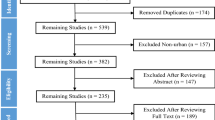
Abstract
This study investigates the sense of place (SoP) as a function of spatial characteristics of Buffalo, New York's Elmwood Village, an award-winning American neighbourhood for its perceived strong SoP. The primary aim is to provide empirical proof of this claimed strength of the neighbourhood’s SoP at the building, street and neighbourhood scales and to offer a multi-dimensional understanding of SoP by investigating its four sub-indicators, namely place attachment, place identity, place dependence and nature bonding. By studying the perceptual dynamics with a survey method, place identity and place attachment were identified as the most important determinants of SoP at the neighbourhood scale, while place identity and place dependence took the lead at smaller scales. The study of spatial dynamics showed that SoP can be improved to varied degrees for each of the four sub-indicators based on variances in building and street characteristics. For instance, residing in single-family houses or houses with three-and-more bedrooms may result in higher SoP; or place identity may be affected by the open sky coverage or vegetation coverage, etc. Elmwood Village has demonstrated the power of SoP at all scales, and the neighbourhood itself undoubtedly holds a special place in the hearts of its residents. Overall, planners and designers should concentrate on which spatial qualities and scales should be prioritised in future improvement plans to maintain and/or build SoP.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkhresheh, M.M. 2007. Enclosure as a function of height-to-width ratio and scale: its influence on user’s sense of comfort and safety in urban street space. Florida: University of Florida.
Alrobaee, T.R., and A.S. Al-Kinani. 2019. Place dependence as the physical environment role function in the place attachment. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering 698: 1–7.
American Community Survey (ACS). 2020. https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/acs. Accessed 15 Aug 2022.
Anton, C.E., and C. Lawrence. 2014. Home is where the heart is: the effect of place of residence on place attachment and community participation. Journal of Environmental Psychology 40: 451–461.
APA. 2022. Great places in America: neighbourhoods (Elmwood Village, Buffalo, New York). American Planning Association. https://www.planning.org/greatplaces/neighbourhoods/2007/elmwoodvillage.htm. Accessed 14 Apr 2022
Ardoin, N.M., R.K. Gould, H. Lukacs, C.C. Sponarski, and J.S. Schuh. 2019. Scale and sense of place among urban dwellers. Ecosphere 10 (9): e02871.
Arifwidodo, S.D., and O. Chandrasiri. 2013. The relationship between housing tenure, sense of place and environmental management practices: a case study of two private land rental communities in Bangkok, Thailand. Sustainable Cities and Society 8: 16–23.
ASLA. 2020. Vegetation in the built environment. Wahington: American Society of Landscape Architects.
Bellet, C. 2019. April 25) The McMansion effect: top house size and positional externalities in U.S. Suburbs. SSRN. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3378131.
Berghauser Pont, M., and P. Haupt. 2010. Spacematrix—space, density and urban form. Rotterdam: NAi Publishers.
Billig, M. 2004. The residential-environment climate sense of place in locations of urban revitalization. Dela 21: 581–592.
Billig, M., and A. Churchman. 2003. Building walls of brick and breaching walls of separation. Environment and Behavior 35 (2): 227–249.
Bonaiuto, M., A. Aiello, M. Perugini, M. Bonnes, and A.P. Ercolani. 1999. Multidimensional perception of residential environment quality and neighbourhood attachment in the urban environment. Journal of Environmental Psychology 19: 331–352.
Bonaiuto, M., F. Fornara, S. Ariccio, U.G. Cancellieri, and L. Rahimi. 2015. Perceived Residential Environment Quality Indicators (PREQIs) relevance for UN-HABITAT City Prosperity Index (CPI). Habitat International 45: 53–63.
Bonaiuto, M., F. Fornara, and M. Bonnes. 2003. Indexes of perceived residential environment quality and neighbourhood attachment in urban environment: a confirmation study on the city of Rome. Landscape and Urban Planning 65: 41–52.
Brown, B.B., and C.M. Werner. 1985. Social Cohesiveness, territoriality and holiday decorations: the influence of cul-de-sacs. Environment and Behaviour 17 (5): 539–565.
