Abstract
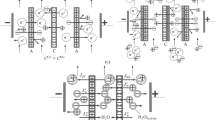
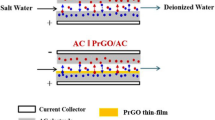
The capacitive deionization of water (CDW) was investigated with the purpose to obtain pure water. To this end, mosaic cation–anion-exchange membranes and activated carbon electrodes were used. The mosaic membranes contained cation- and anion-exchange components embedded in a synthetic-fiber-based matrix. The means of preparation for the pressed mosaic membranes included pressing the cation- and anion-exchange membranes into each other. Another method was via the subsequent formation of cation- and anion-exchange bands in the fibrous matrix (in a banded membrane). The activated carbon electrodes and mosaic membranes possessed sufficient specific ion surface conductivities even in clean water. The specific energy consumption was 31.9 and 111.7 W mol–1 for the CDW devices containing banded and pressed membranes, respectively. Therefore, the banded membrane was preferable for obtaining pure drinking water. It was found that the CDW with the banded mosaic membrane exhibited the best performance at a voltage of 2 V and a solution flow rate of 15 cm3/min.









Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The values of exchange capacities were measured by V.V. Milutin.
REFERENCES
Oren, Y., Desalination, 2008, vol. 228, p. 10.
Avraham, E., Noked, M., Bouhadana, Y., et al., J. Electrochem. Soc., 2009, vol. 156, p. 157.
Suss, M.E., Baumann, T.F., Bourcier, W.L., et al., Energy Environ. Sci., 2012, vol. 5, p. 9511.
Farmer, J.C., Fix, D.V., Mack, G.V., et al., Proc. Low Level Waste Conference, Orlando, FL, 1995.
Strathmann, H., Ion-Exchange Membrane Processes in Water Treatment Sustainability Science and Engineering, Elsevier, 2010.
Rica, R.A., Ziano, R., Salerno, D., et al., Phys. Rev. Lett., 2012, vol. 109, p. 156103.
Porada, S., Zhao, R., Van Der Wal, A., et al., Prog. Mater. Sci., 2013, vol. 58, p. 1388.
Jande, Y.A. and Kim, W.S., Desalination, 2013, vol. 329, p. 29.
Soffer, A. and Folman, M., J. Electroanal. Chem., 1972, vol. 38, p. 25.
Li, H., Pan, L., Lu, T., et al., J. Electroanal. Chem., 2011, vol. 653, p. 40.
Volfkovich, Yu.M., Russ. J. Electrochem., 2020, vol. 56, p. 1.
Kang, J., Kim, T., Jo, K., et al., Desalination, 2014, vol. 352, p. 52.
Kim, T., Dykstra, J.E., Porada, S., et al., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2015, vol. 446, p. 317.
Yang Li, Jiaming Shen, Jiansheng Li, et al., Carbon, 2017, vol. 116, p. 21.
Krüner, B., Srimuk, P., Fleischmann, S., et al., Carbon, 2017, vol. 117, p. 46.
Choi, S., Chang, B., Kang, J.H., et al., J. Membr. Sci., 2017, vol. 541, p. 580.
Andelman, M., Sep. Purif. Technol., 2011, vol. 80, p. 262.
Anderson, M.A., Cudero, A.L., and Palma, J., Electrochim. Acta, 2010, vol. 55, p. 3845.
Xu, P., Jorg, E., Drewes, J.E., et al., Water Res., 2008, vol. 42, p. 2605.
Strathmann, H., Ion-Exchange Membrane Process: Their Principle and Practical Applications, Hopkinton, MA: Balaban Desalination Publ., 2016.
Liu, S., Kyle, C., and Smith, K.C., Electrochim. Acta, 2017, vol. 230, p. 333.
Yang, S.C., Choi, J., Yeo, J., et al., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2016, vol. 50, p. 5892.
Biesheuvel, P.M., Bazant, M.Z., Cusick, R.D., et al., Appl. Phys., 2017, vol. 16, p. 19.
Xie, J., Xue, Y., and He, M., Carbon, 2017, vol. 123, p. 574.
Tang, W., He, D., Zhang, C., et al., Water Res., 2017, vol. 121, p. 302.
Hassanvand, A., Chen, G.Q., Webley, P.A., et al., Desalination, 2017, vol. 417, p. 36.
Conway, B.E., Electrochemical Supercapacitors: Scientific Fundamentals and Technological Applications, Springer, 1999.
