Abstract
Objective
The purpose of this study was to investigate the influence of the preparing process on the properties of pellet-containing granules and tablets.
Methods
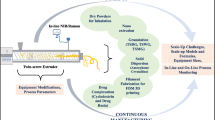
Coated pellets were granulated by centrifugal granulation, and the obtained pellet-containing granules were mixed with cushioning granules and compressed into tablets. Tablets were characterized for a drug release rate as compared with the original coated pellets.
Results
The surface roughness and the angle of repose of pellet-containing granules increased with the granulating ratio. Weight and drug content variations in tablets were diminished by granulation, and great improvement in tablet uniformity was achieved even for large pellets. Granulation showed protection for coated films under different compress forces and at even a low content of cushioning granules.
Conclusions
The uniformity of tablets prepared from pellet-containing granules could be significantly improved by the granulation process at a proper granulating ratio. The granulation process could protect the coated pellets during compaction even under high compression forces and with a low content of cushioning granules.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sawicki W, Łunio R. Compressibility of floating pellets with verapamil hydrochloride coated with dispersion Kollicoat SR 30 D. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2005;60:153–158.
Bodmeier R. Tableting of coated pellets. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 1997;43:1–8.
Wagner KG, Krumme M, Beckert TE, Schmidt PC. Development of disintegrating multiple-unit tablets on a high-speed rotary tablet press. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2000;50:285–292.
Wagner KG, Krumme M, Schmidt PC. Investigation of the pellet-distribution in single tablets via image analysis. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 1999;47:79–85.
Abdul S, Poddar S. A flexible technology for modified release of drugs: multi layered tablets. J Control Release. 2004;97:393–405.
Abbaspour M, Sadeghi F, Afrasiabi Garekani H. Thermal treating as a tool to produce plastic pellets based on Eudragit RS PO and RL PO aimed for tableting. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2007;67:260–267.
Abbaspour M, Sadeghi F, Afrasiabi Garekani H. Design and study of ibuprofen disintegrating sustained-release tablets comprising coated pellets. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2008;68:747–759.
Kim MS, Kim JS, Hwang SJ. The effect of sodium alginate on physical and dissolution properties of Surelease-matrix pellets prepared by a novel pelletizer. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2007;55:1631–1634.
Vergote G, Kiekens F, Vervaet C, Remon JP. Wax beads as cushioning agents during the compression of coated diltiazem pellets. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2002;17:145–151.
Debunne A, Vervaet C, Mangelings D, Remon JP. Compaction of enteric-coated pellets: influence of formulation and process parameters on tablet properties and in vivo evaluation. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2004;22:305–314.
Pan X, Chen M, Han K, et al. Novel compaction techniques with pellet-containing granules. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2010;75:436–442.
Dashevsky A, Kolter K, Bodmeier R. pH-independent release of a basic drug from pellets coated with the extended release polymer dispersion Kollicoat® SR 30 D and the enteric polymer dispersion Kollicoat® MAE 30 DP. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2004;58:45–49.
McGinity J, McGinity JW, Felton LA. Aqueous Polymeric Coatings for Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms. London: Informa Healthcare; 2008.
Bashaiwoldu AB, Podczeck F, Newton J. A study on the effect of drying techniques on the mechanical properties of pellets and compacted pellets. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2004;21:119–129.
Lecomte F, Siepmann J, Walther M, MacRae R, Bodmeier R. Polymer blends used for the aqueous coating of solid dosage forms: importance of the type of plasticizer. J Control Release. 2004;99:1–13.
Tunón Å, Börjesson E, Frenning G, Alderborn G. Drug release from reservoir pellets compacted with some excipients of different physical properties. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2003;20:469–479.
Türkoğlu M, Varol H, Çelikok M. Tableting and stability evaluation of enteric-coated omeprazole pellets. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2004;57:279–286.
Barakat NS, Elbagory IM, Almurshedi AS. Controlled-release carbamazepine matrix granules and tablets comprising lipophilic and hydrophilic components. Drug Deliv. 2009;16:57–65.
Siepmann F, Siepmann J, Walther M, MacRae R, Bodmeier R. Polymer blends for controlled release coatings. J Control Release. 2008;125:1–15.
Bruce LD, Petereit HU, Beckert T, McGinity JW. Properties of enteric coated sodium valproate pellets. Int J Pharm. 2003;264:85–96.
Dashevsky A, Kolter K, Bodmeier R. Compression of pellets coated with various aqueous polymer dispersions. Int J Pharm. 2004;279:19–26.
Schmid W, Picker-Freyer KM. Tableting and tablet properties of alginates: characterisation and potential for soft tableting. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2009;72:165–172.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, X., Huang, Y., Dong, Y. et al. Process Investigation of a Novel Compaction Technique With Pellet-Containing Granules. Ther Innov Regul Sci 47, 593–601 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1177/2168479013495681
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/2168479013495681