Abstract
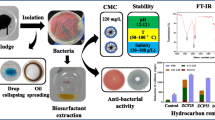
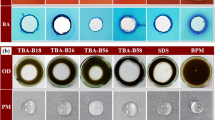
Halophilic bacteria isolated from sediment samples of five oil drilling sites in the Bay of Bengal (BOB) were screened for their biosurfactant-producing ability and for lipase production. The anti-biofilm activity and decolorization efficacy of the biosurfactant was also evaluated. Of 99 isolates, 31 isolates produced extracellular lipases. The optimum temperature and pH for the maximum enzyme activity were 30°C and 6, respectively, at a salt concentration of 15 g/L. Of the various organic substrates used (rice bran oil, gingelly oil, olive oil, and coconut oil), gingelly oil induced the maximum lipase production at a concentration of 5%. The most promising isolate was identified as Halomonas sp. (BOB-3) based on 16S rRNA ribotyping. Halomonas sp. BOB-3 produced lipase with a specific activity of 7777.78 U/mg of protein along with production (0.172 mg/mL) of the biosurfactant, which was characterized by thin layer chromatography, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy (GC-MS) analyses. The biosurfactant exhibited an anti-biofilm property with an inhibition of bacterial cell growth by 99.5% (V. cholerae) and 99.8% (S. typhi) at 125 µg/mL concentration. This is the first report on Halomonas sp. from BOB with lipolytic and biosurfactant-producing ability. The biosurfactant obtained was efficient in decolorization and also inhibited biofilm formation by V. cholerae and S. typhi.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Abalos, A., Pinazo, A., Infante, M.R., Casals, M., Garcia, F., and Manresa, A., Physicochemical and antimicrobial properties of new rhamnolipids produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa AT10 from soybean oil refinery wastes, Langmuir, 2001, vol. 17, no. 5, pp.1367‒1371.
Abdel-Fattah, Y.R., Optimization of thermostable lipase production from a thermophilic Geobacillus sp. using Box-Behnken experimental design, Biotechnol. Lett., 2002, vol. 24, no.14, pp. 1217‒1222.
Ahimou, F., Jacques, P., and Deleu, M., Surfactin effects on Bacillus subtilis surface hydrophobicity, Enzyme Microb. Technol., 2000, vol. 27, no. 10, pp. 749‒754.
Amann, R.I., Ludwig, W., and Schleifer, K.H., Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation, Microbiol. Rev., 1995, vol. 59, no. 1, pp. 143‒169.
Annamalai, N., Elayaraja, S., Vijayalakshmi, S., and Balasubramanian, T., Thermostable, alkaline tolerant lipase from Bacillus licheniformis using peanut oil cake as a substrate, Afr. J. Biochem. Res., 2011, vol. 5, no. 6, pp. 176‒181.
Banat, I. M., Franzetti, A., Gandolfi, I., Bestetti, G., Martinotti, M. G., Fracchia, L., Smyth, T.J., and Marchant, R., Microbial biosurfactants production, applications and future potential, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2010, vol. 87, no. 2, pp. 427‒444.
Bharathi, D., Rajalakshmi, G., and Komathi, S., Optimization and production of lipase enzyme from bacterial strains isolated from petrol spilled soil, J. King Saud Univ.-Sci., 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2017.12.018
Bodour, A.A. and Miller-Maier, R.M., Application of a modified drop-collapse technique for surfactant quantitation and screening of biosurfactant-producing microorganisms, J. Microbiol. Methods, 1998, vol. 32, no. 3, pp. 273‒280.
Borkar, P.S., Bodade, R.G., Rao, S.R., and Khobragade, C.N., Purification and characterization of extracellular lipase from a new strain: Pseudomonas aeruginosa SRT 9, Braz. J. Microbiol., 2009, vol. 40, no. 2, pp. 358‒366.
Corti Monzón, G., Nisenbaum, M., Herrera Seitz, M.K., and Murialdo, S.E., New findings on aromatic compounds’ degradation and their metabolic pathways, the biosurfactant production and motility of the halophilic bacterium Halomonas sp. KHS3. Curr. Microbiol., 2018, vol. 75, no. 8, pp. 1108‒1118.