Carmona, M., S. Tiesdell, T. Heath, and T. Oc. 2010. Public places urban spaces: the dimensions of urban design, 2nd ed. Oxford: Elsevier.
Cheng, A.S., L.E. Kruger, and S.E. Daniels. 2003. “Place” as an integrating concept in natural resource politics: propositions for a social science research Agenda. Society & Natural Resources 16 (2): 87–104.
Clemons, S. A., J. H. Banning, and D. A. McKelfresh. 2004. Importance of sense of place and sense of self in residence hall room design. Colorado State Journal of Student Affairs, 13(8–15).
Cresswell, T. 1996. In place/out of place: geography, ideology, and transgression (NED-new edition). Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
Cross, J.E. 2001. What is sense of place? In: The 12th Headwaters Conference, November 2–4. Western State College.
Day, L.L. 2000. Choosing a house: the relationship between dwelling type, perception of privacy and residential satisfaction. Journal of Planning Education and Research 19 (3): 265–275.
Deutsch, K., S. Yoon, and K. G. Goulias. 2011. Unpacking the theory of sense of place. Is it useful for choice modeling? International Choice Modelling Conference 1–17.
Dovey, K. 2010. Becoming places: Urbanism/architecture/identity/power. New York: Taylor and Francis Group.
Eisenhauer, B., R. Kannich, and D. Blahna. 2000. Attachments to special places on public lands: An analysis of activities, reason for attachments, and community connections. Society & Natural Resources 13: 421–441.
Erfani, G. 2022. Reconceptualising sense of place: towards a conceptual framework for investigating individual-community-place interrelationships. Journal of Planning Literature 1–15.
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. 2016, November 30. Building greener cities: nine benefits of urban trees. http://www.fao.org/zhc/detail-events/en/c/454543/
Ghoomi, H.A., S.-A. Yazdanfar, S.-B. Hosseini, and S.N. Maleki. 2015. Comparing the components of sense of place in the traditional and modern residential neighbourhoods. Elsevier Procedia Social and Behavioral Sciences 201: 275–285.
Gokce, D. 2017. An empirical investigation of the interplay between typo-morphological transformation of house form and sense of place. PhD Thesis, School of Architecture, University of Liverpool.
Gokce, D., and F. Chen. 2018. Sense of place in the changing process of house form: a Turkish perspective. Environment Planning B Urban Analytics and City Science 45: 772–796.
Gokce, D., and F. Chen. 2021. Multimodal and scale-sensitive assessment of sense of place in residential areas of Ankara, Turkey. Journal of Housing and the Built Environment 36: 1077–1101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10901-020-09798-6.
Goldman, M. 2007. City on the edge: Buffalo, New York. Amherst, NY: Prometheus Books.
Gong, F.-Y., Z.-C. Zeng, F. Zhang, X. Li, E. Ng, and L.K. Norford. 2018. Mapping sky, tree, and building view factors of street canyons in a high-density urban environment. Building and Environment 134: 155–167.
Grimmond, C., S.Z. Potter, and C. Souch. 2001. Rapid methods to estimate sky-view factors applied to urban areas. International Journal of Climatology 21: 903–913.
Hadizadeh, A., and A. Nourtaghani. 2022. Sense of place in the process of changing the configuration and activity of rural housing types. Journal of Asian Architecture and Building Engineering 21 (4): 1431–1444.
Hamaina, R., T. Leduc, and G. Moreau. 2012. Towards urban fabrics characterization based on buildings footprints. In Bridging the geographic information sciences, ed. J. Gensel, D. Josselin, and D. Vandenbroucke, 327–346. Berlin: Springer.
Hashemnezhad, H., A.A. Heidari, and P.M. Hoseini. 2013. Sense of place and place attachment. International Journal of Architecture and Urban Development 3 (1): 5–12.
Healey, P. 2005. Editorial. Planning Theory and Practice 6 (1): 5–8.
Hidalgo, M.C., P. Moreno-Jiménez, G. Muiños, and B. Hernández. 2021. Neighbourhood care and neighbourhood bonds: an unequal relationship. Environment and Behavior 53 (6): 571–600.
