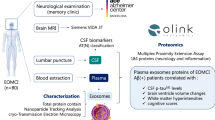
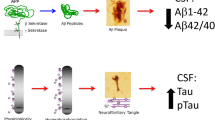
Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common socially significant neurodegenerative pathology, which currently affects more than 30 million elderly people worldwide. Since the number of patients grows every year and may exceed 115 million by 2050, and due to the lack of effective therapies, early prediction of AD remains a global challenge, solution of which can contribute to the timely appointment of a preventive therapy in order to avoid irreversible changes in the brain. To date, clinical assays for the markers of amyloidosis in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) have been developed, which, in conjunction with the brain MRI and PET studies, are used either to confirm the diagnosis based on obligate clinical criteria or to predict the risk of AD developing at the stage of mild cognitive impairment (MCI). However, the problem of predicting AD at the asymptomatic stage remains unresolved. In this regard, the search for new protein markers and studies of proteomic changes in CSF and blood plasma are of particular interest and may consequentially identify particular pathways involved in the pathogenesis of AD. Studies of specific proteomic changes in blood plasma deserve special attention and are of increasing interest due to the much less invasive method of sample collection as compared to CSF, which is important when choosing the object for large-scale screening. This review briefly summarizes the current knowledge on proteomic markers of AD and considers the prospects of developing reliable methods for early identification of AD risk factors based on the proteomic profile.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Aβ:
-
amyloid-β peptides
- ACE:
-
angiotensin converting enzyme
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- APP:
-
amyloid precursor protein
- Apo:
-
apolipoprotein
- BACE1:
-
beta-secretase 1
- CB:
-
candidate biomarker
- CSF:
-
cerebrospinal fluid
- IL:
-
interleukin
- MCI:
-
mild cognitive impairment
- MS:
-
mass spectrometry
- NfL:
-
neurofilament light chain
- sTREM2:
-
soluble form of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2
- t-tau and p-tau:
-
total and phosphorylated tau proteins, respectively
- TNF:
-
tumor necrosis factor
- VILIP-1:
-
visin-like-protein-1
- YKL-40:
-
chitinase-3 like-1
References
Alzheimer’s Association (2021) 2021 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures, Alzheimer’s Dement., 17, 327-406, https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.12328.
Prince, M., Bryce, R., Albanese, E., Wimo, A., Ribeiro, W., et al. (2013) The global prevalence of dementia: A systematic review and metaanalysis, Alzheimer’s Dement., 9, 63-75, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2012.11.007.
Jack, C. R. Jr., Knopman, D. S., Jagust, W. J., Petersen, R. C., Weiner, M. W., et al. (2013) Tracking pathophysiological processes in Alzheimer’s disease: an updated hypothetical model of dynamic biomarkers, Lancet Neurol., 12, 207-216, https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70291-0.
Galluzzi, S., Geroldi, C., Amicucci, G., Bocchio-Chiavetto, L., Bonetti, M., et al. (2013) Supporting evidence for using biomarkers in the diagnosis of MCI due to AD, J. Neurol., 260, 640-650, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-012-6694-0.
Perrin, R. J., Fagan, A. M., and Holtzman, D. M. (2009) Multimodal techniques for diagnosis and prognosis of Alzheimer’s disease, Nature, 461, 916-922, https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08538.
Long, J. M., and Holtzman, D. M. (2019) Alzheimer’s disease: an update on pathobiology and treatment strategies, Cell, 179, 312-339, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.09.001.
Duyckaerts, C., Delatour, B., and Potier, M. C. (2009) Classification and basic pathology of Alzheimer’s disease, Acta Neuropathol., 118, 5-36, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-009-0532-1.
Jack, Jr. C. R., Bennett, D. A., Blennow, K., Carrillo, M. C., Dunn, B., et al. (2018) NIA-AA research framework: toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease, Alzheimer’s Dement., 14, 535-562, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2018.02.018.
Jack, C. R., Petersen, R. C., Xu, Y. C., O’Brien, P. C., Smith, G. E., et al. (1999) Prediction of AD with MRI-based hippocampal volume in mild cognitive impairment, Neurology, 52, 1397-1397, https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.52.7.1397.
Dickerson, B. C., and Wolk, D. A. (2012) MRI cortical thickness biomarker predicts AD-like CSF and cognitive decline in normal adults, Neurology, 78, 84-90, https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e31823efc6c.
Killiany, R. J., Gomez‐Isla, T., Moss, M., Kikinis, R., Sandor, T., et al. (2000) Use of structural magnetic resonance imaging to predict who will get Alzheimer's disease, Ann. Neurol., 47, 430-439.
Hampel, H., Bürger, K., Teipel, S. J., Bokde, A. L., Zetterberg, H., et al. (2008) Core candidate neurochemical and imaging biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease, Alzheimer’s Dement., 4, 38-48, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2007.08.006.
