Summary
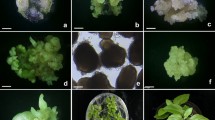
This paper investigates maintenance and proliferation of somatic embryogenesis systems for Ulmus minor and U. glabra. Proliferation occurred with subculture of embryogenic calluses. The calluses were mainly formed by friable nodules composed of meristematic cells organized into proembryogenic cell masses (PEMs) and thin-walled vacuolated parenchymatic cells. Cotyledonary embryos, with procambial strands and differentiation of their vascular tissues as well as visible root meristems, were identifiable after 18d of culture on a proliferation medium with 0.44 μM benzyladenine (BA). The shoot meristem was only occasionally well developed. Somatic embryo multiplication from elm embryogenic calluses is a clearly asynchronic system, and PEMs as well as embryos at all stages of development are observed simultaneously at the end of subculture period. Factors affecting the proliferation of elm embryogenic callus, such as culture medium, carbon source and genotype, were studied. Basal medium (MS) or medium supplemented with 0.44 μM BA produced the highest number of somatic embryos. Somatic embryo production was higher with sucrose or glucose than with maltose, and significant differences were also found among the four embryogenic lines tested. The use of liquid medium with filter paper support is an essential step for the survival of isolated somatic embryos during the germination stage. The addition of 0.22 μM BA′ to liquid MS medium was the best treatment for germination and plantlet conversion of elm somatic embryos.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtar, N.; Kumari, N.; Pandey, S.; Ara, H.; Singh, M.; Jaiswal, U.; Jaiswal, V. S.; Jain, S. M. Somatic embryogenesis in tropical fruit tree. In: Jain, S. M.; Gupta, P. K.; Newton, R. J. eds. Somatic embryogenesis in woody plants, vol. 4. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 2000:93–140.
Bolyard, M. G.; Hajela, R. K.; Sticklen, C. Microprojectile and Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of pioneer elm. J. Arbor. 17:34–37; 1991.
Brasier, C. M. Missing link in tree disease. Nature 372:227–228; 1994.
Corredoira, E. Desarrollo de sistemas embriogénicos en olmo y castaño, Doctoral thesis, University of Santiago de Compostela, Spain; 2002.
Corredoira, E.; Vieitez, A. M.; Ballester, A. Somatic embryogenesis in elm. Ann. Bot. 89:637–644; 2002.
Cuenca, B.; San-José, M. C.; Martínez, M. T.; Ballester, A.; Vieitez, A. M. Somatic embryogenesis from stem and leaf of Quercus robur L. Plant Cell Rep. 18:538–543; 1999.
Daigny, Ng.; Paul, H.; Sangwan, R. S.; Sangwan-Norreel, B. S. Factors influencing secondary somatic embryogenesis in Malus × domestica Borkh. (ev ‘Gloster 69’). Plant Cell Rep. 16:153–157; 1996.
Dorion, N.; Hassairi, A.; Guyon, P.; Godin, B.; bigot, C. In vitro budding ability of woody internode and Agrobacterium susceptibility as prerequisites for elm genetic transformation. J. Plant Physiol. 146:699–703; 1995.
Duval, Y.; Engelmann, F.; Durand-Gasselin, T. Somatic embryogenesis in oilpalm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.). In: Bajaj, Y. P. S., ed. Biotechnology in agriculture and forestry, no. 30. Somatic embryogenesis and synthetic seed. Berlin: Springer-Verlag; 1995:335–352.
Fenning, T. M.; Tymens, S. S.; Gartland, J. S.; Brasier, C. M.; Gartland, K. M. A. Transformation and regeneration of English elm using wild-type Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Sci. 116:37–46; 1996.
Fernández-Guijarro, B.; Celestino, C.; Toribio, M. Influence of external factors on secondary embryogenesis and germination in somatic embryos from leaves of Quercus suber. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 41:99–106; 1995.
Gartland, J. S.; Brasier, C. M.; Fenning, T. M.; Birch, R.; Gartland, K. M. A. Ri-plasmid mediated transformation and regeneration of Ulmus procera (English elm). Plant Growth Reg. 33:123–129; 2001.
