Abstract
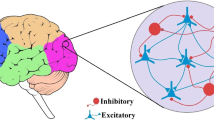
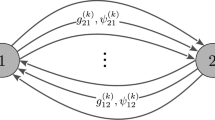
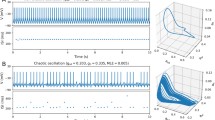
The brain is a complex network consisting of excitatory and inhibitory neurons. The connections between excitatory and inhibitory neurons lead to different dynamical behaviors. The synchronization is a significant behavior among these neurons. In this paper, the synchronization is analyzed by considering a simple neural network model for up-to-down-state oscillation of the cortical network. This neural network model includes a group of excitatory and inhibitory neurons coupled with each other. Synchronization of two neural models is analyzed, and it is revealed that it depends on the coupling of the excitatory neurons rather than the inhibitory ones. The network of neural models is also investigated by considering a one-dimensional and also two-layer structure. The results represent the formation of different dynamical behaviors such as imperfect synchronization, chimera state, and complete synchronization in the networks.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
Data generated during the current study will be made available on reasonable request.
References
L.L. Moroz, Brain Behav. Evol. 74, 177–190 (2009)
A. Foroutannia, M. Ghasemi, F. Parastesh, S. Jafari, M. Perc, Nonlinear Dyn. 100, 2699–2714 (2020)
C. Chen, H. Bao, M. Chen, Q. Xu, B. Bao, AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 111, 152894 (2019)
C. Chen, J. Chen, H. Bao, M. Chen, B. Bao, Nonlinear Dyn. 95, 3385–3399 (2019)
A. Foroutannia, F. Nazarimehr, M. Ghasemi, S. Jafari, J. Theor. Biol. 528, 110837 (2021)
M. Ghasemi, A. Foroutannia, A. Babajani-Feremi, Brain Behav. 11, e02101 (2021)
M. Molinari, M.G. Leggio, M.H. Thaut, The Cerebellum 6, 18–23 (2007)
E.D. Herzog, Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 8, 790–802 (2007)
S. Boccaletti, V. Latora, Y. Moreno, M. Chavez, D.-U. Hwang, Phys. Rep. 424, 175–308 (2006)
R. Albert, A.-L. Barabási, Rev. Mod. Phys. 74, 47 (2002)
R. Cohen and S. Havlin, Complex networks: structure, robustness and function (Cambridge university press, 2010).
D.S. Bassett, O. Sporns, Nat. Neurosci. 20, 353–364 (2017)
M. Saberi, R. Khosrowabadi, A. Khatibi, B. Misic, G. Jafari, Sci. Rep. 11, 1–14 (2021)
C. Hammond, H. Bergman, P. Brown, Trends Neurosci. 30, 357–364 (2007)
L.L. Rubchinsky, C. Park, R.M. Worth, Nonlinear Dyn. 68, 329–346 (2012)
B. Hellwig, B. Schelter, B. Guschlbauer, J. Timmer, C. Lücking, Clin. Neurophysiol. 114, 1462–1467 (2003)
M. Hemami, J.A. Rad, K. Parand, Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 42, 101090 (2020)
Q.Y. Wang, Q.S. Lu, G.R. Chen, Physica A 374, 869–878 (2007)
Q. Xu, X. Tan, D. Zhu, M. Chen, J. Zhou, H. Wu, Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 8218740 (2020).
S.S. Muni, K. Rajagopal, A. Karthikeyan, S. Arun, Chaos Solitons Fract. 155, 111759 (2022)
K. Rajagopal, S. Jafari, A. Karthikeyan, A. Srinivasan, Chaos 31, 083115 (2021)
B. Ramakrishnan, M. Mehrabbeik, F. Parastesh, K. Rajagopal, S. Jafari, Electronics 11, 153 (2022)
S. Rakshit, S. Majhi, J. Kurths, D. Ghosh, Chaos 31, 073129 (2021)
I. Hussain, S. Jafari, D. Ghosh, M. Perc, Nonlinear Dyn. 104, 1–11 (2021)
I. Hussain, S. Jafari, M. Perc, D. Ghosh, Phys. Lett. A 424, 127847 (2022)
D. Ghosh, S. Banerjee, Chaos Solitons Fract. 53, 1–9 (2013)
A. Bahramian, F. Parastesh, V.-T. Pham, T. Kapitaniak, S. Jafari, M. Perc, Chaos 31, 033138 (2021)
Y. Li, Z. Wei, W. Zhang, M. Perc, R. Repnik, Appl. Math. Comput. 354, 180–188 (2019)
Z. Liu, P. Zhou, J. Ma, A. Hobiny, F. Alzahrani, Chaos Solitons Fract. 131, 109533 (2020)
F. Parastesh, M. Mehrabbeik, K. Rajagopal, S. Jafari, M. Perc, Chaos 32, 013125 (2022)
B. Bao, Q. Yang, D. Zhu, Y. Zhang, Q. Xu, M. Chen, Nonlinear Dyn. 99, 2339–2354 (2020)
M. Ghorbani, M. Mehta, R. Bruinsma, A.J. Levine, Phys. Rev. E 85, 021908 (2012)
N.S. Hashemi, F. Dehnavi, S. Moghimi, M. Ghorbani, Neuroimage 189, 71–84 (2019)
L.M. Pecora, T.L. Carroll, Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 2109 (1998)
L. Huang, Q. Chen, Y.-C. Lai, L.M. Pecora, Phys. Rev. E 80, 036204 (2009)
F. Parastesh, S. Jafari, H. Azarnoush, Z. Shahriari, Z. Wang, S. Boccaletti, M. Perc, Phys. Rep. 898, 1–114 (2021)
L.R. Silva, Y. Amitai, B.W. Connors, Science 251, 432–435 (1991)
H.J. Jang, H. Chung, J.M. Rowland, B.A. Richards, M.M. Kohl, J. Kwag, Sci. Adv. 6, eaay333 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi (2021JM-533, 2021JQ-880, 2020JM-646), the Innovation Capability Support Program of Shaanxi (2018GHJD-21), the Support Plan for Sanqin Scholars Innovation Team in Shaanxi Province of China, the Youth Innovation Team of Shaanxi Universities, the Scientific Research Program Funded by Shaanxi Provincial Education Department (21JK0960), the Scientific Research Foundation of Xijing University (XJ21B01), and the Scientific Research Foundation of Xijing University (XJ200202). The work is also partially funded by the Center for Nonlinear Systems, Chennai Institute of Technology, India, vide funding number CIT/CNS/2022/RP-006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, J., Ramadoss, J., Wang, Z. et al. Complete synchronization analysis of neocortical network model. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 231, 4037–4048 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-022-00630-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-022-00630-6