Abstract
Background
Numerous studies examining the relationship between CD44 expression and prognostic impact in patients with osteosarcoma have yielded inconclusive results. The aim of this meta-analysis was carried out to investigate the relationship between CD44 expression and the survival in patients with osteosarcoma.
Methods
We therefore conducted a meta-analysis to provide a comprehensive evaluation of the prognostic role of CD44 expression on the overall survival rate and metastasis, which compared the positive and negative expression of CD44 in patients of the available studies.
Results
A detailed search was made in MEDLINE and EMBASE for relevant original articles published in English. Finally, a total of six studies with 329 osteosarcoma patients were involved to estimate the relationship between CD44 expression and metastasis of tumor and overall survival. Positive expressions of CD44 did not predict neoplasm metastasis (RR = 1.36, 95% CI: 1.00–1.84, P = 0.50), and the results indicated that higher expression of CD44 could not predict poorer survival in osteosarcoma with the pooled HR of 0.55 (95% CI: 0.27–1.13, P = 0.47).
Conclusions
The findings from this present meta-analysis suggest that CD44 expression is not associated with overall survival rate and metastasis in osteosarcoma.
Virtual Slides
The virtual slide(s) for this article can be found here: http://www.diagnosticpathology.diagnomx.eu/vs/1373995521295618
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Osteosarcoma is the most common malignant primary bone tumor and the majority of these tumors occur among children and adolescents [1–3]. Despite the development of neoadjuvant chemotherapy, the 5-year survival rate for patients with high-grade osteosarcoma is still less than 50% [4]. The prognostic factors that have been implicated include demographics (age and sex), tumor size, site, stage, and response to chemotherapy. However, the mechanism of prognosis in osteosarcoma patients is still not fully understood. Therefore, a better understanding into its basic biology is urgently needed to identify its prognostic markers and therapeutic targets [5, 6]. In recent years, the expression of certain biological molecules has been identified as potential prognostic markers for osteosarcoma, including the expression of CD44.
CD44 is the major hyaluronan (HA) receptor [7], and CD44 bound to HA has been proven to participate in various tumor biological activities, including tumor progression, metastasis and proliferation [8, 9]. Some variant isoforms of CD44 (CD44V) are reportedly associated with increased invasion, metastasis, and poor prognosis [10]. It has been reported that CD44V6 can regulate the extracellular matrix, promote cell motility, and suppress tumor apoptosis. In fact, CD44V6 has been implicated in promoting tumor progression [11]. CD44 proteins have been studied in relation to tumor malignancy and metastatic potential. The prognostic value of CD44 for patients with cancer has been reported in various solid tumors, including colon, lung, and breast cancer [12–14]. With respect to osteosarcoma, the relationship between CD44 expression and prognosis was still controversial [15, 16].
Most of earlier studies suggested CD44 high expression was associated with high risk of tumor metastasis and worse survival in patients with osteosarcoma. However, some other studies showed insignificant or opposite results. Therefore, the aim of this meta-analysis was carried out to investigate the relationship between CD44 expression and the survival in patients with osteosarcoma. We also discuss the possibility of using CD44 as a prognostic marker in osteosarcoma.
Methods
Search strategy
The PubMed, EMBASE, and MEDLINE databases were searched, in addition to the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, to locate articles (published between January 1994 and January 2014), including articles referenced in the publications. The search strategy included the following keywords variably combined by “CD44”, “osteosarcoma”, “bone tumor” and “prognosis”. Internet search engines were also used to perform a manual search for abstracts from international meetings, which were then downloaded and studied.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Studies met the inclusion criteria if they studied the patients with osteosarcoma, measured the expression of CD44 in cancer tissue and investigated the association betweenCD44 expression levels and survival out come. When a study reporting the same patient cohort was included in several publications, only the most recent or complete study was selected. Studies of case reports, letters, and reviews without original data; non-English papers; animal or laboratory studies; and studies of nondichotomousCD44 expression levels and absence of survival outcome were excluded. If any doubt of suitability remained after the abstract was examined, the full manuscript was obtained [17].