Burke, A., J. Power Sources, 2000, vol. 91, p. 37.
Volfkovich, Yu.M. and Serdyuk, T.M., Russ. J. Electrochem., 2002, vol. 38, p. 93.
Pandolfo, A.G. and Hollenkamp, A.F., J. Power Sources, 2006, vol. 157, p. 11.
Sharma, P. and Bhatti, T.S., Energy Convers. Manage., 2010, vol. 51, p. 2901.
Volfkovich, Yu.M., Bograchev, D.A., Mikhalin, A.A., and Bagotsky, V.S., J. Solid State Electrochem., 2014, vol. 18, p. 1351.
Volfkovich, Yu.M., Mazin, V.M., and Urisson, N.A., Russ. J. Electrochem., 1998, vol. 34, p. 740.
Bagotsky, V.S., Skundin, A.M., and Volfkovich, Yu.M., Electrochemical Power Sources. Batteries, Fuel Cells, Supercapacitors, Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2015.
Andelman, M., Sep. Purif. Technol., 2011, vol. 80, p. 262.
Volfkovich, Yu.M., Rychagov, A.Yu., Mikhalin, A.A., et al., Desalination, 2018, vol. 426, p. 1.
Kardash, M.M., Volfkovich, Yu.M., Tyurin, I.A., et al., Pet. Chem., 2013, vol. 53, p. 482.
Kardash, M.M. and Terin, D.V., Pet. Chem., 2016, vol. 56, p. 413.
Kardash, M.M., Fedorchenko, N.B., and Epancheva, O.V., Fibre Chem., 2002, vol. 34, p. 466.
http://www.kynol.de/pdf/.
Volfkovich, Yu.M. and Bagotzky, V.S., J. Power Sources, 1994, vol. 48, p. 339.
Volfkovich, Yu.M., Filippov, A.N., and Bagotsky, V.S., Structural Properties of Porous Materials and Powders Used in Different Fields of Science and Technology, London: Springer, 2014.
Volfkovich, Yu.M., Sakars, A.V., and Volinsky, A.A., Int. J. Nanotechnol., 2005, vol. 2, p. 292.
Dzyazko, Yu.S., Ponomaryova, L.N., Volfkovich, Yu.M., et al., Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2014, vol. 198, p. 55.
Rouquerol, J., Baron, G., Denoyel, R., et al., Pure Appl. Chem., 2012, vol. 84, p. 107.
Fedorchenko, N.B., Kardash, M.M., and Fedorchenko, A.A., Fibre Chem., 2003, no. 5, p. 352.
GOST (State Standard) no. 17552-72: Ion-Exchange Membranes. Method for Determination of Total and Equilibrium Exchange Capacity, Moscow: Izd. Standartov, 1972.
Berezina, N.P., Kononenko, N.A., Dyomina, O.A., et al., Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 2008, vol. 139, p. 3.
Volfkovich, Yu.M., Bograchev, D.A., Mikhalin, A.A., and Bagotsky, V.S., J. Solid State Electrochem., 2014, vol. 18, p. 1351.
Kinoshita, K., Carbon: Electrochemical and Physical Properties, New York: Wiley, 1988.
Tarasevich, M.R., Elektrokhimiya uglerodnykh materialov (Electrochemistry of Carbon Materials), Moscow: Nauka, 1984.
Volfkovich, Yu.M., Mikhalin, A.A., and Rychagov, A.Yu., Russ. J. Electrochem., 2013, vol. 49, p. 594.
Volfkovich, Yu.M., Bograchev, D.A., Mikhalin, A.A., et al., in Nanooptics, Nanophotonics, Nanomaterials, and Their Applications, Fesenko, O. and Yatsenko, L., Eds., Springer, 2018, chapter 9, p. 127.
Damaskin, B.B., Petrii, O.A., and Tsirlina, G.A., Elektrokhimiya (Electrochemistry), Moscow: Khimiya, 2001.
Funding
The work was carried out within the framework of the state assignment of the Frumkin Institute of Physical Chemistry and Electrochemistry, Russian Academy of Sciences, (reg. number: АААА-А19-119041890032-6) as well as within the framework of project no. 19-08-00721 of the Russian Foundation of Basic Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by E. Khozina
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Volfkovich, Y.M., Mikhalin, A.A., Rychagov, A.Y. et al. Capacitive Deionization of Water with Electrodes Based on Nanoporous Activated Carbon and a Mosaic Cation–Anion Exchange Membrane. Prot Met Phys Chem Surf 57, 68–79 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070205121010214
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070205121010214