Abstract
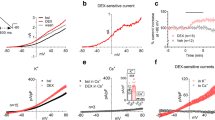
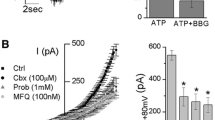
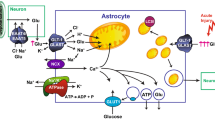
Volume regulated anion channels (VRAC) have been extensively studied in purified single cell systems like cell cultures where they can be activated by cell swelling. This provides a convenient way of analyzing mechanisms and will likely lead to the holy grails of the field, namely the nature or natures of the volume sensor and the nature or natures of VRACs. Important reasons for such an understanding are that these channels are ubiquitous and have important physiological functions which under pathological conditions convert to deleterious effects. Here we summarize data showing the involvement of VRACs in ischemia-induced release of excitatory amno acids (EAAs) in a rat model of global ischemia. Using microdialysis studies we found that reversal of the astrocytic glutamate transporter and VRACs contribute about equally to the large initial release of EAAs and together account for around 80% of the total release. We used the very potent VRAC blocker, tamoxifen, to see if such inhibition of EAA release via VRACs led to significant neuroprotection. Treatment in the focal rat MCA occlusion model led to around 80% reduction in infarct size with an effective post initiation of ischemia therapeutic window of three hours. However, the common problem of other effects for even the most potent inhibitors pertains here, as tamoxifen has other, potentially neuroprotective, effects. Thus it inhibits nitrotyrosine formation, likely due to its inhibition of nNOS and reduction of peroxynitrite formation. Although tamoxifen cannot therefore be used as a test of the “VRAC-excitotxicity” hypothesis it may prove successful for translation of basic stroke research to the clinic because of its multiple targets.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Franco, R., Torres-Márquez, M. E., and Pasantes-Morales, H. 2001. Evidence for two mechanisms of amino acid osmolyte release from hippocampal slices. Pflug. Arch. 442:791–800.
Schousboe, A., Morán, J., and Pasantes-Morales, H. 1990. Potassium-stimulated release of taurine from cultured cerebellar granule neurons is associated with cell swelling. J. Neurosci. Res. 27:71–77.
Pasantes-Morales, H. and Schousboe, A. 1988. Volume regulation in astrocytes: A role for taurine as an osmoeffector. J. Neurosci. Res. 20:503–509.
Pasantes-Morales, H. and Schousboe, A. 1989. Release of taurine from astrocytes during potassium-evoked swelling. Glia 2:45–50.
Pasantes-Morales, H. and Schousboe, A. 1988. Volume regulation in astrocytes: A role for taurine as an osmoeffector. J. Neurosci. Res. 20:505–509.
Cardin, V., Peña-Segura, C., and Pasantes-Morales, H. 1999. Activation and inactivation of taurine efflux in hyposmotic and isosmotic swelling in cortical astrocytes: Role of ionic strength and cell volume decrease, J. Neurosci. Res. 56:659–667.
Moran, J., Morales-Mulia, M., and Pasantes-Morales, H. 2001. Reduction of phospholemman expression decreases osmosensitive taurine efflux in astrocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1538: 313–320.
Nilius, B., Eggermont, J., Voets, T., Buyse, G., Manolopoulos, V., and Droogmans, G. 1997. Properties of volume-regulated anion channels in mammalian cells. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 68:69–119.
Nilius, B. and Droogmans, G. 2003. Amazing chloride channels: An overview. Acta Physiol Scand. 177:119–147.
Roy, G. 1995. Amino acid current through anion channels in cultured human glial cells. J. Membr. Biol. 147:35–44.
Mongin, A. A. and Kimelberg, H. K. 2002. ATP potently modulates anion channel-mediated excitatory amino acid release from cultured astrocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 283:C569–C578.
Phillis, J. W., Song, D., and O'Regan, M. H. 1997. Inhibition by anion channel blockers of ischemia-evoked release of excitotoxic and other amino acids from rat cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 758:9–16.
Seki, Y., Feustel, P. J., Keller, R. W., Jr., Tranmer, B. I., and Kimelberg, H. K. 1999. Inhibition of ischemia-induced glutamate release in rat striatum by dihydrokainate and an anion channel blocker. Stroke 30:433–440.
Anderson, C. M. and Swanson, R. A. 2000. Astrocyte glutamate transport: Review of properties, regulation, and physiological functions. Glia 32:1–14.
Wahl, F., Obrenovitch, T. P., Hardy, A. M., Plotkine, M., Boulu, R., and Symon, L. 1994. Extracellular glutamate during focal cerebral ischaemia in rats: Time course and calcium dependency. J. Neurochem. 63:1003–1011.
Benveniste, H., Drejer, J., Schousboe, A., and Diemer, N. M. 1984. Elevation of the extracellular concentrations of glutamate and aspartate in rat hippocampus during transient cerebral ischemia monitored by intracerebral microdialysis. J. Neurochem. 43:1369–1374.
Rossi, D. J., Oshima, T., and Attwell, D. 2000. Glutamate release in severe brain ischaemia is mainly by reversed uptake. Nature 403:316–321.