Petersen, R. C. (2003) Mild Cognitive Impairment: Aging to Alzheimer’s Disease, Oxford University Press.
Blennow, K. (2017) A review of fluid biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease: moving from CSF to blood, Neurol. Ther., 6, 15-24, https://doi.org/10.1007/s40120-017-0073-9.
Modrego, P. J. (2006) Predictors of conversion to dementia of probable Alzheimer type in patients with mild cognitive impairment, Curr. Alzheimer Res., 3, 161-170, https://doi.org/10.2174/156720506776383103.
Zhang, S., Han, D., Tan, X., Feng, J., Guo, Y., et al. (2012) Diagnostic accuracy of 18 F-FDG and 11 C-PIB–PET for prediction of short-term conversion to Alzheimer’s disease in subjects with mild cognitive impairment, Int. J. Clin. Pract., 66, 185-198, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-1241.2011.02845.x.
Rowe, C. C., Ng, S., Ackermann, U., Gong, S. J., Pike, K., et al. (2007) Imaging β-amyloid burden in aging and dementia, Neurology, 68, 1718-1725, https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000261919.22630.ea.
Rice, L., and Bisdas, S. (2017) The diagnostic value of FDG and amyloid PET in Alzheimer’s disease – A systematic review, Eur. J. Radiol., 94, 16-24, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2017.07.014.
Hampel, H., O’Bryant, S. E., Molinuevo, J. L., Zetterberg, H., Masters, C., et al. (2018) Blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease: mapping the road to the clinic, Nat. Rev. Neurol., 14, 639-652, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-018-0079-7.
Roche, S., Gabelle, A., and Lehmann, S. (2008) Clinical proteomics of the cerebrospinal fluid: towards the discovery of new biomarkers, Proteomics Clin. Appl., 2, 428-436, https://doi.org/10.1002/prca.200780040.
Kroksveen, A. C., Opsahl, J. A., Aye, T. T., Ulvik, R. J., and Berven, F. S. (2011) Proteomics of human cerebrospinal fluid: discovery and verification of biomarker candidates in neurodegenerative diseases using quantitative proteomics, J. Proteomics, 74, 371-388, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2010.11.010.
Tapiola, T., Alafuzoff, I., Herukka, S. K., Parkkinen, L., Hartikainen, P., et al. (2009) Cerebrospinal fluid β-amyloid 42 and tau proteins as biomarkers of Alzheimer-type pathologic changes in the brain, Arch. Neurol., 66, 382-389, https://doi.org/10.1001/archneurol.2008.596.
Ritchie, C., Smailagic, N., Ladds, E. C., Noel-Storr, A. H., Ukoumunne, O., et al. (2013) CSF tau and the CSF tau/ABeta ratio for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI), Cochrane Database Syst. Rev., 3, CD10803, https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD010803.
Grimmer, T., Riemenschneider, M., Fors, H., Henriksen, G., Klunk, W. E., et al. (2009) Beta amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease: increased deposition in brain is reflected in reduced concentration in cerebrospinal fluid, Biol. Psychiatry, 65, 927-934, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.01.027.
Ferreira, D., Perestelo-Pérez, L., Westman, E., Wahlund, L. O., Sarría, A., et al. (2014) Meta-review of CSF core biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease: the state-of-the-art after the new revised diagnostic criteria, Front. Aging Neurosci., 6, 47, https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2014.00047.
McKhann, G. M., Knopman, D. S., Chertkow, H., Hyman, B. T., Jack, Jr. C. R., et al. (2011) The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease, Alzheimer’s Dement., 7, 263-269, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.005.
Schott, J. M., and Petersen, R. C. (2015) New criteria for Alzheimer’s disease: which, when and why? Brain, 138, 1134-1137, https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awv055.
Olsson, B., Lautner, R., Andreasson, U., Öhrfelt, A., Portelius, E., et al. (2016) CSF and blood biomarkers for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Lancet Neurol., 15, 673-684, https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(16)00070-3.
Rosén, C., Hansson, O., Blennow, K., and Zetterberg, H. (2013) Fluid biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease – current concepts, Mol. Neurodegener., 8, 20, https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1326-8-20.
Huynh, R. A., and Mohan, C. (2017) Alzheimer’s disease: biomarkers in the genome, blood, and cerebrospinal fluid, Front. Neurol., 8, 102, https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2017.00102.
Ovod, V., Ramsey, K. N., Mawuenyega, K. G., Bollinger, J. G., Hicks, T., et al. (2017) Amyloid β concentrations and stable isotope labeling kinetics of human plasma specific to central nervous system amyloidosis, Alzheimer’s Dement., 13, 841-849, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2017.06.2266.
Nakamura, A., Kaneko, N., Villemagne, V. L., Kato, T., Doecke, J., et al. (2018) High performance plasma amyloid-beta biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease, Nature, 554, 249-254, https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25456.