Data extraction
Two review authors assessed the methodological quality of potentially eligible studies, without consideration of the results. Extracted data were then crosschecked between the two authors to rule out any discrepancy. Data regarding the following for each included studies were extracted independently: first authors’ surname, publication year, origin country, sample size, CD44 assessment methods and the cut-off definition, and HR of CD44 expression for overall survival (OS) as well as corresponding 95% confidential interval (CI) and P value. Multivariate Cox hazard regression analysis reported in the article was included in the present analysis. Disagreements were discussed by the authors and resolved by consensus.
Statistical analysis
The statistical analysis was carried out using the Review Manager (RevMan) software version 5.0(The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, Copenhagen, Denmark).All these HRs and 95% confidence interval(CI) were calculated following Tierney’s method. Pooled HR was calculated using a fixed-effects model or random-effects model to evaluate the relationship between CD44expression and overall survival. I2 statisticswas used to evaluate the between-study heterogeneity analysis in this meta-analysis [18]. The random effects model was used when an obvious heterogeneity was observed among the included studies (I2 > 50%). The fixed effects model was used when there was no significant heterogeneity between the included studies (I2 ≤ 50%). Publication bias was estimated using a funnel plot with an Egger’s line arregression test; funnel plot asymmetry on the natural logarithm scale of the HR was measured by a line arregression approach.
Results
Eligible studies
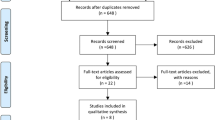
The initial search retrieved a total of 86 references, and after screening titles and abstracts of identified articles, 38 were excluded because they were not related to the current study. Upon further review, 34 were excluded because they were either laboratory studies or records without survival data. Then we evaluated 14 potential candidate studies in full text. It was found that the survival data of one article could not be used in this study. Finally, 6 [19–24] studies were included in this meta-analysis, which were published between1994 and 2014 (Figure 1). All of them were retrospective in design. In each study, the cut-off values of CD44 appeared to be different. The main characteristics of the included studies were summarized in Table 1.
Meta-analysis
For studies evaluating overall survival (OS), there was no between-study heterogeneity among those six studies for CD44 (I2 = 0%), so the fixed-effect model was used to calculate the pooled HR with corresponding 95% CI. The result indicated that positive expressions of CD44 did not predict neoplasm metastasis (RR = 1.36, 95% CI: 1.00–1.84, P = 0.50), and higher expression of CD44 could not predict poorer survival in osteosarcoma with the pooled HR of 0.55 (95% CI: 0.27–1.13, P = 0.47). (Figures 2, 3)
Publication bias
Funnel plot and Egger’s test were used to evaluate the publication bias of the literatures. The shape of the funnel plot did not reveal any evidence of obvious asymmetry (Figures not shown).
Discussion
Osteosarcoma is a life-threatening bone malignancy that often occurs in teenagers. It is the second leading cause of cancer-related death in pediatric age group and young adults [25]. Current treatments for osteosarcoma include surgical resection of both primary and pulmonary lesions, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy. Disease-free survival escalated from <20% prior to the introduction of effective chemotherapy to around 60% and overall survival to 60–70% [26]. At present, the ability to predict the prognosis of osteosarcomas is limited. Therefore, identifying prognostic markers of survival in osteosarcomas could be informative for selecting proper management. Traditional prognostic markers, such as gender, age, tumor location, disease-free interval, tumor doubling time, representation, and number of detectable pulmonary metastases, have had limited success in identifying those patients that need aggressive chemotherapy and those that do not [27]. In recent years, a number of cell surface markers were found to indicate a small group of cancer cells, referred as cancer stem cells, which are responsible for tumor initiation, progression, metastasis and drug resistance [28]. Many researchers have reported that high expression of these markers indicates bad clinical features and poor prognosis [29, 30], and CD44 was one of the most reported cancer stem cells markers.
