Abstract
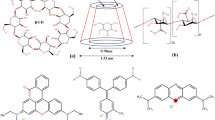
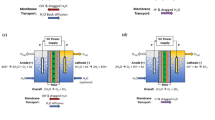
Drinking water shortage is worsening. Capacitive deionization (CDI) of saltwater has gained attention due to its low energy consumption and environmental friendliness. A single anion exchange membrane (AEM) can selectively move anions to positive electrodes for better desalination performances. Poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride)-functionalized reduced graphene oxide (PrGO) serves as an AEM for CDI. The AC and PrGO coated AC electrode pair (AC‖PrGO/AC) for CDI of saltwater under + 1.5 V for 1 h reaches a high optimized-salt removal and electrosorption capacity. This work presents the feasibility using the high-efficiency and facile PrGO anion-selective thin film layer served as an AEM analog for a simplified and low-cost membrane-CDI process to enhance desalination performances for potential water recycling and reuse from salt, inorganic waste or metal-contaminated ground waters.
Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support this study will be shared upon reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
O. Bozorg-Haddad, B. Zolghadr-Asli, P. Sarzaeim, M. Aboutalebi, X. Chu, H.A. Loáiciga, Evaluation of water shortage crisis in the Middle East and possible remedies. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. AQUA 69, 85 (2020)
C.F. Couto, A.V. Santos, M.C.S. Amaral, L.C. Lange, L.H. de Andrade, A.F.S. Foureaux, B.S. Fernandes, Assessing potential of nanofiltration, reverse osmosis and membrane distillation drinking water treatment for pharmaceutically active compounds (PhACs) removal. J. Water Process Eng. 33, 101029 (2020)
Q.J. Wei, C.I. Tucker, P.J. Wu, A.M. Trueworthy, E.W. Tow, Impact of salt retention on true batch reverse osmosis energy consumption: experiments and model validation. Desalination 479, 114177 (2020)
R. Shafique, M. Rani, A. Mahmood, S. Khan, N. Janjua, M. Sattar, K. Batool, T. Yaqoob, Copper chromite/graphene oxide nanocomposite for capacitive energy storage and electrochemical applications. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 7517 (2022)
L. Chang, Y. Fei, Y.H. Hu, Structurally and chemically engineered graphene for capacitive deionization. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 9, 1429 (2021)
H. Nassrullah, S.F. Anis, R. Hashaikeh, N. Hilal, Energy for desalination: a state-of-the-art review. Desalination 491, 114569 (2020)
G.-W. Liu, C.-S. Fan, C.-H. Hsu, C.-H. Hou, H.-P. Lin, Optimizing the micro/mesoporous structure of hierarchical porous carbon synthesized from petroleum pitch using the solvent-free method for ultra-fast capacitive deionization. ACS Omega (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c04119
Z.-H. Huang, Z. Yang, F. Kang, M. Inagaki, Carbon electrodes for capacitive deionization. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 470 (2017)
W. Kong, X. Ge, Q. Zhang, Y. Wang, Y. Wang, J. Lu, M. Zhang, D. Kong, Y. Feng, Ultrahigh content boron and nitrogen codoped hierarchically porous carbon obtained from biomass byproduct okara for capacitive deionization. ACS Omega (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c06449
W. Zhang, B. Jia, Toward anti-fouling capacitive deionization by using visible-light reduced TiO2/graphene nanocomposites. MRS Commun. 5, 613 (2015)
P.A. Chen, H.C. Cheng, H.P. Wang, Activated carbon recycled from bitter-tea and palm shell wastes for capacitive desalination of salt water. J. Clean. Prod. 174, 927 (2018)
A.B. Ganganboina, R.-A. Doong, Nitrogen doped graphene quantum dot-decorated earth-abundant nanotubes for enhanced capacitive deionization. Environ. Sci. Nano 7, 228 (2020)
M. Liu, M. Xu, Y. Xue, W. Ni, S. Huo, L. Wu, Z. Yang, Y.-M. Yan, Efficient capacitive deionization using natural basswood-derived, freestanding, hierarchically porous carbon electrodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 31260 (2018)
S.-W. Tsai, L. Hackl, A. Kumar, C.-H. Hou, Exploring the electrosorption selectivity of nitrate over chloride in capacitive deionization (CDI) and membrane capacitive deionization (MCDI). Desalination 497, 114764 (2021)
F. Gao, L. Wang, J. Wang, H. Zhang, S. Lin, Nutrient recovery from treated wastewater by a hybrid electrochemical sequence integrating bipolar membrane electrodialysis and membrane capacitive deionization. Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol. 6, 383 (2020)
