Abstract
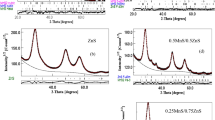
The structure of opal-ZnO composites is studied by transmission electron microscopy and X-ray phase analysis. It is shown that, under thermal treatment of infiltrated samples, a solid-phase reaction proceeds at the opal-ZnO interface. As a result, zinc silicate β-Zn2SiO4 and its high-temperature phase, willemite Zn2SiO4, are formed. The structure and emission properties of the nanocomposite are studied in relation to the degree of filling. For a sample subjected to 25 cycles of filling, luminescence controlled by the β-Zn2SiO4 phase is detected in the blue spectral region (at 430 nm). The angular dependences of the luminescence and reflection spectra of an opal-ZnO composite sample subjected to four cycles of filling show the effect of suppression of a spontaneous emission of zinc oxide in the photonic band gap.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. F. Kraus and R. M. De La Rue, Prog. Quantum Electron. 23, 51 (1999).
J. G. Fleming and S. Y. Lin, Opt. Lett. 24(1), 49 (1999).
S. G. Romanov, T. Maka, C. M. Sotomayor Torres, et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 79, 731 (2001).
S. V. Gaponenko, V. N. Bogomolov, E. P. Petrov, et al., J. Lightwave Technol. 17, 2128 (1999).
V. N. Astratov, V. N. Bogomolov, A. A. Kaplyanskii, et al., Nuovo Cimento D 17, 1349 (1995).
D. J. Norris and Yu. A. Vlasov, Adv. Mater. 13, 371 (2001).
S. G. Romanov and C. M. Sotomayor Torrers, Phys. Rev. E 69, 046611 (2004).
C. M. Mo, Y. H. Li, Y. S. Liu, et al., J. Appl. Phys. 83, 4389 (1998).
A. N. Gruzintsev, V. T. Volkov, G. A. Emel’chenko, et al., Fiz. Tekh. Poluprovodn. (St. Petersburg) 37, 330 (2003) [Semiconductors 37, 314 (2003)].
K. K. Kim, N. Koguchi, Y. W. Ok, et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 3810 (2004).
V. M. Masalov, É. N. Samarov, G. I. Volkodav, et al., Fiz. Tekh. Poluprovodn. (St. Petersburg) 38, 884 (2004) [Semiconductors 38, 849 (2004)].
Current Topics on Materials Science, Ed. by E. Kaldis (North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1981), Vol. 7, p. 244.
X. Xu, P. Wang, Z. Qi, et al., J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 15, L607 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
__________
Translated from Fizika i Tekhnika Poluprovodnikov, Vol. 39, No. 11, 2005, pp. 1375–1379.
Original Russian Text Copyright © 2005 by Emel’chenko, Gruzintsev, Koval’chuk, Masalov, Samarov, Yakimov, Barthou, Zver’kova.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Emel’chenko, G.A., Gruzintsev, A.N., Koval’chuk, M.N. et al. Opal-ZnO nanocomposites: Structure and emission properties. Semiconductors 39, 1328–1332 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1134/1.2128460
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/1.2128460