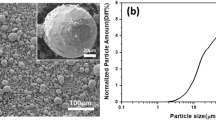
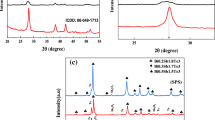
Abstract
Patterns in changes of the microstructure (grain structure) and the thermoelectric properties of the n-type grained Bi1.9Gd0.1Te3 compound, spark-plasma-sintered at different temperatures (TS = 690, 720, 735, 750, 780, and 810 K), have been studied in detail. All the samples studied were highly textured along the 001 direction parallel to the pressing direction, that resulted from preferential orientation of the grains. Orientation factor characterizing a texturing degree and estimated from XRD patterns happened to be weakly TS-dependent. Average grain size measured along the SPS pressing direction was far less as compared to that measured in the perpendicular direction. The thermoelectric properties measured for the perpendicular direction happened to be better than the same properties, but taken for the parallel direction. Of the samples sintered at different temperatures, the highest value of the thermoelectric figure-of-merit equal to ~0.73 for the perpendicular measuring orientation was found for the sample sintered at TS = 750 K. This sample is characterizing by the maximum power factor and the low enough thermal conductivity.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
G. S. Nolas, J. Sharp, and H. J. Goldsmid, Thermoelectrics Basic Principles and New Materials Developments (Springer, Berlin, 2001).
H. J. Goldsmid, Materials 7, 2577 (2014).
H. Kitagawa, T. Nagamori, T. Tatsuta, T. Kitamura, Y. Shinohara, and Y. Noda, Scr. Mater. 49, 309 (2003).
D. B. Hyun, T. S. Oh, J. S. Hwang, J. D. Shim, and N. V. Kolomoets, Scr. Mater. 40, 49 (1998).
S. Miura, Y. Satob, K. Fukuda, K. Nishimura, and K. Ikeda, Sci. Eng. A 277, 244 (2000).
O. Ivanov, O. Maradudina, and R. Lyubushkin, J. Alloys Compd. 586, 679 (2014).
W. Liu, X. Yan, G. Chen, and Z. Ren, Nano Energy 1, 42 (2012).
Y. Li, J. Jiang, G. Xu, W. Li, L. Zhou, Y. Li, and P. Cui, J. Alloys Compd. 480, 954 (2009).
S. S. Kim, S. Yamamoto, and T. Aizawa, J. Alloys Compd. 375, 107 (2004).
Y. Morisaki, H. Araki, H. Kitagawa, M. Orihashi, K. Hasezaki, and K. Kimura, Mater. Trans. 46, 2518 (2005).
X. K. Duan, K. G. Hu, D. H. Ma, W. N. Zhang, Y. Z. Jiang, and S. C. Guo, Rare Met. 34, 770 (2015).
P. Srivastava and K. Singh, Mater. Lett. 136, 337 (2014).
B. Jarivala, D. Shah, and N. M. Ravindra, J. Electron. Mater. 44, 1509 (2015).
O. Ivanov, O. Maradudina, and R. Lyubushkin, Mater. Char. 99, 175 (2015).
O. Ben-Yehuda, R. Shuker, Y. Gelbstein, Z. Dashevsky, and M. P. Dariel, J. Appl. Phys. 101, 113707 (2007).
J. J. Shen, L. P. Hu, T. J. Zhu, and X. B. Zhao, Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 124102 (2011).
X. Yan, B. Poudel, W. S. Liu, G. Joshi, H. Wang, Y. Lan, D. Wang, G. Chen, and Z. F. Ren, Nano Lett. 10, 3373 (2010).
S. D. Bhame, D. Pravarthana, W. Prellier, and J. G. Noudem, Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 2190 (2013).
X. A. Fan, J. Y. Yang, R. G. Chen, H. S. Yun, W. Zhu, S. Q. Bao, and X. K. Duan, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 39, 740 (2006).
J. Jiang, L. Chen, S. Bai, Q. Yao, and Q. Wang, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 117, 334 (2005).
Q. Lognon, F. Gascoin, O. I. Lebedev, L. Lutterotti, S. Gascoin, and D. Chateigner, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 97, 2038 (2014).
J.-J. Shen, T.-J. Zhu, X.-B. Zhao, S.-N. Zhang, S.-H. Yang, and Z.-Z. Yin, Energy Environ. Sci. 3, 1519 (2010).
C. Andre, D. Vasilevskiy, S. Turenne, and R. A. Masut, J. Phys. D.: Appl. Phys. 44, 235401 (2011).
A. Vasil’ev, M. Yaprintsev, O. Ivanov, and E. Danshina, Solid State Sci. 84, 28 (2018).
J. Yang, F. Wu, Z. Zhu, L. Yao, H. Song, and X. Hu, J. Alloys Compd. 619, 401 (2015).
X. H. Ji, X. B. Zhao, Y. H. Zhang, B. H. Lu, and H. L. Ni, J. Alloys Compd. 387, 282 (2005).
F. Wu, H. Song, J. Jia, and X. Hu, Prog. Natl. Sci. Mater. Int. 23, 408 (2013).
F. Wu, W. Shi, and X. Hu, Electron. Mater. Lett. 11, 127 (2015).
X. H. Ji, X. B. Zhao, Y. H. Zhang, B. H. Lu, and H. L. Ni, Mater. Lett. 59, 682 (2005).
F. Wu, H. Z. Song, J. F. Jia, F. Gao, Y. J. Zhang, and X. Hu, Phys. Status Solidi A 210, 1183 (2013).
W. Y. Shi, F. Wu, K. L. Wang, J. J. Yang, H. Z. Song, and X. J. Hu, Electron. Mater. 43, 3162 (2014).
X. B. Zhao, Y. H. Zhang, and X. H. Ji, Inorg. Chem. Commun. 7, 386 (2004).
O. Ivanov, M. Yaprintsev, R. Lyubushkin, and O. Soklakova, Scr. Mater. 146, 91 (2018).
M. Yaprintsev, A. Vasil’ev, and O. Ivanov, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 39, 1193 (2019).
O. Ivanov and M. Yaprintsev, Mater. Res. Express 5, 015905 (2018).
F. J. Humphreys and M. Hatherly, Recrystallization and Related Annealing Phenomena (Elsevier, Oxford, 2004).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
All of studies were carried out by the scientific equipment of joint research center “Technologies and Materials” at the Belgorod State University.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Education and Science, Russia, under grant no. 11.3719.2017/PCh (11.3719.2017/4.6).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yapryntsev, M.N., Vasil’ev, A.E., Ivanov, O.N. et al. Effect of Spark Plasma Sintering Temperature on Thermoelectric Properties of Grained Bi1.9Gd0.1Te3 Compound. Semiconductors 53, 1838–1844 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063782619130219
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063782619130219