Hwang, S.-N., C. Lee, and H.-J. Chen. 2005. The relationship among tourists’ involvement, place attachment and interpretation satisfaction in Taiwan’s national parks. Tourism Management 26: 143–156.
Jackson, J.B. 1994. A sense of place, a sense of time. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press.
Jiven, G., and P.J. Larkham. 2003. Sense of place, authenticity and character: a commentary. Journal of Urban Design 8 (1): 67–81.
Jorgensen, B.S., and R.C. Steadman. 2006. A comparative analysis of predictors of sense of place dimensions: attachment to dependence on, and identification with lakeshore properties. Elsevier Journal of Environmental Management 79: 316–327.
Kahraman, E. D., and E. Cubukcu. 2017. Developing the standards for sense of enclosure: an experimental study in virtual environments. CPUD ’17 / II. International City Planning and Urban Design Conference. DAKAM.
Kaltenborn, P.B. 1998. Effects of sense of place on responses to environmental impacts: a study among residents in Svalbard in the Norwegian High Arctic. Applied Geography 18 (2): 169–189.
Kaltenborn, B.P., and D.R. Williams. 2002. The meaning of place: attachments to Femundsmarka National Park, Norway, among tourists and locals. Nor. J. Geogr 56: 189–198.
Katriina, S., V. Hanne, and P. Eija. 2012. Residents’ sense of place and landscape perceptions at the rural–urban interface. Landscape and Urban Planning 104 (1): 124–134.
Katsamagka, A. 2013. Developing place attachment to the natural surroundings of the school: the role of outdoor education. Master's Dissertation, Linköping University.
Kellert, S., and E. Wilson, eds. 1993. The biophilia hypothesis. Washington, D.C.: Island Press.
Kyle, G., A. Giraefe, and R. Manning. 2005. Testing the dimensionability of place attachment in recreational settings. Environment and Behaviour 37 (1): 53–177.
Kyle, G., A. Graefe, R. Manning, and J. Bacon. 2004. Effects of place attachment on users’ perceptions of social and environmental conditions in a natural setting. Journal of Environmental Psychology 24 (2): 213–225.
Lewicka, M. 2008. Place attachment, place identity, and place memory: restoring the forgotten city past. Journal of Environmental Psychology 28 (3): 209–231.
Lewicka, M. 2010. What makes neighbourhood different from home and city? Effects of place scale on place attachment. Journal of Environment Psychology 30 (1): 35–51.
Lewicka, M. 2011. Place attachment: how far have we come in the last 40 years? Journal of Environmental Psychology 31 (3): 207–230.
Liang, J., J. Gong, J. Sun, J. Zhou, W. Li, Y. Li, and S. Shen. 2017. Automatic sky view factor estimation from street view photographs—a big data approach. MDPI Remote Sensing 9 (411): 2–17.
Low, S., and I. Altman. 1992. Place attachment: a conceptual inquiry. New York: Plenum.
Mao, Y., F. Fornara, S. Manca, M. Bonnes, and M. Bonaiuto. 2015. Perceived residential environment quality indicators (PREQIs) and neighbourhood attachment: a confirmation study on a Chinese sample in Chongqing. PsyCh Journal 4 (3): 123–137.
Miles, R. (2017, October 12) Nature connection: a fast, slow, and portable sense of place. https://findingnature.org.uk/2017/10/12/nature-connection-a-fast-slow-and-portable-sense-of-place/. Accessed 26 July 2022
Milligan, M.J. 1998. Interactional past and potential: the social construction of place attachment. Symbolic Interaction 21 (1): 1–33.
Mlozi, S., O. Pesamaa, A. Haahtii, and S. Salunke. 2012. Determinants of place identity and dependence: the case of international tourism in Tanzania. Tourism, Culture and Communication 12 (2): 97–114.
Montgomery, J. 1998. Making a city: urbanity, vitality and urban design. Journal of Urban Design 3 (1): 93–116.