N. Kim, J. Lee, S.P. Hong, C. Lee, C. Kim, J. Yoon, Performance analysis of the multi-channel membrane capacitive deionization with porous carbon electrode stacks. Desalination 479, 114315 (2020)
A. Rommerskirchen, M. Alders, F. Wiesner, C.J. Linnartz, A. Kalde, M. Wessling, Process model for high salinity flow-electrode capacitive deionization processes with ion-exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 616, 118614 (2020)
L. Kong, E. Palacios, X. Guan, M. Shen, X. Liu, Mechanisms for enhanced transport selectivity of like-charged ions in hydrophobic-polymer-modified ion-exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2022.120645
M. Gaikwad, S. Suman, K. Shukla, A. Sonawane, S. Jain, A review on recent contributions in the progress of membrane capacitive deionization for desalination and wastewater treatment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-04778-z
M. An, Ion removal trends in capacitivedeionization and its applicationfor treating industrial effluents, (2020)
H. Cheng, P. Chen, C. Peng, S. Liu, H. Paul Wang, Sulfonated GO coated carbon electrodes with cation-selective functions for enhanced capacitive deionization of saltwater. Environ. Technol. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2022.2153748
X. Gu, Y. Deng, C. Wang, Fabrication of anion-exchange polymer layered graphene-melamine electrodes for membrane capacitive deionization. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 5, 325 (2016)
W. Wu, Y. Shi, G. Liu, X. Fan, Y. Yu, Recent development of graphene oxide based forward osmosis membrane for water treatment: a critical review. Desalination 491, 114452 (2020)
U. Khan, A. Nairan, J. Gao, Q. Zhang, Current progress in 2D metal-organic frameworks for electrocatalysis. Small Struct (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/sstr.202200109
W. Zhang, L. Wei, J. Ma, S.-L. Bai, Exfoliation and defect control of graphene oxide for waterborne electromagnetic interference shielding coatings. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 132, 105838 (2020)
T. Taniguchi, L. Nurdiwijayanto, N. Sakai, K. Tsukagoshi, T. Sasaki, T. Tsugawa, M. Koinuma, K. Hatakeyama, S. Ida, Revisiting the two-dimensional structure and reduction process of graphene oxide with in-plane X-ray diffraction. Carbon 202, 26 (2023)
G. Wang, C. He, W. Yang, F. Qi, G. Qian, S. Peng, C. Shuai, Surface-modified graphene oxide with compatible interface enhances poly-L-lactic acid bone scaffold. J. Nanomater. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5634096
X. Du, H. Zhang, Y. Yuan, Z. Wang, Semi-interpenetrating network anion exchange membranes based on quaternized polyvinyl alcohol/poly (diallyldimethylammonium chloride). Green Energy Environ. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gee.2020.06.015
L.-G. Chong, P.-A. Chen, J.-Y. Huang, H.-L. Huang, H.P. Wang, Capacitive deionization of a RO brackish water by AC/graphene composite electrodes. Chemosphere 191, 296 (2018)
Y. Zhang, P. Srimuk, M. Aslan, M. Gallei, V. Presser, Polymer ion-exchange membranes for capacitive deionization of aqueous media with low and high salt concentration. Desalination 479, 114331 (2020)
J.-S. Kim, J.-H. Choi, Fabrication and characterization of a carbon electrode coated with cation-exchange polymer for the membrane capacitive deionization applications. J. Membr. Sci. 355, 85 (2010)
Acknowledgments
Financial supports of the Taiwan Ministry of Science and Technology (108-2221-E-006-165-MY3, 109-2221-E-006-042-MY3 and 110-2221-E-006-107-MY2) are gratefully acknowledged.
Funding
Taiwan Ministry of Science and Technology (108-2221-E-006-165-MY3, 109-2221-E-006-042-MY3 and 110-2221-E-006-107-MY2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HCC and HPW contributed to the study conception and design. Material synthesis, data collection, analysis and manuscript preparation were performed by HCC. PAC and HPW have made a major improvement of the 1st-draft manuscript. CYP, SHL, YJT and HPW supervised this work. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, HC., Chen, PA., Peng, CY. et al. Anion-selective capacitive deionization using functionalized rGO thin films. MRS Communications 13, 1342–1348 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43579-023-00465-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43579-023-00465-9