Abstract
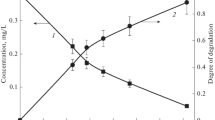
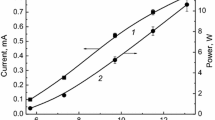
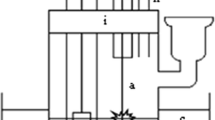
The kinetics of decomposition of ibuprofen in its aqueous solution by the action of atmospheric-pressure direct-current discharge in ambient air has been studied. The treated solution served as both the cathode and the anode of the discharge system. Degradation rates and effective degradation rate constants have been determined. Based on these data, the energy yields and degrees of destruction were calculated for various discharge powers (discharge currents). Discharges in a liquid cathode and anode differ little in the energy yields of degradation. But the rates and rate constants of degradation in the liquid cathode are higher than in the liquid anode. Therefore, the complete destruction of ibuprofen in the liquid cathode is achieved within shorter discharge times. A comparison is made of the destruction efficiencies for the cases of solution treatment using glow, dielectric barrier, and pulsed corona discharges.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Takagi, T., Ramachandran, C., Bermejo, M., Yamashita, S., Yu, L.X., and Amidon, G.L., Mol. Pharm., 2006, vol. 3, p. 631.
Bound, J.P. and Voulvoulis, N., Chemosphere, 2004, vol. 56, p. 1143.
Ternes, T.A. and Joss, A., Human Pharmaceuticals, Hormones and Fragrances: The Challenge of Micropollutants in Urban Water Management, London: IWA, 2006.
Myers, R.L., The 100 Most Important Chemical Compounds: A Reference Guide, Westport, CT: Greenwood, 2007, p. 352.
Ansari, M., Moussavi, G., Ehrampoosh, M.H., and Giannakis, S., J. Water Process Eng., 2023, vol. 51, p. 103371.
Magureanu, M., Bilea, F., Bradu, C., and Hong, D., J. Hazard. Mater., 2021, vol. 417, p. 125481.
Shutov, D.A., Ivanov, A.N., Rakovskaya, A.V., Smirnova, K.V., Manukyan, A.S., and Rybkin, V.V., J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2020, vol. 53, no. 28, p. 445202.
Filippova, N.I., Vainshtein, V.A., Son, A.V., and Minina, S.A., Razrab. Registr. Lekarst. Sredstv, 2017, no. 1, p. 58.
Bobkova, E.S. and Rybkin, V.V., Plasma Chem. Plasma Process., 2015, vol. 35, no. 1, p. 133.
Marković, M., Jović, M., Stanković, D., Kovačević, V., Roglić, G., Gojgić-Cvijović, G., and Manojlović, D., Sci. Total Environ., 2015, vol. 505, p. 1148.
Zeghioud, H., Nguyen-Tri, P., Khezami, L., Amrane, A., and Assadi, A.A., J. Water Process Eng., 2020, vol. 38, p. 101664.
Shutov, D.A., Smirnova, K.V., Ivanov, A.N., and Rybkin, V.V., Plasma Chem. Plasma Process., 2023, vol. 43, no. 3, p. 577.
Shutov, D.A., Batova, N.A., Smirnova, K.V., Ivanov, A.N., and Rybkin, V.V., J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2022, vol. 55, no. 34, p. 345206.
Smirnov, S.A., Zalipaeva, Ya.V., and Rybkin, V.V., Plasma Chem. Plasma Process., 2014, vol. 34, no. 4, p. 721.
Shutov, D.A., Artyukhov, A.I, Ivanov, A.N., and Rybkin, V.V., Plasma Phys. Rep., 2019, vol. 45, no. 11, p. 997.
Aziz, K.H.H., Miessner, H., Mueller, S., Kalass, D., Moeller, D., Khorshid, I., and Rashid, M.A.M., Chem. Eng. J., 2017, vol. 313, p. 1033.
Zeng, J., Yang, B., Wang, X., Li, Z., Zhang, X., and Lei, L., Chem. Eng. J., 2015, vol. 267, p. 282.
Funding
The work was supported by the Ministry of Higher Education and Science of the Russian Federation, project no. FZZW-2023-0010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Translated by S. Zatonsky
Publisher’s Note.
Pleiades Publishing remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ignatiev, A.A., Ivanova, P.A., Ivanov, A.N. et al. Kinetics of Ibuprofen Degradation in Aqueous Solution by the Action of Direct-Current Glow Discharge in Air. High Energy Chem 57, 537–540 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S001814392306005X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S001814392306005X