Cameotra, S. S., and Makkar, R. S., Biosurfactant-enhanced bioremediation of hydrophobic pollutants, Pure A-ppl. Chem., 2010, vol. 82, no. 1, 97‒116.
Da Rosa, C.F.C., Michelon, M., de Medeiros Burkert, J.F., Kalil, S.J., and Burkert, C.A.V., Production of a rhamnolipid-type biosurfactant by Pseudomonas aeruginosa LBM10 grown on glycerol, Afr. J. Biotechnol., 2010, vol. 9, no. 53, pp. 9012‒9017.
Dhasayan, A., Kiran, G.S., and Selvin, J., Production and characterisation of glycolipid biosurfactant by Halomonas sp. MB-30 for potential application in enhanced oil recovery, Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol., 2014, vol. 174, no. 7, pp. 2571‒2584.
Díaz De Rienzo, M.A., Stevenson, P., Marchant, R., and Banat, I.M. Antibacterial properties of biosurfactants against selected Gram-positive and -negative bacteria, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 2015, vol. 363, no. 2, p. fnv224. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnv224
Donio, M.B.S., Ronica, F.A., Viji, V.T., Velmurugan, S., Jenifer, J. S. C.A., Michaelbabu, M., Dhar, P., and Citarasu, T., Halomonas sp. BS4, a biosurfactant producing halophilic bacterium isolated from solar salt works in India and their biomedical importance, SpringerPlus, 2013, vol. 2, no. 1, pp.149‒152.
Donovaro, R., Tselepides, A., Otegui, A., and Della Croce, N., Dynamics of meiofaunal assemblages on the continental shelf and deep-sea sediments of the Cretan Sea (NE Mediterranean): relationships with seasonal changes in food supply, Prog. Oceanog., 2000, vol. 46, nos. 2‒4, pp. 367‒400.
Ebrahimipour, G., Sadeghi, H., and Zarinviarsagh, M. Statistical methodologies for the optimization of lipase and biosurfactant by Ochrobactrum intermedium strain MZV101 in an identical medium for detergent applications, Molecules, 2017, vol. 22, no. 9, pp. 1460‒1470.
Eltaweel, M.A., Rahman, R.N.Z.R.A., Salleh, A.B., and Basri, M., An organic solvent-stable lipase from Bacillus sp. Strain 42, Ann. Microbiol., 2005, vol. 55, no. 3, p. 187.
Fracchia, L., Cavallo, M., Allegrone, G., and Martinotti, M.G., A Lactobacillus-derived biosurfactant inhibits biofilm formation of human pathogenic Candida albicans biofilm producers, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2010, vol. 2, pp. 827‒837.
Franzetti, A., Gandolfi, I., Bestetti, G., Smyth, T.J., and Banat, I.M., Production and applications of trehalose lipid biosurfactants, Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol., 2010, vol. 112, no. 6, pp. 617‒627.
Gaur, R., Gupta, A., and Khare, S.K., Purification and characterization of lipase from solvent tolerant Pseudomonas aeruginosa PseA, Proc. Biochem., 2008, vol. 43, no. 10, pp. 1040‒1046.
Ghori, M.I., Iqbal, M.J., and Hameed, A., Characterization of a novel lipase from Bacillus sp. isolated from tannery wastes, Braz. J. Microbiol., 2011, vol. 42, no. 1, pp. 22‒29.
Gilham, D., and Lehner, R., Techniques to measure lipase and esterase activity in vitro, Methods, 2005, vol. 36, no. 2, pp. 139‒147.
Gutiérrez-Arnillas, E., Arellano, M., Deive, F.J., Rodríguez, A., and Sanromán, M.Á., Unravelling the suitability of biological induction for halophilic lipase production by Halomonas sp. LM1C cultures, Biores. Technol., 2017, vol. 239, pp. 368‒377.
Habibollahi, H. and Salehzadeh, A., Isolation, optimization, and molecular characterization of a lipase producing bacterium from oil contaminated soils, Pollution, 2018, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 119‒128.
