Abstract
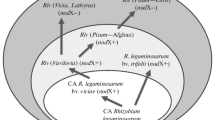
The processes of speciation and macroevolution of root nodule bacteria (rhizobia), based on deep rearrangements of their genomes and occurring in the N2-fixing symbiotic system, are reconstructed. At the first stage of rhizobial evolution, transformation of free-living diazotrophs (related to Rhodopseudomonas) to symbiotic N2-fixers (Bradyrhizobium) occurred due to the acquisition of the fix gene system, which is responsible for providing nitrogenase with electrons and redox potentials, as well as for oxygen-dependent regulation of nitrogenase synthesis in planta, and then of the nod genes responsible for the synthesis of the lipo-chitooligosaccharide Nod factors, which induce root nodule development. The subsequent rearrangements of bacterial genomes included (1) increased volume of hereditary information supported by species, genera (pangenome), and individual strains; (2) transition from the unitary genome to a multicomponent one; and (3) enhanced levels of bacterial genetic plasticity and horizontal gene transfer, resulting in formation of new genera—of which Mesorhizobium, Rhizobium, and Sinorhizobium are the largest—and of over 100 species. Rhizobial evolution caused by development and diversification of the Nod factor-synthesizing systems may result in either relaxed host specificity range (transition of Bradyrhizobium from autotrophic to symbiotrophic carbon metabolism in interaction with a broad spectrum of legumes) or narrowed host specificity range (transition of Rhizobium and Sinorhizobium to “altruistic” interaction with legumes of the galegoid clade). Reconstruction of the evolutionary pathway from symbiotic N2-fixers to their free-living ancestors makes it possible to initiate the studies based on up-to-date genome screening technologies and aimed at the issues of genetic integration of organisms into supraspecies complexes, ratios of the macro- and microevolutionary mechanisms, and development of cooperative adaptations based on altruistic interaction between the symbiotic partners.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berrada, H. and Fikri-Benbrahim, K., Taxonomy of the rhizobia: current perspectives, British Microbiol. Res. J., 2014, vol. 4, no. 6, pp. 616–639.
Black, M., Moolhuijzen, P., Chapman, B., Barrero, R., Howieson, J., Hungria, M., and Bellgard, M., The genetics of symbiotic nitrogen fixation: comparative genomics of 14 rhizobia strains by resolution of protein clusters, Genes, 2012, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 138–166.
Downie, J.A. and Young, J.P.W., The ABC of symbiosis, Nature, 2001, vol. 412, no. 6847, pp. 597–598.
Gianinazzi-Pearson, V., Plant cell responses to arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: getting to the roots of the symbiosis, The Plant Cell, 1996, vol. 8, no. 6, pp. 1871–1883.
Giraud, E., Moulin, L., Vallenet, D., Barbe, V., Cytryn, E., Avarre, J.C., Jaubert, M., Simon, D., Cartieaux, F., Prin, Y., Bena, G., Hannibal, L., Fardoux, J., Kojadinovic, M., Vuillet, L., et al., Legume symbioses: absence of nod genes in photosynthetic bradyrhizobia, Science, 2007, vol. 316, no. 5829, pp. 1307–1312.
González, V., Acosta, J.L., Santamaría, R.I., Bustos, P., Fernández, J.L., Hernández González, I.L., Díaz, R., Flores, M., Palacios, R., Mora, J., and Dávila, G., Conserved symbiotic plasmid DNA sequences in the multireplicon pangenomic structure of Rhizobium etli, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2010, vol. 76, no. 5, pp. 1604–1614.
Gourion, B., Delmotte, N., Bonaldi, K., Nouwen, N., Vorholt, J.A., and Giraud, E., Bacterial RuBisCO is required for efficient Bradyrhizobium/Aeschynomene symbiosis, PLoS One, 2011, vol. 6, no. 7. doi 10.1371/journal. pone.0021900
Guan, S.H., Gris, C., Cruveiller, S., Pouzet, C., Tasse, L., Leru, A., Maillard, A., Médigue, C., Batut, J., Masson-Boivin, C., and Capela, D., Experimental evolution of nodule intracellular infection in legume symbionts, ISME J., 2013, vol. 7, no. 7, pp. 1367–1377.