Zetterberg, H., and Blennow, K. (2021) Moving fluid biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease from research tools to routine clinical diagnostics, Mol. Neurodegener., 16, 10, https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-021-00430-x.
Barthelemy, N. R., Horie, K., Sato, C., and Bateman, R. J. (2020) Blood plasma phosphorylated-tau isoforms track CNS change in Alzheimer’s disease, J. Exp. Med., 217, e20200861, https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20200861.
Zakharova, N. V., Kononikhin, A. S., Indeykina, M. I., Bugrova, A. E., Strelnikova, P., et al. (2022) Mass spectrometric studies of the variety of beta-amyloid proteofprms in Alzheimer’s disease, Mass Spectrom. Rev., e21775, https://doi.org/10.1002/mas.21775.
Evin, G., Zhu, A., Holsinger, R. M. D., Masters, C. L., and Li, Q. X. (2003) Proteolytic processing of the Alzheimer’s disease amyloid precursor protein in brain and platelets, J. Neurosci. Res., 74, 386-392, https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.10745.
Galozzi, S., Marcus, K., and Barkovits, K. (2015) Amyloid-β as a biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease: quantification methods in body fluids, Expert. Rev. Proteomics, 12, 343-354, https://doi.org/10.1586/14789450.2015.1065183.
Gallardo, R., Ranson, N. A., and Radford, S. E. (2020) Amyloid structures: much more than just a cross-β fold, Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 60, 7-16, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2019.09.001.
Kent, S. A., Spires-Jones, T. L., and Durrant, C. S. (2020) The physiological roles of tau and Aβ: implications for Alzheimer’s disease pathology and therapeutics, Acta Neuropathol., 140, 417-447, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-020-02196-w.
Rogers, J., Strohmeyer, R., Kovelowski, C. J., and Li, R. (2002) Microglia and inflammatory mechanisms in the clearance of amyloid β peptide, Glia, 40, 260-269, https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.10153.
Wang, J., Gu, B. J., Masters, C. L., and Wang, Y. J. (2017) A systemic view of Alzheimer disease – Insights from amyloid-β metabolism beyond the brain, Nat. Rev. Neurol., 13, 612-623, https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2017.111.
Kummer, M. P., and Heneka, M. T. (2014) Truncated and modified amyloid-beta species, Alzheimer’s Res. Ther., 6, 28, https://doi.org/10.1186/alzrt258.
Roher, A. E., Kokjohn, T. A., Clarke, S. G., Sierks, M. R., Maarouf, C. L., et al. (2017) APP/Aβ structural diversity and Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis, Neurochem. Int., 110, 1-13, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2017.08.007.
Hansson, O., Lehmann, S., Otto, M., Zetterberg, H., and Lewczuk, P. (2019) Advantages and disadvantages of the use of the CSF Amyloid β (Aβ) 42/40 ratio in the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease, Alzheimers Res. Ther., 11, 1-15, https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-019-0485-0.
Roberts, K. F., Elbert, D. L., Kasten, T. P., Patterson, B. W., Sigurdson, W. C., et al. (2014) Amyloid‐β efflux from the central nervous system into the plasma, Ann. Neurol., 76, 837-844, https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24270.
Li, Q. X., Fuller, S. J., Beyreuther, K., and Masters, C. L. (1999) The amyloid precursor protein of Alzheimer disease in human brain and blood, J. Leukoc. Biol., 66, 567-574, https://doi.org/10.1002/jlb.66.4.567.
Borroni, B., Agosti, C., Marcello, E., Di Luca, M., and Padovani, A. (2010) Blood cell markers in Alzheimer disease: amyloid precursor protein form ratio in platelets, Exp. Gerontol., 45, 53-56, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2009.08.004.
Di Luca, M., Colciaghi, F., Pastorino, L., Borroni, B., Padovani, A., et al. (2000) Platelets as a peripheral district where to study pathogenetic mechanisms of alzheimer disease: the case of amyloid precursor protein, Eur. J. Pharmacol., 405, 277-283, https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-2999(00)00559-8.
Xu, F., Davis, J., Miao, J., Previti, M. L., Romanov, G., et al. (2005) Protease nexin-2/amyloid β-protein precursor limits cerebral thrombosis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 102, 18135-18140, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0507798102.
Eltringham-Smith, L. J., Bhakta, V., and Sheffield, W. P. (2021) Selection and in vitro and in vivo characterization of a Kunitz protease inhibitor domain of protease nexin 2 variant that inhibits factor XIa without inhibiting plasmin, J. Biotechnol., 330, 61-69, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2021.02.016.
Colciaghi, F., Marcello, E., Borroni, B., Zimmermann, M., Caltagirone, C., et al. (2004) Platelet APP, ADAM 10 and BACE alterations in the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease, Neurology, 62, 498-501, https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000106953.49802.9c.
Chen, M., Inestrosa, N. C., Ross, G. S., and Fernandez, H. L. (1995) Platelets are the primary source of amyloid β-peptide in human blood, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 213, 96-103, https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1995.2103.