Gartland, J. S.; McHugh, A. T.; Brasier, C. M.; Irvine, R. J.; Fenning, T. M.; Gartland, K. M. A. Regeneration of phenotypically normal English elm (Ulmus procera) plantlets following transformation with an Agrobacterium tumefaciens binary vector. Tree Physiol. 20:901–907; 2000.
Gupta, P. K. Method for reproducing conifers by somatic embryogenesis using maltose enriched maintenance medium. US patent no. 5,563,061; 1996.
Lelu, M.-A.; Bastien, C.; Klimaszewska, K.; Ward, C.; Charest, P. J. An improved method for somatic planted production in hybrid larch (Larix × leptoeuropaen). Part 1. Soamtic embryo maturation. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 36:107–115; 1994.
Li, Z.; Traore, A.; Maximova, S.; Guiltinan, M. J. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from floral explants of cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) using thidiazuron. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 34:293–299; 1998.
Lloyd, G. B.; McCown, B. H. Commercially feasible micropropagation of mountain laurel (Kalmia latifolia) by use of shoot tip culture. Proc. Int. Plant. Prop. Soc. 30:421–437; 1981.
merkle, S. A. Strategies for dealing with limitations of somatic embryogenesis in hardwood trees. Plant Tiss. Cult. Biotechnol. 1:112–121; 1995.
Merkle, S. A.; Parrot, W. A.; Flinn, B. S. Morphogenic aspects of somatic embryogenesis In: Thorpe, T. A. ed. In vitro embryogenesis in plants. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 1995:155–203.
Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15:473–497; 1962.
Radojevic, L. Somatic embryogenesis in horse chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum L.). In: Jain, S. M.; Gupta, P. K.; Newton, R. J., eds. Somatic embryogenesis in woody plants, vol. 2. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 1995:409–444.
Reidiboym-Talleux, L.; Diemer, F.; Sourdioux, M.; Chapelain, K.; Grenier-De March, G. Improvement of somatic embryogenesis in wild cherry (Prunus avium). Effect of maltose and ABA supplements. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 55:199–209; 1999.
Roberts, A. V.; Smith, E. The preparation in vitro of chrysanthemum for transplantation to soil. I. Protection of roots by cellulose plugs. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 21:129–132; 1990.
Roberts-Oehlschlager, S. L.; Dunwell, J. M.; Faulks, R. Changes in the sugar content of barley anthers during culture on different carbohydrates. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 22:77–85; 1990.
Rugini, E.; Caricato, G. Somatic embryogenesis and plant recovery from mature tissues of olive cultivars (Olea europaea L.) ‘Canino’ and ‘Moraiolo’. Plant Cell Rep. 14:257–260; 1995.
Scott, P.; Lyne, R. L.; Rees, T. A. Metabolism of maltose and sucrose by microspores isolated from barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Planta 197:435–441; 1995.
Sharma, A.; Kumar, A. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from leaf-derived suspensions of a mature tree Thevetia peruviana. Plant Cell Rep. 14:171–174; 1994.
Sokal, R. R.; Rohlf, F. J. Biometry: the principles and practice of statistics and biological research, 2nd edn. New York: Freeman and Co; 1981.
Williams, E. G.; Maheswaran, G. Somatic embryogenesis: factors influencing coordinated behaviour of cells as an embryogenic group. Ann. Bot. 57:443–462; 1986.
Yeung, E. C. Structural and developmental patterns in somatic embryogenesis In: Thorpe, T. A., ed. In vitro embryogenesis in plants. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 1995:205–247.
Zegzouti, R.; Favre, J. M. Histogenesis of secondary embryoids in Quercus robur. In: Espinel, S.; Ritter, E., eds. Proceedings of application of biotechnology to forest genetics. Biofor 99, Vitoria-Gasteiz, Spain; September 22–25, 1999:227–230.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Corredoira, E., Vieitez, A.M. & Ballester, A. Proliferation and maintenance of embryogenic capacity in elm embryogenic cultures. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Plant 39, 394–401 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1079/IVP2003428
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1079/IVP2003428