Abstract
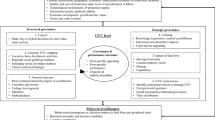
Firm-level data from Swedish manufacturing MNEs show that their local R&D units in emerging countries now mainly develop new technology in co-location with manufacturing plants. This complements findings that co-located units have previously mainly locally adapted parent companies’ existing technology. This implies that co-located R&D units of Western MNEs in emerging countries now play a more important strategic role than was previously assumed, especially in China, India, and other Asian countries with large and growing markets, specific demand characteristics, strong domestic producers, rapid industrial and technological change, and a capability to develop and produce complex products and systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The concept of 'emerging market' is interpreted here broadly, to incorporate all countries outside Western Europe, North America, Japan, Australia and New Zealand.
References
Abele, E., T. Meyer, U. Näher, G. Strube, and R. Sykes (eds.). 2008. Global production: A handbook for strategy and implementation. Berlin: Springer.
Alcacer, J., and M. Delgado. 2016. Spatial organization of firms and location choices through the value chain. Management Science 62 (11): 3213–3234.
Alcacer, J., and M. Zhao. 2012. Local R&D strategies and multilocation firms: The role of internal linkages. Management Science 58 (4): 734–753.
Ambos, B. 2005. Foreign direct investment in industrial research and development: A study of German MNCs. Research Policy 34 (4): 395–410.
Ambos, B., and T.C. Ambos. 2009. Location choice, management and performance of international R&D investments in peripheral economies. International Journal of Technology Management 48 (1): 24–41.
Aoki, M. 1990. Towards an economic model of Japanese firms. Journal of Economic Literature 28 (1): 1–27.
Athreye, S., A. Tuncay-Celikel, and V. Ujjual. 2013. Internationalisation of R&D into emerging markets: Fiat’s R&D in Brazil, Turkey and India. Long Range Planning 47 (1–2): 100–114.
Belderbos, R., B. Leten, and S. Suzuki. 2013. How global is R&D? Firm-level determinants of home-country bias in R&D. Journal of International Business Studies 44 (8): 765–786.
Birkinshaw, J. 2002. Managing internal R&D networks in global firms: What sort of knowledge is involved? Long Range Planning 35 (3): 245–267.
Boothroyd, G., P. Dewhurst, and W.A. Knight. 2010. Product design for manufacture and assembly, 3rd ed. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press.
Boutellier, R., O. Gassmann, and M. von Zedtwitz. 2008. Managing global innovation: Uncovering the secrets of future competitiveness, 3rd ed. Berlin: Springer.
Bruche, G. 2009. The emergence of China and India as new competitors in MNCs’ innovation networks. Competition and Change 13 (3): 267–288.
Cantwell, J. 1995. The globalisation of technology: What remains of the product cycle model? Cambridge Journal of Economics 19 (1): 155–174.
Cantwell, J., and L. Piscitello. 2010. Recent location of foreign-owned research and development activities by large multinational corporations in the European regions: The role of spillovers and externalities. Regional Studies 39 (1): 1–16.
Chen, Y.C. 2007. The upgrading of multinationals’ regional innovation networks in China. Asia Pacific Business Review 13 (3): 373–403.
D’Agostino, L.M.D., and G.D. Santangelo. 2012. Do overseas R&D laboratories in emerging markets contribute to home knowledge creation? An extension of the double diamond model. Management International Review 52 (2): 251–273.
Davies, A., and M. Hobday (eds.). 2005. The business of projects: Managing innovation in complex products and systems. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Dunning, J.H., and S.M. Lundan. 2008. Multinational enterprises and the global economy. Cheltenham: Edward Elgar.
Dunning, J.H., and S.M. Lundan. 2009. The internationalization of corporate R&D: A review of the evidence and some policy implications for home countries. Review of Policy Research 26 (1–2): 13–33.
Commission, European. 2014. The 2014 EU survey on R&D investment business trends. Luxembourg: European Union.
Fors, G., and R. Svensson. 2002. R&D and foreign sales in Swedish multinationals: A simultaneous relationship? Research Policy 31 (1): 95–107.
Gassmann, O., and Z. Han. 2004. Motivations and barriers of foreign R&D activities in China. R&D Management 34 (4): 423–437.
Gerybadze, A. and Merk, S. 2014. Globalisation of R&D and host-country patenting of multinational corporations in emerging countries. International Journal of Technology Management 64(2,3,4): 148–176.
Giroud, A., Y.J. Ha, and M. Yamin. 2014. Foreign subsidiaries’ internal and external R&D cooperation in South Korea: Explanatory factors and interaction. Asian Business & Management 13 (3): 227–256.
Govindarajan, V., and R. Ramamurti. 2011. Reverse innovation, emerging markets and global strategy. Global Strategy Journal 1 (3–4): 191–205.
Granstrand, O. 1999. Internationalization of corporate R&D: A study of Japanese and Swedish corporations. Research Policy 28 (2–3): 275–302.
