Abstract
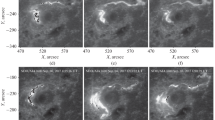
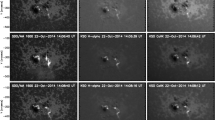
We studied the process of energy release of the confined X2.2 flare, which occurred September 6, 2017 in the active region NOAA 12673. The magnetic reconnection rate and reconnection fluxes were obtained from chromospheric data (SDO/AIA 1600 Å) and magnetograms of the photospheric field (SDO/HMI). The time profiles of the magnetic reconnection rate and microwave emission obtained by the radioastronomical diagnostic complex of solar activity of the Crimean Astrophysical Observatory, Russian Academy of Sciences (KRIM) demonstrate good agreement. This suggests that the magnetic reconnection rate plays an important part in the energy release in flares and in the acceleration of nonthermal electrons with formation of microwave emission. The morphology of the flare radio source in low-frequency emission has been studied. The low-frequency slope of the flux density spectrum is 1.2, which indicates a spatial inhomogeneity of the source. The area of such a source increases with a decrease in frequency.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Alexander, D. and Coyner, A.J., Temporal and spatial relationships between ultraviolet and hard X-ray emission in solar flares, Astrophys. J., 2006, vol. 640, pp. 505–515.
Dulk, G.A., Radio emission from the Sun and stars, Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys., 1985, vol. 23, pp. 169–224.
Dulk, G., Melrose, D., and White, S., The gyrosynchrotron emission from quasi-thermal electrons and applications to solar flares, Astrophys. J., 1979, vol. 234, pp. 1137–1147.
Fleishman, G.D., Loukitcheva, M.A., Kopnina, V.Y., et al., The coronal volume of energetic particles in solar flares as revealed by microwave imaging, Astrophys. J., 2018, vol. 867, no. 1, p. 81.
Forbes, T.G. and Priest, E.R., Numerical simulation of reconnection in an emerging magnetic flux region, Sol. Phys., 1984, vol. 94, no. 2, pp. 315–340.
Forbes, T.G., Linker, J.A., Chen, J., et al., CME theory and models, Space Sci. Rev., 2006, vol. 123, nos. 1–3, pp. 251–302.
Guidice, D.A., Cliver, E.W., Barron, W.R., and Kahler, S., The air force RSTN system, Bull. Am. Astron. Soc., 1981, vol. 13, p. 553.
Hoeksema, J.T., Liu, Y., Hayashi, K., et al., The Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) vector magnetic field pipeline: Overview and performance, Sol. Phys., 2014, vol. 289, pp. 3483–3530.
Hudson, H.S., Solar flares, microflares, nanoflares, and coronal heating, Sol. Phys., 1991, vol. 133, no. 2, pp. 357–369.
Joshi, N.C., Nishizuka, N., Filippov, B., et al., Flux rope breaking and formation of a rotating blowout jet, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 2018, vol. 47, no. 1, pp. 1286–1298.
Kazachenko, M.D., Lynch, B.J., Welsch, B.T., and Sun, X., A database of flare ribbon properties from the solar dynamics observatory. I. Reconnection flux, Astrophys. J., 2017, vol. 845, p. 49.
Klein, K.-L. and Trottet, G., Gyrosynchrotron radiation from a source with spatially varying field and density, Astron. Astrophys., 1984, vol. 141, no. 1, pp. 67–76.
Lau, Y.-T. and Finn, J.M., Three-dimensional kinematic reconnection in the presence of field nulls and closed field lines, Astrophys. J., 1990, vol. 350, pp. 672–691.
Lemen, J.R., Title, A.M., Akin, D.J., et al., The Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) on the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO), Sol. Phys., 2012, vol. 275, nos. 1–2, pp. 17–40.
Miklenic, C.H., Veronig, A.M., Vršnak, B., and Hanslmeier, A., Reconnection and energy release rates in a two-ribbon flare, Astron. Astrophys., 2007, vol. 461, pp. 697–706.
Qiu, J. and Yurchyshyn, V.B., Magnetic reconnection flux and coronal mass ejection velocity, Astrophys. J., 2005, vol. 634, pp. L121–L124.
Qiu, J., Wang, H., Cheng, C.Z., and Gary, D.E., Magnetic reconnection and mass acceleration in flare-coronal mass ejection events, Astrophys. J., 2004, vol. 604, pp. 900–905.
Reid, H.A.S., Vilmer, N., Aulanier, G., and Pariat, E., X‑ray and ultraviolet investigation into the magnetic connectivity of a solar flare, Astron. Astrophys., 2012, vol. 547, p. A52.
Schou, J., Scherrer, P.H., Bush, R.I., et al., Design and ground calibration of the Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) instrument on the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO), Sol. Phys., 2012, vol. 275, pp. 229–259.
Shaik, S.B. and Gary, D.E., Implications of flat optically thick microwave spectra in solar flares for source size and morphology, Astrophys. J., 2021, vol. 919, no. 1, p. 44.
Stähli, M., Gary, D.E., and Hurford, G.J., High resolution microwave spectra of solar bursts, Sol. Phys., 1989, vol. 120, no. 2, pp. 351–368.
Sun, X., On the coordinate system of space-weather HMI active region patches (SHARPs): A technical note, 2013.https://arxiv.org/pdf/1309.2392.
Sun, X., Hoeksema, J.T., Liu, Y., et al., Hot spine loops and the nature of a late-phase solar flare, Astrophys. J., 2013, vol. 778, p. 139.
Veronig, A.M. and Polanec, W., Magnetic reconnection rates and energy release in a confined X-class flare, Sol. Phys., 2015, vol. 290, no. 10, pp. 2923–2942.
Volvach, A.E. and Yakubovskaya, I.V., Diagnostic complex of solar activity based on small radiotelescopes of the Sun service KRIM, Astron. Astrophys. Trans., 2019, vol. 31, no. 3, pp. 389–398.
5. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
SDO is a project of NASA’s Living With a Star Program. The SDO/AIA and SDO/HMI data were presented by the Joint Science Operation Center (JSOC). We are grateful for the free access to Air Force RSTN network data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by A. Nikol’skii
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gopasyuk, O.S., Volvach, A.E. & Yakubovskaya, I.V. Magnetic Reconnection Rates in a Confined X Class Flare. Geomagn. Aeron. 62, 888–894 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016793222070106
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016793222070106