Abstract
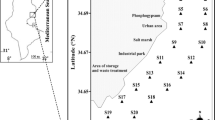
The phytoplankton and ciliate biomasses coupled with environmental factors were investigated in 15 transects in north coasts of Sfax (Tunisia, Eastern Mediterranean Sea) in July 2007. The phytoplankton biomass was dominated by Bacillariophyceae (89.66%), followed by Dinophyceae (10.07%), Coccolithophorideae (0.96%), Cyanobacteriae (0.21%), Chlorophyceae (0.03%) and Euglenophyceae (0.01%). Coscinodiscus sp. (93.26%) was the most abundant species of Bacillariophyceae group and associated with a high nutrient availability. Ciliate biomass was highly variable, with a large dominance of Spirotrichea, up to 96.2%. Biomass followed distinct patterns because of differences in the observed organism biovolumes. The spatial distribution of the ciliates biomass seems to be dependent on environmental factors and probably on their capacity to exploit a wide range of food resources including phytoplankton. The pollution generated by the phosphate-treating manufactory influenced the spatial phytoplankton and ciliate community’s distribution and their diversity along the north coast of Sfax.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aktan, Y., Tüfekçi, V., Tüfekçi, H., and Aykulu, G., Distribution patterns, biomass estimates and diversity of phytoplankton in Izmit Bay (Turkey), Estuarine, Coastal Shelf Sci., 2005, no. 64, pp. 372–384.
Alder, V.A., Tintinnoinea, in South Atlantic Zooplankton, Boltovsky, D., Ed., Leiden, The Netherlands: Backhuys Publishers, 1999, pp. 321–384.
Aleya, L., The seasonal succession of phytoplankton in a eutrophic lake through the coupling of biochemical composition of particulates, metabolic parameters and environmental conditions, Arch. Hydrobiol., 1992, no. 124, pp. 69–88.
Balech, E., Tintinnoinea del Mediterraneo, Trabajos del Instituto Espanol de Oceanografia, 1959, no. 28, pp. 1–88.
Balech, E., Los dinoflagelados del Atlantico sudoccidental, Madrid: Instituto Espanol de Oceanografia (Publicaciones especiales), 1988, p.309.
Brahim, M., Hamza, A., Hannachi, I., Rebai, A., Jarboui, O., Bouain, A., and Aleya, L., Variability in the structure of epiphytic assemblages of Posidonia oceanica in relation to human interferences in the Gulf of Gabes, Tunisia, Mar. Environ. Res., 2010, no. 70, pp. 411–421.
Burkill, P.H., Mantoura, R.F.C., Llewellyn, C.A., and Owens, N.J.P., Microzooplankton grazing and selectivity of phytoplankton in coastal waters, Mar. Biol., 1987, no. 93, pp. 581–590.
Bel Hassen, M., Drira, Z., Hamza, A., Ayadi, H., Akrout, F., and Issaoui, H., Summer phytoplankton pigments and community composition related to water mass properties in the Gulf of Gabes, Estuar. Coast Shelf Sci., 2008, no. 77, pp. 645–656.
Campbell, A.S., The open sea Tintinnoina of the plankton gathered during the last cruise of the Carnegie, Scientific Results of Cruise VII of the Carnegie during 1928–1929 under Command of Captain J.P. Ault, Richmond, VA: Byrd Press and Carnegie Institution of Washington, Publications 537, 1942, pp. 1–163.
D.G.P.A., Direction Générale de la pêche et de l‘aquaculture, Ministère de l’agriculture, Tunisie, annuaire statistique, 2005–2009.
Dolédec, S., and Chessel, D., Rythmes saisonniers et composantes stationnelles en milieu aquatique, II. Prise en compte et élimination d’effets dans un tableau faunistique, Oecol. Oec. Gen., 1989, no. 10, pp. 207–332.
Drira, Z., Hamza, A., Bel Hassen, M., Ayadi, H., Bouain, A., and Aleya, L., Dynamics of dinoflagellates and environmental factors during the summer in the Gulf of Gabes (Tunisia, Eastern Mediterranean Sea), Sci. Mar., 2008, no. 72, pp. 59–71.
Dodge, J.D., Atlas of Dinoflagellates. A Scanning Electron Microscope Survey, London: Ferrand Press, 1985, p.119.
Epstein, S., and Shiaris, M., Size-selective grazing of coastal bacterioplankton by natural assemblages of pigmented flagellates, colorless flagellates and ciliates, Microb. Ecol., 1992, no. 23, pp. 211–225.
Fenchel, T., Relation between particle size selection and clearance in suspension-feeding ciliates, Limnol. Oceanogr., 1980, no. 4, pp. 733–738.
Fogg, G.E., The phytoplanktonic ways of life, New Phytol., 1991, no. 118, pp. 191–232.
Fileman, E., Smith, T., and Harris, R., Grazing by Calanus helgolandicus and Para-Pseudocalanus spp. On phytoplankton and protozooplankton during the spring bloom in the Celtic Sea, J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 2007, no. 348, pp. 70–84.
