Cheng R, Wang Y, Zhang S. F-box genes: genome-wide expansion, evolution and their contribution to pollen growth in pear (Pyrus bretschneideri). Plant Sci. 2016;253:164–75.
Starr TK, Jameson SC, Hogquist KA. Positive and negative selection of T cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:139–76.
Yang ZH. PAML 4: phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol Biol Evol. 2007;24(8):1586–91.
Saha J, Chatterjee C, Sengupta A, Gupta K, Gupta B. Genome-wide analysis and evolutionary study of sucrose non-fermenting 1-related protein kinase 2 (SnRK2) gene family members in Arabidopsis and Oryza. Comput Biol Chem. 2014;49(APR.):59–70.
Fujita Y, Nakashima K, Yoshida T, Katagiri T, Kidokoro S, Kanamori N, Umezawa T, Fujita M, Maruyama K, Ishiyama K, et al. Three SnRK2 protein kinases are the Main positive regulators of Abscisic acid signaling in response to water stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009;50(12):2123–32.
Fujii H, Verslues PE, Zhu JK. Identification of two protein kinases required for abscisic acid regulation of seed germination, root growth, and gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2007;19(2):485–94.
Mustilli AC, Merlot S, Vavasseur A, Fenzi F, Giraudat J. Arabidopsis OST1 protein kinase mediates the regulation of stomatal aperture by abscisic acid and acts upstream of reactive oxygen species production. Plant Cell. 2002;14:3089–99.
Boudsocq M, Barbier-Brygoo H, Lauriere C. Identification of nine sucrose nonfermenting 1-related protein kinases 2 activated by hyperosmotic and saline stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:41758–66.
Mizoguchi M. Umezawa, Taishi, Nakashima, Kazuo, Kidokoro, Satoshi, Takasaki, Hironori: two closely related subclass II SnRK2 protein kinases cooperatively regulate drought-inducible gene expression. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010;51:842–7.
Bai J, Mao J, Yang H, Khan A, Fan A, Liu S, Zhang J, Wang D, Gao H, Zhang J. Sucrose non-ferment 1 related protein kinase 2 (SnRK2) genes could mediate the stress responses in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). BMC Genet. 2017;18(1):41.
Wang Y, Li X, Lin Y, Wang Y, Wang K, Sun C, Lu T, Zhang M. Structural variation, functional differentiation, and activity correlation of the cytochrome P450 gene superfamily revealed in ginseng. Plant Genome. 2017;11(3):1–11.
Liu Z, Ge X, Yang Z, Zhang C, Zhao G, Chen E. Genome-wide identification and characterization of SnRK2 gene family in cotton ( Gossypium hirsutum L.). BMC Genet. 2017;18(1).
Eddy SR. Accelerated profile HMM searches. PLoS Comput Biol. 2011;7(10):e1002195.
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30(12):2725–9.
Bailey TL, Williams N, Misleh C, Li WW. MEME: discovering and analyzing DNA and protein sequence motifs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34:W369–73.
Lee TH, Tang HB, Wang XY, Paterson AH. PGDD: a database of gene and genome duplication in plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41(D1):D1152–8.
Tang HB, Wang XY, Bowers JE, Ming R, Alam M, Paterson AH. Unraveling ancient hexaploidy through multiply-aligned angiosperm gene maps. Genome Res. 2008;18(12):1944–54.
Krzywinski M, Schein J, Birol I, Connors J, Gascoyne R, Horsman D, Jones SJ, Marra MA. Circos: an information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009;19(9):1639–45.
Acknowledgements
Not Applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by the Talent Introduction Research Project for Huaiyin Institute of Technology (Z301B19573), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31801829), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20170463, BK20170462, BK20181062), the Natural Science Research Project in Colleges of Jiangsu Province of China (18KJD210001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CGD designed the research, performed the experiments, analyzed the results, and drafted the manuscript. WJZ managed the experiments analyzed the results and revising the final manuscript. QX analyzed the results and participated in revising the final manuscript. JC, DWK and SXC participated in carrying out the experiments and revising the final manuscript. WJY managed the experiments and revising the final manuscript. The authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Figure S1.
Phylogenetic relationship of conserved motif of SnRK2 genes from pear and Arabidopsis thaliana. A.A phylogenetic tree constructed with CluxtalX2.0 using the full-length amino acid sequences of SnRK2 genes from pear and Arabidopsis. Bootstrap analysis was performed using 1000 replicates. The species in which SnRK2 proteins were functionally characterized are displayed as icons, and the different colors in the branches represent the different subfamilies. B. MEME tools were used to identify conserved motifs of SnRK2 proteins, different colors represent different motifs. The scale bar indicates 50 aa.
Additional file 2: Figure S2.
Chromosomal localization and synteny of SnRK2 genes in Rosaceae genomes. SnRK2 genes in Chinese plum, black raspberry, cherry, and European pear were mapped onto different chromosomes. Chromosome number is indicated on the inner side in the inner circle corresponding to different SnRK2 genes. Gene pairs with a syntenic relationship are joined by a line.
Additional file 3: Figure S3.
Analysis of the expression levels of PbrSnRK2 in different pear tissues. A heat map depicting the overall trend of the differential expression profiles of PbrSnRK2 genes in different pear tissues was constructed using MeV. The rows in the heat map represent genes and columns represent tissues. The colors of heat map cells indicate the scaled expression levels of genes across different tissues. The color gradient from blue to yellow corresponds to low-to-high transcript levels.
Additional file 4: Table S1.
Sequence identity of protein sequences between PbrSnRK2s and AtSnRK2s based on pairwise comparison.
Additional file 5: Table S2.
Number of SnRK2 genes from different origins in eight Rosaceae genomes.
Additional file 6: Table S3.
Primers used in this study.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, G., Wang, J., Qiao, X. et al. Genome-wide survey of sucrose non-fermenting 1-related protein kinase 2 in Rosaceae and expression analysis of PbrSnRK2 in response to ABA stress. BMC Genomics 21, 781 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-020-07201-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-020-07201-w