Håkanson, L. 1981. Organization and evolution of foreign R&D in Swedish multinationals. Geografiska Annaler B 63 (1): 47–56.
Håkanson, L. 1995. Learning through acquisitions: Management and integration of foreign R&D laboratories. International Studies of Management and Organisation 25 (1–2): 121–157.
Håkanson, L. 2014. Internationalisation of research and development. In The Oxford handbook of innovation management, ed. M. Dodgson, D.M. Gann, and N. Phillips, 548–558. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Håkanson, L., and R. Nobel. 1993a. Foreign research and development in Swedish multinationals. Research Policy 22 (5–6): 373–396.
Håkanson, L., and R. Nobel. 1993b. Determinants of foreign R&D in Swedish MNCs. Research Policy 22 (5–6): 397–411.
Håkanson, L., and U. Zander. 1988. International management of R&D: The Swedish experience. R&D Management 18 (3): 217–226.
Hobday, M. 1998. Product complexity, innovation and industrial organisation. Research Policy 26 (6): 689–710.
Hobday, M. 2000. The project-based organisation: An ideal form for managing complex products and systems? Research Policy 29 (7–8): 871–893.
Hobday, M., and H. Rush. 2007. Upgrading the technological capabilities of foreign transnational subsidiaries in developing countries: The case of electronics in Thailand. Research Policy 36 (9): 1335–1356.
Iammarino, S., and P. McCann. 2013. Multinationals and economic geography: Location, technology and innovation. Cheltenham: Elgar.
Iguchi, C. 2012. Globalisation of R&D by TNC subsidiaries: The case of South-East Asian countries. Asian Business & Management 11 (1): 79–100.
ITPS. 2011. Forskning och utveckling i internationella företag 2009 (R&D in international corporations). Tillväxtanalys, Statistik 2011:03. Available www.tillvaxtanalys.se/in-english/publications/statistics/statistics/2013-05-30-research-and-development-in-enterprises-in-2011.html, accessed 13 December 2016.
ITPS. 2013. Forskning och utveckling i internationella företag 2011 (R&D in international corporations). Tillväxtanalys, Statistik 2013: 04. Available www.tillvaxtanalys.se/in-english/publications/statistics/statistics/2013-05-30-research-and-development-in-enterprises-in-2011.html, accessed 13 December 2016.
Ivarsson, I., Alvstam, C. and Vahlne, J.E. 2016. Global technology development by co-locating R&D and manufacturing: The case of Swedish manufacturing MNEs. Industrial and Corporate Change, forthcoming.
Ivarsson, I., and T. Jonsson. 2003. Local technological competence and asset-seeking FDI: An empirical study of manufacturing and wholesale affiliates in Sweden. International Business Review 12 (3): 369–386.
Johansson, B., and H. Lööf. 2006. Global location of R&D. In The internationalization of corporate R&D: Leveraging the changing geography of innovation, ed. M. Karlsson, 89–103. Swedish Institute for Growth Policy Studies: Stockholm.
Karabag, S.F., A. Tuncay-Celikel, and C. Berggren. 2011. The limits of R&D internationalization and the importance of local initiatives: Turkey as a critical case. World Development 39 (8): 1347–1357.
Kenney, M., and R. Florida. 1994. The organization and geography of Japanese R&D: Results from a survey of Japanese electronics and biotechnology firms. Research Policy 23 (3): 305–323.
Ketokivi, M., and J. Ali-Yrkkö. 2009. Unbundling R&D and manufacturing: Post-industrial myth or economic reality? Review of Policy Research 26 (1–2): 35–54.
Kuemmerle, W. 1999a. Foreign direct investment in industrial research in the pharmaceutical and electronics industries—results from a survey of multinational firms. Research Policy 28 (2–3): 179–193.
Kuemmerle, W. 1999b. The drivers of foreign direct investment into research and development: An empirical investigation. Journal of International Business Studies 30 (1): 1–24.
Li, J., and D.R. Yue. 2005. Managing global research and development in China: Patterns of R&D configuration and evolution. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management 17 (3): 317–337.
Manolopoulus, D., K.E. Söderquist, and R. Pearce. 2011. Coordinating decentralized research and development laboratories: A survey analysis. Journal of International Management 17 (2): 97–113.
Mariani, M. 2002. Next to production or to technological clusters? The economics and management of R&D location. Journal of Management and Governance 6 (2): 131–152.
Martin, R., and J. Moodysson. 2013. Comparing knowledge bases: On the geography and organization of knowledge-sourcing in the regional innovation system of Scania. Sweden. European Urban and Regional Studies 20 (2): 170–187.
Mathews, J.A. 2006. Dragon multinationals: New players in 21st-century globalization. Asia Pacific Journal of Management 23 (1): 5–27.
Medcof, J.W. 1997. A taxonomy of internationally dispersed technology units and its application to management issues. R&D Management 27 (4): 301–328.
