Abstract
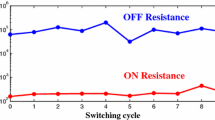
How to improve the storage density and solve the sneak path current problem has become the key to the design of nonvolatile memristive memory. In this paper, a high storage density and high reading/writing speed 3D crossbar array non-volatile memory based on pure memristors is proposed. The main works are as follows: (1) an extensible memristive cluster is proposed, (2) a memristive switch is designed, and (3) a 3D crossbar array non-volatile memory is constructed. The memory cell of the 3D crossbar array non-volatile memory is constructed by pure memristors and can be extended by adding memristor in a memristive cluster or adding memristive clusters in a memory cell to realize multi-value storage. The memristive switch can effectively reduce the sneak path current effect. The pure memristive memory cell solves the conflict between the storage density and sneak path current effect and greatly improves the storage density of memory cells. Furthermore, the 3D cross-array structure allows different memory cells on the same layer or different layers to be read and written in parallel, which greatly improves the speed of reading and writing. Simulations with PSpice verifies that the proposed memristive cluster can realize stable multi-value storage, has higher storage density, faster reading and writing speed, fewer input ports and output ports, better stability, and lower power consumption. Moreover, the structure proposed in this paper can also be used in the circuit design of the neuromorphic network, logic circuit, and other memristive circuits.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Chua, Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Transactions on Circuit Theory 18, 507–519 (1971)
D. B. Strukov, G. S. Snider, D. R. Stewart, and R. S. Williams, "The missing memristor found," Nature, 453(2008), 80–83
H. Lin, C. Wang, Q. Hong, Y. Sun. A multi-stable memristor and its application in a neural network. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II: Brief Pap. 67(12), 3472–3476 (2020)
Q. Hong, R. Yan, C. Wang, J. Sun, Memristive circuit implementation of biological nonassociative learning mechanism and its applications. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 14, 1036–1050 (2020)
C. Wang, L. Xiong, J. Sun, and W. Yao, Memristor-based neural networks with weight simultaneous perturbation training, Nonlinear dynamics, 95(2019): 2893–2906
F. Parastesh, S. Jafari, H. Azarnoush et al., Chimera in a network of memristor-based Hopfield neural network. The European Physical Journal Special Topics 228, 2023–2033 (2019)
H. Lin, C. Wang, Q. Deng, C. Xu, Z Deng, Chao Zhou. Review on chaotic dynamics of memristive neuron and neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 106(1), 959–973 (2021)
C. Xu, C. Wang, Y. Sun, Q. Hong, Q. Deng, H. Chen. Memristor-based neural network circuit with weighted sum simultaneous perturbation training and its applications. Neurocomputing 462, 581–590 (2021)
C. Li, Y. Yang, J. Du et al., A simple chaotic circuit with magnetic flux-controlled memristor. The European Physical Journal Special Topics 230(7), 1723–1736 (2021)
S.G. Rohani, N. Taherinejad, D. Radakovits, A semiparallel full-adder in imply logic. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration Systems 28, 297–301 (2020)
S. Kvatinsky, G. Satat, N. Wald, E.G. Friedman, A. Kolodny, U.C. Weiser, Memristor-based material implication (imply) logic: Design principles and methodologies. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration Systems 22, 2054–2066 (2014)
S. Kvatinsky, D. Belousov, S. Liman, G. Satat, N. Wald, E.G. Friedman, A. Kolodny, U.C. Weiser, Magic–memristor-aided logic. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 61, 895–899 (2014)
L. Guckert, E.E. Swartzlander, Optimized memristor-based multipliers. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 64, 373–385 (2017)
Q. Hong, Z. Shi, J. Sun, and S. Du, Memristive self-learning logic circuit with application to encoder and decoder, Neural Computing and Applications, 33 (2020): 4901–4913
W. Xie, C Wang, H Lin. A fractional-order multistable locally active memristor and its chaotic system with transient transition, state jump. Nonlinear Dyn. 104, 4523–4541 (2021)
L. Zhou, C. Wang, L. Zhou. A novel no-equilibrium hyperchaotic multi-wing system via introducing memristor. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 46(1), 84–98 (2018)
G. M. Huang, Y. Ho, P. Li, Memristor system properties and its design applications to circuits such as nonvolatile memristor memories. International Conference on Communications,Circuits and Systems, 2: 805–810 (2010)