Gubin, S.V. and Lupachev, A.V., Approaches to isolation and investigation of buried soils in permafrost deposits of an ice complex, Kriosfera Zemli, 2012, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 79–84.
Haag, A.F., Arnold, M.F., Myka, K.K., Kerscher, B., Dall’Angelo, S., Zanda, M., Mergaert, P., and Ferguson, G.P., Molecular insights into bacteroid development during Rhizobium-legume symbiosis, FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 2013, vol. 37, no. 3, pp. 364–383.
Harrison, P.W., Lower, R.P., Kim, N.K., and Young, J.P., Introducing the bacterial “chromid”: not a chromosome, not a plasmid, Trends Microbiol., 2010, vol. 18, no. 4, pp. 141–148.
Heinrich, K., Ryder, M.H., and Murphy P.J., Early production of rhizopine in nodules induced by Sinorhizobium meliloti strain L5-30, Can. J. Microbiol., 2001, vol. 47, no. 2, pp. 165–171.
Kaminskii, P., Batut, J., and Biostard, P., Control of symbiotic nitrogen fixation by rhizobia, in The Rhizobiaceae. Molecular Biology of Model Plant-Associated Bacteria, Spaink, H.P., Kondorosi, A., and Hooykaas, P.J.J., Eds., Boston: Kluwer Academic, 1998. [Russ. Transl. SPb.: Biont, 2002, pp. 465–492.]
Kaneko, T., Nakamura, Y., Sato, S., Minamisawa, K., Uchiumi, T., Sasamoto, S., Watanabe, A., Idesawa, K., Iriguchi, M., Kawashima, K., Kohara, M., Matsumoto, M., Shimpo, S., Tsuruoka, H., Wada, T., Yamada, M., and Tabata, S., Complete genomic sequence of nitrogen-fixing symbiotic bacterium Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA110, DNA Res., 2002, vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 189–197.
Kimeklis, A.K., Safronova, V.I., Kuznetsova, I.G., Sazanova, A.L., Belimov, A.A., Pinaev, A.G., Chizhevskaya, E.P., Pukhaev, A.R., Popov, K.P., Andronov, E.E., and Provorov, N.A., Phylogenetic analysis of Rhizobium strains isolatedfrom Vavilovia formosa (Stev.) Fed. root nodules, Sel’skokhoz. Biol., 2015, no. 5 (in press).
Laranjoa, M., Alexandrea, A., and Oliveira, S., Legume growth-promoting rhizobia: an overview on the Mesorhizobium genus, Microbiol. Res., 2014, vol. 169, no. 1, pp. 2–17.
Ma, S.W. and Iyer, V.N., New field isolates of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae that nodulate the primitive pea cultivar Afghanistan in addition to modern cultivars, Appl. Envion. Microbiol., 1990, vol. 56, no. 12, pp. 2206–2212.
Marchetti, M., Capela, D., Glew, M., Cruveiller, S., Chane-Woon-Ming, B., Gris, C., Timmers, T., Poinsot, V., Gilbert, L.B., Heeb, P., Médigue, C., Batut, J., and Masson-Boivin, C., Experimental evolution of a plant pathogen into a legume symbiont, PLoS Biol., 2010, vol. 8, no. 1. doi 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000280
Margaret, I., Becker, A., Blom, J., Bonilla, I., Goesmann, A., Göttfert, M., Lloret, J., Mittard-Runte, V., Rückert, C., Ruiz-Sainz, J.E., Vinardell, J.M., and Weidner, S., Symbiotic properties and first analyses of the genomic sequence of the fast growing model strain Sinorhizobium fredii HH103 nodulating soybean, J. Biotechnol., 2011, vol. 155, no. 1, pp. 11–19.
