Abstract
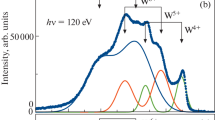
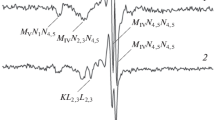
IT has recently been shown1 that even at low coverages of a fraction of a monolayer, nitrogen is simultaneously adsorbed on tungsten in different states of binding, of which three have so far been isolated. The temperatures above which these individual species are unstable have been estimated semi-quantitatively as 800° K. for state α, 2,000° K. for β and 200° K. for γ. In order to define the spectrum of binding energies of the molecular species adsorbed on the surface, it is necessary to measure the concentration of adsorbed entities as a function of sorbent temperature. We have now been able to do this by a simultaneous recording of the rise in pressure and the increase in electrical resistance when the tungsten wire sample is heated in a flash-filament cell. Since the variation of electrical resistance of tungsten with temperature is known, the flash filament can be used both as adsorption sample and resistance thermometer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ehrlich, G., J. Chem. Phys., 23, 1543 (1955); and in the press.
An adsorption spectrometer, utilizing a d.c. bridge circuit, has been described by Hagstrum, H. D., Rev. Sci. Instr., 24, 1122 (1953).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
EHRLICH, G., HICKMOTT, T. Adsorption Spectrum of Nitrogen on Tungsten. Nature 177, 1045–1046 (1956). https://doi.org/10.1038/1771045b0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/1771045b0
- Springer Nature Limited