Abstract
Background
Investigation of the OPA1 mutation spectrum in autosomal dominant optic atrophy (ADOA) in Denmark.
Methods
Index patients from 93 unrelated ADOA families were assessed for a common Danish founder mutation (c.2826_2836delinsGGATGCTCCA) inOPA1. If negative, direct DNA sequencing of the coding sequence and multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) were performed. Results from MLPA analysis have been previously reported. Haplotype analysis was carried out analysing single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP). Retrospective clinical data were retrieved from medical files.
Results
Probably causative mutations were identified in 84 out of 93 families (90%) including 15 novel mutations. Three mutations c.983A > G, c.2708_2711delTTAG and c.2826_2836delinsGGATGCTCCA, were responsible for ADOA in10, 11 and 28 families, respectively, corresponding to 11%, 12% and 30%. A common haplotype in nine of ten c.983A > G families suggests that they descend from a single founder. The c.2708_2711delTTAG mutation was present on at least two haplotypes and has been repeatedly reported in various ethnic groups,thus represents a mutational hotspot. Clinical examinations of index patients with the two latter mutations demonstrated large inter- and intra-familial variations apparently.
Conclusions
Genetic testing for OPA1mutations assist in the diagnosis. We have identified mutations in OPA1 in 90% of families including 15 novel mutations. Both DNA sequencing and MLPA analysis are necessary to achieve a high detection rate. More than half of the affected families in Denmark are represented by three common mutations, at least two of which are due to a founder effect, which may account for the high prevalence of ADOA in Denmark.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Autosomal dominant optic atrophy (ADOA) is characterized by bilateral visual loss, preferential temporal disk pallor, dyschromatopsia, relative or absolute centrocoecalscotoma, and subnormal thickness of the retinal ganglion cell and nerve-fiber layers. The disease has incomplete penetrance and variable expressivity, ranging from subclinical visual dysfunction to legal blindness. The highly variable phenotype, both within and between families, suggests that modifier genes and/or environmental factors influence the expression of the disease. The prevalence of 1:12,000 in Denmark is remarkably high compared to 1:35,000 in other populations. [1, 2] Monosymptomatic optic atrophy shows genetic heterogeneity with at least eight loci; OPA1 (OMIM 605290) is the major ADOA gene. OPA2 (OMIM 311050) has been mapped to Xp11.4-p11.21, mutations in the OPA3 gene (OMIM 606580) have been reported in ADOA associated with cataract (ADOAC) (OMIM 165300), [3] OPA4 (OMIM 605293) has been mapped to chromosome 18q12.2-q12.3, OPA5 (OMIM 610708) to chromosome 22q12.1-q13.1 and OPA6 (OMIM 258500) to chromosome 8q. OPA7 (OMIM 612989) is caused by mutations in TMEM126A (OMIM 612988). [4] Recently the OPA8 locus has been mapped to chromosome 16q21-q22 [5].
OPA1is located on chromosome 3q28-q29, [6, 7] and more than 200 unique pathogenic mutations associated with Kjer-type optic atrophy (OMIM 165500) have been identified (http://lbbma.univ-angers.fr/eOPA1). [8] Mutation detection rates of OPA1 in ADOA patients rangefrom 32% to 89%. [9–11] Aninsertion and deletion mutation in exon 28 (c.2826_2836delinsGGATGCTCCA) causing a frameshift has previously been shown to be common in Denmark due to a founder effect [12].
OPA1 spans approximately 100 kb and is composed of 30 coding exons. Alternative splicing generates several isoforms. The main isoform is 960 amino acids long,encoded by 28 exons. The OPA1 protein is a ubiquitously expressed mitochondrial protein with similarity to dynamin-related GTPases.
Here we report the results of molecular genetic analyses of ADOApatients from Denmark. We identified two frequent mutations, besides the already known frequent founder mutation, and provide evidence for a founder effect in one and a probable mutational hotspot in the other. We report clinical data from families with the two new frequent mutations.
