Abstract
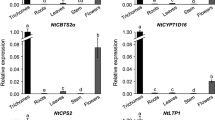
A prototypical characteristic of the Brassicaceae is the presence of the myrosinase-glucosinolate system. Myrosinase, the only known S-glycosidase in plants, degrades glucosinolates, thereby initiating the formation of isothiocyanates, nitriles and other reactive products with biological activities. We have used myrosinase gene promoters from Brassica napusand Arabidopsis thaliana fused to the β-glucuronidase (GUS) reporter gene and introduced into Arabidopsis thaliana, Brassica napus and/or Nicotiana tabacum plants to compare and determine the cell types expressing the myrosinase genes and the GUS expression regulated by these promoters. The A. thaliana TGG1 promoter directs expression to guard cells and phloem myrosin cell idioblasts of transgenic A. thaliana plants. Expression from the same promoter construct in transgenic tobacco plants lacking the myrosinase enzyme system also directs expression to guard cells. The B. napus Myr1.Bn1 promoter directs a cell specific expression to idioblast myrosin cells of immature and mature seeds and myrosin cells of phloem of B. napus. In A. thaliana the B. napus promoter directs expression to guard cells similar to the expression pattern of TGG1. The Myr1.Bn1 signal peptide targets the gene product to the reticular myrosin grains of myrosin cells. Our results indicate that myrosinase gene promoters from Brassicaceae direct cell, organ and developmental specific expression in B. napus, A. thaliana and N. tabacum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul, S.F., Gish, W., Miller, W., Meyers, E.W. and Lipman, D.J. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215: 403-419.
Attieh, J., Djiana, R., Koonjul, P., Etienne, C., Sparace, S.A. and Saini, H.S. 2002. Cloning and functional expression of two plant thiol methyltransferases: a new class of enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of sulphur volatiles. Plant Mol. Biol. 50: 511-521.
Blau, P.A., Feeny, P., Contardo, L. and Tobson, D.S. 1987. Allylglucosinolate and herbivorous caterpillars: a contrast in toxicity and tolerance. Science 200: 1296-1298.
Bones, A.M. 1990. Distribution of b-thioglucosidase activity in intact plants, cell and tissue cultures and regenerated plants of Brassica napus L. J. Exp. Bot. 41: 737-744.
Bones, A. and Iversen, T.H. 1985. Myrosin cells and myrosinase. Isr. J. Bot. 34: 351-375.
Bones, A.M. and Rossiter, J.T. 1996. The myrosinase-glucosinolate system, its organisation and biochemistry. Physiol. Plant 97: 194-208.
Bones, A.M. and Slupphaug, G. 1989. Purification, characterization and partial amino acid sequencing of b-thioglucosidase from Brassica napus L. J. Plant. Physiol. 134: 722-729.
Bones, A.M., Thangstad, O.P., Haugen, O. and Espevik, T. 1991. Fate of myrosin cells. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against myrosinase. J. Exp. Bot. 42: 1541-1549.
Borgen, B.H., 2002. Functional analysis of plant idioblasts (myrosin cells) and their role in defence, development and growth. PhD thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, ISBN 82-471-5134-0.
Burmeister, W.P., Cottaz, S., Driguez, H., Iori, R., Palmieri, S. and Henrissat, B. 1997. The crystal structures of Sinapis alba myrosinase and a covalent glycosyl-enzyme intermediate provide insights into the substrate recognition and active-site machinery of an S-glycosidase. Structure 5: 663-675.
Chadchawan, S., Bishop, J., Thangstad, O.P., Bones, A.M., Mitchell-Olds, T. and Bradley, D. 1993. Arabidopsis cDNA sequence encoding myrosinase. Plant Physiol. 103: 671-672.
Devereux, J., Haeberli, P. and Smithies, O. 1984. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucl. Acids Res. 12: 387-396.
Drobnica, L., Zemanova, M., Nemec, P., Antos, K., Kristian, P., Stullerova, A., Knoppova, V. and Nemec, P. Jr. 1967. Antifungal activity of isothiocyanates and related com-pounds. I. Naturally occuring isothiocyanates and their analogues. Appl. Microb. 15: 701-709.