He, Y.Q. and Tan, T.W., Use of response surface methodology to optimize culture medium for production of lipase with Candida sp. 99-125, J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym., 2006, vol. 43, nos. 1‒4, pp. 9‒14.
Irie, Y., O’toole, G.A., and Yuk, M.H., Pseudomonas aeruginosa rhamnolipids disperse Bordetella bronchiseptica biofilms, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 2005, vol. 250, no. 2, pp. 237‒243.
Jadhav, V.V., Pote, S.S., Yadav, A., Shouche, Y.S., and Bhadekar, R.K., Extracellular cold active lipase from the psychrotrophic Halomonas sp. BRI 8 isolated from the Antarctic sea water, Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol., 2013, vol. 35, no. 6, pp. 1‒8.
Jaeger, K.E. and Reetz, M.T., Microbial lipases form versatile tools for biotechnology, Trend. Biotechnol., 1998, vol. 16, no. 9, pp. 396‒403.
Jain, D.K., Collins-Thompson, D.L., Lee, H., and Trevors, J.T., A drop-collapsing test for screening surfactant-producing microorganisms, J. Microbiol. Methods, 1991, vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 271‒279.
Jaiswal, A., Preet, M., and Tripti, B., Production and optimization of lipase enzyme from mesophiles and thermophiles, J. Microb. Biochem. Technol., 2017, vol. 9, no. 3. pp. 1‒10.
Jørgensen, B.B., and Boetius, A., Feast and famine‒microbial life in the deep-sea bed, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2007, vol. 5, no. 10, p. 770.
Jørgensen, L., Stedmon, C.A., Kragh, T., Markager, S., Middelboe, M., and Søndergaard, M., Global trends in the fluorescence characteristics and distribution of marine dissolved organic matter, Mar. Chem., 2011, vol. 126, no. 1-4, pp. 139‒148.
Kemp, W., Organic Spectroscopy, New York: Palgrave, 1991, pp. 243‒269.
Kiran, G.S., Thomas, T.A., Selvin, J., Sabarathnam, B., and Lipton, A.P., Optimization and characterization of a new lipopeptide biosurfactant produced by marine Brevibacterium aureum MSA13 in solid state culture, Biores. Technol., 2010, vol. 101, no. 7, pp. 2389‒2396.
Kumar, V.M., Janakiram, P., Sivaprasad, B., and Jayasree, L., Physico-chemical parameters and bacterial abundance in coastal water of Visakhapatnam, Bay of Bengal India, with special reference to Pseudomonas sp. and Vibrio sp., Ind. J. Geo-Mar. Sci., 2017, vol. 46, no. 8, pp. 1588‒1595
Kumarevel, T.S., Gopinath, S.C., Hilda, A., Gautham, N., and Ponnusamy, M.N., Purification of lipase from Cunninghamella verticillata by stepwise precipitation and optimized conditions for crystallization, World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2005, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 23‒26.
Larbidaouadi, K., Benattouche, Z., and Abbouni, B., Screening selection identification production and optimization of bacterial lipase isolated from industrial rejection of gas station, Int. J. Biotechnol. Allied Field., 2015, vol. 3, no. 9, pp.146‒153.
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., and Randall, R.J., Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent, J. Biol. Chem., 1951, vol. 193, no. 1, pp. 265‒275.
Mandal, S.M., Barbosa, A.E., and Franco, O.L., Lipopeptides in microbial infection control: scope and reality for industry, Biotechnol. Adv., 2013, vol. 31, no. 2, pp. 338‒345.
Mobarak-Qamsari, E., Kasra-Kermanshahi, R., and Moosavi-Nejad, Z., Isolation and identification of a novel, lipase-producing bacterium, Pseudomonas aeruginosa KM110, Iran. J. Microbiol., 2011, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 92‒99.
Mohanram, R., Jagtap, C., and Kumar, P., Isolation, screening, and characterization of surface-active agent-producing, oil-degrading marine bacteria of Mumbai Harbor, Mar. Pollut. Bullet., 2016, vol. 105, no. 1, pp. 131‒138.