Moore, R.L., and A. Graefe. 1994. Attachments to recreation settings: the case of rail-trail users. Leisure Sciences 16: 17–31.
Musaab, S.A.-O., and H.A. Turki. 2017. Examining the functional roles of street characteristics in influencing the sense of place. International Journal of Advanced Multidisciplinary Research 4 (4): 23–31.
Nanzer, B. 2004. Measuring sense of place: a scale for Michigan. Administrative Theory and Praxis 26 (3): 362–382.
Nes, A. V., M. Berghauser Pont, and B. Mashhoodi. 2012. Combination of space syntax with spacematrix and the mixed-use Index. The Rotterdam South test case. Eighth International Space Syntax Symposium. Santiago.
Ng, S.L., and X. Feng. 2020. Residents’ sense of place, involvement, attitude, and support for tourism: a case study of Daming Palace, a Cultural World Heritage Site. Asian Geographer 37 (2): 189–207.
Ng, M. K., T. C. Yeung, M.-P. Kwan, H. Tieben, T. Y. Lau, J. Zhu, and Y. Xu. 2021. Place qualities, sense of place and subjective well-being: a study of two typical urban neighbourhoods in Hong Kong. Cities and Health.
Norberg-Schulz, C. 1979. Genius Loci: towards a phenomenology of architecture. New York: Rizzoli.
Norton, B., and B. Hannon. 1997. Environmental values: a place-based theory. Environmental Ethics 19: 227–245.
Nugroho, S., and J. Zhang. 2022. Explorations of young people’s sense of place using urban design qualities in Surabaya, Indonesia. Sustainability 14: 472.
Proshansky, H., A. Fabian, and R. Kaminoff. 1983. Place identity: physical world socialization of the self. Journal of Environmental Psychology 3: 57–83.
Punter, J. 1991. Participation in the design of urban space. Landscape Design 200: 24–27.
Qodsi, S.S., and J. Soheili. 2016. Study of the impact of form enclosure in residential complexes on the sense of place attachment of residents. Specialty Journal of Architecture and Construction 2 (2): 43–52.
Rapoport, A. 1969. House form and culture. London: Prentice-Hall Inc.
Raymond, C., G. Brown, and D. Weber. 2010. The measurement of place attachment: personal, community, and environmental connections. Journal of Environmental Psychology 30: 422–434.
Raymond, C.M., M. Kyttä, and R. Stedman. 2017. Sense of place, fast and slow: the potential contributions of affordance theory to sense of place. Frontiers in Psychology 8: 1674.
Relph, E. 1976. Place and placelessness. London: Pion Limited.
Ryan, R.L. 2005. Exploring the effects of environmental experience on attachment to urban natural areas. Environment and Behavior 37 (1): 3–42. https://doi.org/10.1177/0013916504264147.
Sattarzadeh, D., and L.B. Asl. 2015. Identification of the components of sense of place in architecture of houses in First Pahlavi Era in Iran (Case Study: Tabriz). European Online Journal of Natural and Social Sciences 3: 436–450.
Scannell, L., and R. Gifford. 2010. The relations between natural and civic place attachment and pro-environmental behavior. Journal of Environmental Psychology 30 (3): 289–297.
Shamai, S. 1991. Sense of place: an empirical measurement. Geoforum 22 (3): 347–358.
Shamai, S., S. Arnon, and I. Schnell. 2012. From home to community and settlement: sense of place in different scales. Stud Home Com Sci 6 (3): 153–163.
Shamai, S., and Z. Ilatov. 2005. Measuring sense of place: methodological aspects. Tijdschrift Voor Economische En Sociale Geographie 96 (5): 467–476.
Sigmon, S.T., S.R. Whitcomb, and C.R. Snyder. 2002. Psychological home. In Psychological sense of community. The Plenum series in social/clinical psychology, ed. A.T. Fisher, C.C. Sonn, and B.J. Bishop. Boston: Springer.
Stedman, R.C. 2006. Understanding place attachment among second homeowners. American Behavioral Scientist 50: 187–205.
Steele, F. 1981. The sense of place. Boston: CBI Publishing Company Inc.