P. Liu, Z. You, J. Wu, B. Liu, Y. Han, K. Chakrabarty, Fault Modeling and Efficient Testing of Memristor-Based Memory. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 68(11), 4444–4455 (2021)
J. Lee, J. Park, S. Jung, F. Hwang, F. Hyunsang, Scaling effect of device area and film thickness on electrical and reliability characteristics of rram, in International interconnect technology conference and 2011 materials for advanced metallization, Dresden, Germany, vol. 2011 (2011), pp. 1–3
Y. Guo, J. Robertson, Ab initio calculations of materials selection of oxides for resistive random access memories, Microelectronic Engineering, 147(2015), 339–343
M. Guo, Z. Gao, Y. Xue, G. Dou, Y. Li, Dynamics of a physical SBT memristor-based Wien-bridge circuit, Nonlinear Dynamics, 93(3)(2018): 1681–1693
W. Xue, Y. Li, G. Liu et al., Controllable and stable quantized conductance states in a Pt/HfOx/ITO memristor. Advanced Electronic Materials 6, 1901055 (2020)
Y. Peng, S. He, K. Sun, Parameter identification for discrete memristive chaotic map using adaptive differential evolution algorithm, Nonlinear Dynamics, 2021:1-13 (2021)
Y. Peng, S. He, K. Sun, A higher dimensional chaotic map with discrete memristor. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 129, 153539 (2021)
S. He, K. Sun, Y. Peng, L. Wang, Modeling of discrete fracmemristor and its application. AIP Advances 10, 015332 (2020)
X. Wang, P. Zhou, J. Eshraghian et al., High-density memristor-cmos ternary logic family. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 68(1), 264–274 (2020)
S. Kvatinsky, E.G. Friedman, A. Kolodny, U.C. Weiser, Team: Threshold adaptive memristor model. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. I Regul. Pap. 60, 211–221 (2013)
S. Kvatinsky, M. Ramadan, E.G. Friedman, A. Kolodny, Vteam: A general model for voltage-controlled memristors. IEEE Transactions on Circuits & Systems II Express Briefs 62, 786–790 (2015)
M. Teimoori, A. Amirsoleimani, A. Ahmadi, M. Ahmadi, A 2M1M crossbar architecture: Memory. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration Systems 26, 2608–2618 (2018)
Y. Yilmaz and P. Mazumder, A drift-tolerant read/write scheme for multilevel memristor memory, IEEE Transactions on Nanotechnology, 16(2017), 1016–1027
X. Wang, S. Li, H. Liu, Z. Zeng, A compact scheme of reading and writing for memristor-based multi-valued memory. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 37, 1505–1509 (2017)
J. Sun. M. Li, K. Kang, P. Zhu, Y. Sun (2021) Design of Heterogeneous Memristor Based 1T2M Multi-value Memory Crossbar Array. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology 43 : 1533–1540
L. Shi, G. Zheng, B. Tian, B. Dkhil, C. Duan, Research progress on solutions to the sneak path issue in memristor crossbar arrays, Nanoscale. Advances 2, 1811–1827 (2020)
V.S.S. Srinivasan, S. Chopra, P. Karkare, P. Bafna, S. Lashkare, P. Kumbhare, Y. Kim, S. Srinivasan, S. Kuppurao, S. Lodha, U. Ganguly, Punchthrough-diode-based bipolar RRAM selector by Si epitaxy. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 33, 1396–1398 (2012)
H. Manem, G.S. Rose, A read-monitored write circuit for 1t1m multi-level memristor memories, in IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, vol. 2011 (2011), pp. 2938–2941
S. Yu, H. Wong, Compact modeling of conducting-bridge random-access memory (cbram). IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 58, 1352–1360 (2011)
E. Lehtonen, J.H. Poikonen, M. Laiho, P. Kanerva, Large-scale memristive associative memories. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration Systems 22, 562–574 (2014)
V. Ravi, S. Singh, S. Reka-Sofana. Memristor-based 2D1M architecture: Solution to sneak paths in multilevel memory. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 32(1) : e4143 (2021)
Y. Zhang, Y. Shen, X. Wang, L. Cao, A novel design for memristor-based logic switch and crossbar circuits. IEEE Transactions on Circuits & Systems I Regular Papers 62, 1402–1411 (2015)
S. Kim, H. Y. Jeong, S. K. Kim, S. Y. Choi, and K. J. Lee, Flexible memristive memory array on plastic substrates, Nano Letters, 11(2011), 5438–5442
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 62171182) and Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (Grant no. 2021JJ30147).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, J., Kang, K., Sun, Y. et al. A multi-value 3D crossbar array nonvolatile memory based on pure memristors. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 231, 3119–3130 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-022-00576-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-022-00576-9