Nandhini, B. and Josephine, R.M., A study on bacterial and fungal diversity in potted soil, Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci., 2013, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 1‒5.
Nathan, K.V., Rani, M.E., Gunaseeli, R.R., and Kannan, N.D., Lipase production using Aspergillus japonicus MF-1 through biotransformation of agro-waste and medicinal oil effluent, Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci., 2017, vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 2005‒2020.
Ng, H.J., Lopez-Perez, M., Webb, H.K., Gomez, D., Sawabe, T., Ryan, J., Vyssotski, M., Bizet, C., Malherbe, F., Mikhailov, V.V., and Crawford, R.J., Marinobacter salarius sp. nov. and Marinobacter similis sp. nov., isolated from sea water, PLoS One, 2014, vol. 9, no. 9, p. e106514.
Odisi, E.J., Silvestrin, M.B., Takahashi, R.Y.U., da Silva, M.A.C., and Lima, A.O.D.S., Bioprospection of cellulolytic and lipolytic South Atlantic deep-sea bacteria, Electron. J. Biotechnol., 2012, vol. 15, no. 5, pp. 18‒21.
Padmavathi, A.R., Abinaya, B., and Pandian, S.K., Phenol, 2, 4-bis (1, 1-dimethylethyl) of marine bacterial origin inhibits quorum sensing mediated biofilm formation in the uropathogen Serratia marcescens, Biofouling, 2014, vol. 30, no. 9, pp. 1111‒1122.
Pandey, A., Benjamin, S., Soccol, C.R., Nigam, P., Krieger, N., and Soccol, V.T., The realm of microbial lipases in biotechnology, Biotechnol, Appl. Biochem., 1999, vol. 29, no. 2, pp.119‒131.
Patowary, K., Patowary, R., Kalita, M.C., and Deka, S., Characterization of biosurfactant produced during degradation of hydrocarbons using crude oil as sole source of carbon, Front. Microbiol., 2017, vol. 8, p. 279.
Pekdemir, T., Ishigami, Y., and Uchiyama, H., Characterization of aescin as a biosurfactant for environmental remediation, J. Surfactants Deterg., 1999, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 337‒341.
Pornsunthorntawee, O., Wongpanit, P., Chavadej, S., Abe, M., and Rujiravanit, R., Structural and physicochemical characterization of crude biosurfactant produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa SP4 isolated from petroleum-contaminated soil, Biores. Technol., 2008, vol. 99, no. 6, pp. 1589‒1595.
Priji, P., Sajith, S., Unni, K.N., Anderson, R.C., and Benjamin, S., Pseudomonas sp. BUP6, a novel isolate from Malabari goat produces an efficient rhamnolipid type biosurfactant, J. Bas. Microbiol., 2017, vol. 57, no. 1, pp. 21‒33.
Ramesh, S., Rajesh, M., and Mathivanan, N., Characterization of a thermostable alkaline protease produced by marine Streptomyces fungicidicus MML1614, Bioproc. Biosys. Eng., 2009, vol. 32, no. 6, pp. 791‒800.
Rosenberg, M., Bacterial adherence to hydrocarbons: a useful technique for studying cell surface hydrophobicity, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 1984, vol. 22, no. 3, pp. 289‒295.
Satpute, S.K., Banat, I.M., Dhakephalkar, P.K., Banpurkar, A.G., and Chopade, B.A., Biosurfactants, bioemulsifiers and exopolysaccharides from marine microorganisms, Biotechnol. Adv., 2010, vol. 28, no. 4, pp. 436‒450.
Saxena, R.K., Microbial lipases: potential biocatalysts for the future industry, Curr. Sci., 1999, vol. 77, pp. 101‒115.
Sharma, R., Chisti, Y., and Banerjee, U.C., Production, purification, characterization, and applications of lipases, Biotechnol. Adv., 2001, vol. 19, no. 8, pp. 627‒662.
Sharma, P., Sharma, N., Pathania, S., and Handa, S., Purification and characterization of lipase by Bacillus methylotrophicus PS3 under submerged fermentation and its application in detergent industry, J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol., 2017, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 369‒377.