Inyushin, M. Y., Sanabria, P., Rojas, L., Kucheryavykh, Y., and Kucheryavykh, L. (2017) Aβ peptide originated from platelets promises new strategy in anti-Alzheimer’s drug development, Biomed. Res. Int., 2017, 3948360, https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3948360.
Casoli, T., Di Stefano, G., Giorgetti, B., Grossi, Y., Balietti, M., et al. (2007) Release of β-amyloid from high‐density platelets: implications for Alzheimer’s disease pathology, Ann. N Y Acad. Sci., 1096, 170-178, https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1397.082.
Schindler, S. E., Bollinger, J. G., Ovod, V., Mawuenyega, K. G., Li, Y., et al. (2019) High-precision plasma β-amyloid 42/40 predicts current and future brain amyloidosis, Neurology, 93, e1647-e1659, https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000008081.
Portelius, E., Tran, A. J., Andreasson, U., Persson, R., Brinkmalm, G., et al. (2007) Characterization of amyloid β peptides in cerebrospinal fluid by an automated immunoprecipitation procedure followed by mass spectrometry, J. Proteome Res., 6, 4433-4439, https://doi.org/10.1021/pr0703627.
Gao, Y., Tan, L., Yu, J. T., and Tan, L. (2018) Tau in Alzheimer’s disease: Mechanisms and therapeutic strategies, Curr. Alzheimer Res., 15, 283-300, https://doi.org/10.2174/1567205014666170417111859.
Gong, C. X., Liu, F., Grundke-Iqbal, I., and Iqbal, K. (2005) Post-translational modifications of tau protein in Alzheimer’s disease, J. Neural Transm., 112, 813-838, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-004-0221-0.
Iqbal, K., Liu, F., Gong, C. X., and Grundke-Iqbal, I. (2010) Tau in Alzheimer disease and related tauopathies, Curr. Alzheimer Res., 7, 656-664, https://doi.org/10.2174/156720510793611592.
De Souza, L. C., Chupin, M., Lamari, F., Jardel, C., Leclercq, D., et al. (2012) CSF tau markers are correlated with hippocampal volume in Alzheimer’s disease, Neurobiol. Aging, 33, 1253-1257, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.02.022.
Seppälä, T. T., Nerg, O., Koivisto, A. M., Rummukainen, J., Puli, L., et al. (2012) CSF biomarkers for Alzheimer disease correlate with cortical brain biopsy findings, Neurology, 78, 1568-1575, https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182563bd0.
Barthélemy, N. R., Li, Y., Joseph-Mathurin, N., Gordon, B. A., Hassenstab, J., et al. (2020) A soluble phosphorylated tau signature links tau, amyloid and the evolution of stages of dominantly inherited Alzheimer’s disease, Nat. Med., 26, 398-407, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-0781-z.
Janelidze, S., Stomrud, E., Smith, R., Palmqvist, S., Mattsson, N., et al. (2020) Cerebrospinal fluid p-tau217 performs better than p-tau181 as a biomarker of Alzheimer’s disease, Nat. Commun., 11, 1-12, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15436-0.
Zetterberg, H., Wilson, D., Andreasson, U., Minthon, L., Blennow, K., et al. (2013) Plasma tau levels in Alzheimer’s disease, Alzheimers Res. Ther., 5, 1-3, https://doi.org/10.1186/alzrt163.
Sjogren, M., Vanderstichele, H., Ågren, H., Zachrisson, O., Edsbagge, M., et al. (2001) Tau and Aβ42 in cerebrospinal fluid from healthy adults 21-93 years of age: establishment of reference values, Clin. Chem., 47, 1776-1781, https://doi.org/10.1093/clinchem/47.10.1776.
Mielke, M. M., Hagen, C. E., Xu, J., Chai, X., Vemuri, P., et al. (2018) Plasma phospho-tau181 increases with Alzheimer’s disease clinical severity and is associated with tau-and amyloid-positron emission tomography, Alzheimer’s Dement., 14, 989-997, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2018.02.013.
Karikari, T. K., Pascoal, T. A., Ashton, N. J., Janelidze, S., Benedet, A. L., et al. (2020) Blood phosphorylated tau 181 as a biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease: a diagnostic performance and prediction modelling study using data from four prospective cohorts, Lancet Neurol., 19, 422-433, https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30071-5.
Palmqvist, S., Janelidze, S., Quiroz, Y. T., Zetterberg, H., Lopera, F., et al. (2020) Discriminative accuracy of plasma phospho-tau217 for Alzheimer’s disease vs other neurodegenerative disorders, JAMA, 324, 772-781, https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.12134.
Sato, C., Barthélemy, N. R., Mawuenyega, K. G., Patterson, B. W., Gordon, B. A., et al. (2018) Tau kinetics in neurons and the human central nervous system, Neuron, 97, 1284-1298, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2018.02.015.
