Abstract
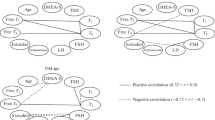
The concentrations of cortisol, its precursors, and its active form in human blood, as well as its relationship to changes in the concentration of central and peripheral hormonal regulators (a total of 36 parameters), were studied in healthy male volunteers aged 18–72 years. The study demonstrated a significant decrease in the blood concentrations of unutilized cortisol precursors (pregnenolone and progesterone) with age accompanied by the maintenance of constant total and free cortisol concentrations. We found an age-related decrease in the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) level that is a well-known pituitary stimulant of cortisol and cortisol precursor synthesis in the adrenal glands. The cortisol and ACTH levels in the age interval studied exhibited different correlations with the central and peripheral regulators of the hormonal axes. The conclusion was drawn that the cortisol level remains stable with increasing age in men, despite the decrease in the steroidogenic activity and blood ACTH level. This may be due to the imbalance in the regulation of cortisol and ACTH production by the central and peripheral regulators, especially by the hormones of the reproductive and somatotrophic axes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papadimitriou, A. and Priftis, K., Regulation of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis, Neuroimmunomodulation, 2009, vol.16, p. 265.
Veldhuis, J., Roelfsema, F., Iranmanesh, A., et al., Basal, Pulsatile, Entropic (Patterned), and Spiky (Staccato-Like) Properties of ACTH Secretion: Impact of Age, Gender, and Body Mass Index, J. Clin. Endocr. Metab., 2009, vol. 10, p. 4045.
Ferrary, M. and Mantero, F., Male Aging and Hormones: Adrenal Cortex, J. Endocr. Invest., 2005, vol. 28, p. 92.
Buford, T. and Willoughby, D., Impact of DHEA(S) and Cortisol on Immune Function in Aging: a Brief Review, Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab., 2008, vol. 33, p. 429.
Guazzo, E., Kirkpatrick, P., Goodyer, I., et al., Cortisol, Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), and DHEA Sulfate in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of Man: Relation to Blood Levels and the Effects of Age, J. Clin Endocr. Metab., 1996, vol. 81, p. 3951.
Bergendahl, M., Iranmanesh, A., Mulligan, T., and Veldhuis, J., Impact of Age on Cortisol Secretory Dynamics Basally and as Driven by Nutrient-Withdrawal Stress, J. Clin. Endocr. Metab., p. 2000, vol. 85, p. 2203.
McCann, S., Antunes-Rodrigues, J., Franci, C., et al., Role of the Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal Axis in the Control of the Response to Stress and Infection, Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res., 2000, vol. 33, p. 1121.
Engelmann, M., Landgraf, R., and Wotjak, C., The Hypothalamic-Neurohypophysial System Regulates the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis Under Stress: An Old Concept Revisited, Front. Neuroend., 2004, vol. 25, p. 132.
Uvnas-Moberg, K. and Peterson, M., Oxitocin, a Mediator of Anti-Stress, Well-Being, Social Interaction, Growth and Healing, Z. Psyh. Med. Psychother., 2005, vol. 51, p. 57.
Ruginsk, S., da Silva, A., Ventura, R., et al., Central Actions of Glucocorticoids in the Control of Body Fluid Homeostasis: Review, Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res.-, 2009, vol. 42, p. 61.
Bao, A., Meynen, G., and Swaab, D., The Stress System in Depression and Neurodegeneration: Focus on the Human Hypothalamus, Brain Res. Rev., 2008, vol. 57, p. 531.
Hu, G., Lian, Q., Latif, S., et al., Rapid Mechanisms of Glucocorticoid Signaling in the Luydig Cell, Steroids, 2008, vol. 73, p. 1018.
Demura, R., Kubo, O., Suzuki, R., et al., Demonstration of Activin in Normal Pituitary and in Various Human Pituitary Adenomas by Immunohistochemistry, Endocr. J., 1996, vol. 43, p. 429.
Suzuki, J., Otsuka, F., Inagaki, K., et al., Novel Action of Activin and Bone Morphogenetic Protein in Regulation Aldosterone Production by Human Adrenocortical Cells, Endocrinology, 2004, vol. 145, p. 639.
Vanttinen, T., Liu, J., Kuulasmaa, T., et al., Expressiom of Activin/Inhibin Signaling Components in the Human Adrenal Gland and the Effects of Activins and Inhibins on Adrenocortical Steroidogenesis and Apoptosis, J. Endocrinol., 2003, vol. 178, p. 479.
Farnworth, P., Wang, Y., Leembruggen, P., et al., Rodent Adrenocortical Cells Display High Affinity Binding Sites and Proteins for Inhibin A, and Express Components Required for Autocrine Signaling by Activins and Bone Morphogenetic Proteins, J. Endocrinol., 2006, vol. 188, p. 451.
Vogl, J., Hoing, A., Schuze, S., et al., Expression of Inhibins in the Endometrial Carcinoma Cell Line RL-95-2 After Stimulation with Cortisol and Estradiol, Anticancer Rs., 2007, vol. 27, p. 1989.