CD44 was previously thought to be a transmembrane adhesion molecule, which also played a role in the metabolism of its principal ligand hyaluronan. It may exist in three distinct physical phases, as a transmembrane cell surface receptor, an integral component of the matrix and in a fluid phase, each with the potential for being functionally significant. CD44 is known to be a major hyaluronic acid receptor in vitro, although it is not known how often CD44 is expressed or what role it plays in normal bone tissues. CD44 proteins have been observed in osteoclasts and osteocytes by means of immunohistochemical analysis on bone tissue, but there have been some controversial reports that CD44 proteins were found in osteoblasts [31]. As CD44 reacts with the extracellular matrix, several published reports have suggested that CD44 expression is related to metastatic potential, prognosis, and the biologic properties of human malignancies. Investigations of CD44 over the past 20 years have established additional functions for CD44, including its capacity to mediate inflammatory cell function, tumor growth, adhesion, migration and metastasis. It has also become evident that intricate post-translational modifications of CD44 regulate the affinity of the receptor for its ligands [32]. Whether CD44 is a prognostic marker in osteosarcoma patients has been studied extensively, but the conclusions are inconsistent. This meta-analysis was carried out by critically reviewing six studies on the association of CD44 with prognosis in osteosarcoma.
The present meta-analysis showed that high CD44 expression did not indeed predict poor survival and metastasis in patients with osteosarcoma. However, it should be circumspect to make a verdict of the association with CD44 and osteosarcoma, because there are still several issues should be considered. First, since the number of included studies in this meta-analysis was only six, it might weaken the reliability of our results. More well-designed clinical studies with large cases of osteosarcoma should be performed in the future to validate the relationship between CD44 expression level and prognosis of osteosarcoma patients. Second, lack of abundant CD44 expression data in global population makes it difficult to set a standard value for the measurement of CD44. Third, the methods used for the evaluation of the levels of markers in osteosarcoma patients and the use of standard threshold, are both likely to impact on our results. Although immunohistochemistry was the most commonly applied method, the cut-off value was defined differently in inclusion studies. Therefore, we strongly suggest conducting more prognostic studies for high CD44 expression in osteosarcoma.
Moreover, recently studies have demonstrated that microRNAs might influence chemoresistance of osteosarcomas with different pathways including CD44, resistance to chemotherapeutic agents is still one of the major reasons for the failure of osteosarcoma treatment, while we did not excluded the role of CD44 in chemoresistance of osteosarcoma. The identification of cancer-specific miRNAs and their targets is pivotal for understanding their role in tumorigenesis and metastasis, and may be important for the discovery of novel therapeutic targets. CD44 which contained the corresponding binding site of microRNAs’ 3′UTR, was regulated by some microRNAs, such as miR-34a, miR-140 and miR-215 [33–35]. The results of these published studies showed that the CD44 level inversely correlated with the microRNAs level. So in the future research, we will discuss the role of CD44 in chemoresistance of osteosarcoma.
On the other hand, many researchers have reported that high expression of some markers indicates bad clinical features. Such as clinical stage, positive distant metastasis and poor response to chemotherapy [36, 37]. In this present study, we also discussed the relationship between overexpression of CD44 and clinicopathological parameters in osteosarcoma patients. Nonetheless, the result showed that no significant difference was observed between the expression of CD44 and patients’ age, gender, tumor size, clinical stage, positive distant metastasis and poor response to chemotherapy (data not shown).
Despite the inherent limitations of meta-analysis on prognostic literature, this meta-analysis, representing a quantified synthesis of all published studies of CD44, has shown that the high expressed CD44 is not significantly associated with poor survival and metastasis in patients with osteosarcoma. For better analysis the relationship between CD44 expression and prognostic with the osteosarcoma, it is necessary to improve the experimental methods and detection methods, and to clear a unified quantitative standard. Future adequately multi-center designed prospective with larger sample size were of great value to confirm these findings and more clinical studies should be carried out before the application of CD44 in prognosis of osteosarcoma.
Conclusions
The findings from this present meta-analysis suggest that CD44 expression is not associated with overall survival rate and metastasis in osteosarcoma. CD44 may not be a useful marker to predict prognosis of osteosarcoma.
Authors’ information
Yu Liu and Yongwei Wu: co-first authors.
References
Bertucci F, Araujo J, Giovannini M: Pancreatic metastasis from osteosarcoma and Ewing sarcoma: literature review. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2013, 48: 4-8.
