Abstract
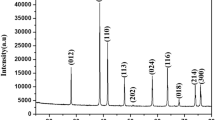
Nanowires have been formed from FeNi and FeCo alloys by the template synthesis method based on galvanic filling of pores of track membranes. A change in the nanowire elemental composition with a change in the electrolyte composition and with a change in the deposition potential has been studied. FeNi nanowires exhibit the effect of anomalous Fe codeposition: the iron content in the nanowires is much higher than that in the electrolyte. The difference increases with an increase in the initial concentration and with a decrease in the growth potential. It has also been found that the iron concentration increases in nanowire vertices. For FeCo nanowires, their composition corresponds to the electrolyte composition and changes only slightly with a change in the potential. An analysis of the X-ray diffraction data has determined the character of change in the spectra under varying growth conditions. The X-ray spectra of FeNi are found to depend on the growth potential (the intensity of phase peaks changes). Mössbauer measurements have revealed spontaneous magnetization for all samples of arrays of nanowires along their axes. The dependence of hyperfine magnetic field strength Bhf at 57Fe nuclei on the composition of nanowires of FexCo1 – x and FexNi1 – x solid solutions is obtained for the first time. It is found that the Bhf value decreases with an increase in the electrodeposition rate (or with an increase in deposition potential U).







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
G. E. Possin, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 41, 772 (1970).
S. Kawai and R. J. Ueda, Electrochem. Soc. 112, 32 (1975).
S. K. Chakarvarti and J. Vetter, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 62, 109 (1991).
J. Vetter and R. Spohr, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 79, 691 (1993).
T. M. Whitney, J. S. Jiang, P. S. Searson, and C. L. Chien, Science (Washington, DC, U. S.) 261, 1316 (1993).
C. R. Martin, Science (Washington, DC, U. S.) 266, 1961 (1994).
H. Masuda and K. Fukuda, Science (Washington, DC, U. S.) 268, 1466 (1995).
N. Lupu, Electrodeposited Nanowires and Their Applications (InTech, Croatia, 2010).
Magnetic Nano- and Microwires: Design, Synthesis, Properties and Applications, Ed. by M. Vázquez (Woodhead, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2015).
A. A. Davydov and V. M. Volgin, Russ. J. Electrochem. 52, 806 (2016).
D. J. Sellmyer, M. Zheng, and R. Skomski, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 13, R433 (2001).
Y. P. Ivanov, J. Leliaert, A. Crespo, M. Pancaldi, C. Tollan, J. Kosel, A. Chuvilin, and P. Vavassori, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 4 (2019).
M. Vazquez, K. Pirota, J. Torrejon, D. Navas, and M. Hernandez-Velez, J. Magn. Mater. 294, 174 (2005).
J. Alonso, H. Khurshid, V. Sankar, Z. Nemati, M. H. Phan, E. Garayo, J. A. Garcia, and H. Srikanth, J. Appl. Phys. 117, 17D113 (2015).
L. Elbaile, R. D. Crespo, V. Vega, and J. A. Garcıa, J. Nanomater. 13, 198453 (2012).
D. C. Leitao, C. T. Sousa, J. Ventura, J. S. Amaral, F. Carpinteiro, K. R. Pirota, M. Vazquez, J. B. Sousa, and J. P. Araujo, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 354, 5241 (2008).
M. Almasi Kashi, A. Ramazani, S. Doudafkan, and A. S. Esmaeily, Appl. Phys. A 102, 761 (2011).
K. V. Frolov, D. L. Zagorskii, I. S. Lyubutin, M. A. Chuev, I. V. Perunov, S. A. Bedin, A. A. Lomov, V. V. Artemov, and S. N. Sul’yanov, JETP Lett. 105, 319 (2017).
D. L. Zagorskii, K. V. Frolov, S. A. Bedin, I. V. Perunov, M. A. Chuev, A. A. Lomov, and I. M. Doludenko, Phys. Solid State 60, 2115 (2018).
K. V. Frolov, M. A. Chuev, I. S. Lyubutin, D. L. Zagorskii, S. A. Bedin, I. V. Perunov, A. A. Lomov, V. V. Artemov, D. N. Khmelenin, S. N. Sulyanova, and I. M. Doludenko, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 489, 165415 (2019).
A. M. Afanas’ev and M. A. Chuev, J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 80, 560 (1995).
M. A. Chuev, Dokl. Phys. 56, 318 (2011).
C. Johnson, M. S. Ridout, and T. E. Cranshaw, Proc. Phys. Soc. 81, 1079 (1963).
A. M. Afanas’ev, M. A. Chuev, and J. Hesse, J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 89, 533 (1999).
M. Chuev and J. Hesse, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 9, 506201 (2007).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to P.Yu. Apel’ (Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna) for supplying samples of polymer matrices.
Funding
This study was supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation within State assignments for the Federal Scientific Research Centre “Crystallography and Photonics” and Valiev Institute of Physics and Technology of the Russian Academy of Sciences and by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project no. 18-32-01066) in the part concerning synthesis of nanowires and Mössbauer measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by A. Sin’kov
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Doludenko, I.M., Zagorskii, D.L., Frolov, K.V. et al. Nanowires Made of FeNi and FeCo Alloys: Synthesis, Structure, and Mössbauer Measurements. Phys. Solid State 62, 1639–1646 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063783420090061
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063783420090061