Kirk, J. and Kirk, K. 1994. Inhibition of volume-activated l− and taurine efflux from HeLa cells by P-glycoprotein blockers correlates with calmodulin inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 269:29389–29394.
Fisher, M. and Brott, T. G. 2003. Emerging therapies for acute ischemic stroke: New therapies on trial. Stroke 34, 359–361.
Renodon, A., Boucher, J. L., Sari, M. A., Delaforge, M. Ouazzani, J. and Mansuy, D. 1997. Strong inhibition of neuronal nitric oxide synthase by the calmodulin antagonist and anti-estrogen drug tamoxifen Biochem. Pharmacol. 54:1109–1114.
Samdani, A. F., Dawson, T. M., and Dawson, V. L. 1997. Nitric oxide synthase in models of focal ischemia. Stroke 28:1283–1288.
Kimelberg, H. K., Jin, Y., and Feustel, P. J. 2003. Neuroprotective activity of tamoxifen in permanent focal ischemia. J. Neurosurg. 99:138–142.
Ginsberg, M. D. 2003. Adventures in the pathophysiology of brain ischemia: Penumbra, gene expression, neuroprotection—The 2002 Thomas Willis lecture. Stroke 34:214–223.
Oike, M., Droogmans, G., and Nilius, B. 1994. The volume-activated chloride current in human endothelial cells depends on intracellular ATP. Pflug. Arch. 427:184–186.
Okada, Y. 1997. Volume expansion-sensing outward-rectifier Cl− channel: Fresh start to the molecular identity and volume sensor. Am. J. Physiol. 273:C755–C789.
Kirk, K. and Strange, K. 1998. Functional properties and physiological roles of organic solute channels. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 60: 719–739.
Eggermont, J., Trouet, D., Carton, I., and Nilius, B. 2001. Cellular function and control of volume-regulated anion channels. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 35:263–274.
Aitken, P. G., Borgdorff, A. J., Juta, A. J. A., Kiehart, D. P., Somjen, G. G., and Wadman, W. J. 1998. Volume changes induced by osmotic stress in freshly isolated rat hippocampal neurons. Pflug. Arch. 436:991–998.
Pasantes-Morales, H., Maar, T. E., and Morán, J. 1993. Cell volume regulation in cultured cerebellar granule neurons. J. Neurosci. Res. 34:219–224.
Kimelberg, H. K. 2000. Cell volume in the CNS: Regulation and implications for nervous system function and pathology. Neuroscientist 6:13–24.
Barron, K. D., Dentinger, M. P., Kimelberg, H. K., Nelson, L. R., Bourke, R. S., Keegan, S., Mankes, R., and Cragoe, E. J., Jr. 1988. Ultrastructural features of a brain injury model in cat: I. Vascular and neuroglial changes and the prevention of astroglial swelling by a fluorenyl (aryloxy) alkanoic acid derivative (L-644, 711). Acta Neuropathol. (Berl.) 75:295–307.
Liu, K. F., Li, F. H., Tatlisumak, T., Garcia, J. H., Sotak, C. H., Fisher, M., and Fenstermacher, J. D. 2001. Regional variations in the apparent diffusion coefficient and the intracellular distribution of water in rat brain during acute focal ischemia. Stroke 32:1897–1905.
Kucinski, T., Vaterlein, O., Glauche, V., Fiehler, J., Klotz, E., Eckert, B., Koch, C., Rother, J., and Zeumer, H. 2002. Correlation of apparent diffusion coefficient and computed tomography density in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 33: 1786–1791.
Biegon, A., Brewster, M., Degani, H., Pop, E., Somjen, D., and Kaye, A. M. 1996. A permanently charged tamoxifen derivative displays anticancer activity and improved tissue selectivity in rodents. Cancer Res. 56:4328–4331.
Osuka, K., Feustel, P. J., Mongin, A. A., Tranmer, B. I., and Kimelberg, H. K. 2001. Tamoxifen inhibits nitrotyrosine formation after reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. J. Neurochem. 76:1842–1850.
Zhang, Z. G., Chopp, M., Gautam, S., Zaloga, C., Zhang, R. L., Schmidt, H. H., Pollock, J. S., and Forstermann, U. 1994. Upregulation of neuronal nitric oxide synthase and mRNA, and selective sparing of nitric oxide synthase-containing neurons after focal cerebral ischemia in rat. Brain Res. 654:85–95.
Bolton, J. L. 2002. Quinoids, quinoid radicals, and phenoxyl radicals formed from estrogens and antiestrogens. Toxicology 177:55–65.
Kimelberg, H. K., Feustel, P. J., Jin, Y., Paquette, J., Boulos, A., Keller, R. W., and Tranmer, B. I. 2000. Acute treatment with tamoxifen reduces ischemic damage following middle cerebral artery occlusion. Neuroreport 11:2675–2679.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kimelberg, H.K., Nestor, N.B. & Feustel, P.J. Inhibition of Release of Taurine and Excitatory Amino Acids in Ischemia and Neuroprotection. Neurochem Res 29, 267–274 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NERE.0000010455.78121.53
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NERE.0000010455.78121.53