Kong C, Hansen MF: Biomarkers in Osteosarcoma. Expert Opin Med Diagn. 2009, 3: 13-23.
Ottaviani G, Jaffe N: The etiology of osteosarcoma. Cancer Treat Res. 2009, 152: 15-32.
Picci P, Mercuri M, Ferrari S, Alberghini M, Briccoli A, Ferrari C, Pignotti E, Bacci G: Survival in high-grade osteosarcoma: improvement over 21 years at a single institution. Ann Oncol. 2010, 21: 1366-1373.
Durnali A, Alkis N, Cangur S, Yukruk FA, Inal A, Tokluoglu S, Seker MM, Bal O, Akman T, Inanc M, Isikdogan A, Demirci A, Helvaci K, Oksuzoglu B: Prognostic factors for teenage and adult patients with high-grade osteosarcoma: an analysis of 240 patients. Med Oncol. 2013, 30: 624-
Gorlick R: Osteosarcoma: clinical practice and the expanding role of biology. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2002, 2: 549-551.
Wibulswas A, Croft D, Pitsillides AA, Bacarese-Hamilton I, McIntyre P, Genot E, Kramer IM: Influence of epitopes CD44v3 and CD44v6 in the invasive behavior of fibroblast-like synoviocytes derived from rheumatoid arthritic joints. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46: 2059-2064.
Fehon RG, McClatchey AI, Bretscher A: Organizing the cell cortex: the role of ERM proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010, 11: 276-287.
Lamontagne CA, Grandbois M: PKC-induced stiffening of hyaluronan/CD44 linkage; local force measurements on glioma cells. Exp Cell Res. 2008, 314: 227-236.
Zhang XG, Lu XF, Jiao XM, Chen B, Wu JX: PLK1 gene suppresses cell invasion of undifferentiated thyroid carcinoma through the inhibition of CD44v6, MMP-2 and MMP-9. Exp Ther Med. 2012, 4: 1005-1009.
Jung T, Gross W, Zoller M: CD44v6 coordinates tumor matrix-triggered motility and apoptosis resistance. J Biol Chem. 2011, 286: 15862-15874.
Brown RL, Reinke LM, Damerow MS, Perez D, Chodosh LA, Yang J, Cheng C: CD44 splice isoform switching in human and mouse epithelium is essential for epithelial-mesenchymal transition and breast cancer progression. J Clin Invest. 2011, 121: 1064-1074.
Leung EL, Fiscus RR, Tung JW, Tin VP, Cheng LC, Sihoe AD, Fink LM, Ma Y, Wong MP: Non-small cell lung cancer cells expressing CD44 are enriched for stem cell-like properties. PLoS One. 2010, 5: e14062-
Su YJ, Lai HM, Chang YW, Chen GY, Lee JL: Direct reprogramming of stem cell properties in colon cancer cells by CD44. EMBO J. 2011, 30: 3186-3199.
Esteban F, Bravo JJ, Gonzalez-Moles MA, Bravo M, Ruiz-Avila I, Gil-Montoya JA: Adhesion molecule CD44 as a prognostic factor in laryngeal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25: 1115-1121.
Xu YP, Zhao XQ, Sommer K, Moubayed P: Correlation of matrix metalloproteinase-2, -9, tissue inhibitor-1 of matrix metalloproteinase and CD44 variant 6 in head and neck cancer metastasis. J Zhejiang Univ Sci. 2003, 4: 491-501.
Bradburn MJ, Deeks JJ, Berlin JA, Russell LA: Much ado about nothing: a comparison of the performance of meta-analytical methods with rare events. Stat Med. 2007, 26: 53-77.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG: Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003, 327: 557-560.
Boldrini E, Peres SV, Morini S, de Camargo B: Immunoexpression of Ezrin and CD44 in patients with osteosarcoma. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2010, 32: e213-e217.