Frontier, S., Etude statistique de la dispersion du zooplankton, J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 1973, no. 12, pp. 229–262.
Gallegos, C.L., and Jordan, T.E., Seasonal progression of factors limiting phytoplankton pigment biomass in the Rhode River estuary, Maryland (USA), I. Controls on phytoplankton growth, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 1997, no. 161, pp. 185–198.
Gifford, D.J., Impact of grazing by microzooplankton in the Northwest Arm of Halifax Harbour, Nova Scotia, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 1988, no. 47, pp. 249–258.
Hamza-Chaffai, A., Amiard-Triquet, C., and El Abed, A., Metallothionein-like protein, is it an efficient biomarker of metal contamination? A case study based on fish from the Tunisian coast, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 1997, no. 33, pp. 53–62.
Huber-Pestalozzi, G., Das phytoplankton des Susswassars, Halfte, Cryptophyceae, Chloromonadophyceae, Dinophyceae, Stuttgart: E. Schweizerbart Verlag, 1968, p.322.
Johansson, M., Gorokhirra, E., and Larsson, U.L.F., Annual variability in ciliate community structure, potential prey and predators in the open northern Baltic Sea proper, J. Plankton Res., 2004, no. 26, pp. 67–80.
Kchaou, N., Elloumi, J., Drira, Z., Hamza, A., Ayadi, H., Bouain, A., and Aleya, L., Distribution of ciliates in relation to environmental factors along the coastline of the Gulf of Gabes, Tunisia, Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci., 2009, no. 83, pp. 414–424.
Kivi, K. and Setala, O., Simultaneous measurement of food particle selection and clearance rates of planktonic oligotrich ciliates (Ciliophora: Oligotrichina), Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 1995, no. 119, pp. 125–137.
Kofoid, C.A. and Campbell, A.S., A conspectus of the marine and freshwater Ciliata belonging to the suborder Tintinnoinea, with descriptions of new species principally from the Agassiz expedition to the eastern tropical Pacific 1904–1905, Univ. California Publ. Zool., 1929, no. 34, pp. 1–403.
Kofoid, C.A. and Campbell, A.S., The Tintinnoinea of the eastern tropical Pacific, Bull. Museum of Comparative Zool. Harvard College, 1939, no. 84, pp. 1–473.
Latasa, M., Landry, M.R., Schluter, L., and Bidigare, R.R., Pigment-specific growth and grazing rates of phytoplankton in the central equatorial Pacific, Limnol. Oceanogr., 1997, no. 42, pp. 289–298.
Landry, M.R., Brown, S.L., Campbell, L., Constantinou, J., and Liu, H., Spatial patterns in phytoplankton growth and microzooplankton grazing in the Arabian Sea during monsoon forcing, Deep Sea Res. II, 1998, no. 45, pp. 2353–2368.
Lohrenz, S.E., Carroll, C.L., Weidermann, A.D., and Tuel, M., Variations in phytoplankton pigments, size structure and community composition related to wind forcing and water mass properties on the North Carolina inner shelf, Cont. Shelf Res., 2003, no. 23, pp. 1447–1464.
Lohman, H., Untersuchungen zur Feststellung des Vollständigen Gehaltes des Meeres an Plankton, Wiss Meeresunters., 1908, no. 10, pp. 131–170.
Louati, A., Elleuch, B., Kallel, A., Saliot, A., Dagaut, J., and Oudot, J., Hydrocarbon contamination of coastal sediments from the Sfax area (Tunisia), Mediterranean Sea, Mar. Pollut. Bull., 2001, no. 42, pp. 445–452.
Lynn, D.H. and Small, E.B., A revised classification of the phylum Ciliophora Doflein, 1901, Revista de la Sociedad de la Historia Natural de Mexico, 1997, no. 47, pp. 65–78.
Menden-Deuer, S. and Lessard, E.J., Carbon to volume relationships for dinoflagellates, diatoms, and other protist plankton, Limnol. Oceanogr., 2000, no. 45, pp. 569–579.
McManus, G.B. and Ederington-Cantrell, M.C., Phytoplankton pigments and growth rates and microzooplankton grazing in a large temperate estuary, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 1992, no. 87, pp. 77–85.
Nuccio, C., Melillo, C., Massi, L., and Innamorati, M., Phytoplankton abundance, community structure and diversity in eutrophycated Otbetello lagoon (Tuscany) from 1995 to 2001, Ocean. Acta, 2003, no. 26, pp. 15–25.
Petz, W., Ciliophora, in South Atlantic Zooplankton, Boltovsky, D., Ed., Leiden, The Netherlands, 1999, pp. 265–319.
Piehler, M.F., Twomey, L.J., Hall, N.S., and Pearl, H.W., Impacts of inorganic nutrient enrichment on phytoplankton community structure and function Pamlico Sound, NC, USA, Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci., 2004, no. 61, pp. 197–209.