Mazur, A., Stasiak, G., Wielbo, J., Kubik-Komar, A., Marek-Kozaczuk, M., and Skorupska, A., Intragenomic diversity of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii clover nodule isolates, BMC Microbiol., 2011, vol. 11, 123. doi 10.1186/1471-2180-11-123
Medini, D., Donati, C., Tettelin, H., Masignani, V., and Rappuoli, R., The microbial pan-genome, Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 2005, vol. 15, no. 6, pp. 589–594.
Minamisawa, K., Nakatsuka, Y., and Isawa, T., Diversity and field site variation of indigenous populations of soybean bradyrhizobia in Japan by fingerprints with repeated sequences RSa and RSß, FEMS Microbiol. Ecol., 1999, vol. 29, no. 2, pp. 171–178.
Mira, A., Martín-Cuadrado, A.B., D’Auria, G., and Rodríguez-Valera, F., The bacterial pan-genome: a new paradigm in microbiology, Int. Microbiol., 2010, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 45–57.
Mornico, D., Miché, L., Béna, G., Nouwen, N., Verméglio, A., Vallenet, D., Smith, A.T., Giraud, E., Médigue, C., and Moulin, L., Comparative genomics of Aeschynomene symbionts: insights into the ecological lifestyle of nod-independent photosynthetic bradyrhizobia, Genes, 2012, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 35–61.
Muntyan, A.N., Andronov, E.E., Belova, V.S., Rumyantseva, M.L., and Simarov, B.V., Associated symbiotic populations. Part I: Analysis of genetic diversity of the rhizobial component, Ekol. Genet., 2012, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 3–11.
Oda, Y., Larimer, F.W., Chain, P.S., Malfatti, S., Shin,M.V., Vergez, L.M., Hauser, L., Land, M.L., Braatsch, S., Beatty, J.T., Pelletier, D.A., Schaefer, A.L., and Harwood, C.S., Multiple genome sequences reveal adaptations of a phototrophic bacterium to sediment microenvironments, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2008, vol. 105, no. 47, pp. 18543–18548.
Ormeño-Orrillo, E., Menna, P., Almeida, L.G.P., Ollero, F.J., Nicolás, M.F., Rodrigues, E.P., Nakatani, A.S., Batista, J.S.S., Chueire, L.M.O., Souza, R.C., Vasconcelos, A.T.R., Megías, M., Hungria, M., and Martínez-Romero, E., Genomic basis of broad host range and environmental adaptability of Rhizobium tropici CIAT 899 and Rhizobium sp. PRF 81 which are used in inoculants for common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.), BMC Genomics, 2012. 13:735. doi 10.1186/1471-2164-13-735
Österman, J., Marsh, J., Laine, P.K., Zeng, Z., Alatalo, E., Sullivan, J.T., Young, J.P., Thomas-Oates, J., Paulin, L., and Lindström, K., Genome sequencing of two Neorhizobium galegae strains reveals a noeT gene responsible for the unusual acetylation of the nodulation factors, BMC Genomics, 2014, vol. 15:500. doi 10.1186/1471-2164-15-500
Ovtsyna, A.O. and Tikhonovich, I.A., Structure, functions, and possible practical applications of the signal molecules initiating development of a legumen–rhizobial symbiosis, Ekol. Genet., 2004, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 14–24.
Porozov, Yu.B., Muntyan, A.N., Chizhevskaya, E.P., Simarov, B.V., and Andronov, E.E., Associated symbiotic populations. Part II: Analysis of polymorphism of the nfr5 receptor gene using molecular docking, Ekol. Genet., 2012, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 12–18.
Provorov, N.A. and Dolgikh, E.A., Metabolic integration of organisms in symbiotic systems, Zh. Obshch. Biol., 2006, vol. 67, no. 6, pp. 403–422.
Provorov, N.A. and Vorob’ev, N.I., Geneticheskie osnovy evolyutsii rastitel’no-mikrobnogo simbioza (Genetic Basics of the Evolution of Plant–Microbial Symbioses), St.-Petersburg: Inform-Navigator, 2012.
Provorov, N.A. and Vorobyev, N.I., Evolution of host-beneficial traits in nitrogen-fixing bacteria: modeling and construction of systems for interspecies altruism, Appl. Biochem. Microbiol., 2015, vol. 51, no. 4, pp. 381–387.