Randall, J., Mörtberg, E., Provuncher, G. K., Fournier, D. R., Duffy, D. C., et al. (2013) Tau proteins in serum predict neurological outcome after hypoxic brain injury from cardiac arrest: results of a pilot study, Resuscitation, 84, 351-356, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resuscitation.2012.07.027.
Shi, M., Sui, Y. T., Peskind, E. R., Li, G., Hwang, H., et al. (2011) Salivary tau species are potential biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease, J. Alzheimer’s Dis., 27, 299-305, https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-2011-110731.
Davidsson, P., and Blennow, K. (1998) Neurochemical dissection of synaptic pathology in Alzheimer’s disease, Int. Psychogeriatr., 10, 11-23, https://doi.org/10.1017/s1041610298005110.
Kvartsberg, H., Duits, F. H., Ingelsson, M., Andreasen, N., Öhrfelt, A., et al. (2015) Cerebrospinal fluid levels of the synaptic protein neurogranin correlates with cognitive decline in prodromal Alzheimer’s disease, Alzheimer’s Dement., 11, 1180-1190, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2014.10.009.
Hellwig, K., Kvartsberg, H., Portelius, E., Andreasson, U., Oberstein, T. J., et al. (2015) Neurogranin and YKL-40: independent markers of synaptic degeneration and neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease, Alzheimer’s Res. Ther., 7, 1-8, https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-015-0161-y.
Portelius, E., Zetterberg, H., Skillbäck, T., Törnqvist, U., Andreasson, U., et al. (2015) Cerebrospinal fluid neurogranin: relation to cognition and neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease, Brain, 138, 3373-3385, https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awv267.
Wellington, H., Paterson, R. W., Portelius, E., Törnqvist, U., Magdalinou, N., et al. (2016) Increased CSF neurogranin concentration is specific to Alzheimer’s disease, Neurology, 86, 829-835, https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000002423.
Öhrfelt, A., Brinkmalm, A., Dumurgier, J., Brinkmalm, G., Hansson, O., et al. (2016) The pre-synaptic vesicle protein synaptotagmin is a novel biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease, Alzheimer’s Res. Ther., 8, 1-10, https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-016-0208-8.
Goetzl, E. J., Kapogiannis, D., Schwartz, J. B., Lobach, I. V., Goetzl, L., et al. (2016) Decreased synaptic proteins in neuronal exosomes of frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer’s disease, FASEB J., 30, 4141-4148, https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201600816R.
Brinkmalm, A., Brinkmalm, G., Honer, W. G., Frölich, L., Hausner, L., et al. (2014) SNAP-25 is a promising novel cerebrospinal fluid biomarker for synapse degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease, Mol. Neurodegener., 9, 1-13, https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1326-9-53.
Lashley, T., Schott, J. M., Weston, P., Murray, C. E., Wellington, H., et al. (2018) Molecular biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and prospect, Dis. Model. Mech., 11, dmm031781, https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.031781.
Wennström, M., Surova, Y., Hall, S., Nilsson, C., Minthon, L., et al. (2015) The inflammatory marker YKL-40 is elevated in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with Alzheimer’s but not Parkinson’s disease or dementia with Lewy bodies, PLoS One, 10, e0135458, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0135458.
Janelidze, S., Hertze, J., Zetterberg, H., Landqvist Waldö, M., Santillo, A., et al. (2016) Cerebrospinal fluid neurogranin and YKL‐40 as biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease, Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol., 3, 12-20, https://doi.org/10.1002/acn3.266.
Morenas-Rodríguez, E., Li, Y., Nuscher, B., Franzmeier, N., Xiong, C., et al. (2022) Soluble TREM2 in CSF and its association with other biomarkers and cognition in autosomal-dominant Alzheimer’s disease: a longitudinal observational study, Lancet Neurol., 21, 329-341, https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(22)00027-8.
Mattsson, N., Tabatabaei, S., Johansson, P., Hansson, O., Andreasson, U., et al. (2011) Cerebrospinal fluid microglial markers in Alzheimer’s disease: elevated chitotriosidase activity but lack of diagnostic utility, Neuromolecular Med., 13, 151-159, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-011-8147-9.
Tarawneh, R., D’Angelo, G., Macy, E., Xiong, C., Carter, D., et al. (2011) Visinin‐like protein‐1: diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in Alzheimer’s disease, Ann. Neurol., 70, 274-285, https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.22448.
Khalil, M., Teunissen, C. E., Otto, M., Piehl, F., Sormani, M. P., et al. (2018) Neurofilaments as biomarkers in neurological disorders, Nat. Rev. Neurol., 14, 577-589, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-018-0058-z.
Gisslén, M., Price, R. W., Andreasson, U., Norgren, N., Nilsson, S., et al. (2016) Plasma concentration of the neurofilament light protein (NFL) is a biomarker of CNS injury in HIV infection: a cross-sectional study, EBioMedicine, 3, 135-140, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.11.036.
