Abstract
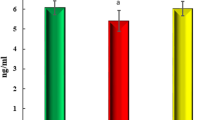
Diabetes mellitus is characterized by increased platelet activation which is determined by many factors including changes in the expression of membrane proteins. The aim of this study was to investigate the sensitivity of human platelets to the insulin-like growth factor (IGF) system in patients with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM2). Ligand binding was analyzed using 125I-labelled IGF-1 and insulin, and relative expression of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) and insulin receptor (IR) was evaluated by Western blotting. Platelet aggregation in the presence of IGF-1 was studied by the plate aggregometry assay. We found that platelets from DM2 patients exhibited significantly higher IGF-1 binding and up regulation of IGF-1R expression in comparison with healthy individuals. Both insulin binding and IR expression were lower in the DM2 group, but the differences with the healthy control were statistically insignificant. The potentiating effect of IGF-1 on the thrombin-induced activation of platelets was detected in both groups but was significantly more pronounced in the DM2 patients. The initial rate of platelet activation in the presence of IGF-1 positively correlated with the concentration of glycated hemoglobin. Platelets isolated from DM2 patients displayed elevated expression of the IGF-1R subunits, which might have contributed to the higher sensitivity of these cells to IGF-1 in thrombin-initiated aggregation by increasing the rate of platelet activation. However, further experiments are needed to investigate the role of IGF-1 in thrombotic complications that usually accompany diabetes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DM2:
-
type 2 diabetes mellitus
- HbA1c:
-
glycated hemoglobin
- IGF:
-
insulin-like growth factor
- IGF-1R:
-
insulin like growth factor 1 receptor
- IR:
-
insulin receptor
References
Tripodi, A., Branchi, A., Chantarangkul, V., Clerici, M., Merati, G., Artoni, A., and Mannucci, P. M. (2011) Hypercoagulability in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus detected by a thrombin generation assay, J. Thromb. Thrombolysis, 31, 165–172.
Carr, M. E. (2001) Diabetes mellitus. A hypercoagulable state, J. Diabetes Complications, 15, 44–54.
Vazzana, N., Ranalli, P., Cuccurullo, C., and Davi, G. (2012) Diabetes mellitus and thrombosis, Thromb. Res., 129, 371–377.
Dunn, E. J., Ariens, R. A., and Grant, P. J. (2005) The influence of type 2 diabetes on fibrin structure and function, Diabetologia, 48, 1198–1206.
Dunn, E. J., Philippou, H., Ariens, R. A., and Grant, P. J. (2006) Molecular mechanisms involved in the resistance of fibrin to clot lysis by plasmin in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus, Diabetologia, 49, 1071–1080.
Dunn, E. J., and Ariens, R. A. (2004) Fibrinogen and fibrin clot structure in diabetes, Herz, 29, 470–479.
Kim, J. H., Bae, H. Y., and Kim, S. Y. (2013) Clinical marker of platelet hyperreactivity in diabetes mellitus, Diabetes Metab. J., 37, 423–428.
Pomero, F., Di Minno, M. N. D., Fenoglio, L., Gianni, M., Ageno, W., and Dentali, F. (2015) Is diabetes a hypercoagu-lable state? A critical appraisal, Acta Diabetol., 52, 1007–1016.
Kakouros, N., Rade, J. J., Kourliouros, A., and Resar, J. R. (2011) Platelet function in patients with diabetes mellitus: from a theoretical to a practical perspective, Int. J. Endocrinol., 2011, 742719.
Hu, L., Chang, L., Zhang, Y., Zhai, L., Zhang, S., Qi, Z., Yan, H., Yan, Y., Luo, X., Zhang, S., Wang, Y., Kunapuli, S. P., Ye. H., and Ding, Z. (2017) Platelets express activated P2Y12 receptor in patients with diabetes mellitus, Circulation, 136, 817–833.
Di Minno, M. N. D., Lupoli, R., Palmieri, N. M., Russolillo, A., Buonauro, A., and Di Minno, G. (2012) Aspirin resistance, platelet turnover, and diabetic angiopathy: a 2011 update, Thromb. Res., 129, 341–344.
Randriamboavonjy, V., and Fleming, I. (2009) Insulin, insulin resistance, and platelet signaling in diabetes, Diab. Care, 32, 528–530.
Ferreiro, J. L., Gomez-Hospital, J. A., and Angiolillo, D. J. (2010) Platelet abnormalities in diabetes mellitus, Diab. Vasc. Dis. Res., 7, 251–259.
Annunziata, M., Granata, R., and Ghigo, E. (2011) The IGF system, Acta Diabetol., 48, 1–9.