Stephenson, J. 2010. People and place. Planning Theory and Practice 11 (1): 9–21.
Stokols, D., and S. Shumaker. 1981. People in places: a transactional view of settings. In Cognition, social behaviour and the environment, ed. J. Harvey. New Jersey: Erlbaum.
Swapan, M.S., S. Sadeque, and M. Ashikuzzaman. 2021. Role of place satisfaction and residents’ ambassadorship behaviours (RAB) on place attachment to city and neighbourhood. Journal of Place Management and Development. 15 (4): 442–459.
Tournois, L. 2018. Liveability, sense of place and behavioural intentions: an exploratory investigation of the Dubai urban area. Journal of Place Management and Development 11(1).
Tsaur, S.-H., Y.-W. Liang, and S.-C. Weng. 2014. Recreationist-environment fit and place attachment. Journal of Environmental Psychology 40: 421–429.
Tuan, Y.-F. 1974. Topophilia: a study of environmental perception, attitudes, and values. Morningside. New York: Colombia University Press.
Tuan, Y.F. 1977. Space and place. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
United States Census Bureau. 2020. 2020 census results. https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/decennialcensus/decade/2020/2020-census-results.html. Accessed 15 Aug 2022.
Uslu, A., and S. Gokce. 2010. Social interaction in urban areas and the characteristics of urban outdoor spaces. African Journal of Agricultural Research 5 (20): 2801–2810.
Vanclay, F. 2008. Place matters. In Making sense of place: exploring concepts and expressions of place through different sense and lenses, vol. 1, ed. F. Vanclay, M. Higgings, and A. Blackshaw, 3–11. Canbera: National Museum of Australia Press.
Walker, A.J., and R.L. Ryan. 2008. Place attachment and landscape preservation in rural New England: a Maine case study. Landscape and Urban Planning 86 (2): 141–152.
Wang, Z., D. Li, H. Cheng, and T. Luo. 2020. Multifaceted influences of urbanization on sense of place in the rural–urban fringes of China: growing, dissolving, and transitioning. Journal of Urban Planning and Development 146 (1): 04019026.
Wen Li, W., D. Hodgetts, and E. Ho. 2010. Gardens, transitions and identity reconstruction among older Chinese immigrants to New Zealand. Journal of Health Psychology 15 (5): 786–796.
Willer, Christopher J. 2016. “It takes a village”: urban change in the Elmwood neighborhood, 1990–2016. Thesis: Kent State University.
Williams, D.R., M.E. Patterson, J.W. Roggenbuck, and A.E. Watson. 1992. Beyond the commodity metaphor: examining emotional and symbolic attachment to Place. Leisure Sciences 14: 29–46.
Williams, D.R., and J.J. Vaske. 2003. The measurement of place attachment: validity and generalizability of a psychometric approach. Forest Science 49: 830–840.
Wolf, K. L. (2010) Green cities and good health. Accessed 27 Sept 2015, from https://depts.washington.edu/hhwb/Thm_Place.html
Yassein, G. 2019. Urban enclosure movement: the impact of gating a previously non- gated residential area. Journal of Urban Research 33: 131–153.
Zhou, Y., F. Du, K.L. Xiong, and X. Zou. 2022. The development of rural residents’ sense of place in an ecological restoration area: a case study from Huajiang Gorge, China. Mountain Research and Development 42 (1): 20–28.
Zia, A., B. Norton, S. Metcalf, P. Hirsch, and B. Hannon. 2014. Spatial discounting, place attachment, and environmental concern: toward an ambit-based theory of sense of place. Journal of Environmental Psychology 40: 283–295.
Acknowledgements
This research was conducted with the financial support of Fulbright Program and the Turkish Fulbright Commission (Fulbright Grant for 12 months, Grant Number: FY-2021-TR-PD-04). The authors would also like to thank the anonymous reviewers of this paper for their constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gokce, D., Kickert, C. What if “sense of place” is already strong? An in-depth investigation in an award-winning American neighbourhood. Urban Des Int 29, 39–55 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41289-023-00226-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1057/s41289-023-00226-z