Methods
Patients
The cohort consisted of unrelated index patients from 93 families of Danish origin, clinically diagnosed with ADOA. In total 266 family members, 210 affected and 56 unaffected individuals were studied. Only cases from families with at least two affected members and a pattern compatible with autosomal dominant inheritance were included.
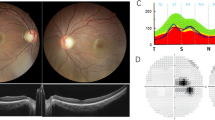
The diagnosis was based on routine clinical procedures, including refraction and determination of best-corrected visual acuity, color vision testing (various combinations of Farnsworth 100, Farnsworth-Roth 28, Americal Optical Hand-Hardy-Rittler, Farnsworth 15 Standard, Farnsworth 15 unsaturated, Lantony’sTritan album, and Nagel’s anomaloscope), direct ophthalmoscopy, slitlampbiomicroscopy of the anterior segment, vitreous, and posterior pole, fundus photography, Goldmann manual kinetic perimetry, and visual evoked potential recording. Clinical data from 19 families with one of two frequent mutations were retrospectively retrieved from a period of several decades.
The study followed the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the local medical ethics committee (The Ethical Committee of Central Region (De VidenskabsetiskeKomiteer for Region Hovedstaden) H-B-2007-110). Patients and healthy relatives were informed of the nature of the study and written informed consent was obtained.
Molecular genetic studies
Genomic DNA was extracted from leucocytes using Chemagic Magnetic Separation Module I (Chemagen, Baesweiler, Germany).
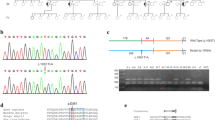
Analysis for c.2826_2836delinsGGATGCTCCA was performed by two separate PCR reactions using one common primer (OPA1R: TTG ATA GAC TAT AGG CAA GAA GAA) together with either a primer specific for the mutated allele (OPA1mutF: ACA GAG AAA GTG GAT GCT CC) or a primer specific for the wild type allele (OPA1wtF: CCA CAG AGA AAG TTA GAG AAA TTC). Fiftynanogram of genomic DNA was amplified in 30 μl volume using 10 pmol of each primer and AmpliTaq-Gold polymerase (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA), with initial denaturation for 5 minutes at 95°C followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 30 seconds, 56°C for 45 seconds and 72°C for 60 seconds, and a final extension at 72°C for 10 minutes. PCR products were analysed on agarose gel and ethidium bromide staining using standard methods.
DNA sequencing was performed of all 30 coding regions plus 20 bp of flanking sequences by PCR amplification using 50 ng of genomic DNA in a 50 μl volume using AmpliTaq Gold polymerase and 15 pmol each primer (see Additional file 1 for primer sequences). After initial denaturation at 95°C for 10 minutes, the samples were amplified for 35 cycles at 95°C for 30 seconds, 60°C for 30 seconds and 72°C for 30 seconds; final extension for 9 minutes at 72°C. Bidirectional sequencing was performed using BigDye v3.1 chemistry and ABI3130 (AppliedBiosystems). SeqScape software (version 2.5; Applied Biosystems) was used for analysis using reference sequence GenBank accession number NG_011605.1. GenBank transcript NM_015560 was used for numbering the variants with A in ATG as number 1.
Haplotype analysis was performed analysing 14 SNP’s surrounding the OPA1 gene (position chr3:188,391,767–196,005,479, human genome version hg19/GRCh37) (Table 1). The analysis was performed by KBiosciences (Hoddesdon, Herts, United Kingdom). SNPs with minor allele frequency >25% in European descendents were selected for the study.
Investigation of c.1313A > C, c.1376 G > A and c.2496 G > C in a control group, was performed by searching the gene database generated by LuCamp (http://www.lucamp.org) by whole exome sequencing (average coverage of X 8) [13] of 1000 healthy Danish controls and 1000 Danish individuals with the combined phenotypes of type 2 diabetes, obesity and hypertension (Additional file 2).