Rey, F. and Harwood, C.S., FixK, a global regulator of microaerobic growth, controls photosynthesis in Rhodopseudomonas palustris, Mol. Microbiol., 2010, vol. 75, no. 6, pp. 1007–1020.
Rinke, C., Schwientek, P., Sczyrba, A., Ivanova, N.N., Anderson, I.J., Cheng, J.F., Darling, A., Malfatti, S., Swan, B.K., Gies, E.A., Dodsworth, J.A., Hedlund, B.P., Tsiamis, G., Sievert, S.M., Liu, W.T., et al., Insights into the phylogeny and coding potential of microbial dark matter, Nature, 2013, vol. 499, no. 7459, pp. 431–437.
Safronova, V.I., Kuznetsova, I.G., Sazanova, A.L., Kimeklis, A.K., Belimov, A.A., Andronov, E.E., Pinaev, A.G., Chizhevskaya, E.P., Pukhaev, A.R., Popov, K.P., Willems, A., and Tikhonovich, I.A., Bosea vaviloviae sp. nov., a new species of slow-growing rhizobia isolated from nodules of the relict species Vavilovia formosa (Stev.) Fed., Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 2015, vol. 107, no. 4, pp. 911–920.
Schuldes, J., Rodriguez Orbegoso, M., Schmeisser, C., Krishnan, H.B., Daniel, R., and Streit, W.R., Complete genome sequence of the broad-host-range strain Sinorhizobium fredii USDA257, J. Bacteriol., 2012, vol. 194, no. 16, pp. 4483.
Sprent, J.I., West African legumes: the role of nodulation and nitrogen fixation, New Phytologist, 2005, vol. 167, no. 3, pp. 326–330.
Terpolilli, J.J., Hood, G.A., and Poole, P.S., What determines the efficiency of N2-fixing Rhizobium-legume symbioses?, Adv. Microb. Physiol., 2012, vol. 60, pp. 325–389.
Tian, C.F., Zhou, Y.J., Zhang, Y.M., Li, Q.Q., Zhang, Y.Z., Li, D.F., Wang, S., Wang, J., Gilbert, L.B., Li, Y.R., and Chen, W.X., Comparative genomics of rhizobia nodulating soybean suggests extensive recruitment of lineage-specific genes in adaptations, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2012, vol. 109, no. 22, pp. 8629–8634.
Vorontsov, N.N., Razvitie evolyutsionnykh idei v biologii (Development of Evolutionary Ideas in Biology), Moscow: Progress-Traditsiya, 1999.
Wang, D., Yang, S., Tang, F., and Zhu, H., Symbiosis specificity in the legume—rhizobial mutualism, Cell Microbiol., 2012, vol. 14, no. 3, pp. 334–342.
Wisniewski-Dyé, F., Lozano, L., Acosta-Cruz, E., Borland, S., Drogue, B., Prigent-Combaret, C., Rouy, Z., Barbe, V., Herrera, A.M., González, V., and Mavingui, P., Genome sequence of Azospirillum brasilense CBG497 and comparative analyses of Azospirillum core and accessory genomes provide insight into niche adaptation, Genes, 2012, vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 576–602.
Yakovlev, G.P., Bobovye zemnogo shara (Legumens of the Globe), Leningrad: Nauka, 1991.
Young, J.P., Downer, H.L., and Eardly, B.D., Phylogeny of the phototrophic rhizobium strain BTAi1 by polymerase chain reaction-based sequencing of a 16S rRNA gene segment, J. Bacteriol., 1991, vol. 173, no. 7, pp. 2271–2277.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © N.A. Provorov, E.E. Andronov, 2016, published in Mikrobiologiya, 2016, Vol. 85, No. 2, pp. 115–125.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Provorov, N.A., Andronov, E.E. Evolution of root nodule bacteria: Reconstruction of the speciation processes resulting from genomic rearrangements in a symbiotic system. Microbiology 85, 131–139 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261716020156
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261716020156