Shukla, B.N. and Desai, P.V., Isolation, characterization and optimization of lipase producing Pseudomonas sp. from oil contaminated sites, Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci., 2016, vol. 5, no. 5, pp. 902‒909.
Shukla, S.K. and Rao, T.S., An improved crystal violet assay for biofilm quantification in 96-well microtitre plate, BioRxiv, 2017, p. 100214.
Sivapathasekaran, C., Das, P., Mukherjee, S., Saravanakumar, J., Mandal, M., and Sen, R., Marine bacterium derived lipopeptides: characterization and cytotoxic activity against cancer cell lines, Int. J. Peptide Res. Therap., 2010, vol. 16, no. 4, pp. 215‒222.
Sugihara, A., Tani, T., and Tominaga, Y., Purification and characterization of a novel thermostable lipase from Bacillus sp., J. Biochem., 1991, vol. 109, no. 2, pp. 211‒216.
Thanomsub, B., Watcharachaipong, T., Chotelersak, K., Arunrattiyakorn, P., Nitoda, T., and Kanzaki, H., Monoacylglycerols: glycolipid biosurfactants produced by a thermotolerant yeast, Candida ishiwadae, J. Appl. Microbiol., 2004, vol. 96, no. 3, pp. 588‒592.
Toribio, J., Escalante, A.E., and Soberón-Chávez, G., Rhamnolipids: production in bacteria other than Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol., 2010, vol. 112, no. 10, pp. 1082‒1087.
Veerasingam, S., Venkatachalapathy, R., Sudhakar, S., Raja, P., and Rajeswari, V., Petroleum hydrocarbon concentrations in eight mollusc species along Tamilnadu coast, Bay of Bengal, India, J. Environ. Sci., 2011, vol. 23, no. 7, pp. 1129‒1134.
Yang, J. and Dang, H., Cloning and characterization of a novel cold-active endoglucanase establishing a new subfamily of glycosyl hydrolase family 5 from a psychrophilic deep-sea bacterium, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 2011, vol. 325, no. 1, pp. 71‒76.
Youssef, N.H., Duncan, K.E., Nagle, D.P., Savage, K.N., Knapp, R.M., and McInerney, M.J., Comparison of methods to detect biosurfactant production by diverse microorganisms, J. Microbiol. Methods, 2004, vol. 56, no. 3, pp. 339‒347.
Yu, E.Y., Kwon, M.A., Lee, M., Oh, J.Y., Choi, J.E., Lee, J.Y., Song, B.K., Hahm, D.H., and Song, J.K., Isolation and characterization of cold-active family VIII esterases from an arctic soil metagenome, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2011, vol. 90, no. 2, pp. 573‒581.
Zarinviarsagh, M., Ebrahimipour, G., and Sadeghi, H., Lipase and biosurfactant from Ochrobactrum intermedium strain MZV101 isolated by washing powder for detergent application, Lipids Health Dis., 2017, vol. 16, no. 1, p. 177.
Zouaoui, B. and Bouziane, A., Isolation, optimisation and purification of lipase production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, J. Biotechnol. Biomat., 2011, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 345‒351.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are grateful to the Director, NIO, Goa and Scientist- in- charge, CSIR-NIO (RC), Kochi for their support and advice. We also thank Dr. R. Joythibabu for the help rendered for sample collections.
Funding
NVK acknowledges the financial support of Science and Engineering Board (SERB), Government of India through National Post-Doctoral fellowship [PDF/2016/000438]. This is NIO contribution number 6393. Authors acknowledge Kerala Forest Research Institute (KFRI), Central Instrumentation Unit, Peechi for GC-MS analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
STATEMENT ON THE WELFARE OF ANIMALS
This article does not contain any studies involving animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kayanadath, S., Nathan, V.K. & Ammini, P. Anti-Biofilm Activity of Biosurfactant Derived from Halomonas sp., a Lipolytic Marine Bacterium from the Bay of Bengal. Microbiology 88, 585–599 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261719050072
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261719050072