Nass, R. and Thorner, M., Impact of the GH-Cortisol Ratio on the Age-Dependent Changes in Body Composition, Growth Hormone and IGF Res., 2002, vol. 12, p. 147.
Hofland, L., Somatostatin and Somatostatin Receptors in Cushing’s Disease, Mol. Cell. Endocr., 2008, vol. 286, p. 199.
de Bruin, C., Feelders, R., Lamberts, S., et al., Somatostatin and Dopamine Receptors as Targets for Medical Treatment of Cushing’s Syndrome, Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord., 2009, vol. 10, p. 91.
Kageyama, K., Kushibiki, M., Hanada, K., et al., Growth Hormone-Releasing Peptide-2 Stimulates Secretion and Synthesis of Adrenocorticotropic Hormone in Mouse Pituitary, Regul. Pept., 2009, vol. 158, p. 116.
Agna, A. and Monson, P., Modulation of Glucocorticoid Metabolism by the Growth Hormone — IGF-1 Axis, Clin. Endocr., 2007, vol. 66, p. 459.
Ceda, G., Dall’Aglio, E., Maggio, M., et al., Clinical Implications of the Reduced Activity of the GH-IGF-I Axis in Older Men, J. Endocr. Invest., 2005, vol. 28, p. 96.
Giovannini, S., Marzetti, E., Borst, S., and Leeuwenburgh, C., Modulation of GH/IGF-1 Axis: Potential Strategies to Counteract Sarcopenia in Older Adults, Mech. Ageing Dev., 2008, vol. 129, p. 593.
Raposinho, P., Broqua, P., Pierroz, D., et al., Evidence That the Inhibition of Luteinizing Hormonr Secretion Exerted by Central Administration of Neuropeptide Y (NPY) in the Rat is Predominantly Mediated by the NPY-5 Receptor Subtype, Endocrinology, 1999, vol. 140, p. 4046.
Morgan, C., Rasmusson, M., Wang, S., et al., Neuropeptide-Y, Cortisol, and Subjective Distress in Humans Exposed to Acute Sress: Replication and Extention of Previous Report, Biol. Psychiatry., 2002, vol. 52, p. 136.
Konturek, S., Konturek, T., Pawlik, T., and Brzozowki, T., Brain-Gut Axis and Its Role in the Control of Food Intake, J. Physiol. Pharmacol., 2004, vol. 55, p. 137.
Nissdorfer, G., Spinazzi, R., and Mazzocchi, G., Cholecystokinin and Adrenal-Cortex Secretion, Vitam. Horm., 2005, vol. 71, p. 433.
Aoyadi, T., Kusakawa, S., Sanbe, A., et al., Enhanced Effect of Neuropeptide Y on Food Intake Caused by Blocade of the V(1A) Vasopressin Receptor, Eur. J. Pharmacol., 2009, vol. 622, p. 32.
Swali, A., Walker, E., Lavery, G., et al., 11beta-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1 Regulates Insulin and Glucagon Secretion in Pancreativ Islets, Diabetologia, 2008, vol. 51, p. 2003.
Wiedemann, K., Jahn, H., and Kellner, M., Effects of Natriuretic Peptides Upon Hypothalamo-Pituitary-Adrenocortical System Activity and Anxiety Behavior, Exp. Clin. Endocr. Diabetes, 2000, vol. 108, p. 5.
Yamaji, M., Tsutamoto, T., Kawahara, C., et al., Serum Cortisol as a Useful Predictor of Csrdiac Events in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure: the Impact of Oxidative Stress, Circ. Heart Fail., 2009, vol. 2, p. 608.
Auchus, J. and Rainey, W., Adrenarche—Physiology, Biochemistry and Human Disease, Clin. Endocrinol, 2004, vol. 60, p. 288.
Akhtar, M., Kelly, S., and Kaderbhai, M., Cytochrome B5 Modulation of 17 Hydroxylase and 17–20 Lyase (CYP17) Activities in Steroidogenesis, J. Endocrinol, 2005, vol. 187, p. 267.
Luo, L., Chen, H., and Zirkin, B., Temporal Relationships Among Testosterone Production, Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein (StAR), and P450 Side-Chain Cleavage Enzyme (P450scc) during Leidig Cell Aging, J. Androl., 2005, V. 26, p. 25.
Audige, A., Dick, B., Frey, B., et al., Glucocorticoids and 11 Beta-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 2 Gene Expression in the Aging Kidney, Eur. J. Clin. Invest., 2002, vol. 32, p. 411.
Koeva, Y., Bakalska, M., Atanasova, N., et al., Age-Related Changes in the Expression of 11beta-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 2 in Rat Leydig Cells, Folia Histochem. Cytobiol., 2009, vol. 47, p. 281.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © I.N. Kuzina, V.V. Kilikovsky, O.V. Smirnova, 2010, published in Fiziologiya Cheloveka, 2010, Vol. 36, No. 5, pp. 101–109.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuzina, I.N., Kilikovsky, V.V. & Smirnova, O.V. Age-related changes in the blood concentrations of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis hormones in healthy men: Relations with other hormonal axes. Hum Physiol 36, 582–589 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119710050105
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119710050105