Putt, M. and Stoecker, D.K., An experimentally determined carbon: volume ratio for marine “oligotrichous” ciliates from estuarine and coastal waters, Limnol. Oceanogr., 1989, no. 34, pp. 1097–1103.
Rekik, A., Drira, Z., Guermazi, W., Elloumi, J., Maalej, S., Aleya, L., and Ayadi, H., Impacts of an uncontrolled phosphogypsum dumpsite on summer distribution of phytoplankton, copepods and ciliates in relation to abiotic variables along the near-shore of the southwestern Mediterranean coast, Mar. Pollut. Bull., 2012, no. 64, pp. 336–346.
Rekik, A., Maalej, S., Ayadi, H., and Aleya, L., Restoration impact of an uncontrolled phosphogypsum dump site on the seasonal distribution of abiotic variables, phytoplankton and zooplankton along the near shore of the south-western Mediterranean coast, Envi ron. Sci. Pollut. Res., 2013. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1297-y
Rekik, A., Denis, M., Aleya, L., Maalej, S., and Ayadi, H., Spring plankton community structure and distribution in the north and south coasts of Sfax (Tunisia) after north coast restoration, Mar. Pollut. Bull., 2013, no. 67, pp. 82–93.
Rekik, A., Denis, M., Dugenne, M., Barani, A., Maalej, S., and Ayadi, H., Seasonal distribution of ultraphytoplankton and heterotrophic prokaryotes in relation to abiotic variables on the north coast of Sfax after restoration, Mar. Pollut. Bull., 2014, no. 84, pp. 280–305.
Sabetta, L., Alberto Basset, A., and Spezie, G., Marine phytoplankton size–frequency distributions: Spatial patterns and decoding mechanisms, Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci., 2008, no. 80, pp. 181–192.
Schnepf, E., Meier, R., and Drebes, G., Stability and deformation of diatom chloroplasts during food uptake of the parasitic dinoflagellate, Paulsenella (Dinophyta), Phycologia, 1988, no. 2, pp. 283–290.
SCOR-UNESCO, Determination of Photosynthetic Pigments in Sea Water, Paris: UNESCO, 1966.
Song, X., Huang, L., Zhang, J., Huang, X., Zhang, J., Yin, J., Tan, Y., and Liu, S., Variation of phytoplankton biomass and primary production in Daya Bay during spring and summer, Mar. Pollut. Bull., 2004, no. 49, pp. 1036–1044.
Stelfox-Widdicombe, C.E., Archer, S.D., Burkill, P.H., and Stefels, J., Microzooplankton grazing in Phaeocystis and diatom-dominated waters in the southern North Sea in spring, J. Sea Res., 2004, no. 51, pp. 37–51.
Strüder-Kypke, M.C. and Montagnes, D.J.S., Development of web-based guides to planktonic protests, Aquat. Microb. Ecol., 2002, no. 27, pp. 203–207.
Smetacek, V., The annual cycle of protozooplankton in the Kiel Bight, Mar. Biol., 1981, no. 63, pp. 1–11.
Tayibi, H., Choura, M., Lopez, F.A., Alguacil, F.A., and Lopez-Delgado, A., Environmental impact and management of phosphogypsum, J. Environ. Manag., 2009, pp. 1–10.
Tillmann, U., Interactions between planktonic microalgae and protozoan grazers, J. Phycol., 2004, no. 2, pp. 156–168.
Tomas, C.R., Hasle, G.R., Steidinger, A.K., Syvertsen, E.E., and Tangen, C., Identifing Marine Diatoms and Dinoflagellates, Academic Press Inc., 1996.
Tregouboff, G. and Rose, M., Manuel de planctonologie mediterraneenne, Vol. II, Paris: CNRS, 1957, p.592.
Utermöhl, H., Zurvervolkommungder quantitativen phytoplankton Methodik. Mitteilungen Internationale Vereinigung fur Theoretische und Angewandte, Limnol., 1958, no. 9, pp. 1–38.
Vadrucci, M.R., Cabrini, M., and Basset, A., Biovolume determination of phytoplankton guilds in transitional water ecosystems of Mediterranean Ecoregion, Transitional Wat. Bull., 2007, no. 2, pp. 83–102.
Vitousek, P.M. and Howarth, R.W., Nitrogen limitation on land and in the sea-how can it occur?, Biogeochem., 1991, no. 13, pp. 87–115.
Zhang, L.Y., Sun, J., Liu, D.Y., and Yu, Z.S., Studies on growth rate and grazing mortality rate by microzooplankton of size-fractionated phytoplankton in spring and summer in the Jiaozhou Bay, China, Acta Oceanol. Sin., 2005, no. 24, pp. 85–101.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rekik, A., Elloumi, J., Drira, Z. et al. Coupling of phytoplankton and ciliate biomasses to environmental factors along the north coast of Sfax (Tunisia, Eastern Mediterranean Sea). Water Resour 44, 849–863 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807817090019
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807817090019