Nightingale, P., T. Brady, A. Davies, and J. Hall. 2003. Capacity utilisation revisited: Software, control and large technical systems. Industrial and Corporate Change 12 (3): 477–517.
Olausson, D., T. Magnusson, and N. Lakemond. 2009. Preserving the link between R&D and manufacturing: Exploring challenges related to vertical integration and product/process newness. Journal of Purchasing and Supply Management 15 (2): 79–88.
Pavitt, K. 2005. Innovation processes. In The Oxford handbook of innovation, ed. J. Fagerberg, D. Mowery, and R. Nelson, 86–114. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Pearce, R.D. 1989. The internationalization of research and development by multinational enterprises. London: MacMillan.
Pisano, G., and W.C. Shih. 2012a. Does America really need manufacturing? Harvard Business Review 90 (3): 94–102.
Pisano, G., and W.C. Shih. 2012b. Producing prosperity: Why America needs a manufacturing renaissance. Boston: Harvard Business Review Press.
Pogrebnyakov, N., and J. Kristensen. 2011. Building innovation subsidiaries in emerging markets: The experience of Novo Nordisk. Research-Technology Management 54 (4): 30–37.
Qi, M., Wang, Y., Zhang, M.Y. and Zhu, H. 2014. The evolution of R&D capability in multinational corporations in emerging markets: Evidence from China. International Journal of Technology Management 64(2,3,4): 210–231.
Reddy, P. 2010. Global innovation in emerging economies. New York, London: Routledge.
Ronstadt, R. 1977. Research and Development Abroad by U.S. Multinationals, New York: Praeger.
Schanz, C., S. Hüsig, M. Dowling, and A. Gerybadze. 2011. ‘Low cost-high tech’ innovations for China: Why setting up a separate R&D unit is not always the best approach. R&D Management 41 (3): 307–317.
Siedschlag, I., D. Smith, C. Turcue, and X. Zhang. 2013. What determines the location choice of R&D activities by multinational firms? Research Policy 42 (8): 1420–1430.
Simon, S., U. Näher, and M.D. Lauritzen. 2008. R&D: Aligning the interface with production. In Global production: A handbook for strategy and implementation, ed. E. Abele, T. Meyer, U. Näher, G. Strube, and R. Sykes, 350–371. Berlin: Springer.
Storm, P., T. Lager, and P. Samuelsson. 2013. Managing the manufacturing-R&D interface in the process industries. R&D Management 43 (3): 252–270.
Sun, Y., and K. Wen. 2007. Uncertainties, imitative behaviours and foreign R&D location: Explaining the overconcentration of foreign R&D in Beijing and Shanghai within China. Asia Pacific Business Review 13 (3): 405–424.
Susman, G.I. (ed.). 1992. Integrating design and manufacturing for competitive advantage. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Thompson, J.D. 1967. Organizations in action: Social science bases of administrative theory. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Tseng, C.-H. 2011. Subsidiaries’ local linkage characteristics and R&D assignments in a small developing economy. Asian Business & Management 10 (2): 209–232.
UNCTAD. 2005. World investment report: Transnational corporations and the internationalization of R&D. New York and Geneva: UNCTAD.
Vahlne, J.-E., and I. Ivarsson. 2014. Globalization of Swedish MNCs: Empirical evidence and theoretical explanations. Journal of International Business Studies 45 (3): 227–247.
Vahlne, J.-E., I. Ivarsson, and J. Johanson. 2011. The tortuous road to globalization for Volvo´s heavy truck business: Extending the scope of the Uppsala model. International Business Review 20 (1): 1–14.
von Zedtwitz, M., S. Corsi, P.W. Søberg, and R. Frega. 2014. A typology of reverse innovation. Journal of Product Innovation Management Innovation 32 (1): 1–17.
von Zedtwitz, M., and O. Gassmann. 2002. Market versus technology drive in R&D internationalization: Four different patterns of managing research and development. Research Policy 31 (4): 569–588.
Wheelwright, S.C., and K.B. Clark. 1992. Revolutionizing product development: Quantum leaps in speed, efficiency and quality. New York: Free Press.
Williamson, P.J. 2010. Cost innovation: Preparing for a ‘value-for-money’ revolution. Long Range Planning 43 (2–3): 343–353.
Williamson, P.J., R. Ramamurti, A. Fleury, and M.Z. Fleury. 2013. The competitive advantage of emerging-country multinationals. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Zeschky, M., Widenmayer, B. and Gassmann, O. (2014) Organising for reverse innovation in Western MNCs: The role of frugal product innovation capabilities. International Journal of Technology Management 64(2,3,4): 255–275.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ivarsson, I., Alvstam, C.G. New technology development by Swedish MNEs in emerging markets: the role of co-location of R&D and production. Asian Bus Manage 16, 92–116 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41291-016-0013-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1057/s41291-016-0013-z