Aghdam, S. Y., Eming, S. A., Willenborg, S., Neuhaus, B., Niessen, C. M., Partridge, L., Krieg, T., and Bruning, J. C. (2012) Vascular endothelial insulin/IGF-1 signaling controls skin wound vascularization, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 421, 197–202.
Hunter, R. W., and Hers, I. (2009) Insulin/IGF-1 hybrid receptor expression on human platelets: consequences for the effect of insulin on platelet function, J. Thromb. Haemost., 7, 2123–2130.
Andersen, M., Norgaard-Pedersen, D., Brandt, J., Pettersson, I., and Slaaby, R. (2017) IGF1 and IGF2 specificities to the two insulin receptor isoforms are determined by insulin receptor amino acid 718, PLoS One, 12, e0178885.
Kim, S., Garcia, A., Jackson, S. P., and Kunapuli, S. P. (2007) Insulin-like growth factor-1 regulates platelet activation through PI3-Kα isoform, Blood, 110, 4206–4213.
Hers, I. (2007) Insulin-like growth factor-1 potentiates platelet activation via the IRS-PI3Kα pathway, Blood, 110, 4243–4252.
Moore, S. F., Williams, C. M., Brown, E., Blair, T. A., Harper, M. T., Coward, R. J., Poole, A. W., and Hers, I. (2015) Loss of the insulin receptor in murine megakaryo-cytes/platelets causes thrombocytosis and alterations in IGF signaling, Cardiovasc. Res., 107, 9–19.
Stolla, M. C., Li, D., Lu, L., and Woulfe, D. S. (2013) Enhanced platelet activity and thrombosis in a murine model of type I diabetes are partially insulin-like growth factor 1-dependent and phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent, J. Thromb. Haemost., 11, 919–929.
Hunter, W. M., and Greenwood, F. C. (1963) Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity, Biochem. J., 89, 114–123.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4, Nature, 227, 680–685.
Bednar, B., Condra, C., Gould, R. J., and Connolly, T. M. (1995) Platelet aggregation monitored in a 96 well microplate reader is useful for evaluation of platelet agonists and antagonists, Thromb. Res., 77, 453–463.
Motani, A. S., Anggard, E. E., and Ferns, G. A. A. (1996) Recombinant insulin-like growth factor-1 modulates aggregation in human platelets via extracellular calcium, Life Sci., 58, 269–274.
Blair, P., and Flaumenhaft, R. (2009) Platelet α-granules: basic biology and clinical correlates, Blood Rev., 23, 177–189.
Taylor, V. L., and Spencer, E. M. (2001) Characterization of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 binding to a novel receptor on human platelet membranes, J. Endocrinol., 168, 307–315.
Simic, D., Bogdan, N., Teng, F., and Otieno, M. (2017) Blocking α5β1 integrin attenuates sCD40L-mediated platelet activation, Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost., 23, 607–614.
Campbell, P. G., Durham, S. K., Hayes, J. D., Suwanichkul, A., and Powell, D. R. (1999) Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 binds fibrinogen and fibrin, J. Biol. Chem., 274, 30215–30221.
Gligorijevic, N., and Nedic, O. (2016) Interaction between fibrinogen and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 in human plasma under physiological conditions, Biochemistry (Moscow), 81, 135–140.
Udvardy, M., Pfliegler, G., and Rak, K. (1985) Platelet insulin receptor determination in non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus, Experimentia, 41, 422–423.
Boucher, J., Kleinridders, A., and Khan, R. (2014) Insulin receptor signaling in normal and insulin-resistant states, Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol., 6, a009191.
Vestergaard, P. F., Hansen, M., Frystyk, J., Espelund, U., Christiansen, J. S., Jorgensen, J. O., and Fisker, S. (2013) Serum levels of bioactive IGF1 and physiological markers of ageing in healthy adults, Eur. J. Endocrinol., 170, 229–236.
Wilcox, G. (2005) Insulin and insulin resistance, Clin. Biochem. Rev., 26, 19–39.
Benyoucef, S., Katharina, H., Surinya, K. H., Hadaschik, D., and Siddle, K. (2007) Characterization of insulin/IGF hybrid receptors: contributions of the insulin receptor L2 and Fn1 domains and the alternatively spliced exon 11 sequence to ligand binding and receptor activation, Biochem. J., 403, 603–613.
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia (grant no. 173042).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest. The authors declare no conflict of interest in financial or any other area.
Compliance with ethical standards. This study was approved by the Ethical Committee of the Institute for the Application of Nuclear Energy (INEP). All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Published in Russian in Biokhimiya, 2019, Vol. 84, No. 10, pp. 1511–1518.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gligorijevic, N., Robajac, D. & Nedic, O. Enhanced Platelet Sensitivity to IGF-1 in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Biochemistry Moscow 84, 1213–1219 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297919100109
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297919100109