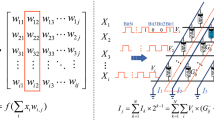
Abstract
The training of neural networks involves numerous operations on the weight matrix. If neural networks are implemented in hardware, all weights will be updated in parallel. However, neural networks based on CMOS technology face many challenges in the updating phase of weights. For example, derivation of the activation function and error back propagation make it difficult to be realized at the circuit level, even though the back propagation algorithm is rather efficient and popular in neural networks. In this paper, a novel synaptic unit based on double identical memristors is designed, on the basis of which a new neural network circuit architecture is proposed. The whole network is trained by a hardware-friendly weight simultaneous perturbation (WSP) algorithm. The hardware implementation of neural networks based on WSP algorithm only involves the feedforward circuit and does not require the bidirectional circuit. Furthermore, two forward calculations are merely needed to update all weight matrices for each pattern, which significantly simplifies the weight update circuit and allows simpler and easier implementation of the neural network in hardware. The practicability, utility and simplicity of this scheme are demonstrated by the supervised learning tasks.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tao, F., Busso, C.: Gating neural network for large vocabulary audiovisual speech recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. (TASLP) 26(7), 1286–1298 (2018)
Talaśka, T., Kolasa, M., Dlugosz, R., Pedrycz, W.: Analog programmable distance calculation circuit for winner takes all neural network realized in the CMOS technology. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 27(3), 661–673 (2016)
Talaśka, T., Kolasa, M., Dlugosz, R., Farine, P.A.: An efficient initialization mechanism of neurons for Winner Takes All Neural Network implemented in the CMOS technology. Appl. Math. Comput. 267, 119–138 (2015)
Sengupta, A., Banerjee, A., Roy, K.: Hybrid spintronic-CMOS spiking neural network with on-chip learning: devices, circuits, and systems. Phys. Rev. Appl. 6(6), 064003 (2016)
Dlugosz, R., Kolasa, M., Pedrycz, W., Szulc, M.: Parallel programmable asynchronous neighborhood mechanism for Kohonen SOM implemented in CMOS technology. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 22(12), 2091–2104 (2011)
Wu, X., Saxena, V., Zhu, K., Balagopal, S.: A CMOS spiking neuron for brain-inspired neural networks with resistive synapses and in situ learning. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II 62(11), 1088–1092 (2015)
Pan, C., Naeemi, A.: Non-Boolean computing benchmarking for beyond-CMOS devices based on cellular neural network. IEEE J. Explor. Solid-State Comput. Devices Circuits 2, 36–43 (2016)
Goknar, I.C., Yildiz, M., Minaei, S., Deniz, E.: Neural CMOS-integrated circuit and its application to data classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 23(5), 717–724 (2012)
Valov, I., Kozicki, M.: Non-volatile memories: organic memristors come of age. Nat. Mater. 16, 1170–1172 (2017)
Wang, Z., Joshi, S., Savel’ev, S.E., Jiang, H., Midya, R., Lin, P., Wu, Q.: Memristors with diffusive dynamics as synaptic emulators for neuromorphic computing. Nat. Mater. 16(1), 101 (2017)
Herrmann, E., Rush, A., Bailey, T., Jha, R.: Gate controlled three-terminal metal oxide memristor. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 39(4), 500–503 (2018)
van de Burgt, Y., Lubberman, E., Fuller, E.J., Keene, S.T., Faria, G.C., Agarwal, S., Salleo, A.: A non-volatile organic electrochemical device as a low-voltage artificial synapse for neuromorphic computing. Nat. Mater. 16(4), 414–418 (2017)
Gupta, I., Serb, A., Khiat, A., Zeitler, R., Vassanelli, S., Prodromakis, T.: Sub 100 nW volatile nano-metal-oxide memristor as synaptic-like encoder of neuronal spikes. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 12(2), 351–359 (2018)
Strukov, D.B., Snider, G.S., Stewart, D.R., Williams, R.S.: The missing memristor found. Nature 453(7191), 80 (2008)
Zhou, L., Wang, C., Zhou, L.: Generating hyperchaotic multi-wing attractor in a 4D memristive circuit. Nonlinear Dyn. 85(4), 2653–2663 (2016)
Zhou, L., Wang, C., Zhou, L.: A novel no-equilibrium hyperchaotic multi-wing system via introducing memristor. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 46(1), 84–98 (2018)
Panwar, N., Rajendran, B., Ganguly, U.: Arbitrary spike time dependent plasticity (STDP) in memristor by analog waveform engineering. IEEE Electron Device Letters. 38(6), 740–743 (2017)
Cai, W., Ellinger, F., Tetzlaff, R.: Neuronal synapse as a memristor: modeling pair- and triplet-based STDP rule. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 9(1), 87–95 (2015)