Eriksson, S., Andreasson, E., Ekbom, B., Graner, G., Pontoppidan, B., Taipalensuu, J., Zhang, J., Rask, L. and Meijer, J. 2002. Complex formation of myrosinase isoenzymes in oilseed rape seeds are dependent on the presence of myrosinase-binding proteins. Plant Physiol. 129: 1592-1599.
Falk, A., Xue, J., Lenman, M. and Rask, L. 1992. Sequence of a cDNA clone encoding the enzyme myrosinase and expression of myrosinase in different tissues of Brassica napus. Plant Sci. 83: 181-186.
Foo, H.L., Grønning, L.M., Goodenough, L., Bones, A.M., Danielsen, B.E., Whiting, D.A. and Rossiter, J.T. 2000. Purification and characterisation of epithiospecifier protein from Brassica napus: enzymic intramolecular sulphur addition within alkenyl thiohydroximates derived from alkenyl glucosinolate hydrolysis. FEBS Lett. 468: 243-246.
Geshi, N. and Brandt, A. 1998. Two jasmonate-inducible myrosinase-binding proteins from Brassica napus L. seedlings with homology to jacalin. Planta 204: 295-304.
Höglund, A.S., Lenman, M., Falk, A. and Rask, L. 1991. Distribution of myrosinase in rapeseed tissues. Plant Physiol. 95: 213-221.
Höglund, A.S., Lenman, M. and Rask, L. 1992. Myrosinase is localized to the interior of myrosin grains and is not associated to the surrounding tonoplast membrane. Plant Sci. 85: 165-170.
Husebye, H., Chadchawan, S., Winge, P., Thangstad, O.P. and Bones, A.M. in press. Guard cell-and phloem-idioblast specific expression of thioglucoside glucohydrolase 1 myrosinase in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. 28: 1180-1188.
Jefferson, R.A., Kavanagh, T.A. and Bevan, M.W. 1987. GUS fusions: beta-glucoronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J. 6: 3901-3907.
Kawagoe, Y. and Murai, N. 1992. Four distinct nuclear protiens recognize in vitro the proximal promoter of the bean storage protein beta-phaseolin gene conferring spatial and temporal control. Plant J. 2: 927-936.
Kelly, P.J., Bones, A. and Rossiter, J.T. 1998. Subcellular immunolocalization of the glucosinolate sinigrin in seedlings of Brassica juncea. Planta 206: 370-377.
Koroleva, O.A., Davies, A., Deeken, R., Thorpe, M.R., Tomos, A.D. and Hedrich, R. 2000. Identification of a new glucosinolate-rich cell type in Arabidopsis flower stalk. Plant Physiol. 124: 599-608.
Kwak, J.M., Kim, S.A., Hong, S.W. and Nam, H.G. 1997. Evaluation of 515 expressed sequence tags obtained from guard cells of Brassica campestris. Planta 202: 9-17.
Lambrix, V., Reichelt, M., Mitchell-Olds, T., Kliebenstein, D.J. and Gershenzon, J. 2001. The arabidopsis epithiospecifier protein promotes the hydrolysis of glucosinolates to nitriles and influences trichoplusia ni herbivory. Plant Cell 12: 2793-2807.
Lee, H.S. and Chen, Z.J. 2001. Protein-coding genes are epigenetically regulated in Arabidopsis polyploids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 12: 6753-6758.
Lenman, M., Falk, A., Rödin, J., Höglund, A.S., Ek, B. and Rask, L. 1993a. Differential expression of myrosinase gene families. Plant Physiol. 103: 703-711.
Lenman, M., Falk, A., Xue, J. and Rask, L. 1993b. Characterization of a Brassica napus myrosinase pseudogene: myrosinases are members of the BGA family of glucosidases. Plant Mol. Biol. 24: 463-474.
Ludevid, D., Höfte, H., Himelblau, E. and Chrispeels, M.J. 1992. The expression pattern of the tonoplast intrinsic protein c-TIP in Arabidopsis thaliana correlated with cell enlargement. Plant Physiol. 100: 722-731.
Machlin, S., Mitchell-Olds, T. and Bradley, D. 1993. Sequence of Brassica campestris myrosinase gene. Plant Physiol. 102: 1359-1360.
Mauch-Mani, B. and Slusarenko, A.J. 1994. Systemic aquiredresistance in Arabidopsis thaliana induced by a predisposing infection with a pathogenic isolate of Fusarium oxysporum. Mol. Plant Microbe. Interact. 7: 378-383.