Results
Results from mutational analysis are shown in Table 2. The c.2826_2836delinsGGATGCTCCA mutation was found in 28 index patients. This mutation causes a frameshift and extension of the protein beyond the normal stopcodon (p. Arg943Aspfs*25). Sixty-five patients were left for further investigation. MLPA analysis showed deletions in 10 index patients, as previously reported. [14] In the remaining 55 index patients, DNA sequencing revealed a total of 24 sequence variations in 46 families including 15 novel mutations. The sequence variations were consisting of 16 nucleotide substitutions, six deletions, one insertion andtwo indels. On the protein level the sequence variations were predicted to cause three in-frame deletions, four nonsense mutations, fourmissense mutations, nine splice mutations and five frameshifts causing premature translation stop.
Fifteensequence variations were novel; of these, eleven introduced a premature stopcodon, caused deletion of an amino acid or were located in consensus splice sites. Threewere nucleotide substitutions, c.1313A > C, c.1376 G > A and c.2496 G > C. The c.1313A > C mutation is located as the first basepair in exon 14. In silico analysis using the splice site prediction of Berkeley Drosophila Genome Project (http://www.fruitfly.org/seq_tools/splice.html) predicts that c.1313A > C does not affect the splice site. Thus, this sequence variation probably causes a missense mutation p. Asp438Ala, predicted by SIFT (http://sift.jcvi.org/) to be damaging (SIFT score 0.01) and by Polyphen2 (http://genetics.bwh.harvard.edu/pph2/) to be probably damaging (Polyphen2 score 1.0). The c.1376 G > A variation is predicted to cause an aminoacid substitution, p. Gly459Glu, which is predicted to be pathogenic with SIFT score 0 and Polyphen2 score 1.0 and is probably a pathogenic missense mutation. Two unaffected family members did not have the variation.C.2496 G > C is the last basepair in exon 24 and is predicted by in silico analysis to destroy the donor splice site. Three unaffected family members did not have the variation. These three nucleotide substitutions no family members were available for segregation, however none were present in 1070 healthy Danish controls and 1000 Danish individuals with metabolic phenotypes (described under Materials and Methods section Molecular Genetic Studies). The indel c.2496 + 4_2496 + 5delinsGTAAC is located in intron 24. In silico analysis predicts that it destroys the splice site. The mutation segregated with the disease in this family (five affected and one unaffected).
Two sequence variations, c.983A > G and c.2708_2711delTTAG were present in 10 and 11 families, respectively. The c.983A > G mutation is reported to cause skipping of exon 9, resulting in an in-frame deletion of 38 amino acids. [16] The c.2708_2711delTTAG mutation is located as the first four nucleotides in exon 27. [2, 9–11, 15, 16, 19–21]Insilico analysis of the splice site predicts normal splicing; thus the sequence variation is predicted to cause a frameshift with incorporation of two amino-acids followed by a premature stop codon (p. Val903Glyfs*3). Haplotype analysis was performed using both affected and unaffected individuals from 10 families with c.983A > G and 10 families with c.2708_2711delTTAG (Table 1). Nine out of 10 families with c.983A > G shared the same haplotype of size 1,8 Mb while one family had a different haplotype distal to OPA1. At least two haplotypes were present for c.2708_2711delTTAG.