Deng Z, Niu G, Cai L, Wei R, Zhao X: The prognostic significance of CD44V6, CDH11, and beta-catenin expression in patients with osteosarcoma. Biomed Res Int. 2013, 2013: 496193-
Gvozdenovic A, Arlt MJ, Campanile C, Brennecke P, Husmann K, Li Y, Born W, Muff R, Fuchs B: CD44 enhances tumor formation and lung metastasis in experimental osteosarcoma and is an additional predictor for poor patient outcome. J Bone Miner Res. 2013, 28: 838-847.
Kim HS, Park YB, Oh JH, Jeong J, Kim CJ, Lee SH: Expression of CD44 isoforms correlates with the metastatic potential of osteosarcoma. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002, 396: 184-190.
Kuryu M, Ozaki T, Nishida K, Shibahara M, Kawai A, Inoue H: Expression of CD44 variants in osteosarcoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1999, 125: 646-652.
Ma Q, Zhou Y, Ma B, Chen X, Wen Y, Liu Y, Fan Q, Qiu X: The clinical value of CXCR4, HER2 and CD44 in human osteosarcoma: A pilot study. Oncol Lett. 2012, 3: 797-801.
Siclari VA, Qin L: Targeting the osteosarcoma cancer stem cell. J Orthop Surg Res. 2010, 5: 78-
Osborne TS, Khanna C: A review of the association between osteosarcoma metastasis and protein translation. J Comp Pathol. 2012, 146: 132-142.
Nakajima G, Patino-Garcia A, Bruheim S, Xi Y, San Julian M, Lecanda F, Sierrasesumaga L, Muller C, Fodstad O, Ju J: CDH11 expression is associated with survival in patients with osteosarcoma. Canc Genomics Proteomics. 2008, 5: 37-42.
Nguyen LV, Vanner R, Dirks P, Eaves CJ: Cancer stem cells: an evolving concept. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012, 12: 133-143.
Wang K, Xu J, Zhang J, Huang J: Prognostic role of CD133 expression in colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 2012, 12: 573-
Ni C, Zhang Z, Zhu X, Liu Y, Qu D, Wu P, Huang J, Xu AX: Prognostic value of CD166 expression in cancers of the digestive system: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2013, 8: e70958-
Jamal HH, Aubin JE: CD44 expression in fetal rat bone: in vivo and in vitro analysis. Exp Cell Res. 1996, 223: 467-477.
Iwaya K, Ogawa H, Kuroda M, Izumi M, Ishida T, Mukai K: Cytoplasmic and/or nuclear staining of beta-catenin is associated with lung metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2003, 20: 525-529.
Song B, Wang Y, Titmus MA, Botchkina G, Formentini A, Kornmann M, Ju J: Molecular mechanism of chemoresistance by miR-215 in osteosarcoma and colon cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 2010, 9: 96-
Song B, Wang Y, Xi Y, Kudo K, Bruheim S, Botchkina GI, Gavin E, Wan Y, Formentini A, Kornmann M, Fodstad O, Ju J: Mechanism of chemoresistance mediated by miR-140 in human osteosarcoma and colon cancer cells. Oncogene. 2009, 28: 4065-4074.
Zhao H, Ma B, Wang Y, Han T, Zheng L, Sun C, Liu T, Zhang Y, Qiu X, Fan Q: miR-34a inhibits the metastasis of osteosarcoma cells by repressing the expression of CD44. Oncol Rep. 2013, 29: 1027-1036.
Zhu H, Tang J, Tang M, Cai H: Upregulation of SOX9 in osteosarcoma and its association with tumor progression and patients' prognosis. Diagn Pathol. 2013, 8: 183-
Nada OH, Ahmed NS, Abou Gabal HH: Prognostic significance of HLA EMR8-5 immunohistochemically analyzed expression in osteosarcoma. Diagn Pathol. 2014, 9: 72-
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Authors' contributions
YL, YW and SG conceived the study idea and designed the study. ZS, YR, YL, HL and JW reviewed the literature and performed statistical analyses. YL and YW extracted data and drafted the manuscript. YL, KX and PS reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Yu Liu, Yongwei Wu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Wu, Y., Gu, S. et al. Prognostic role of CD44 expression in osteosarcoma: evidence from six studies. Diagn Pathol 9, 140 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-1596-9-140
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-1596-9-140