Mattsson, N., Andreasson, U., Zetterberg, H., Blennow, K., and Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (2017) Association of plasma neurofilament light with neurodegeneration in patients with Alzheimer’s disease, JAMA Neurol., 74, 557-566, https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2016.6117.
Fernandes, B. S., Steiner, J., Berk, M., Molendijk, M. L., Gonzalez-Pinto, A., et al. (2015) Peripheral brain-derived neurotrophic factor in schizophrenia and the role of antipsychotics: meta-analysis and implications, Mol. Psychiatry, 20, 1108-1119, https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2014.117.
Qin, X. Y., Cao, C., Cawley, N. X., Liu, T. T., Yuan, J., et al. (2017) Decreased peripheral brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in Alzheimer’s disease: a meta-analysis study (N = 7277), Mol. Psychiatry, 22, 312-320, https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2016.62.
Balietti, M., Giuli, C., Casoli, T., Fabbietti, P., and Conti, F. (2020) Is blood brain-derived neurotrophic factor a useful biomarker to monitor mild cognitive impairment patients? Rejuvenation Res., 23, 411-419, https://doi.org/10.1089/rej.2020.2307.
Morozova, A., Zorkina, Y., Abramova, O., Pavlova, O., Pavlov, K., et al. (2022) Neurobiological highlights of cognitive impairment in psychiatric disorders, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 23, 1217, https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031217.
Shen, X. N., Niu, L. D., Wang, Y. J., Cao, X. P., Liu, Q., et al. (2019) Inflammatory markers in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment: a meta-analysis and systematic review of 170 studies, J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry, 90, 590-598, https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2018-319148.
Marques, S. C. F., Lemos, R., Ferreiro, E., Martins, M., De Mendonca, A., et al. (2012) Epigenetic regulation of BACE1 in Alzheimer’s disease patients and in transgenic mice, Neuroscience, 220, 256-266, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.06.029.
Zhong, Z., Ewers, M., Teipel, S., Bürger, K., Wallin, A., et al. (2007) Levels of β-secretase (BACE1) in cerebrospinal fluid as a predictor of risk in mild cognitive impairment, Arch. Gen. Psychiatry, 64, 718-726, https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.64.6.718.
Bellenguez, C., Grenier-Boley, B., and Lambert, J. C. (2020) Genetics of Alzheimer’s disease: where we are, and where we are going, Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 61, 40-48, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2019.11.024.
Kunkle, B. W., Grenier-Boley, B., Sims, R., Bis, J. C., Damotte, V., et al. (2019) Genetic meta-analysis of diagnosed Alzheimer’s disease identifies new risk loci and implicates Aβ, tau, immunity and lipid processing, Nat. Genet., 51, 414-430, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-019-0358-2.
Karch, C. M., and Goate, A. M. (2015) Alzheimer’s disease risk genes and mechanisms of disease pathogenesis, Biol. Psychiatry, 77, 43-51, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.05.006.
Kim, J., Basak, J. M., and Holtzman, D. M. (2009) The role of apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer’s disease, Neuron, 63, 287-303, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2009.06.026.
Rehiman, S. H., Lim, S. M., Neoh, C. F., Majeed, A. B. A., Chin, A. V., et al. (2020) Proteomics as a reliable approach for discovery of blood-based Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Ageing Res. Rev., 60, 101066, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2020.101066.
Nazeri, A., Ganjgahi, H., Roostaei, T., Nichols, T., Zarei, M., et al. (2014) Imaging proteomics for diagnosis, monitoring and prediction of Alzheimer’s disease, Neuroimage, 102, 657-665, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.08.041.
Guo, L. H., Alexopoulos, P., Wagenpfeil, S., Kurz, A., Perneczky, R., et al. (2013) Plasma proteomics for the identification of Alzheimer’s disease, Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord., 27, 337-342, https://doi.org/10.1097/WAD.0b013e31827b60d2.
Mancera-Páez, O., Estrada-Orozco, K., Mahecha, M. F., Cruz, F., Bonilla-Vargas, K., et al. (2019) Differential methylation in APOE (Chr19; Exon four; from 44,909,188 to 44,909,373/hg38) and increased apolipoprotein E plasma levels in subjects with mild cognitive impairment, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 20, 1394, https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061394.
Calero, M., Rostagno, A., Matsubara, E., Zlokovic, B., Frangione, B., et al. (2000) Apolipoprotein J (clusterin) and Alzheimer’s disease, Microsc. Res. Tech., 50, 305-315, https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0029(20000815)50:4<305::AID-JEMT10>3.0.CO;2-L.
DeMattos, R. B., O’dell, M. A., Parsadanian, M., Taylor, J. W., Harmony, J. A., et al. (2002) Clusterin promotes amyloid plaque formation and is critical for neuritic toxicity in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease, Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 99, 10843-10848, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.162228299.