Analysis of the clinical characteristicsof affected individuals with c.983A > G or c.2708_2711delTTAG revealed a broad spectrum of phenotype variation in both groups (Figure 1 and Additional file 3). For c.983A > G the age at clinical onset varied from 3 to 62 years of age (mean 13.8, median 7 years) while visual acuity ranged from 6/6 to 2/60. For c.2708_2711delTTAG the age at clinical onset varied from 3 to 48 years of age (mean 13.3, median 8 years) and visual acuity also ranged from 6/6 to 2/60. Figure 1 shows the visual acuities converted from Snellen acuities into Log Mar. A very large intrafamilial variation is evident and there is no obvious difference between the two groups of patients. The distribution seems to be dichotomous, one clusterhaving visual acuities 6/18 (Log Mar 0.5) or above, the other cluster with visual acuities 6/24 (Log Mar 0.6) or below. Among the two mutation groups 57% and 54% was in the best visual acuitycluster. There was no clear effect of age and in broad terms the full spectrum of variation in visual acuity was present throughout the age range that was surveyed. Patients for whom data from more than one examination was available (Figure 1) showed considerable variations in the rate of acuity loss. Colordiscrimination also exhibited large variations, tritan defects being common and with no correlation to visual acuity. Additionally, some patients had red-green defects of different magnitudes, whileothers had no detectable color vision defect. Full-field visual evoked potentials (ffVEP) were ofreduced amplitudes and somewhat prolongedlatencies with occasionalabnormal configurations, including “spike-trains”. Pattern VEP (pVEP) regularlypresented reduced or nearly undetectable amplitudes, but some patients had both normal ffVEP and pVEP even despite having moderately reducedvisual acuity. The most frequent clinical sign was temporal pallor of the optic discs.
Discussion
In 84 of the 93 index patients (90%) we found sequence variations that were either obviously pathogenic or predicted to be pathogenic by in silico analysis. 53% were attributableto one of only threesequence variations (c.983A > G, c.2708_2711delTTAG, or c.2826_2836delinsGGATGCTCCA). This might explain the high prevalence 1:12,000 of Kjer-type optic atrophy in Denmark. The high mutation detection rate may reflect the clinical selection of the cohort from families with affected individuals in at least two generations and compatibility with autosomal dominant inheritance.
On the basis of the present study and the previously published MLPA study have lead us to perform mutational analysis in the most cost-effective manner: initially targeted analysis for c.2826_2836delinsGGATGCTCCA followed by MLPA analysis for deletions and duplications are performed. If these are negative, exon 9 and exon 27 are sequenced. In Danish patients this procedure can be expected to detect causative mutations in more than 60% of cases. Obviously, this strategy only applies to Danish ADOA patients, however, it must be emphasized that for other populations the fraction of deletions detectable by MLPA analysis and mutations detectable by DNA sequence analysis must be determined and probably both kinds of analyses must be performed to achieve a high detection rate.
In nine patients we did not detect pathogenic mutations. This might be due to mutations in regions not investigated (deep intronic mutations or mutations in regulatory regions) or mutations in other genes.
The two frequent mutations, c.983A > G and c.2708_2711delTTAG, have been reported previously in other ethnic groups. [2, 9–11, 15, 16, 19–21] Wefound evidence for a founder effect of c.983A > G while c.2708_2711delTTAG seems to be a mutational hotspot.
Clinical details of patients with c.983A > G mutation versus patients with c. 2708_2711delTTAG mutation revealed no obvious differences with respect to age at onset, visual acuity, refractive values, progression rate, color vision or VEP. In our study temporal pallor of the optical disc was the most constant clinical finding. This observation is in disagreement with the observations of Votruba et al. [22], who found a significant fraction of patients with a diffuse disc atrophy. The studydemonstrates no correlation between the included clinical parameters. The clinical data analysis is retrospective, however, and based on records collected over a long period where diagnostic practices may have varied. Nevertheless, thephenotype variation is conspicuous, even among patients with one and the same mutation. This allows for considerable optimism concerning the search for genes and environmental factors that modify the impact of OPA1 mutations on the mitochondrial machinery and the associated phenotypes.
Conclusions
Based on mutational analysis of Danish patients with ADOA we conclude that genetic testing for OPA1mutations assist in the diagnosis. Using a strategy based on MLPA analysis and DNA sequencing we have identified mutations in OPA1 in 90% of families including 15 novel mutations. More than half of the affected families in Denmark are represented by three common mutations.
