Abstract
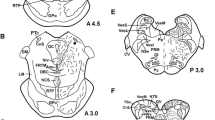
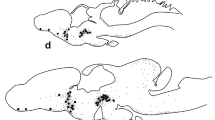
Although it has long been known that the hypothalamus contains substances which stimulate the release of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)1,2, corticoliberin (CRF) has only recently been identified and synthesized3,4. Here we describe the results of immunocytochemical staining of the neuroglandular system using an antiserum raised against this synthetic peptide. Neurone bodies containing CRF-like immunoreactivity (CLI) were stained in the paraventricular nuclei (PVN) of colchicine-injected rats whereas in normal rats, CLI was detected only in nerve fibres. These CLI-positive processes were abundant in the zona externa of the median eminence and in the pituitary stalk; they terminated close to capillaries of the primary portal plexus. In the rat fetus, CLI-containing fibres were detected only after the 18th day of development. After birth, a transitory disappearance of CLI was followed by its accumulation in fibres and perikarya. Morphological and physiological results corroborate recent biochemical studies 3,4; these will have to be taken into account in studies of the phenomena implicating participation of the adrenal cortex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guillemin, R. & Rosenberg, B. Endocrinology 57, 599–607 (1955).
Saffran, M. & Schally, A. V. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 33, 408–415 (1955).
Vale, W., Spiess, J., Rivier, C. & Rivier, J. Science 213, 1394–1397 (1981).
Rivier, C., Brownstein, M., Spiess, J., Rivier, J. & Vale, W. Endocrinology 110, 272–278 (1982).
Bugnon, C., Bloch, B., Lenys, D., Gouget, A. & Fellmann, D. Neurosci. Lett. 14, 43–48 (1979).
Bugnon, C., Bloch, B. & Fellmann, D. C.r. hebd. Séanc. Acad. Sci., Paris 282, 1625–1628 (1976).
Bugnon, C., Fellmann, D. & Bloch, B. Cell Tissue Res. 183, 319–328 (1977).
Fellmann, D., Bloch, B., Bugnon, C. & Lenys, D. J. Physiol., Paris 75, 37–43 (1979).
Fuxe, K., Ganten, D., Hökfelt, H. & Bolme, P. Neurosci. Lett. 2, 229–234 (1976).
Fuxe, K. et al. Colloques INSERM, Neuroendocrinologie 65, 17–40 (1976).
Lang, R. E., Voigt, K. H., Fehm, H. L. & Pfeiffer, E. F. Neurosci. Lett. 2, 19–22 (1976).
Makara, G. B., Stark, E., Karteszi, M., Palkovits, M. & Rappay, Gy. Am. J. Physiol. 240, E441–E446 (1981).
Jost, A. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 22, 541–574 (1966).
Chatelain, A. & Dupouy, J. P. Neuroendocrinology 33, 148–152 (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bugnon, C., Fellmann, D., Gouget, A. et al. Ontogeny of the corticoliberin neuroglandular system in rat brain. Nature 298, 159–161 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1038/298159a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/298159a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for ovine corticotropin-releasing factor precursor
Nature (1983)
-
Immunohistochemical detection of growth hormone-releasing factor in brain
Nature (1983)
-
The corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) neurosecretory system in intact, adrenalectomized, and adrenalectomized-dexamethasone treated rats
Histochemistry (1983)