Nishitani, Y., Kaneko, Y., Ueda, M.: Supervised learning using spike-timing-dependent plasticity of memristive synapses. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 26(12), 2999–3008 (2015)
Boyn, S., Grollier, J., Lecerf, G., Xu, B., Locatelli, N., Fusil, S., et al.: Learning through ferroelectric domain dynamics in solid-state synapses. Nat. Commun. 8, 14736 (2017)
Kheradpisheh, S.R., Ganjtabesh, M., Thorpe, S.J., Masquelier, T.: STDP-based spiking deep convolutional neural networks for object recognition. Neural Netw. 99, 56–67 (2018)
Sheri, A.M., Hwang, H., Jeon, M., Lee, B.G.: Neuromorphic character recognition system with two PCMO memristors as a synapse. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 61(6), 2933–2941 (2014)
Legenstein, R., Naeger, C., Maass, W.: What can a neuron learn with spike-timing-dependent plasticity? Neural Comput. 17(11), 2337–2382 (2005)
Alibart, F., Zamanidoost, E., Strukov, D.B.: Pattern classification by memristive crossbar circuits using ex situ and in situ training. Nat. Commun. 4, 2072 (2013)
Prezioso, M., Merrikh-Bayat, F., Hoskins, B.D., Adam, G.C., Likharev, K.K., Strukov, D.B.: Training and operation of an integrated neuromorphic network based on metal-oxide memristors. Nature 521, 61–64 (2015)
Li, C., Belkin, D., Li, Y., Yan, P., Hu, M., Ge, N., Song, W., et al.: Efficient and self-adaptive in-situ learning in multilayer memristor neural networks. Nat. Commun. 9, 2385 (2018)
Bayat, F.M., Prezioso, M., Chakrabarti, B., Nili, H., Kataeva, I., Strukov, D.: Implementation of multilayer perceptron network with highly uniform passive memristive crossbar circuits. Nat. Commun. 9, 2331 (2018)
Hu, X., Feng, G., Duan, S., Liu, L.: A memristive multilayer cellular neural network with applications to image processing. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 28(8), 1889–1901 (2016)
Zeng, X., Wen, S., Zeng, Z., Huang, T.: Design of memristor-based image convolution calculation in convolutional neural network. Neural Comput. Appl. 30(2), 503–508 (2018)
Adhikari, S.P., Yang, C., Kim, H., Chua, L.O.: Memristor bridge synapse-based neural network and its learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 23(9), 1426–1435 (2012)
Soudry, D., Di Castro, D., Gal, A., Kolodny, A., Kvatinsky, S.: Memristor-based multilayer neural networks with online gradient descent training. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 26(10), 2408–2421 (2015)
Adhikari, S.P., Kim, H., Budhathoki, R.K., Yang, C., Chua, L.O.: A circuit-based learning architecture for multilayer neural networks with memristor bridge synapses. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 62(1), 215–223 (2015)
Alspector, J., Meir, R., Yuhas, B., Jayakumar, A., Lippe, D.: A parallel gradient descent method for learning in analog VLSI neural networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 836–844 (1993)
Kvatinsky, S., Friedman, E.G., Kolodny, A., Weiser, U.C.: Team: threshold adaptive memristor model. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 60(1), 211–221 (2013)
Belli, M.R., Conti, M., Turchetti, C.: Analog Brownian weight movement for learning of artificial neural networks. In: European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks (ESANN), pp. 19–21 (1995)
Conti, M., Orcioni, S., Turchetti, C.: A new stochastic learning algorithm for analog hardware implementation. In: International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks (ICANN), pp. 1171–1176 (1998)
Kvatinsky, S., Satat, G., Wald, N., Friedman, E.G., Kolodny, A., Weiser, U.C.: Memristor-based material implication (imply) logic: design principles and methodologies. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 22(10), 2054–2066 (2014)
Yang, C., Kim, H., Adhikari, S.P., Chua, L.O.: A circuit-based neural network with hybrid learning of backpropagation and random weight change algorithms. Sensors 17, 16 (2016)
Bache, K., Lichman, M.: UCI machine learning repository. http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml (2018)
Murray, A.F., Edwards, P.J.: Enhanced MLP performance and fault tolerance resulting from synaptic weight noise during training. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 5(5), 792–802 (1994)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61571185), the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China (No. 2016JJ2030) and the Open Fund Project of Key Laboratory in Hunan Universities (No. 15K027).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Xiong, L., Sun, J. et al. Memristor-based neural networks with weight simultaneous perturbation training. Nonlinear Dyn 95, 2893–2906 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4730-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4730-z