Abbreviations
- ADOA:
-
Autosomal Dominant Optic Atrophy
- B-Y:
-
Blue- Yellow
- Indel:
-
insertion and deletion mutation
- KB:
-
Kilo base
- L:
-
Left
- Mb:
-
Mega bite
- MLPA:
-
Multiplex ligation-dependent amplification
- ND:
-
No Data
- OMIM:
-
Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphisms
- Sph.eq:
-
Spherical equivalent
- TP:
-
Temporal pallor of the optic disc
- R:
-
Right
- R-G:
-
Red-Green
- VA:
-
Visual acuity
- pVA:
-
Pattern visual acuity
- ffVEP:
-
Full-field visual evoked potentials
- VEP:
-
Visual evoked potentials.
References
Kjer B, Eiberg H, Kjer P, Rosenberg T: Dominant optic atrophy mapped to chromosome 3q region. II. Clinical and epidemiological aspects. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 1996, 74: 3-7.
Yu-Wai-Man P, Griffiths PG, Burke A, Sellar PW, Clarke MP, Gnanaraj L, et al: The prevalence and natural history of dominant optic atrophy due to OPA1 mutations. Ophthalmology. 2010, 117: 1538-46. 10.1016/j.ophtha.2009.12.038. 1546
Reynier P, Amati-Bonneau P, Verny C, Olichon A, Simard G, Guichet A, et al: OPA3 gene mutations responsible for autosomal dominant optic atrophy and cataract. J Med Genet. 2004, 41: e110-10.1136/jmg.2003.016576.
Hanein S, Perrault I, Roche O, Gerber S, Khadom N, Rio M, et al: TMEM126A, encoding a mitochondrial protein, is mutated in autosomal-recessive nonsyndromic optic atrophy. Am J Hum Genet. 2009, 84: 493-498. 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.03.003.
Carelli V, Schimpf S, Fuhrmann N, Valentino ML, Zanna C, Iommarini L, et al: A clinically complex form of dominant optic atrophy (OPA8) maps on chromosome 16. Hum Mol Genet. 2011, 20: 1893-1905. 10.1093/hmg/ddr071.
Eiberg H, Kjer B, Kjer P, Rosenberg T: Dominant optic atrophy (OPA1) mapped to chromosome 3q region. I. Linkage analysis. Hum Mol Genet. 1994, 3: 977-980.
Jonasdottir A, Eiberg H, Kjer B, Kjer P: Rosenberg T. Refinement of the dominant optic atrophy locus (OPA1) to a 1.4-cM interval on chromosome 3q28–3q29, within a 3-Mb YAC contig. Hum Genet. 1997, 99: 115-120.
Ferre M, Amati-Bonneau P, Tourmen Y, Malthiery Y, Reynier P: eOPA1: an online database for OPA1 mutations. Hum Mutat. 2005, 25: 423-428. 10.1002/humu.20161.
Pesch UE, Leo-Kottler B, Mayer S, Jurklies B, Kellner U, Apfelstedt-Sylla E, et al: OPA1 mutations in patients with autosomal dominant optic atrophy and evidence for semi-dominant inheritance. Hum Mol Genet. 2001, 10: 1359-1368. 10.1093/hmg/10.13.1359.
Toomes C, Marchbank NJ, Mackey DA, Craig JE, Newbury-Ecob RA, Bennett CP, et al: Spectrum, frequency and penetrance of OPA1 mutations in dominant optic atrophy. Hum Mol Genet. 2001, 10: 1369-1378. 10.1093/hmg/10.13.1369.
Delettre C, Griffoin JM, Kaplan J, Dollfus H, Lorenz B, Faivre L, et al: Mutation spectrum and splicing variants in the OPA1 gene. Hum Genet. 2001, 109: 584-591. 10.1007/s00439-001-0633-y.
Thiselton DL, Alexander C, Morris A, Brooks S, Rosenberg T, Eiberg H, et al: A frameshift mutation in exon 28 of the OPA1 gene explains the high prevalence of dominant optic atrophy in the Danish population: evidence for a founder effect. Hum Genet. 2001, 109: 498-502. 10.1007/s004390100600.