Thambisetty, M., Simmons, A., Velayudhan, L., Hye, A., Campbell, J., et al. (2010) Association of plasma clusterin concentration with severity, pathology, and progression in Alzheimer’s disease, Arch. Gen. Psychiatry, 67, 739-748, https://doi.org/10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.78.
Yu, J. T., and Tan, L. (2012) The role of clusterin in Alzheimer’s disease: pathways, pathogenesis, and therapy, Mol. Neurobiol., 45, 314-326, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-012-8237-1.
Morgan, A. R., Touchard, S., Leckey, C., O’Hagan, C., Nevado-Holgado, A. J., et al. (2019) Inflammatory biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease plasma, Alzheimer’s Dement., 15, 776-787, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2019.03.007.
Toropygin, I. Y., Kugaevskaya, E. V., Mirgorodskaya, O. A., Elisseeva, Y. E., Kozmin, Y. P., et al. (2008) The N-domain of angiotensin-converting enzyme specifically hydrolyzes the Arg-5-His-6 bond of Alzheimer’s Aβ-(1-16) peptide and its isoAsp-7 analogue with different efficiency as evidenced by quantitative matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom., 22, 231-239, https://doi.org/10.1002/rcm.3357.
Akatsu, H., Ogawa, N., Kanesaka, T., Hori, A., Yamamoto, T., et al. (2011) Higher activity of peripheral blood angiotensin-converting enzyme is associated with later-onset of Alzheimer’s disease, J. Neurol. Sci., 300, 67-73, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2010.09.030.
Miners, S., Ashby, E., Baig, S., Harrison, R., Tayler, H., et al. (2009) Angiotensin-converting enzyme levels and activity in Alzheimer’s disease: differences in brain and CSF ACE and association with ACE1 genotypes, Am. J. Transl. Res., 1, 163-177.
Kinney, J. W., Bemiller, S. M., Murtishaw, A. S., Leisgang, A. M., Salazar, A. M., et al. (2018) Inflammation as a central mechanism in Alzheimer’s disease, Alzheimer’s Dement., 4, 575-590, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trci.2018.06.014.
Kiddle, S. J., Sattlecker, M., Proitsi, P., Simmons, A., Westman, E., et al. (2014) Candidate blood proteome markers of Alzheimer’s disease onset and progression: a systematic review and replication study, J. Alzheimer’s Dis., 38, 515-531, https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-130380.
Mi, H., Ebert, D., Muruganujan, A., Mills, C., Albou, L. P., et al. (2021) PANTHER version 16: a revised family classification, tree-based classification tool, enhancer regions and extensive API, Nucleic Acids Res., 49, D394-D403, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa1106.
Ray, S., Britschgi, M., Herbert, C., Takeda-Uchimura, Y., Boxer, A., et al. (2007) Classification and prediction of clinical Alzheimer’s diagnosis based on plasma signaling proteins, Nat. Med., 13, 1359-1362, https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1653.
Doecke, J. D., Laws, S. M., Faux, N. G., Wilson, W., Burnham, S. C., et al. (2012) Blood-based protein biomarkers for diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease, Arch. Neurol., 69, 1318-1325, https://doi.org/10.1001/archneurol.2012.1282.
O’Bryant, S. E., Xiao, G., Barber, R., Reisch, J., Doody, R., et al. (2010) A serum protein-based algorithm for the detection of Alzheimer disease, Arch. Neurol., 67, 1077-1081, https://doi.org/10.1001/archneurol.2010.215.
O’Bryant, S. E., Edwards, M., Johnson, L., Hall, J., Villarreal, A. E., et al. (2016) A blood screening test for Alzheimer’s disease, Alzheimer’s Dement., 3, 83-90, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dadm.2016.06.004.
Hye, A., Riddoch-Contreras, J., Baird, A. L., Ashton, N. J., Bazenet, C., et al. (2014) Plasma proteins predict conversion to dementia from prodromal disease, Alzheimer’s Dement., 10, 799-807, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2014.05.1749.
Yu, S., Liu, Y. P., Liu, H. L., Li, J., Xiang, Y., et al. (2018) Serum protein-based profiles as novel biomarkers for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease, Mol. Neurobiol., 55, 3999-4008, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0609-0.
Shi, L., Buckley, N.J., Bos, I., Engelborghs, S., Sleegers, K., et al. (2021) Plasma proteomic biomarkers relating to Alzheimer’s disease: a meta-analysis based on our own studies, Front. Aging Neurosci., 13, 712545, https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2021.712545.
Henkel, A. W., Muller, K., Lewczuk, P., Muller, T., Marcus, K., et al. (2012) Multidimensional plasma protein separation technique for identification of potential Alzheimer’s disease plasma biomarkers: A pilot study, J. Neural. Transm., 119, 779-788, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-012-0781-3.