Mithen, R.F., Lewis, B.G. and Fenwick, G.R. 1986. In vitro activity of glucosinolates and their products against Leptosphaeria maculans. Trans. Brit. Mycol. Soc. 87: 433-440.
Moloney, M.M., Walker, J.M. and Sharma, K.K. 1989. High efficiency transformation of Brassica napus using agrobacterium vectors. Plant Cell Rep. 8: 238-242.
Müller-Röber, B., Ehrhardt, T. and Plesch, G. 1998. Molecular features of stomatal guard cells. J. Exp. Bot. 49: 293-304.
Plesch, G., Ehrhardt, T. and Mueller-Roeber, B. 2001. Involvement of TAAAG elements suggests a role for Dof transcription factors in guard cell-specific expression. Plant J 28: 455-464.
Rask, L., Andreasson, E., Ekbom, B., Eriksson, S., Pontoppidan, B. and Meijer, J. 2000. Myrosinase: gene family evolution and herbivore defense in Brassicaceae. Plant Mol. Biol. 42: 93-113.
Rodman, J.E. 1991. A taxonomic analysis of glucosinolateproducing plants. Syst. Bot. 16: 598-618.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F. and Maniatis, T. 1989. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor University Press, NY.
Tatusova, T.A. and Madden, T.L. 1999. Blast 2 sequences-a new tool for comparing protein and nucleotide sequences. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 174: 247-250.
Thangstad, O.P., Bones, A., Holtan, S., Moen, L. and Rossiter, J.T. 2001. Microautoradiographic localisation of a glucosinolate precursor to specific cells in Brassica napus L. embryos indicates a separate transport pathway into myrosin cells. Planta 213: 207-213.
Thangstad, O.P., Evjen, K. and Bones, A. 1991. Immunogold-EM localization of myrosinase in Brassicaceae. Protoplasma 161: 85-93.
Thangstad, O.P., Iversen, T.H., Slupphaug, G. and Bones, A. 1990. Immunocytochemical localization of myrosinase in Brassica napus L. Planta 180: 245-248.
Thangstad, O.P., Winge, P., Husebye, H. and Bones, A. 1993. The myrosinase (thioglucoside glucohydrolase) gene family in Brassicaceae. Plant Mol. Biol. 23: 511-524.
Vercammen, J., Pham-Tuan, H., Arickx, I., Van der Straeten, D. and Sandra, P. 2001. Monitoring of isothiocyanates emanating from Arabidopsis thaliana upon paraquat spraying. J. Chromatogr. A. 912: 127-134.
Werker, E. and Vaughan, J.G. 1974. Anatomical and ultrastructural changes in aleurone and myrosin cells of Sinapis alba during germination. Planta 116: 243-255.
Werker, E. and Vaughan, J.G. 1976. Ontogeny and distribution of myrosin cells in the shoot of Sinapis alba L. A light and electron-microscope study. Isr. J. Bot. 25: 140-151.
Xue, J.P., Jörgensen, M., Pihlgren, U. and Rask, L. 1995. The myrosinase gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana: gene organization, expression and evolution. Plant Mol. Biol. 27: 911-922.
Xue, J., Lenman, M., Falk, A. and Rask, L. 1992. The glucosinolate-degrading enzyme myrosinase in Brassicaceae is encoded by a gene family. Plant Mol. Biol. 18: 387-398.
Xue, J.P., Philgren, U. and Rask, L. 1993. Temporal, cell specific, and tissue preferential expression of myrosinase genes during embryo and seedling development in Sinapis alba. Planta 191: 95-101.
Yanagisawa, S. and Schmidt, R.J. 1999. Diversity and similarity among recognition sequences of Dof transcription factors. Plant J. 17: 209-214.
Zhu, C., Poulsen, H.E. and Loft, S. 2000. Inhibition of oxidative DNA damage in vitro by extracts of brussels sprouts. Free Radic. Res. 33: 187-196.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thangstad, O.P., Gilde, B., Chadchawan, S. et al. Cell Specific, Cross-Species Expression of Myrosinases in Brassica Napus, Arabidopsis Thaliana and Nicotiana Tabacum . Plant Mol Biol 54, 597–611 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PLAN.0000038272.99590.10
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PLAN.0000038272.99590.10