Li Y, Vinckenbosch N, Tian G, Huerta-Sanchez E, Jiang T, Jiang H, et al: Resequencing of 200 human exomes identifies an excess of low-frequency non-synonymous coding variants. Nat Genet. 2010, 42: 969-972. 10.1038/ng.680.
Almind GJ, Gronskov K, Milea D, Larsen M, Brondum-Nielsen K, Ek J: Genomic deletions in OPA1 in Danish patients with autosomal dominant optic atrophy. BMC Med Genet. 2011, 12: 49-
Thiselton DL, Alexander C, Taanman JW, Brooks S, Rosenberg T, Eiberg H, et al: A comprehensive survey of mutations in the OPA1 gene in patients with autosomal dominant optic atrophy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002, 43: 1715-1724.
Baris O, Delettre C, Amati-Bonneau P, Surget MO, Charlin JF, Catier A, et al: Fourteen novel OPA1 mutations in autosomal dominant optic atrophy including two de novo mutations in sporadic optic atrophy. Hum Mutat. 2003, 21: 656-10.1002/humu.9152.
Ferre M, Bonneau D, Milea D, Chevrollier A, Verny C, Dollfus H, et al: Molecular screening of 980 cases of suspected hereditary optic neuropathy with a report on 77 novel OPA1 mutations. Hum Mutat. 2009, 30: E692-E705. 10.1002/humu.21025.
Schimpf S, Schaich S, Wissinger B: Activation of cryptic splice sites is a frequent splicing defect mechanism caused by mutations in exon and intron sequences of the OPA1 gene. Hum Genet. 2006, 118: 767-771. 10.1007/s00439-005-0096-7.
Delettre C, Lenaers G, Griffoin JM, Gigarel N, Lorenzo C, Belenguer P, et al: Nuclear gene OPA1, encoding a mitochondrial dynamin-related protein, is mutated in dominant optic atrophy. Nat Genet. 2000, 26: 207-210. 10.1038/79936.
Hamahata T, Fujimaki T, Fujiki K, Miyazaki A, Mizota A, Murakami A: OPA1 mutations in Japanese patients suspected to have autosomal dominant optic atrophy. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2012, 56: 91-97. 10.1007/s10384-011-0096-1.
Nakamura M, Lin J, Ueno S, Asaoka R, Hirai T, Hotta Y, et al: Novel mutations in the OPA1 gene and associated clinical features in Japanese patients with optic atrophy. Ophthalmology. 2006, 113: 483-488. 10.1016/j.ophtha.2005.10.054.
Votruba M, Thiselton D, Bhattacharya SS: Optic disc morphology of patients with OPA1 autosomal dominant optic atrophy. Br J Ophthalmol. 2003, 87: 48-53. 10.1136/bjo.87.1.48.
Pre-publication history
The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2350/13/65/prepub
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank all the patients and their relatives for participating in this study. The work was funded by the Michaelsen Foundation, The Danish Eye Research Foundation, Fight for Sight, Denmark and The A.P. MøllerogHustruChastine Mc-Kinney Møller Foundation. LuCamp, The Lundbeck Foundation Centre for Applied Medical Genomics in Personalized Disease Prediction, Prevention and Care (http://www.lucamp.org) is acknowledged for screening of the whole-genome exome sequencing data of 2000 Danish individuals for the novel missense mutations found in this study. Thomas Sparsø is acknowledged for help with check of LuCamp data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
All authors have read, edited and approved the final manuscript. GJA performed experiments, analyzed data and drafted the manuscript. KG helped designed the study, analyzed data and drafting the manuscript. JE and KG designed the study and experiments. KBN, ML, TR, HE contributed to writing of the paper. ML and TR helped with the ophthalmological clinical information.
Electronic supplementary material
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Almind, G.J., Ek, J., Rosenberg, T. et al. Dominant optic atrophy in Denmark – report of 15 novel mutations in OPA1, using a strategy with a detection rate of 90%. BMC Med Genet 13, 65 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2350-13-65
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2350-13-65