Walke, K. A., Chen, J., Zhang, J., Fornage, M., Yang, Y., et al. (2021) Large-scale plasma proteomic analysis identifies proteins and pathways associated with dementia risk, Nat. Aging, 1, 473-489, https://doi.org/10.1038/s43587-021-00064-0.
Whelan, C. D., Mattsson, N., Nagle, M. W., Vijayaraghavan, S., Hyde, C., et al. (2019) Multiplex proteomics identifies novel CSF and plasma biomarkers of early Alzheimer’s disease, Acta Neuropathol. Commun., 7, 169, https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-019-0795-2.
Jiang, Y., Zhou, X., Ip, F. C., Chan, P., Chen, Y., et al. (2021) Large-scale proteomic profiling identifies a high-performance biomarker panel for Alzheimer’s disease screening and staging, Alzheimer’s Dement., 18, 88-102, https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.12369.
Dayon, L., Wojcik, J., Galindo, N., Corthesy, J., Cominetti, O., et al. (2017) Plasma proteomic profiles of cerebrospinal fluid-defined Alzheimer’s disease pathology in older adults, J. Alzheimer’s Dis., 60, 1641-1652, https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-170426.
Dey, K.K., Wang, H., Niu, M., Bai, B., Wang, X., et al. (2019) Deep undepleted human serum proteome profiling toward biomarker discovery for Alzheimer’s disease, Clin. Proteomics, 16, 16, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12014-019-9237-1.
Park, J. C., Han, S.H., Lee, H., Jeong, H., Byun, M. S., et al. (2019) Prognostic plasma protein panel for Aβ deposition in the brain in Alzheimer’s disease, Prog. Neurobiol., 183, 101690, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2019.101690.
Ashton, N. J., Nevado-Holgado, A. J., Barber, I. S., Lynham, S., Gupta, V., et al. (2019) A plasma protein classifier for predicting amyloid burden for preclinical Alzheimer’s disease, Sci. Adv., 5, eaau7220, https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aau7220.
Chen, M., and Xia, W. (2020) Proteomic profiling of plasma and brain tissue from Alzheimer’s disease patients reveals candidate network of plasma biomarkers, J. Alzheimer’s Dis., 76, 349-368, https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-200110.
Jain, A. P., and Sathe, G. (2021) Proteomics landscape of Alzheimer’s disease, Proteomes, 9, 13, https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes9010013.
Kitamura, Y., Usami, R., Ichichara, S., Kida, H., Satoh, M., et al. (2017) Plasma protein profiling for potential biomarkers in the early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease, Neurol. Res., 39, 231-238, https://doi.org/10.1080/01616412.2017.1281195.
Kumar, A., Singh, S., Verma, A., and Mishra, V. N. (2018) Proteomics based identification of differential plasma proteins and changes in white matter integrity as markers in early detection of mild cognitive impaired subjects at high risk of Alzheimer’s disease, Neurosci. Lett., 676, 71-77, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2018.04.015.
Zhao, X., Lejnine, S., Spond, J., Zhang, C., Ramaraj, T. C., et al. (2015) A candidate plasma protein classifier to identify Alzheimer’s disease, J. Alzheimer’s Dis., 43, 549-563, https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-141149.
Bader, J. M., Geyer, P. E., Müller, J. B., Strauss, M. T., Koch, M., et al. (2020) Proteome profiling in cerebrospinal fluid reveals novel biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease, Mol. Syst. Biol., 16, e9356, https://doi.org/10.15252/msb.20199356.
Gaither, C., Popp, R., Mohammed, Y., and Bochers, C. H. (2020) Determination of the concentration range for 267 proteins from 21 lots of commercial human plasma using highly multiplexed multiple reaction monitoring mass spectrometry, Analyst, 145, 3634-3644, https://doi.org/10.1039/c9an01893j.
Ayton, S., Janelidze, S., Roberts, B., Palmqvist, S., Kalinowski, P., et al. (2021) Acute phase markers in CSF reveal inflammatory changes in Alzheimer’s disease that intersect with pathology, APOE ε4, sex and age, Prog. Neurobiol., 198, 101904, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2020.101904.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Megagrant of Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation [Agreement with Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology, no. 075-10-2022-090 (075-10-2019-083)].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, N.V.Z., A.S.K., S.I.G., and E.N.N.; analysis of publications, selection of material, N.V.Z., A.E.B., M.I.I., Y.B.F., and I.V.K.; data analysis and preparation of table and figures, N.V.Z., A.E.B., M.I.I., and A.S.K.; writing – original draft preparation, N.V.Z., A.E.B., M.I.I., and Y.B.F.; writing – review and editing, A.S.K., I.V.K., S.I.G., and E.N.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in financial or any other sphere. This article does not include the experiments involving humans or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zakharova, N.V., Bugrova, A.E., Indeykina, M.I. et al. Proteomic Markers and Early Prediction of Alzheimer’s Disease. Biochemistry Moscow 87, 762–776 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297922080089
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297922080089